Biodiversity
Ecosystem Services
Regulating
Natural Phenomenon
Climate Control
Pollination
Preventing Erosion
Purifying Water
Cultural
(Interacting with Nature)
Recreational
Aesthetics
Spiritual aspects
Educational
Extraction from Nature (Provisioning)
Food
Water
Oxygen
Minerals
Fuel
Medicine
Supporting
Fundamentals
Photosynthesis
Habitats
Nutrient Cycling
Soil Formation
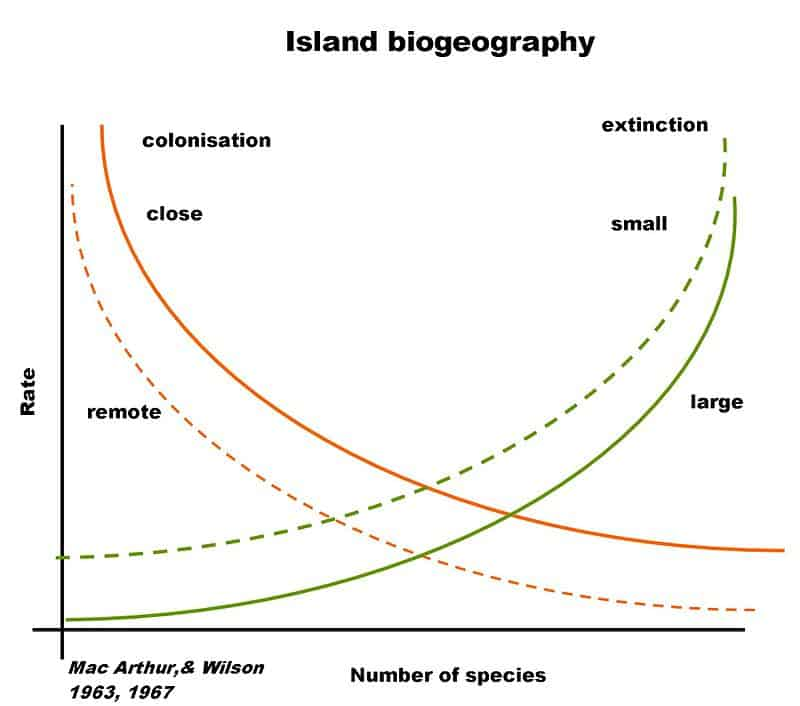
Island Biogeography Theory
Island biogeography theory explains how species richness on an island is influenced by island size and distance from the mainland. It predicts that larger islands and islands closer to the mainland will have higher species diversity due to factors like colonization and extinction rates.
Habitat Fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation is the process where large continuous habitats are divided into smaller, isolated patches, leading to disruption of ecosystems and impacting biodiversity.
What are ways habitat is fragmented on the mainland?
Roads and buildings
Why does biodiversity decrease?
Species cannot move between habitats
What are edge effects?
Species are more susceptible to illness on the edge of habitats
How do we mitigate?
Create wildlife preserves: Habitat corridor
Ecological Tolerance
A range of conditions an organism can tolerate
Not all species are affected in the same way by environmental changes
Species with a broad range of tolerance tend to survive longer than species with narrow ranges of tolerance.
Ecological Succession
Primary Succession
The process of ecological succession that occurs in an area where no soil is present, such as on bare rock or sand. It begins with pioneer species like lichens and mosses that gradually break down the substrate and create soil for other plants to grow. Over time, more complex plant and animal communities are established, leading to a stable ecosystem.
Secondary Succession
The process where an ecosystem recovers after a disturbance that leaves soil intact. It involves the reestablishment of a community in an area that was previously inhabited. Pioneer species colonize the area first, followed by more complex species, leading to a stable ecosystem.