12-09: Energy From Food
Chemical Potential Energy
- food energy is stored by the relatively high potential energy of electrons in the bonds of molecules like glucose compared to the low potential energy of electrons in bonds of molecules like carbon dioxide and water
- cellular respiration releases that energy and transfers it to the bonds of ATP molecules
Redox Reactions
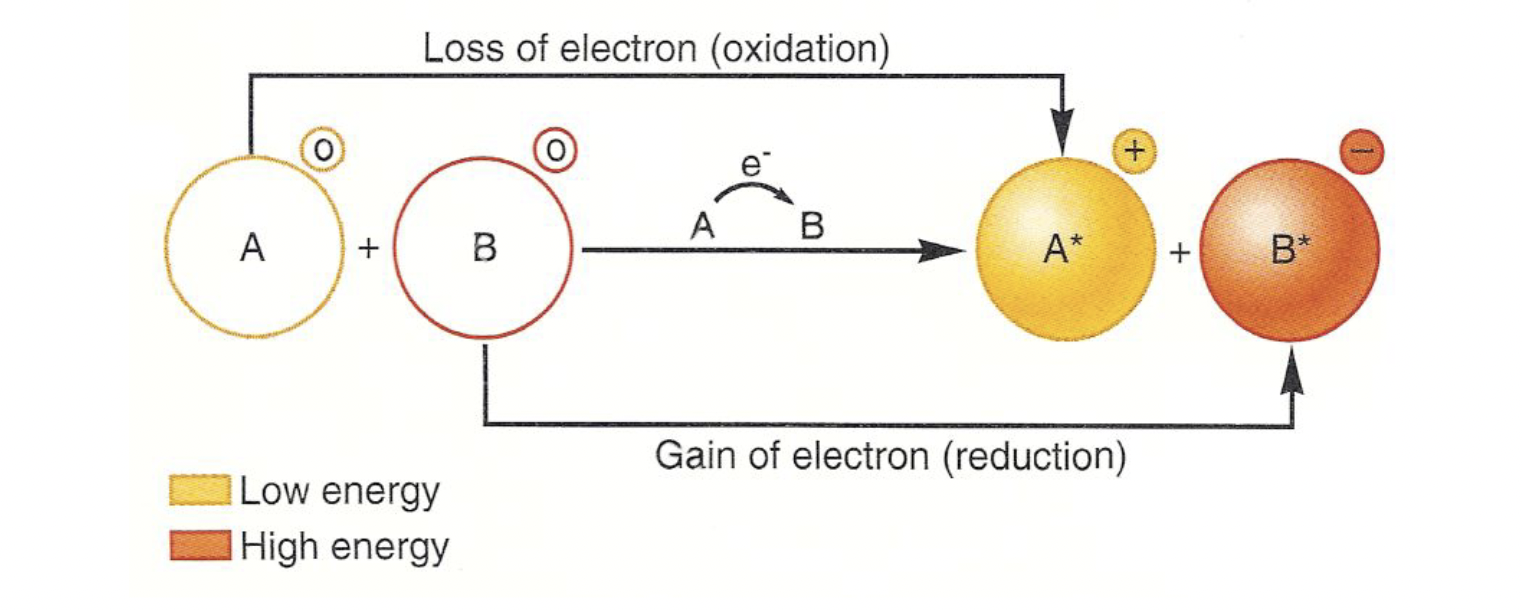
oxidation is the process of losing electrons
reduction is the process of gaining electrons
redox reactions involve both
- all of cellular respiration depends on electron transfer - when an electron moves to a more electronegative molecule
oxidizing agents are reduced, reducing agents are oxidized
Respiration Redox
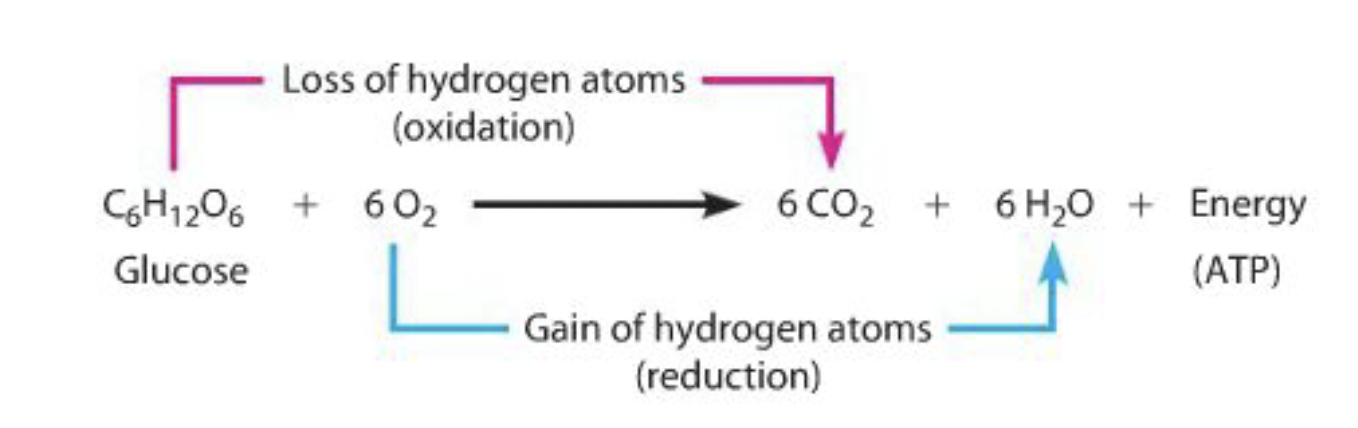
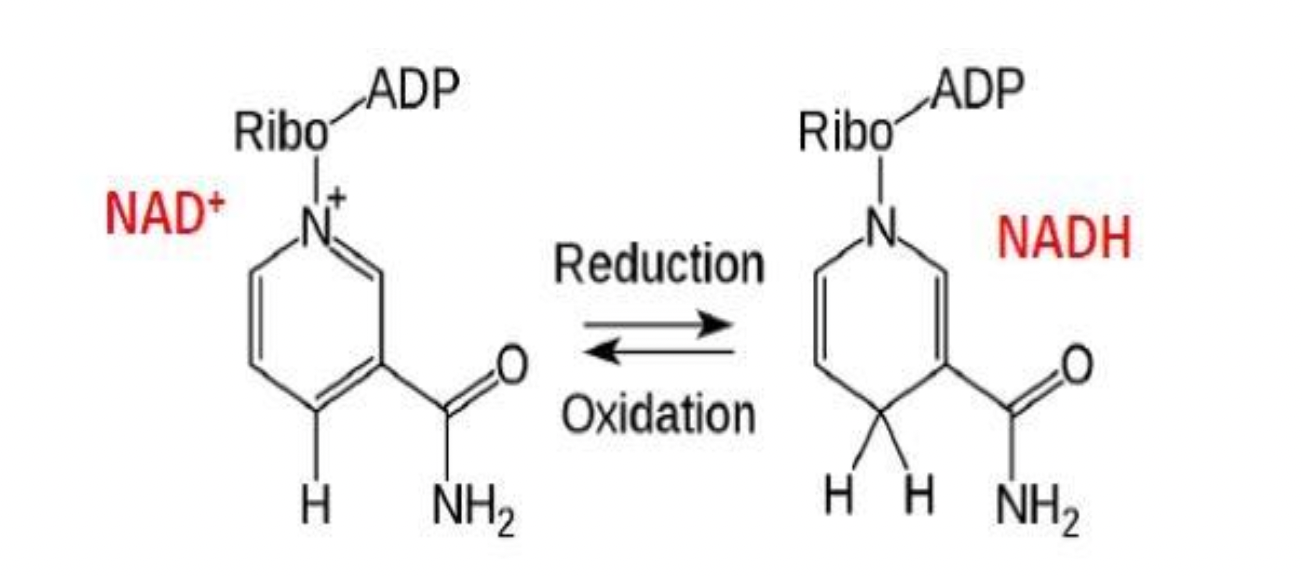
oxidation = the removal of hydrogen
reduction = the gaining of hydrogen
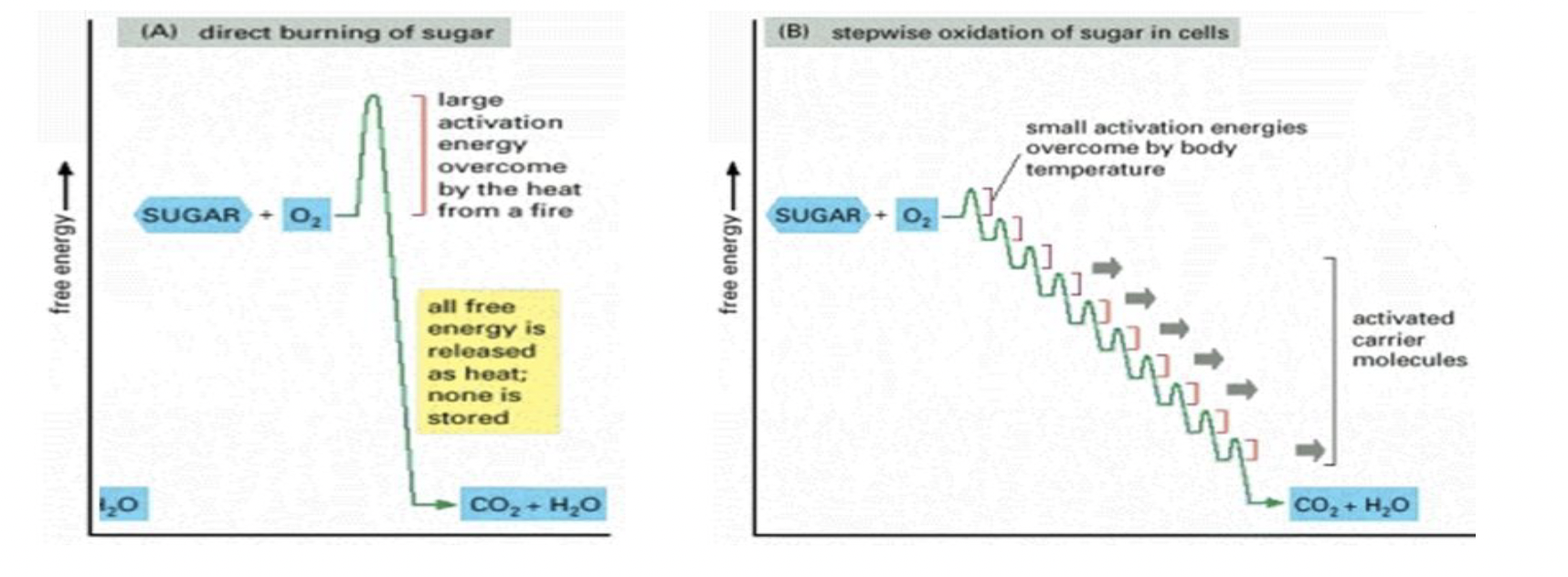
Combustion vs. Controlled Oxidation
combustion = a rapid oxidation of fuel (like glucose)
for cellular purposes a stepwise, controlled process provides every to carrier molecules that are then used to make ATP
if a sugar is combusted - the energy is thermal/heat → do not want this for cellular processes
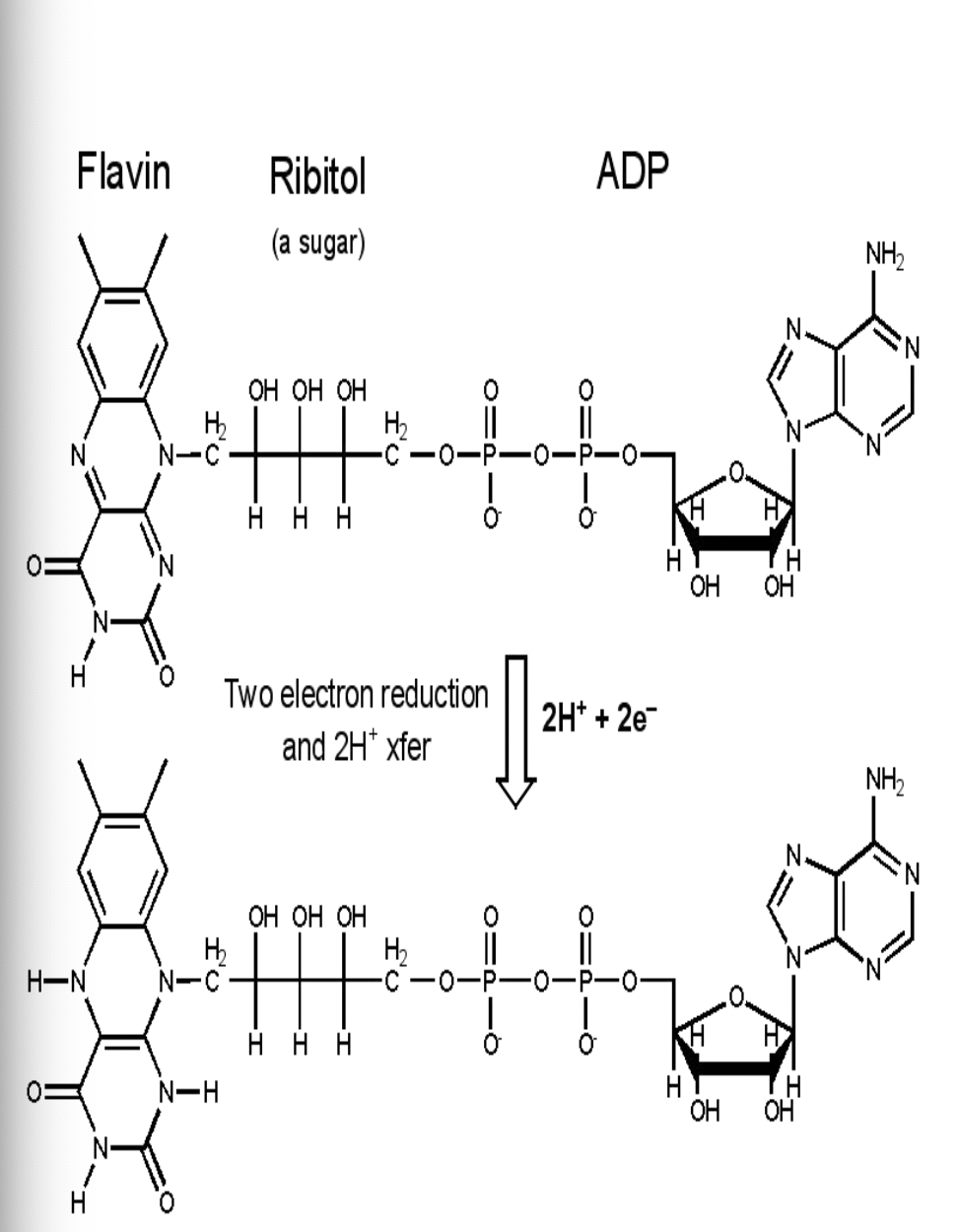
Energy Carriers
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) & flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) are coenzymes, the help the enzymes catalyze the oxidation of glucose
NAD+ and FAD are energy carriers used in the oxidation of food
dehydrogenase enzymes remove hydrogen ions (oxidize) and pass them to carriers which get reduced
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
this process extracts energy from glucose with oxygen producing ATP
it is divided into 4 stages - it starts in the cytoplasm and most occur in the mitochondria
glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain
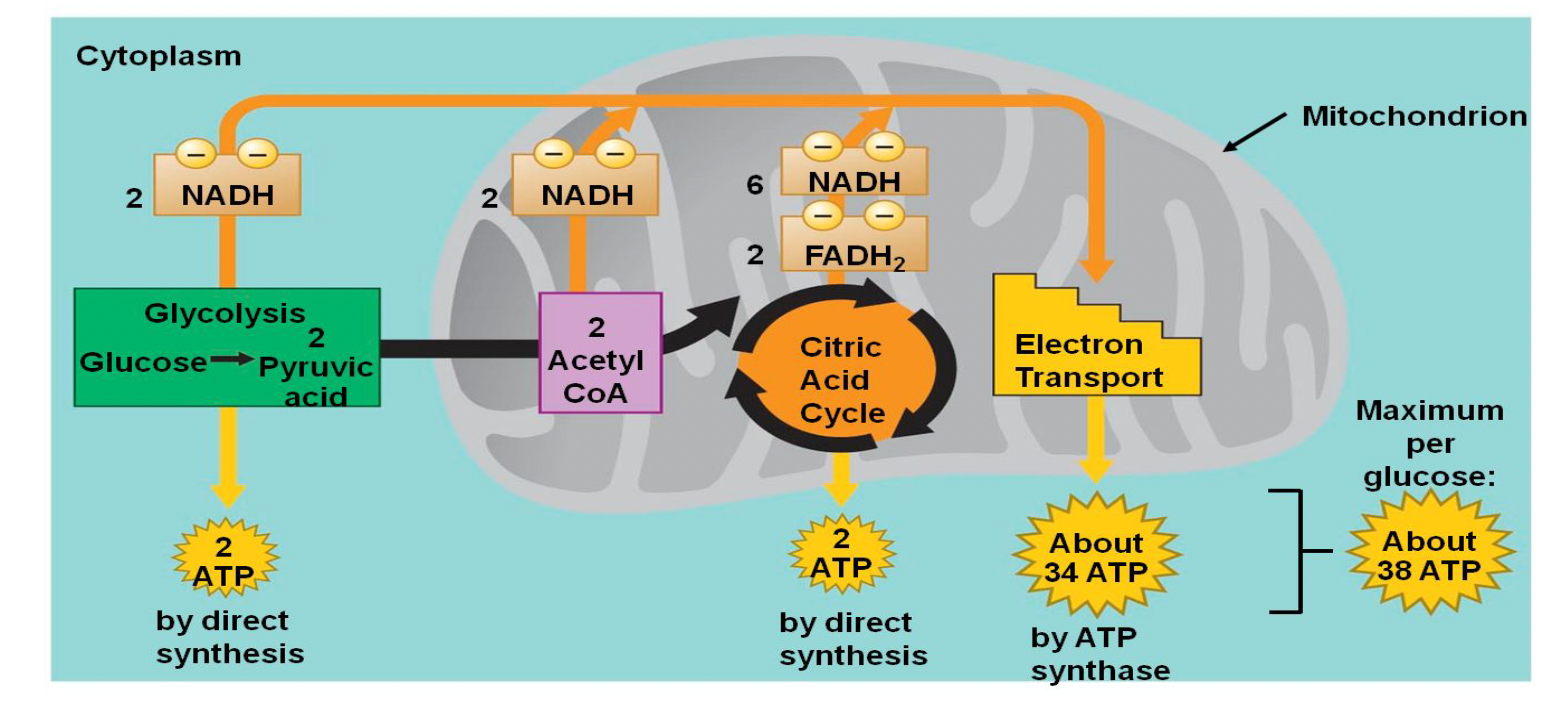
Mitochondrial Map
- glycolysis: cytoplasm/cytosol (liquid)
- pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle: matrix
- electron transfer chain: inner membrane
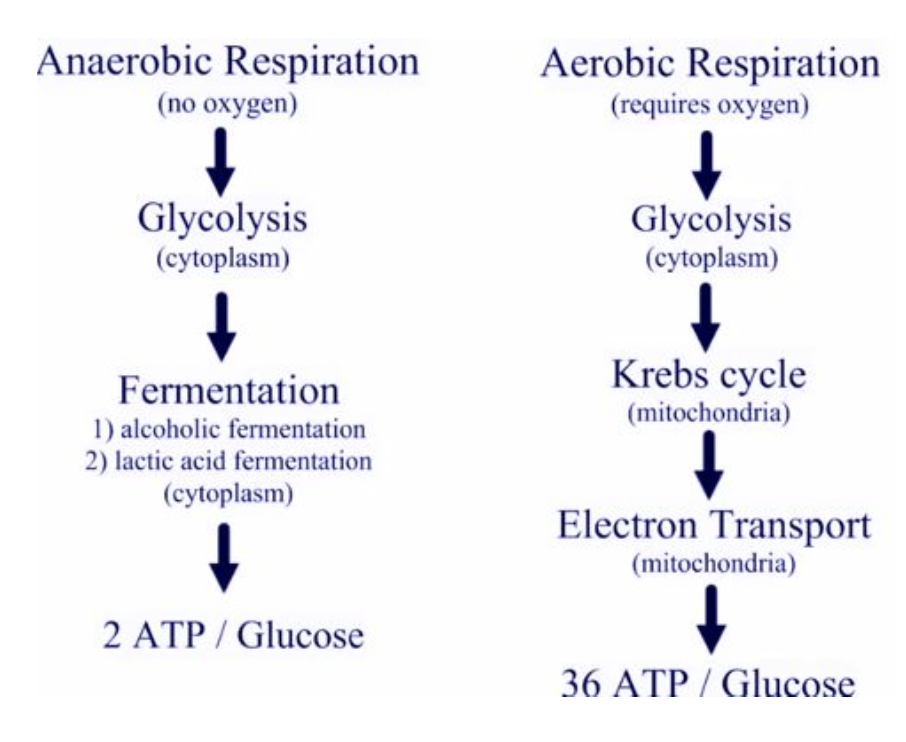
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration
energy can be produced without oxygen via fermentation but it is much less efficient and produces toxic byproducts