AP Human Geography Unit 7 Exam Review
Economic Sectors and Patterns
The world economy can be separated into distinct categories called sectors
Primary production is the most basic economic activity that deals with the extraction of natural raw materials from the earth.
Ex: Agriculture, mining, energy, forestry & fisheries
Secondary production deals with the processing of the raw materials that are from the primary activities & making them into finished goods/products.
Ex: include MANUFACTURING!!!!!!
Tertiary production includes the retailing and transportation of the finished goods to the people who buy them or consumers.
Most tertiary activities are the sale of goods that fall into more specialized quaternary & quinary activities
Quaternary production includes standard business services for research and administration
Ex: finance, insurance, marketing, and wholesaling.
Quinary production is the highest level that includes consumer services that consist of the highest level of decision making and large-scale research
Ex: high-paying & high-role jobs like government officials, CEOs, healthcare & higher education leaders
In world trade, core (MDCs, First World) countries have the advantage in trade over to LDC, such as semi-periphery (NIC, 2nd world) & periphery (3rd World) countries.
Deindustrialization is a process happening in many core countries to have a service (vs manufacturing) based economy since they can get cheap raw materials from the periphery countries
These resources can be processed & manufactured in periphery or semi- periphery countries
Then exported to core countries for cheaper wages & overall costs for the core countries
Alfred Weber least cost theory explain the key decisions made by businesses about where to locate factories
Attempt to predict the location of manufacturing site relative to the location of resources need for production
Weber’s key variables are transportation, labor & agglomeration
Considers two main inputs:
Distance of transportation to market
Weight of goods being transported
Measures of Development
Human Development Index (HDI): social welfare index measure:
life expectancy
Years of schooling
Standard of Living or GNI per capita
measures total value of goods & service produced within a country together with the balance of income & payments from/or to other countries
HDI can...
measure differences within a country as well as between countries
highlight where poverty is worst, within & between countries
measure of how far a country has developed and whether there are improvements
help a country set goals to improve life quality, healthcare and education
Women and Economic Development
Women and Income Inequality:
In almost all countries in the world (besides in North America & Australia), women work more hours than men & still make less money per hour
Although there are more women in the workforce
Woman do not have equity in wages or employment opportunities
Effects of Employment for Women:
When women can get jobs, they receive healthcare & higher education
Receive specialized ways to work and start a family to improve their status in society
As countries develop economically, women can have more rights which allows for more education & less “traditional” roles in homes
Their role in society can change & improve with an education
Can earn a better job, make money & live without dependency on men

U.N. thinks that correcting gender inequality is so important that they made it No, 5 on their 19 goals for sustainable development:
Understanding that a countries improve economically, roles the women play in society change dramatically
Microloans are small credit or loans given to people in developing countries to start small businesses and help improve the economy.
In Bangladesh, for example, the Grameen Bank gives microloans to women to start personal small businesses & provide for their families
Allowing women to move out of poverty
The U.N. developed a mandate called the Millennium Development Goals that were created in 2015 with eight goals in mind.
One of these goals is to promote gender equality & empower women through the provision of better women’s health care
Other goals include eradication of hunger, basic universal education & an end to abject poverty
Theories of Development
Rostow's Stages of Development:
Rostow’s Stages of Development is a model that analyzes the 5 steps that it takes to move from an agricultural society to a service-based economy
Main assumption in creating the model was that each country had comparative advantage
Critics of this model state that it does not account for colonial legacy or government corruption in developing countries
Rostow’s Stages of Development Are:
Traditional Society
Economy is focused on primary production & has little technical knowledge
Preconditions to Takeoff
Country’s leadership begins to invest in infrastructure with some technical knowledge to stimulate the economy
Takeoff
Economy shifts to industrialization & some labor shifts to factories with new urban infrastructure
Drive to Maturity
Technical advancements power a country where workers mostly get skill-based education.
High Mass Consumption
Technical knowledge and education levels are high & industrial trade economy develops
Wallerstein's World Systems Theory:
Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory attempts to explain the relationship between the core & periphery countries.
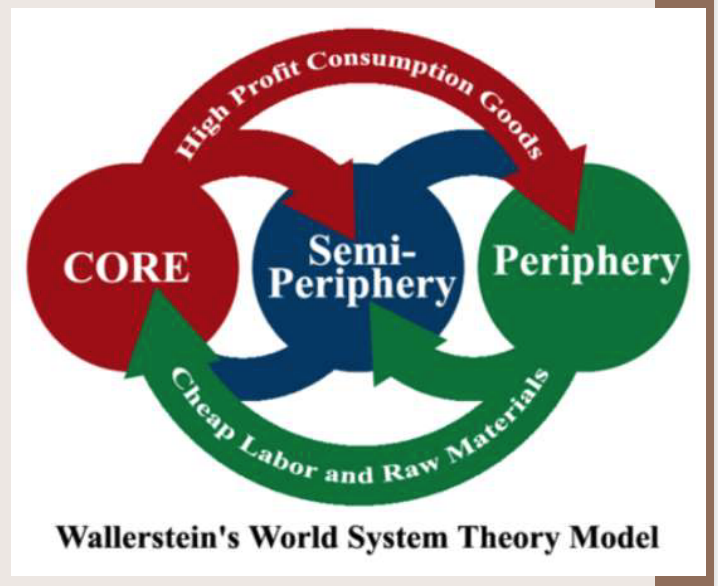 The image basically shows how the core benefits from the periphery & semi-periphery
The image basically shows how the core benefits from the periphery & semi-peripheryAlso shows how the semi-periphery can benefit from the periphery while still benefiting the core
Dependency Theory:
Dependency Theory holds that Less Developed Countries (LDCs) are highly dependent on foreign factories & technologies from More Developed Countries (MDCs) to provide employment and infrastructure.
LDCs in this theory get stuck in the continuous cycle of dependency on the MDCs which never allow their economies to fully develop