Geography Notes
————————————————————————————————————————————
Section 1 - The Environment
Learn how to read a Topographic map
Learn how to read a complex block diagram
Learn how to Compare Aerial Photographs
Section 2 - The Environment
Environmental Ethics
Environmental ethics is the philosophical discipline that considers the moral and ethical relationship of human beings to the environment.
Four functions associated with environmental sustainability
These functions can be grouped into four main types – source, sink, service and spiritual.
Source - refers to the capacity of the environment to provide us with materials
Sink - refers to the ability of the environment to remove and breakdown waste
Service - refers to the processes that occur that enable our existence
Spiritual - refers to how environments can provide us with psychological benefits or spiritual connections
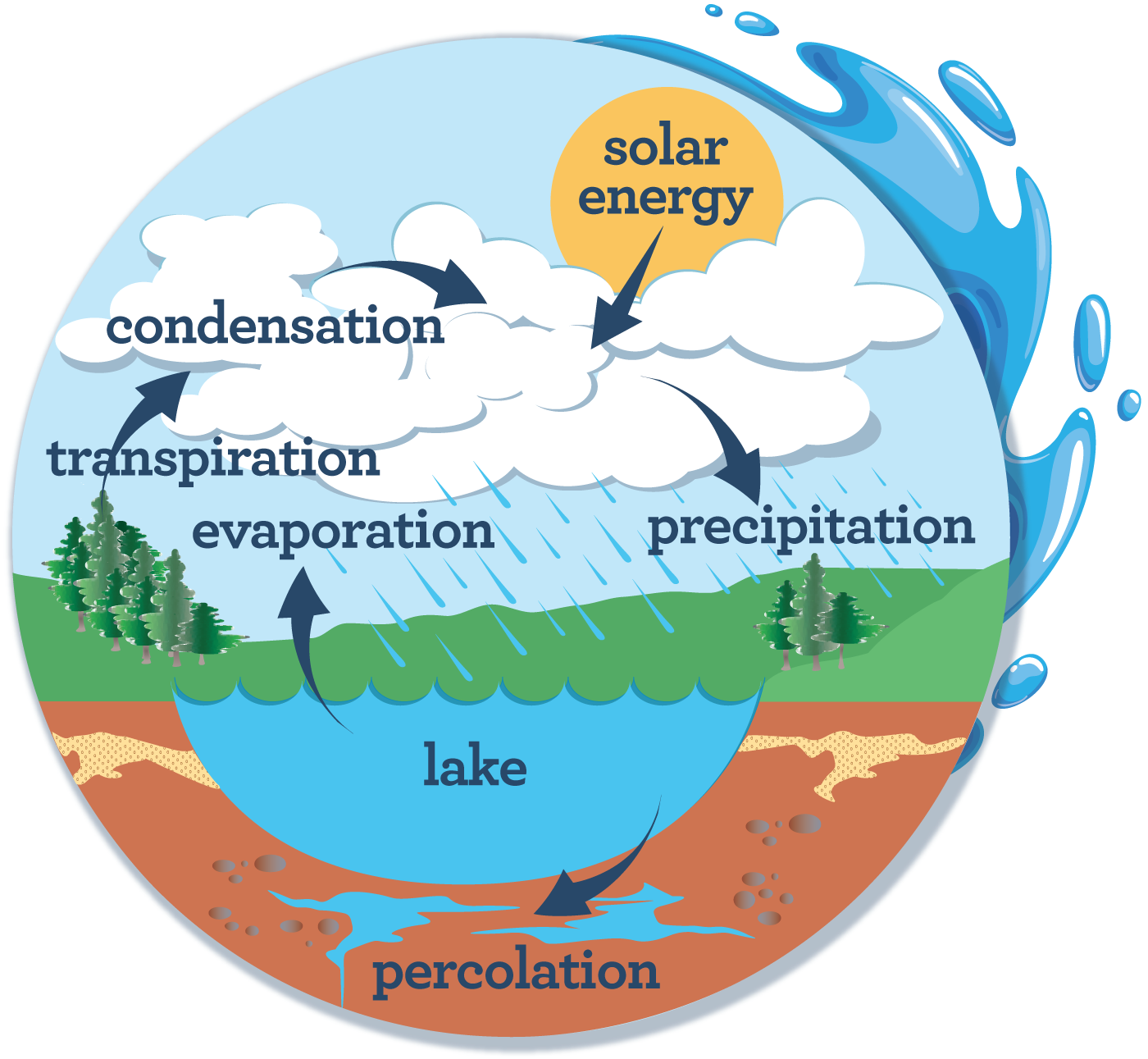
Water Cycle
The water cycle is the path that all water follows as it moves around Earth in different states.
How an area is changed by deforestation
When forests are destroyed, entire ecosystems are disrupted. There's an immediate decline in biodiversity furthermore, large-scale deforestation could push some Australian animals to the brink of extinction.
Questions
1 ) How is the water cycle affected by deforestation of an area
Deforestation results in less evapotranspiration, reducing the amount of water available to create precipitation. This in turn causes droughts and the land is no longer kept fertile by the rain. Additionally, erosion increases as does sediment concentration in rivers.
2) How can roads stabilise a hill slope ?
Roads built into hillsides can use a variety of techniques to stabilize the slope and prevent erosion. Here are some common methods:
Reinforcement: Walls or structures made of concrete, rock, or metal can be built to support the slope and hold the soil in place.
Drainage: Proper drainage systems can help prevent water from accumulating behind the slope, which can put pressure on the soil and cause it to weaken.
Vegetation: Planting grass, shrubs, or trees on the slope can help to hold the soil in place with their roots. The root systems create a network that reinforces the soil and prevents erosion.
3) Why does erosion and land slippage occur ?
Land slippage is when mass movement of material, such as rock, earth or debris, becomes unstable and slips downhill ,due to deep soils or scree on sloping land
Erosion - Erosion is defined as the displacement of solids by wind, water, and ice.
4) How can a dust storm pick up topsoil ?
The drought dried the topsoil and over time it became weak and drained of its nutrients and was reduced to a powdery consistency in some places ,due to this the plains' high winds picked up the topsoil and created massive dust storms.
5) Where does the Silt that blocks rivers come from ?
The introduction of silt into watercourses can result from natural causes such as heavy run-off as well as from human conduct such as overgrazing or deforestation.
The Difference between Erosion and Weathering
Erosion is defined as the displacement of solids by wind, water, and ice. Weathering is defined as the decomposition of rocks, soil, and minerals by direct contact with the atmosphere
The Difference between Erosion and Deposition
Erosion is when materials, like soil or rocks, are moved by wind or water. Deposition is when sediments are deposited in a different location.
Salinity
Salinity is the accumulation of salt in land and water to a level that damages the natural and built environment
Drainage Area
The term "drainage area" is defined as the land area where precipitation falls off into creeks, streams, rivers, lakes, and reservoirs
Swash and Backwash
The swash is when a wave washes up onto the shoreline and backwash is when the water from a wave retreats back into the sea.
Longshore Drift
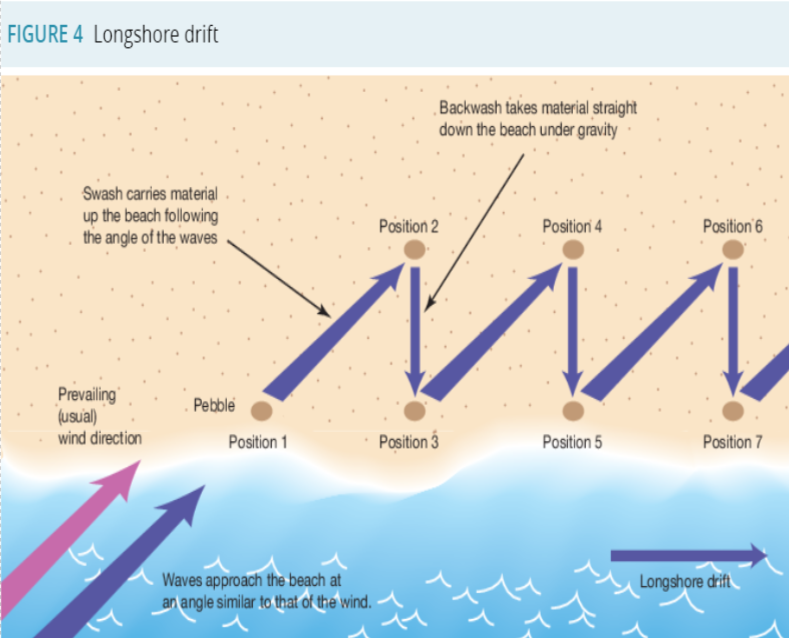
Longshore drift moves sand along a coastline by the following process:
Waves approach the beach at an angle similar to that of the wind.
The swash carries material up the beach following the angle of the waves.
Backwash takes material down the beach.
The material is carried along the coastline in a zig-zag action.
12 landforms Labelled
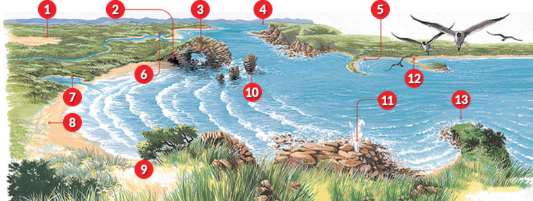
Dune Blowout
Cave
Arch
Cliff
Spit
Estuaries
Lagoon
Beach
Dune
Stack
Blowhole
Tombolo
Headland
How do these Landforms form
Dune Blowout
Blowouts tend to form when wind erodes patches of bare sand on stabilized vegetated dunes.
Caves
Caves are formed by the dissolution of limestone
Arch
An arch starts off as two caves on a headland, but erosion takes it one step further and joins them together as an arch.
Cliff
Cliffs are usually formed because of processes called erosion and weathering.
Spit
Spits are formed by the longshore movement of sediment.
Estuaries
Estuaries are created when sea levels rise and fill in an existing river valley
Lagoon
Formed when a sandbar begins to develop ,eventually closing an estuary
Beach
Beaches are formed as a result of the weathering and coastal erosion of nearby rock cliffs.
Dune
Form when sand on a beach is stabilised by vegetation
Stack
created by ongoing erosion of an arch ,where one section of the arch collapses
Blowhole
Blowholes form when the roof of a cave collapses as a result of the action of waves
Tombolo
A spit joining two land areas
Headland
Headlands are formed through the process of coastal erosion caused by the action of waves on the coastline
Which will have a greater impact on the native animals living in coastal dunes -litter or removing natural vegetation on sand dunes?
Litter, especially plastics, can be consumed by animals causing digestive issues or death which would impact the ecosystems food web.Moreover ,natural vegetation plays an important role as resources of food and habitats for native animals ,stabilising our coastal landscapes and protecting sand dunes from wind erosion.The loss of Natural vegetation would have a greater impact on the sand dunes.
Read the paragraph and think about the most effective coastal protection strategy. Give reasons
The vast majority of Australia's settlements (and therefore transport hubs) are located on the coast. Our tourist attractions and people's ability to access them would be undermined by both sea level rises and coastal erosion. Australia is known as a tourist destination with a strong beach culture and natural attractions along the coast. Sea level rises would make coastal land uninhabitable, and the sands of the beaches and other coastal attractions would be lost. The most effective coastal protection works would be breakwaters, rock retaining walls and sea walls to contain the rising seas and reduce storm surges.
The most effective coastal protection strategy would be Sea walls to contain sea levels rising.
Section 3 - Climate Change
a) Describe the biophysical processes that relate to the environment
The term “biophysical” describes the abiotic and biotic conditions of an environment and includes chemical, biological, physical and ecological components by processes such as ocean warming,currents and energy transfers
Ocean warming: refers to increases in temperature associated with greenhouse gas emissions. Monitoring of ocean temperature has shown that sea surface temperatures are rising globally and heat energy storage is increasing in the top half-mile of water. Warmer temperatures can lead to changes in coral reef and rocky intertidal ecosystems, fisheries, and storms.
Currents: are continuous and directed movements of water that are driven by winds, water density, tides, and influenced by coastal and seafloor features. Currents affect marine organisms in several ways by transporting nutrients, larvae and small organisms. These processes are extremely important for species with limited mobility, particularly for feeding and reproduction.
Energy Transfer: Sunlight is the primary energy source for most ecosystems. Plants capture this energy through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy stored in organic molecules. This energy then gets transferred through the food chain as herbivores eat plants and carnivores eat herbivores.Decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down dead organisms and returning energy to the environment.
b) Examine the causes of the environmental change
Generating power : Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas causes a large chunk of global emissions.
Manufacturing goods : Manufacturing and industry produce emissions, mostly from burning fossil fuels to produce energy for making things like cement, iron, steel, electronics, plastics, clothes and other goods
Consuming too much
c) Explain the short-term and long-term consequences of climate change
Short term consequences
drought
smog
flooding
volcanic eruption
blizzards
pollution
Long term consequences
Loss of sea ice,
Sea level rise
An increase in permafrost thawing
An increase in heat waves and heavy precipitation,
d) Suggest possible management strategies to address the environmental change
upgrading the electricity grid to support more renewable power
reducing the price of electric vehicles
supporting businesses and industries to innovate and adopt smarter practices and technologies
encouraging businesses and consumers to reduce emissions
regulating and reporting on greenhouse gas emissions