Unit 8 AP CHEMISTRY Part 1
1. Properties of Acids and Bases 💡
What Are Acids and Bases?
• Definition of Acids: Substances that increase hydrogen ion (H⁺) concentration in water.
• Example: HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻.
• Definition of Bases: Substances that increase hydroxide ion (OH⁻) concentration in water.
• Example: NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻.
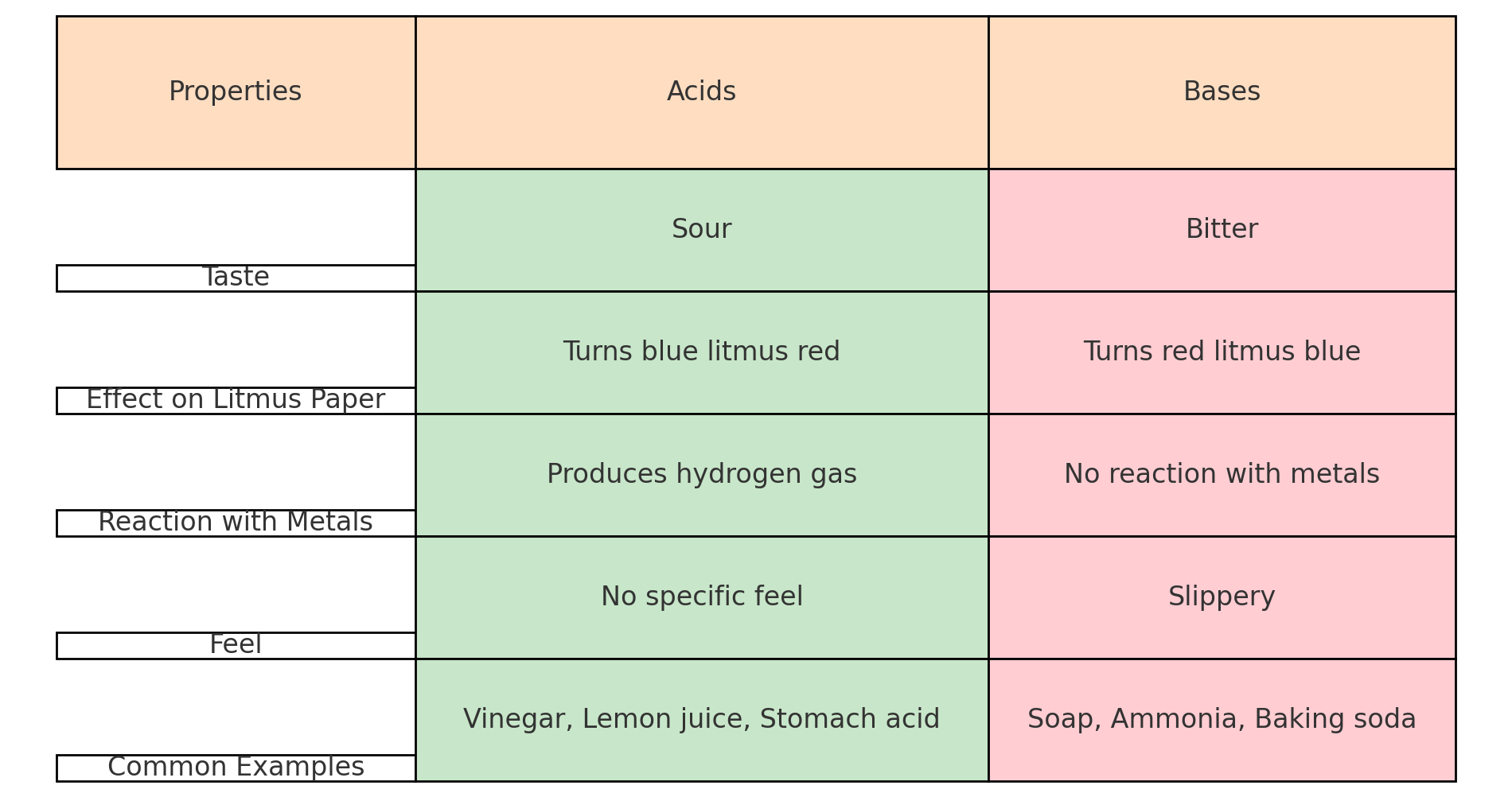
Key Properties of Acids 🔴
• Sour taste (e.g., lemon juice).
• Turn blue litmus paper red.
• React with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
Key Properties of Bases 🔵
• Bitter taste and slippery feel (e.g., soap).
• Turn red litmus paper blue.
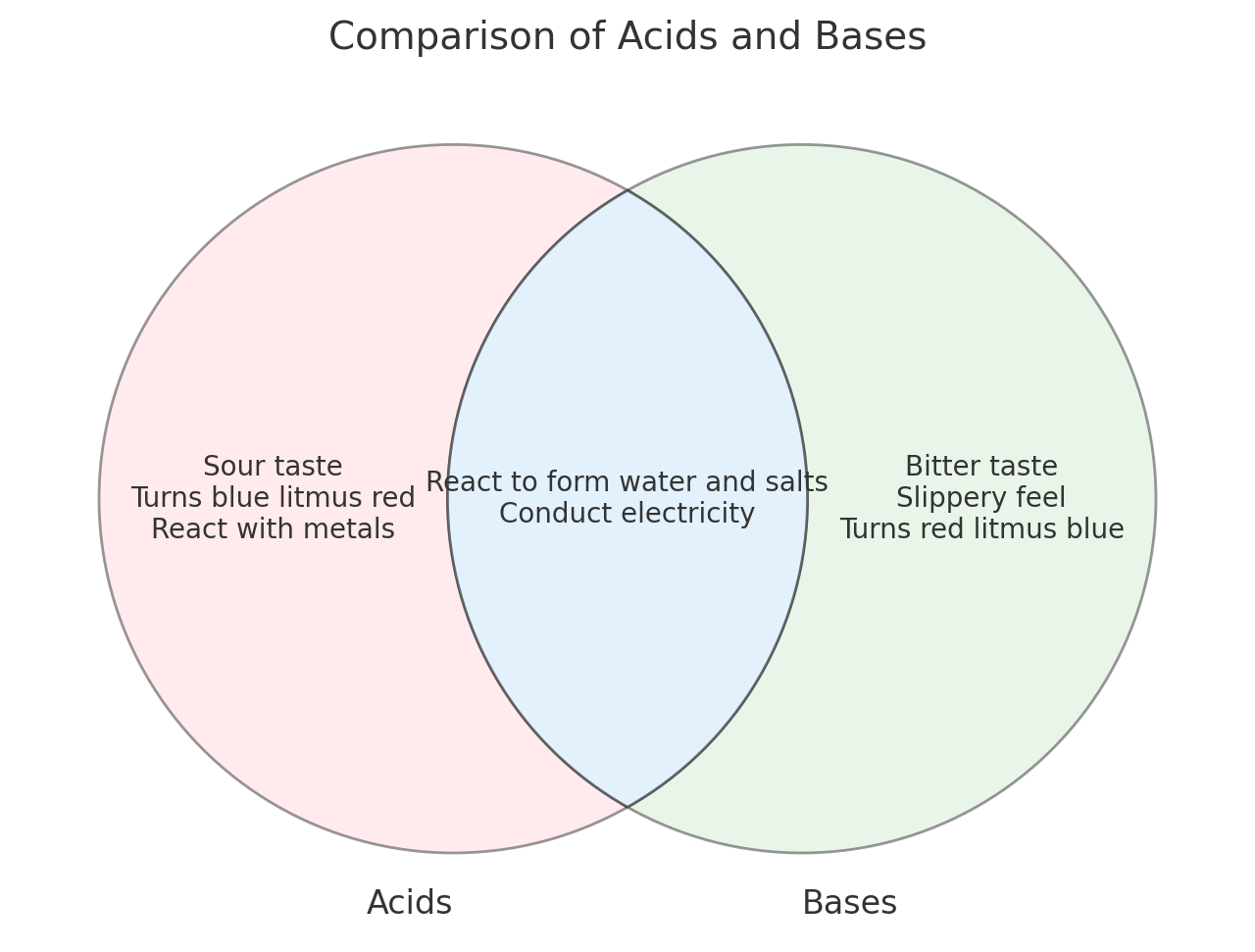
• React with acids to form water and salts.
Repetition
• “Acids give H⁺, bases give OH⁻.”
• “Acids are sour, bases are bitter and slippery!”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. What ion does an acid produce in water?
2. Which will turn red litmus blue: an acid or a base?
2. Common Examples of Acids and Bases 🧪
Examples of Acids
• Vinegar: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH).
• Lemon juice: Citric acid.
• Stomach acid: Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
Examples of Bases
• Soap: Contains hydroxide ions.
• Ammonia: A common household cleaner.
• Baking soda: Weak base.
Repetition
• “Acids are found in food (sour stuff), while bases are often in cleaning products.”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. Name one acid and one base found in your home.
2. Is lemon juice acidic or basic? Why?
3. Reactions of Acids and Bases ⚗
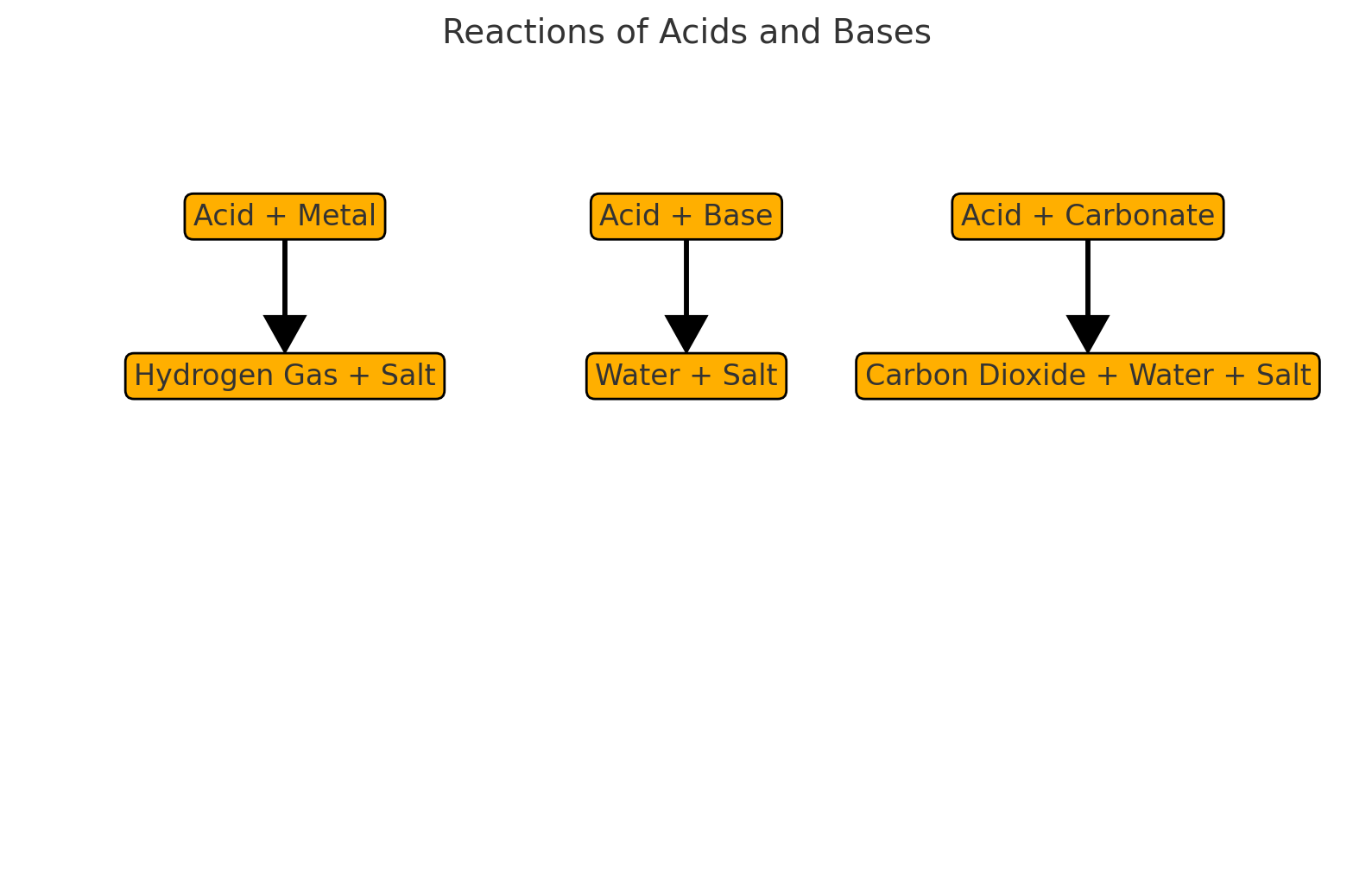
Reactions of Acids
• With Metals: Produces hydrogen gas.
• Example: Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen gas.
• With Bases: Forms water and a salt.
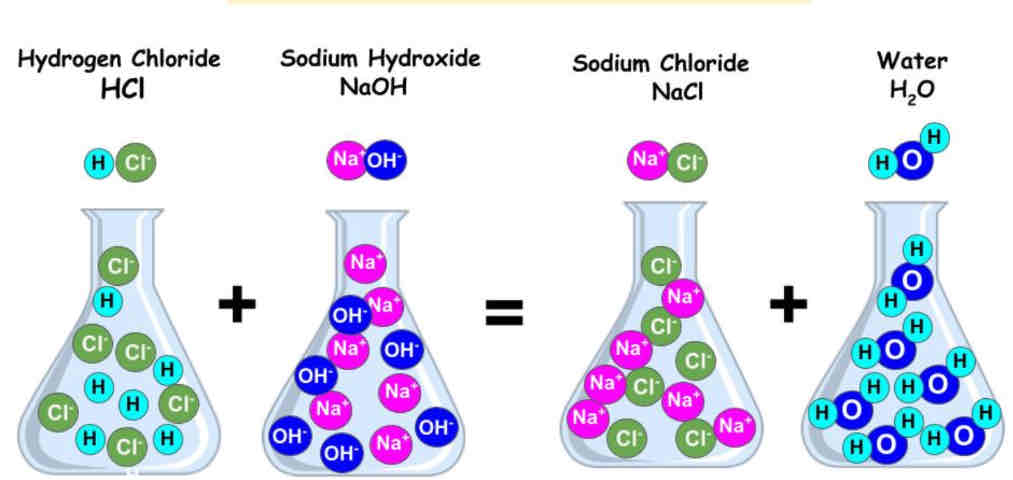
• Example: Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water.
Reactions of Bases
• With Acids: Neutralization reaction (forms water).
• Example: Potassium hydroxide + Nitric acid → Potassium nitrate + Water.
Repetition
• “Acids react with metals to give hydrogen gas. Bases react with acids to form water and salts!”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. What gas is produced when acids react with metals?
2. Write the balanced reaction: Sulfuric acid + Sodium hydroxide.
4. Indicators 🌈
What Are Indicators?
• Substances that change color to show if something is acidic or basic.
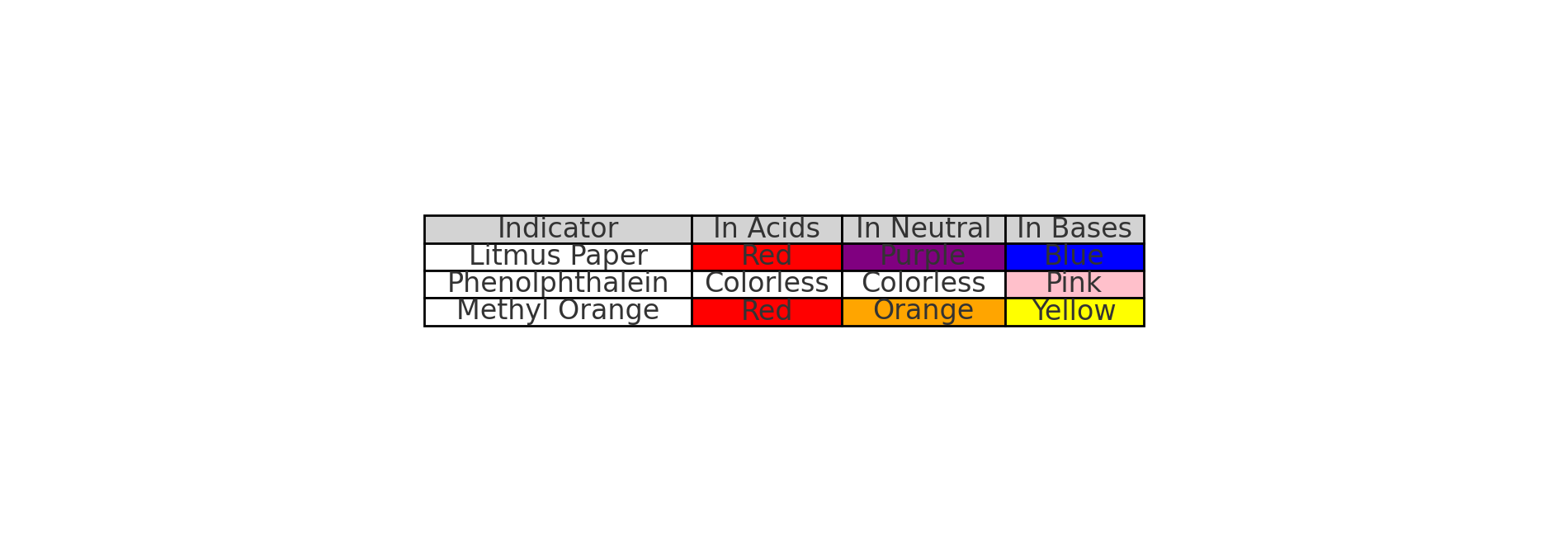
Common Indicators
• Litmus Paper:
• Acids → Red.
• Bases → Blue.
• Phenolphthalein:
• Acids → Colorless.
• Bases → Pink.
• Methyl Orange:
• Acids → Red.
• Bases → Yellow.
Repetition
• “Litmus is red in acids and blue in bases. Phenolphthalein is pink in bases!”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. What color will litmus turn in vinegar?
2. If phenolphthalein is pink, is the solution acidic or basic?
5. Neutralization Reactions ⚖
What Is Neutralization?
• A reaction where an acid and a base react to form water and a salt.
• Example: Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water.
Why Is Neutralization Important?
1. In Medicine: Antacids neutralize stomach acid (HCl) to relieve heartburn.
• Example: Magnesium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Water.
2. In Agriculture: Lime (calcium hydroxide) neutralizes acidic soil.
Repetition
• “Neutralization reactions always form water and salt. Think of it as balancing the acidic and basic forces!”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. Write the balanced neutralization reaction: Sulfuric acid + Potassium hydroxide.
2. Why do antacids neutralize stomach acid?
Detailed Content for Pages 6–10
6. Everyday Examples of Acids and Bases 🌍
Acids in Everyday Life
1. Vinegar (Acetic Acid):
• Found in kitchens for cooking and cleaning.
• Adds sour taste to food.
2. Lemon Juice (Citric Acid):
• Found in fruits like lemons, oranges, and limes.
• Gives tangy flavor to drinks and candies.
3. Stomach Acid (Hydrochloric Acid):
• Aids digestion by breaking down food.
• Too much can cause heartburn.
Bases in Everyday Life
1. Soap:
• Contains bases that break down oils and grease.
• Feels slippery on skin.
2. Ammonia:
• Used in household cleaners to remove stains.
• Strong-smelling liquid.
3. Baking Soda (Sodium Bicarbonate):
• A mild base used in baking and cleaning.
• Neutralizes acidic odors.
Repetition
• “Acids are common in food (like vinegar and lemon juice). Bases are common in cleaning products (like soap and ammonia).”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. Name two acids you use at home.
2. Which base helps break down grease in cleaning products?
Visual Suggestion 🎨
• Two labeled pictures: one showing food with acids (vinegar, lemons) and one showing cleaning products with bases (soap, ammonia).
7. Reactions of Acids and Bases with Metals ⚗
Acids Reacting with Metals
• Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and a salt.
• Example: Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen gas.
What Does This Reaction Look Like?
• If you drop a piece of zinc in hydrochloric acid, bubbles of hydrogen gas form.
Repetition
• “When acids meet metals, they make hydrogen gas and a salt.”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. What gas is produced when acids react with metals?
2. Write the reaction of magnesium with sulfuric acid.
Visual Suggestion 🎨
• A drawing of bubbles forming when a piece of zinc reacts with acid.
8. Neutralization Reactions in Everyday Life ⚖
What Is Neutralization?
• A reaction where an acid and a base form water and a salt.
• Example: Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water.
Applications of Neutralization
1. Antacids:
• Neutralize excess stomach acid.
• Example: Magnesium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Water.
2. Soil Treatment:
• Farmers add lime (calcium hydroxide) to neutralize acidic soil.
Repetition
• “Neutralization is when an acid and base balance each other to make water and salt.”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. Write the balanced reaction for hydrochloric acid and potassium hydroxide.
2. Why are antacids used for stomach acid?
Visual Suggestion 🎨
• A diagram showing acid and base molecules reacting to form water and salt.
9. Indicators: Identifying Acids and Bases 🌈
What Are Indicators?
• Substances that change color to show if a solution is acidic or basic.
Common Indicators
1. Litmus Paper:
• Acids turn blue litmus red.
• Bases turn red litmus blue.
2. Phenolphthalein:
• Acids → Colorless.
• Bases → Pink.
3. Methyl Orange:
• Acids → Red.
• Bases → Yellow.
Repetition
• “Litmus turns red for acids and blue for bases. Phenolphthalein is pink in bases!”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. What color does methyl orange turn in an acidic solution?
2. If phenolphthalein is pink, is the solution acidic or basic?
Visual Suggestion 🎨
• A chart showing the color changes of indicators in acids and bases.
10. Summary of Properties of Acids and Bases 📋
Acids
1. Taste sour.
2. Turn blue litmus red.
3. React with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
4. Produce H⁺ ions in water.
Bases
1. Taste bitter and feel slippery.
2. Turn red litmus blue.
3. React with acids to form water and salts.
4. Produce OH⁻ ions in water.
Repetition
• “Acids give H⁺ and are sour. Bases give OH⁻ and are slippery!”
Understanding Check 🧠
1. What ions do acids and bases produce in water?
2. Write one property of acids and one property of bases.
Visual Suggestion 🎨
• A summary table comparing acids and bases with key properties side by side.
This concludes Pages 6–10. Let me know if you’d like to proceed further or adjust the details!