Inflation: An Overview - Section 3, Module 14
hyperinflation - very high and accelerating rates of inflation
misconception about inflation - it makes everyone poorer
real wage - the wage rate divided by the price level (to adjust for inflation/deflation) doesn’t change
income and prices are both reduced
real income - income divided bye the price level to adjust for the effects of inflation or deflation
the level of prices does not matter
inflation rate - the percentage increase in the overall level of prices per year
calculation:
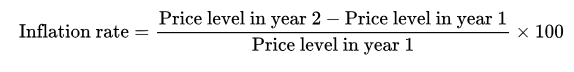
high rates of inflation impose economic costs: shoe-leather costs, menu costs, and unit of account costs
shoe-leather costs - increased costs of transactions caused by inflation
happens because during high inflation, people are discouraged from holding money beacause their purchasing power steadily decreases as the overall prices increases
menu costs - the real cost of changing a listed price
during inflation, firms have to change prices more often, which means higher prices for the economy as a whole
unit of account role of money - the role of the dollar as a basis of contracts/calculations
unit of account costs - costs arising form the way inflation makes money a less realiable unit of measurement
super important in taxes bc inflation can distort the measures of income on which a tax is collected
inflation can hurt some and hurt others
interest rate - percentage of the loan amount that the borrower must pay to the lended in addition to the repayment of the loan
nominal interest rate - the interest rate that is actually paid for a loan, unadjusted for the effects of inflation
real interest rate - nominal interest rate ajdusted for inflation (subtract the inflation rate from the nominal interest rate)
IF INFLATION IS HIGHER THAN EXPECTED - borrowers benefit because they get to pay the money back in cheaper dollars
IF INFLATION IS LOWER THAN EXPECTED - lenders benefit because buyers have to pay the loans back with funds that have a higehr real value
disinflation - bringing the inflation rate down → very difficult and costly once a higher inflation rate has become established in a country
sometimes the only way to end inflation is through disinflation and creating a temporary depression