TOPIC 3: Law of Supply
Law of Supply
The law of demand represents the consumers’ side, while the law of supply represents the producers’ side
Supply describes the behavior of firms that are producing and selling goods and services
It also points out the relationship between price and the amount or quantity of goods and services that producers are willing and able to sell at that price, holding all other factors constant (ceteris paribus)
The law of supply states that the higher the price, the higher the quantity of goods and/or services that will be produced
In the same way, the lower the price, the lower the quantity of goods and/or services that will be produced
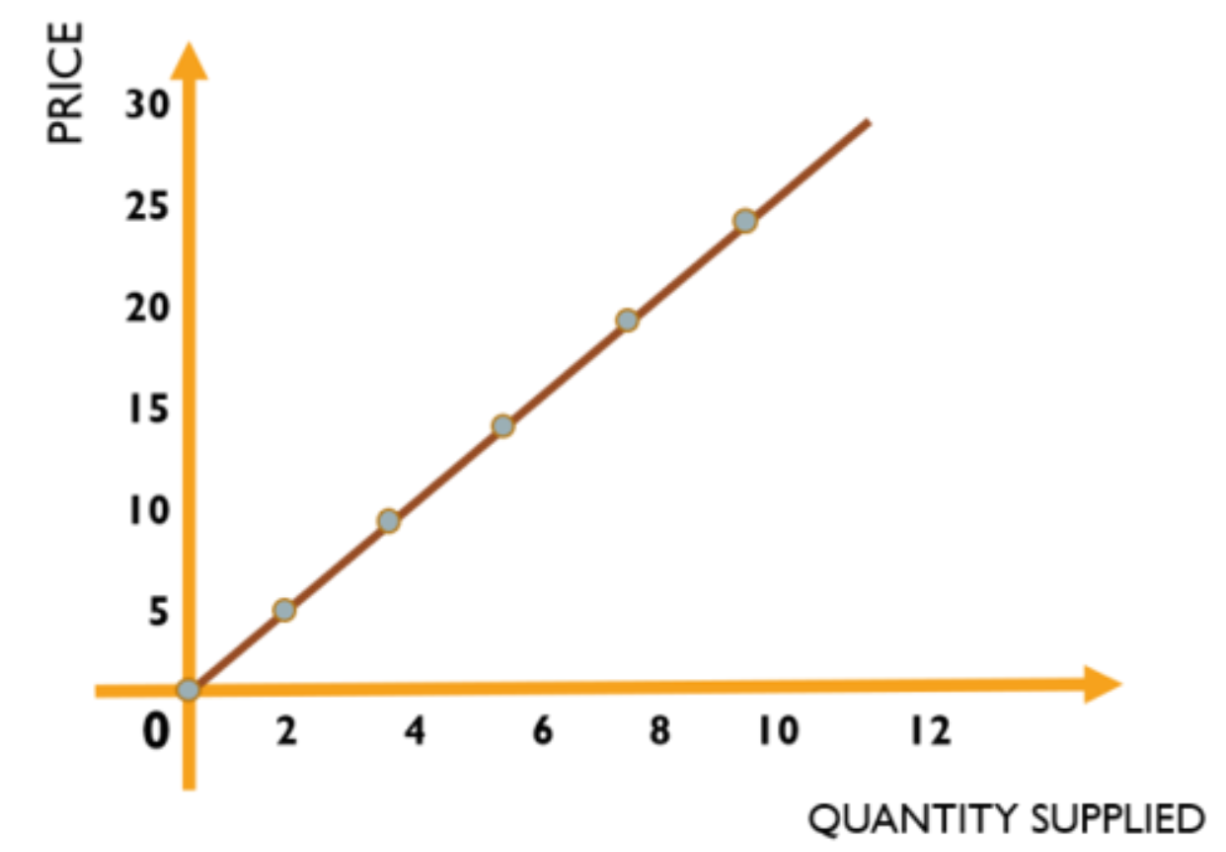
The supply-price relationship can also be expressed using the supply equation/function, which can be written as:
Qs = c + dP
Where Qs is the quantity supplied, and P is the price
The term c is the intercept or the quantity supplied when the price is zero
The variable d is the slope of the function, which tells us the change in quantity supplied per unit change in price
The positive sign captures the direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
The Model of Supply and Demand
Demand function
Qd = a - bP
Supply function
Qs = c + dP
To achieve equilibrium
Qd = Qs
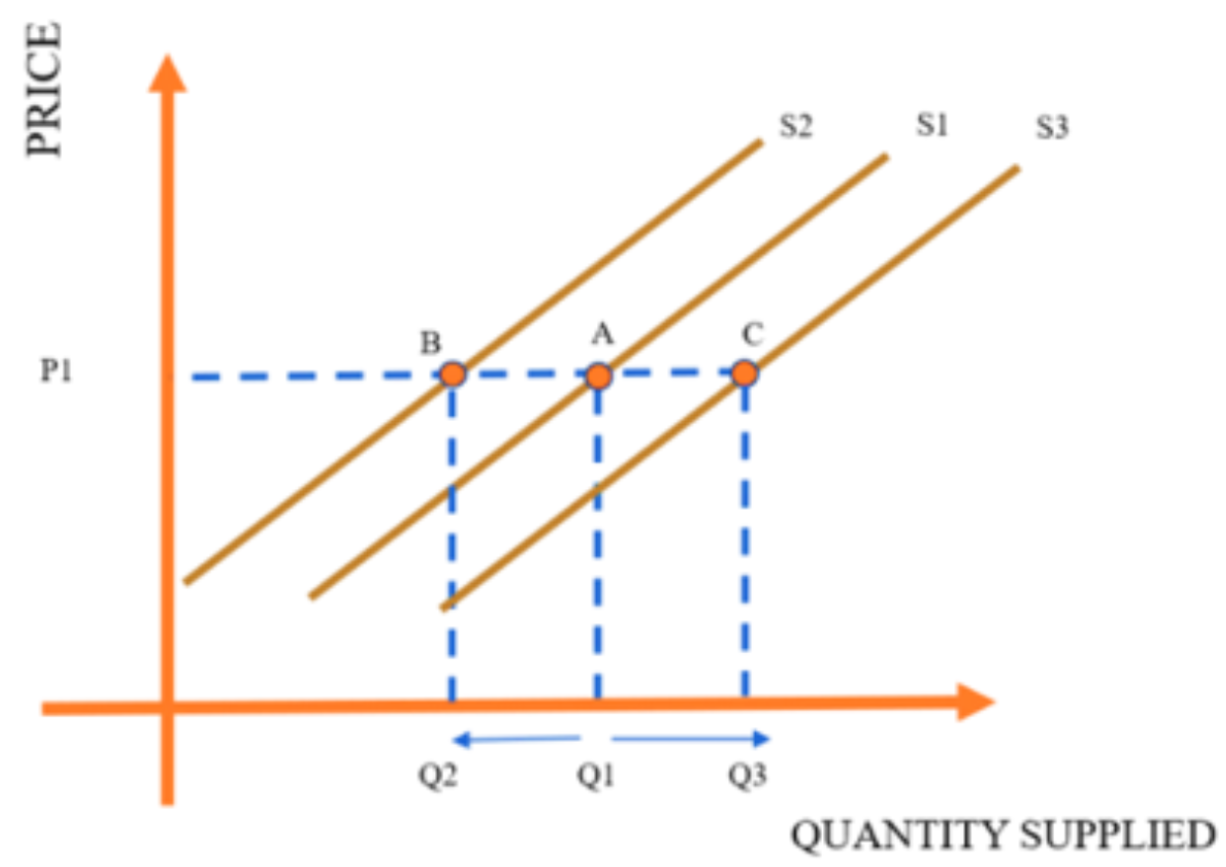
Change in Supply and Quantity Supplied
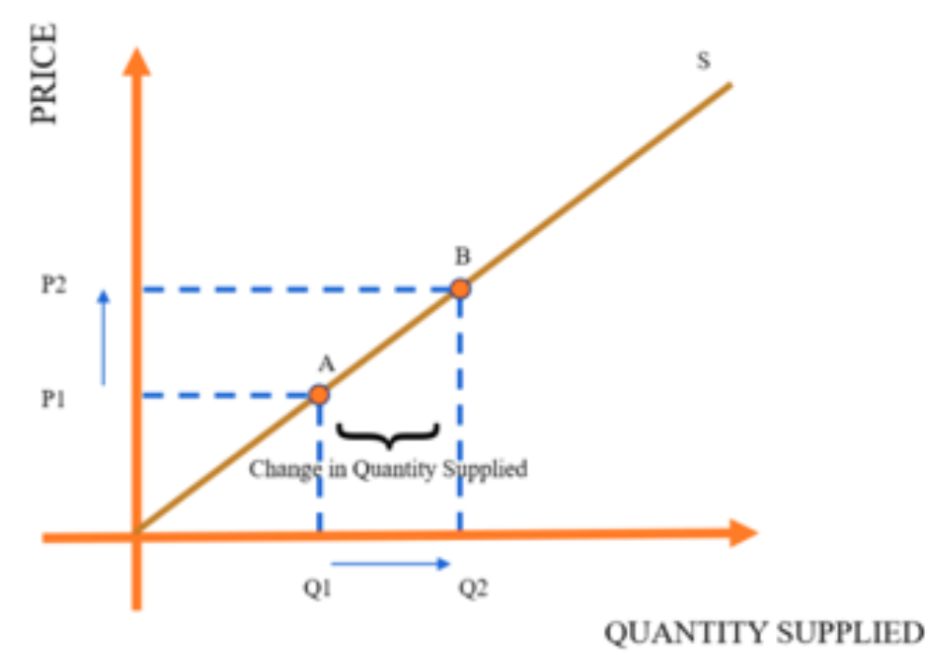
It is referred to as a change in quantity supplied since the term “supply” refers to the entire supply curve, while the term “quantity supplied” refers to a point on the supply curve
Factors Affecting the Supply
Technology
An improvement in technology or innovation makes the production costs of a firm decrease; hence, more output can be produced
Technological advancement consists of breakthroughs or new scientific discoveries in various fields
Change in the Prices of Inputs
An increase in the prices of inputs such as labor costs, raw materials, land, and equipment makes the production costs increase as well
This would make the sellers reduce the supply of their product at any given price, resulting in the supply curve shifting to the left
In the same manner, a decrease in the price of inputs will entice the sellers to produce more since it is less costly for them. This would make the supply curve shift to the right
Price of Related Goods
Raw materials and other factors of production can produce not just one type of commodity
There are commodities produced that share the same resources. Say there is a seller of puto and leche flan that shares common ingredients: sugar and condensed milk. When the price of puto decreases, the seller can utilize the ingredients and produce more leche flan, since it would be more profitable for the seller
As a result, there is a decline in the production of puto, and the supply curve will shift to the left
Government Policies
Tax and subsidies are some of the most common government policies that could affect the production of goods and services
The imposition of taxes means additional costs for the producers. Increased production cost hinders production, making the supply curve shift to the left
On the other hand, subsidies are a form of support from the government, such as a fertilizer subsidy, that helps farmers to lessen their cost of production. This would help increase their production, making the supply curve shift to the right