Edexcel GCSE Higher Maths - Circle Theorems
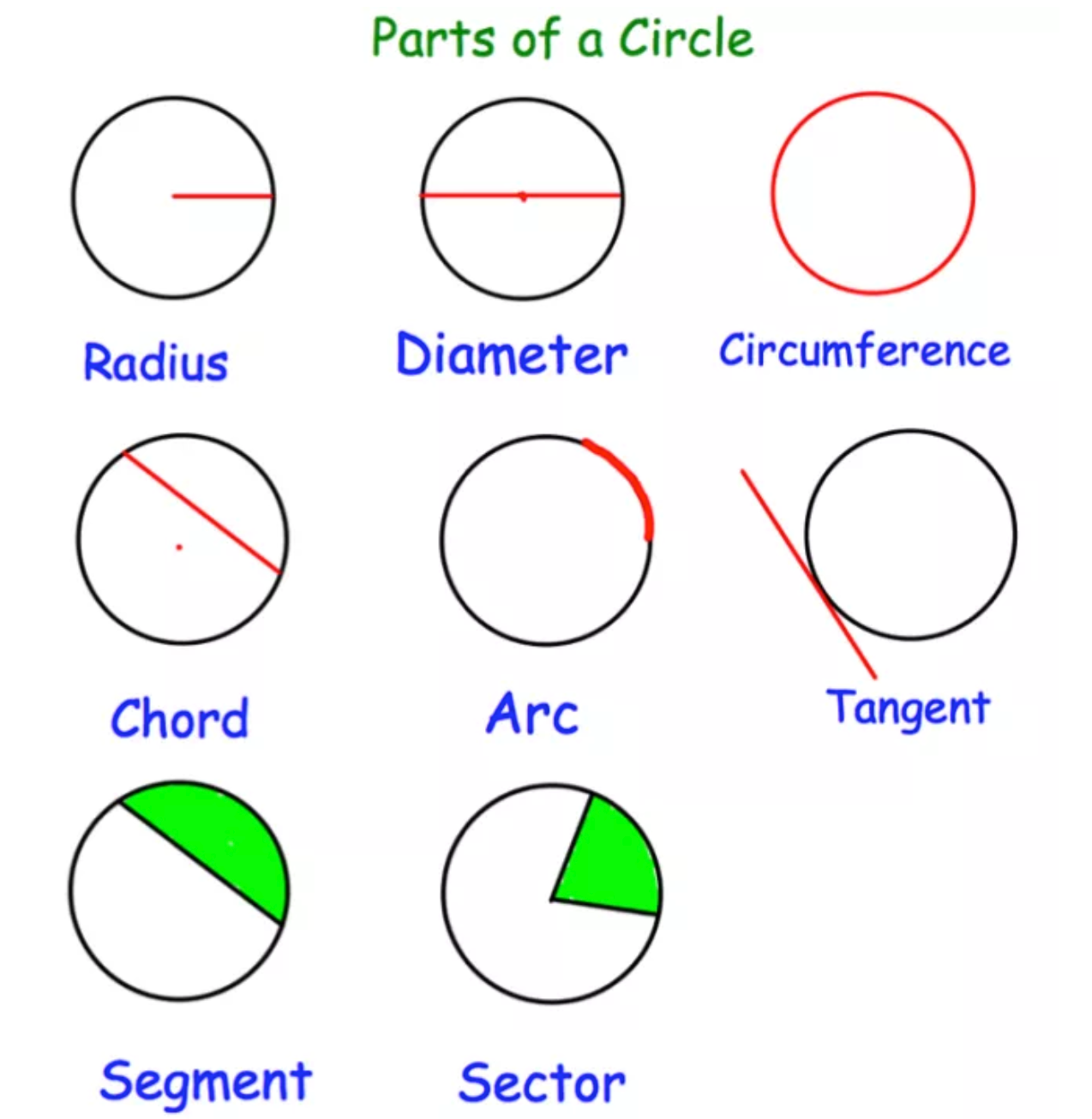
Parts of a Circle:
Circle Theorems:
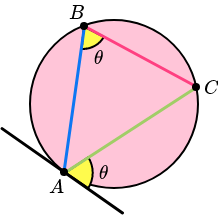
Alternate Angle Theorem:
The alternate segment theorem is the angle that lies between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle subtended by the same chord in the alternate segment.
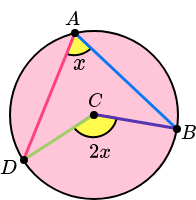
Angles at the Centre Theorem:
The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference.
Angles in the Same Segment Theorem:
Angles in the same segment are equal.
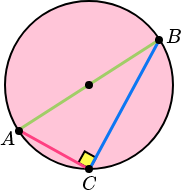
Angles in a Semicircle Theorem:
The angle in a semicircle is 90 degrees.
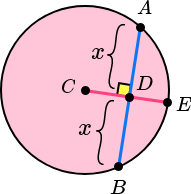
Chord of a Circle Theorem:
The perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord (splits the chord into two equal parts).
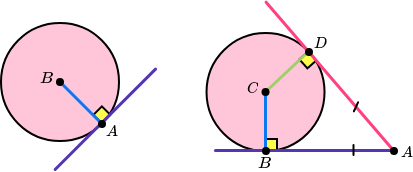
Tangent of a Circle Theorems:
The angle between a tangent and a radius is 90 degrees. Tangents which meet at the same point are equal in length.
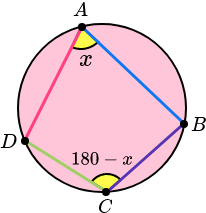
Cyclic Quadrilateral Theorem:
The opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral total 180 degrees.