W3 Lecture 3-MSIN0144-Understanding the Market and the Opportunity
Lecture Overview
Understanding the Market and the Opportunity
Business Scalability
Business Viability
Models Used:
PESTLE Model
CAGE Model
VRIO Model
Porter’s 5 Forces
SWOT Analysis
Instructor: Dr. Evangelos Markopoulos
Course Code: MSIN0144
Module Engagement
Pulse Check 1: Assess understanding and engagement with the module.
Questions include:
Understanding of module learning objectives (Yes/No)
Awareness of assessment types and weightings (Yes/No)
Contact support resources (Yes/No)
Access to necessary resources (Yes/No)
Current progress rating (1-5)
Online engagement tool: www.menti.com (Voting code: 2791 2130)
Global Business Perspectives
Global Start-ups and Debates
Explores the concept of globalization discussed by Thomas Friedman.
"The World is Flat" - Video Resource: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oM2BguxRSyY
Three Eras of Globalization:
First Era (1492-1800): Localized conditions within states.
Second Era (1800-2000): Increased global interdependence spurred by the Industrial Revolution.
Third Era (2000-Present): Individual participation in globalization from diverse regions and backgrounds.
Market Understanding
Business Scalability
Analysis Tools: PESTLE, CAGE, VRIO, Porter Five Forces, SWOT.
PESTLE Analysis
Framework used to identify macro external forces affecting an organization.
Components include:
Political Factors: Government policies, stability, trade regulations.
Economic Factors: Interest rates, raw material costs, foreign exchange rates.
Social Factors: Demographic changes, cultural trends, lifestyle shifts.
Technological Factors: Innovation rate, automation, distribution methods.
Environmental Factors: Climate, sustainability practices, waste management.
Legal Factors: Local laws, regulations, employment law.
Useful in identifying threats and weaknesses for SWOT analysis.
CAGE Model
CAGE Framework by Pankaj Ghemawat focuses on:
Cultural Distance: Language, ethnicity, religion, social norms.
Administrative Distance: Government policies, colonial ties.
Geographic Distance: Physical remoteness, country size, communication barriers.
Economic Distance: Consumer income disparities, resource costs.
Explore trade patterns and international business strategies.
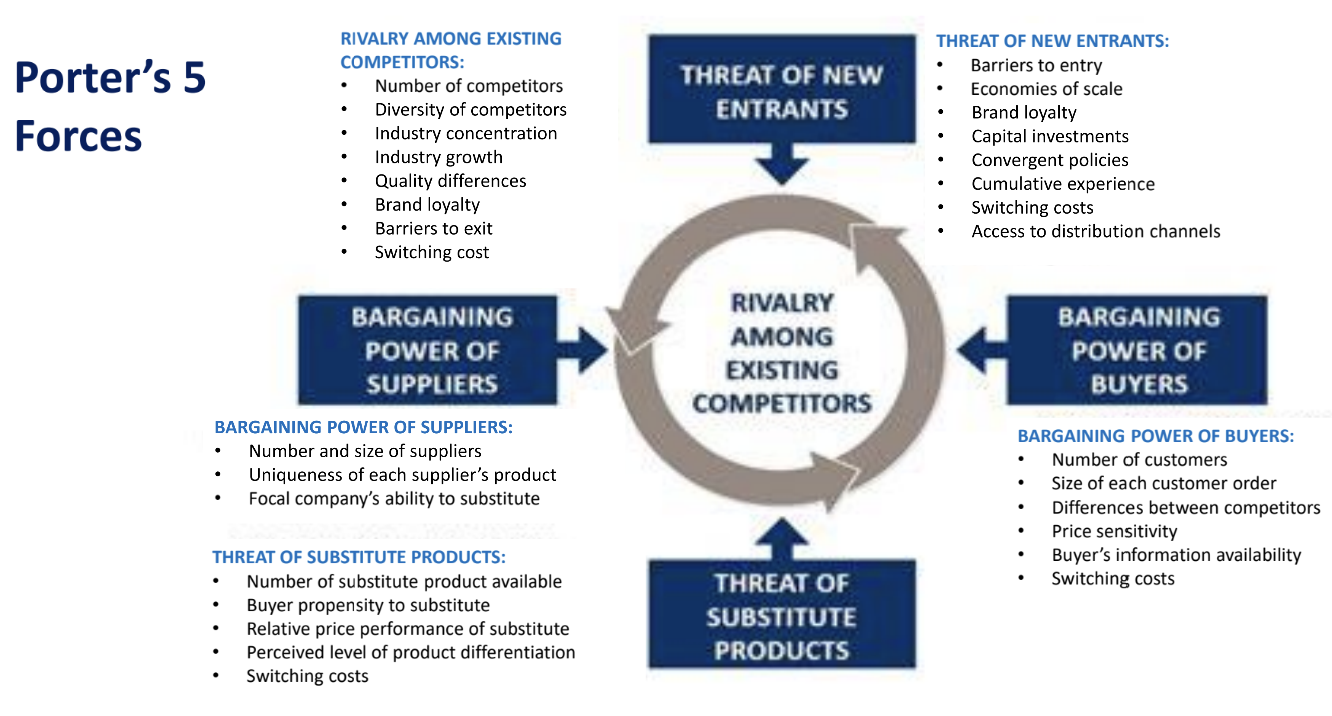
Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis
Competitive Dynamics:
Competitive Rivalry: Number of competitors, industry growth.
Threat of New Entrants: Entry barriers, industry economies of scale.
Buyer Power: Price sensitivity, buying volume.
Supplier Power: Number of suppliers, uniqueness of their products.
Threat of Substitutes: Availability and appeal of alternatives.
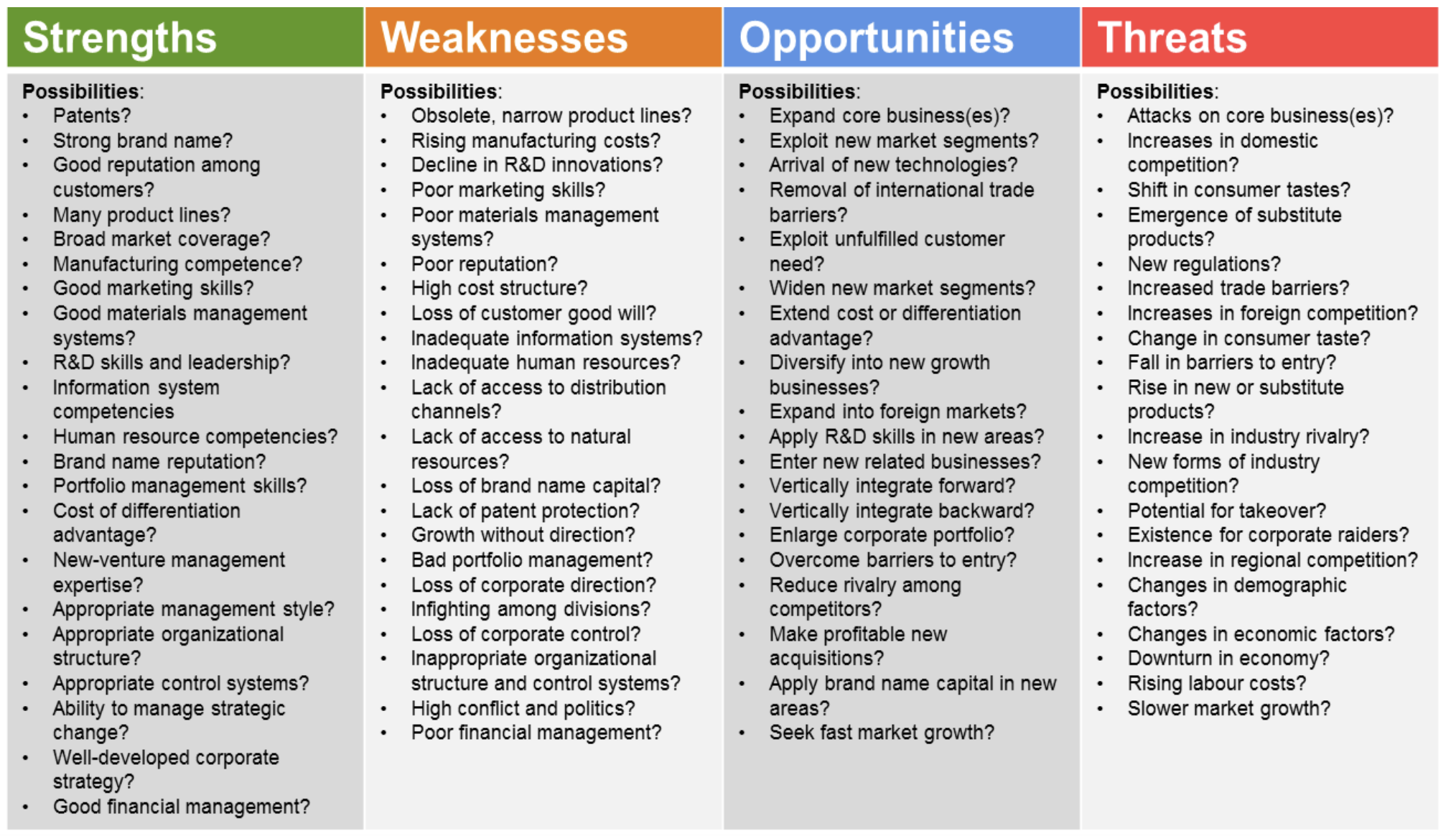
SWOT Analysis
Framework for Strategic Planning: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats.
Strengths: Core competencies, market coverage, brand reputation.
Weaknesses: Marketing skills, product line obsolescence.
Opportunities: Market expansion, exploitation of new trends.
Threats: Increased competition, and regulatory changes.
VRIO Model
Framework for assessing resources:
Value: Ability to leverage opportunities or fend off threats.
Rarity: Scarcity adds competitive advantage.
Inimitability: Hard to replicate or substitute.
Organization: Capability to exploit resources effectively.
Tools for competitive analysis and strategy formulation.
Summary of VRIO Model
Evaluate whether a resource provides:
Competitive Advantage: If valued, rare and not easily imitable.
Temporary Advantages: If difficult to imitate but others can catch up.
Competitive Disadvantage: If not valuable or rare.
Resources and Capabilities
List Resources: Financial, Human, Material, Non-material.
Use VRIO Analysis: Assess based on value, rarity, inimitability, organization.
Effective Strategy Building utilizing assessed resources.
