UNIT 6- International Trade
Reasons We Trade With Other Countries
To improve our standard of living
Every country lacks some vital resources it can only get through trade
Each country’s climate, labor force, natural resources make it efficient in some production and inefficient in others
Specialization allows for mass production and greater efficiency
Determining What to Trade
Absolute Advantage → occurs when one nation produces a product more efficiently than another nation
Comparative Advantage → occurs when one nation can produce a product at a lower opportunity cost than another nation
How to determine absolute/comparative advantage:
Input or output problem:
input = resources (time, land, etc.) to produce a constant output
output = production given a constant resource (input)
Absolute advantage: input → less resources, output → more production
Comparative advantage: input = into/under, output = over
**Comparative Advantage is always based on the lower OPPORTUNITY COST**
whichever you have comparative advantage in is what you will export
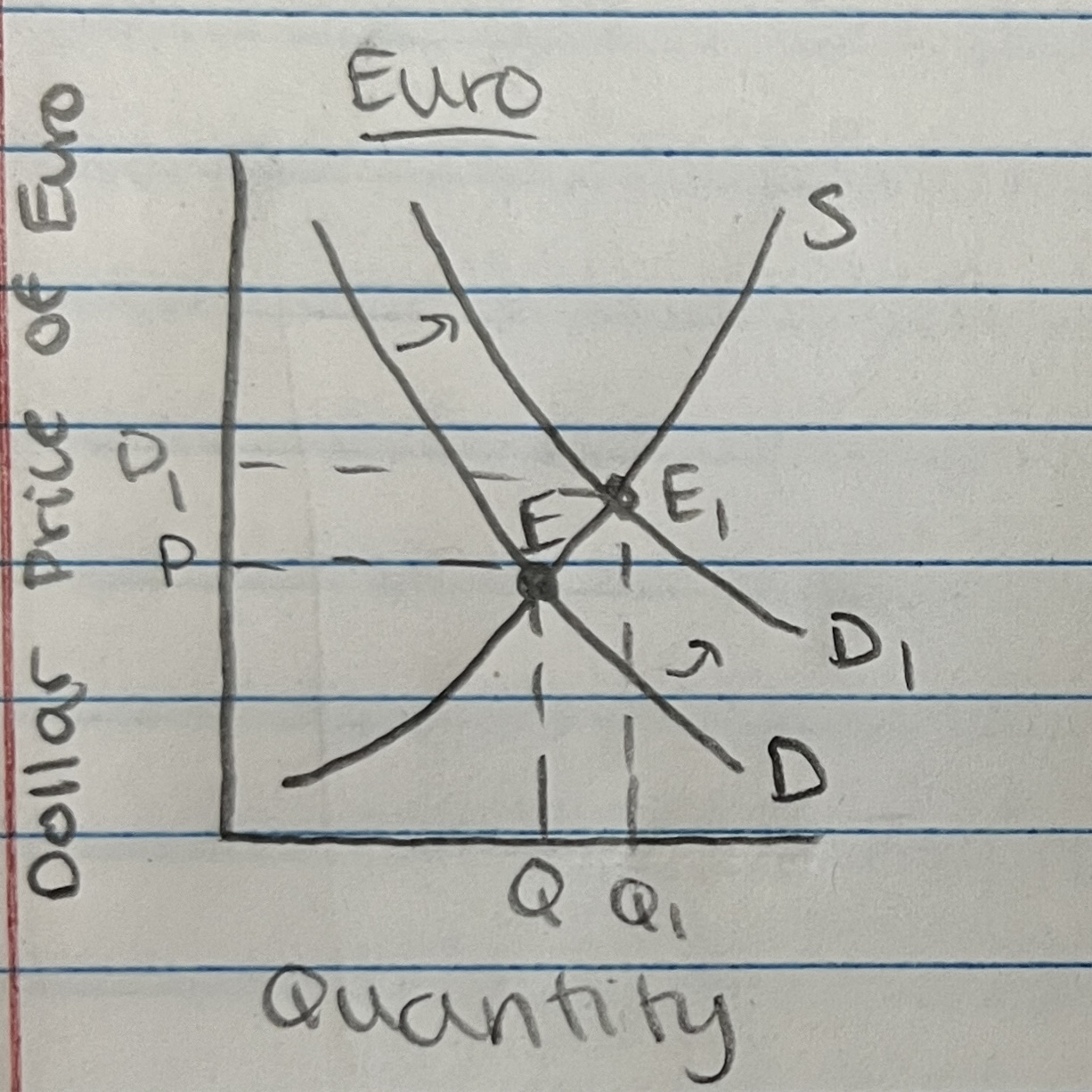
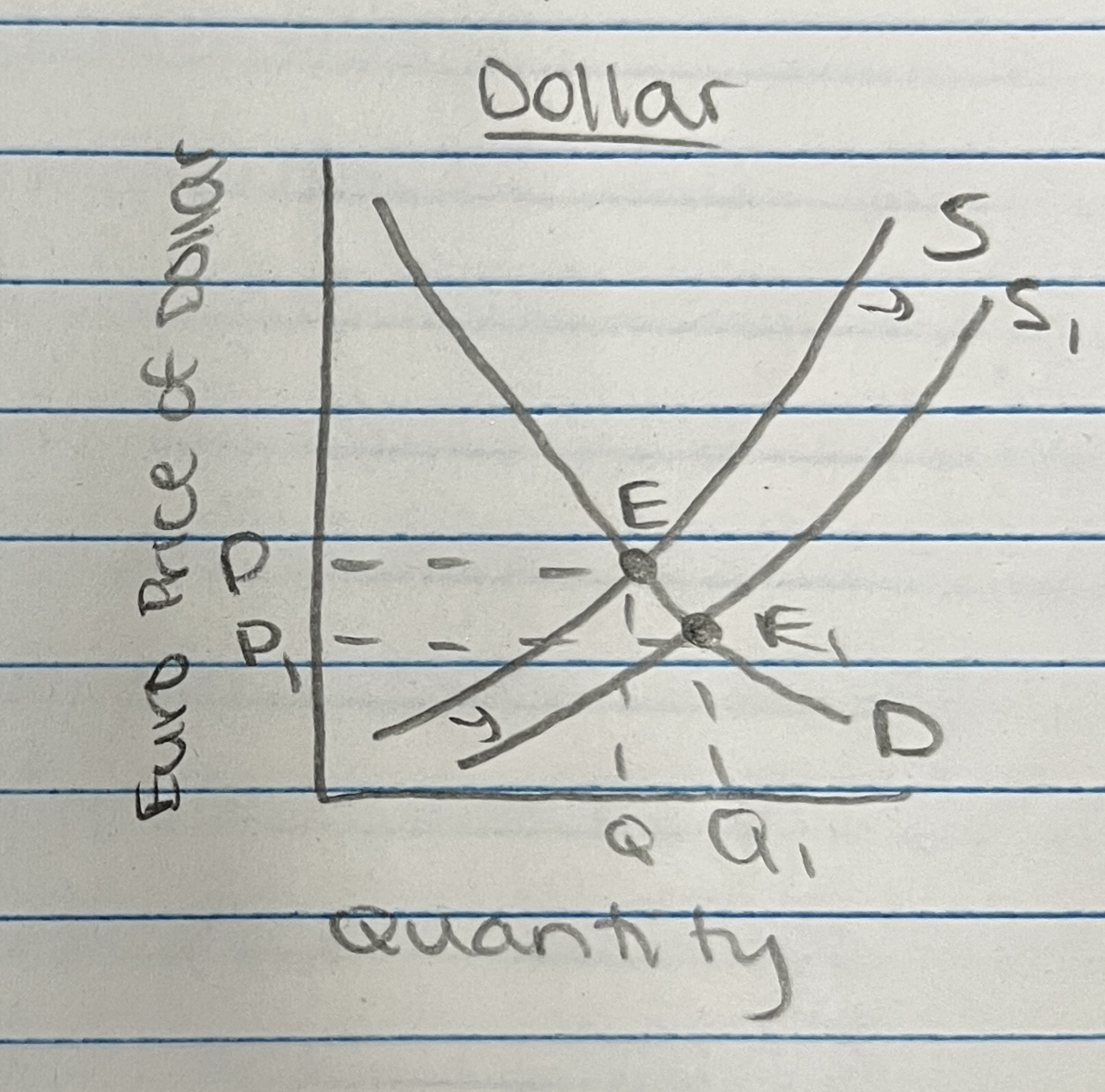
Exchange Rates
Exchange rate states the price in terms of one currency at which another currency can be bought
Dollar vs. Euro, vs. Peso, etc.
Fixed Exchange Rates:
government sets exchange rate
Devaluation → decrease the value of the currency
used to boost tourism, increase exports, improve trade balance
makes goods cheaper
used to fight recession because it increases aggregate demand
Revaluation → increase the value of the currency
used to fight inflation because it decreases aggregate demand
Floating Exchange Rates:
exchange rate is determined by the market forces of supply and demand for that currency
Currency Depreciation → value of currency decreases; a weak dollar
caused by a decrease in interest rates, increase in domestic inflation, less demand for US goods
weak dollar causes increase in exports and decrease in imports (trade balance)
Currency Appreciation → the value of the currency increases; a strong dollar
caused by an increase in interest rates, a decrease in domestic inflation, increased demand for U.S. goods
strong dollar causes decrease in exports and increase in imports
Effects of Fiscal Policy:
expansionary fiscal policy increases interest rates → dollar appreciates
contractionary fiscal policy decreases interest rates → dollar depreciates
Effects of Monetary Policy:
expansionary monetary policy decreases interest rates → dollar depreciates
contractionary monetary policy increases interest rates → dollar appreciates
Foreign Exchange Market Graph:
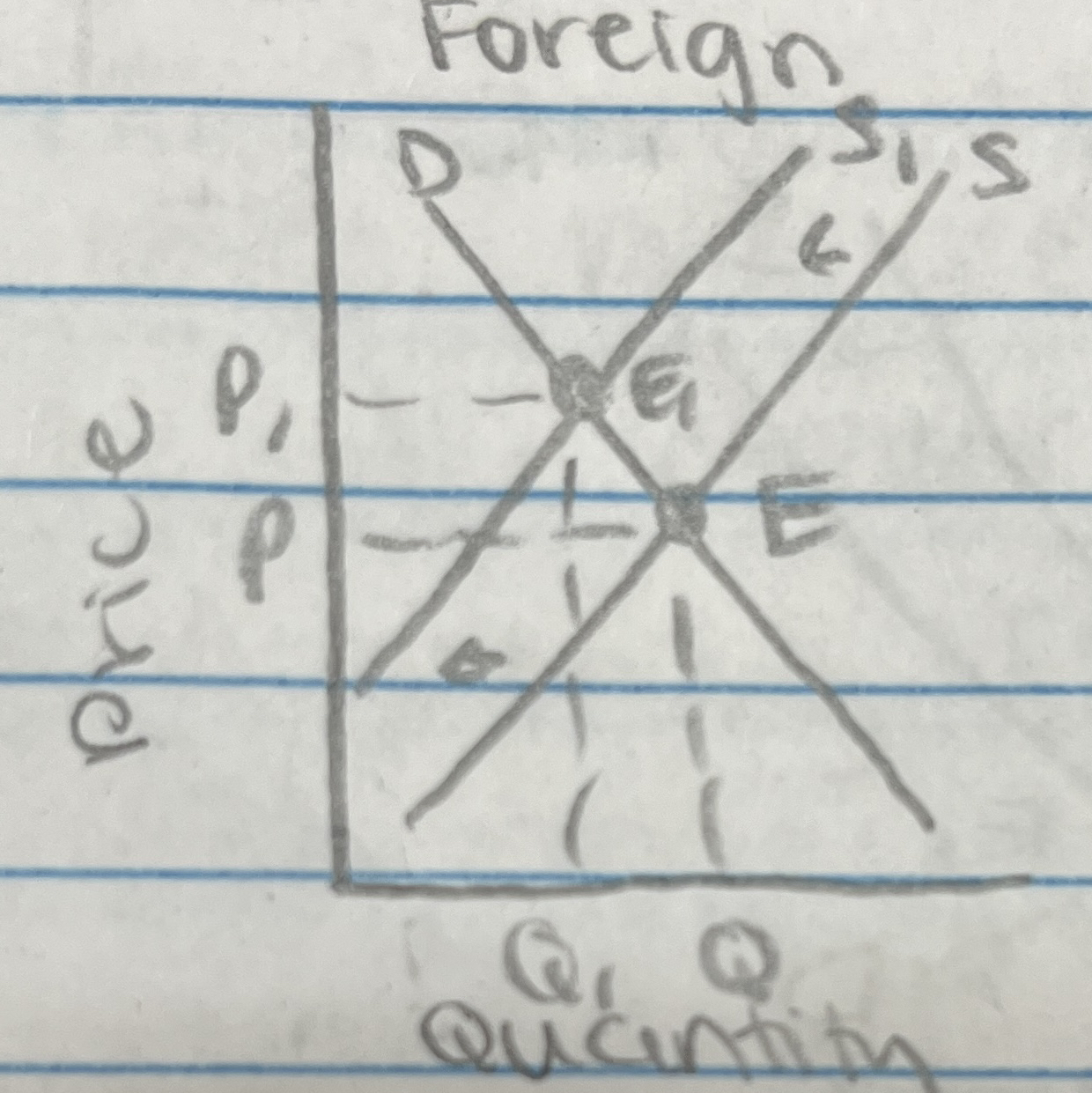
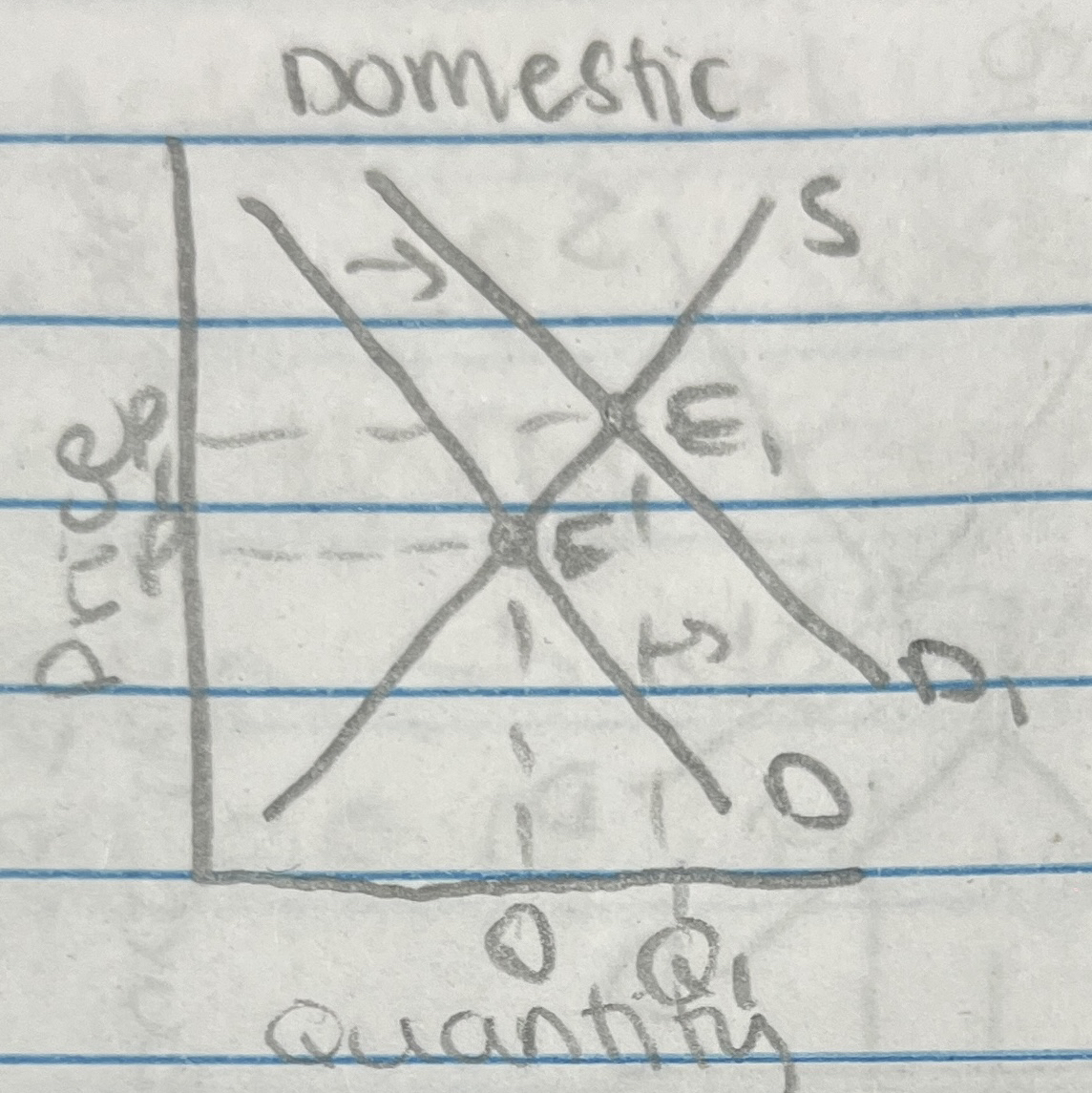
Free Trade vs. Protectionism
Free trade → no tariffs, no quotas, no barriers to trade
Protectionism → workers in import competing firms
Arguments for protectionism:
self-sufficient military → the industries that produce for the military don’t want to have to import in the time of war
preserve domestic goods → protect your job
cheap foreign labor argument → how can Americans compete
protection against dumping → where a foreign government gives an export subsidy to a foreign company so they can sell goods below market price in the home market
infant industry argument → protect new industries long enough until they have a chance to compete
Tariff = a tax on imported goods
Quotas = a limit on a good that is imported
Balance of Payments
The balance of spending flowing into the country from other countries and spending flowing out of the country into other countries
Credit (+) → money flowing into country
Debit (-) → money flowing out of country
Tracks all money coming into the country and all money that leaves the country
Current Account:
Balance of Trade = exports - imports
Net Investment Income = interest/dividends
Net Transfer Payments → government aid to another country
Net Services → a foreign company providing services for a U.S. company and vice versa