AP World Final
Unit 1 - The Global Tapestry
*most events are connected to religion!
main religions:
buddhism
- india, china, southeast asia, japan
- buddhism spread from india to east asia through silk roads
context:
founded by siddhartha gautama, hindu prince (563-483 BCE), rejected wealth + worldly possessions, became buddha
4 noble truth: (1) all life is suffering, (2) suffering caused by desire, (3) can be freed of desire, (4) freed of desire following a prescribed path
death of buddha split buddhism into theravada buddhism and mahayana buddhism
theravada buddhism: meditation , simplicity
mahayana buddhism: great ritual, spiritual comfort, more complex
impact: rejects caste system - appealed to those of lower rank
india: reabsorbed in hinduism
china, japan, southeast asia: buddhism continued to thrive
further: spread via trade routes
christianity
- started as group of jews, expanded into europe, northeastern africa, middle east
context:
based around jesus of nazareth, figure who was the messiah the hews had awaited, teachings of devotion to god and love for others
jesus crucified by roman and jewish leaders in 30 CE and he rose from dead into heaven
based on bible teachings
world was created by god, but world has fallen from god
impact: compassion, grace through faith appealed to lower classes and women
became most influential religion in mediterranean basin by 3rd century
became official religion of roman empire, branching north and west
connection with roman empire had profound impact on global culture
confucianism
- china (400 BCE+)
context:
founded by confucius ,educator and political advisory
deals with how to restore political and social order, not with philosophical or religious topics
impact:
compatible with other religions, making it likeable
bed to distinctive chinese culture of tight knit communities
stayed within chinese culture
hinduism
- india
context:
belief in one supreme force called brahma who created everything
gods are manifestations of brahma (vishnu = preserver, shiva = destroyer)
goal of believer is to merge with brahma - believe it takes multiple lives to accomplish and believers live to determine who they will be in their next life
following dharma (rules of your own caste) will move you closer to brahma - moksha is highest state of being
impact:
religion and social caste system, prevented global acceptance of hinduism
recently hindus are rebelling caste system
islam
- caliphates (islamic kingdoms), north africa, central asia, europe
*sufism = part of islam, mystical, deep connection with god
context:
7th century - muslims are the believers
allah presented words through prophet muhammad, whose words were recorded in the qur’an
salvation is won through submission god
5 pillars of islam: (1) confession, (2) prayer 5 times a day, (3) charity, (4) fasting during ramadam, (5) pilgrimage to mecca
2 groups, shia and sunni disagreed who should succeed muhammad
abbasid caliphate
- islamic empire from 750-1258 CE
capital in baghdad (iraq)
house of wisdom was a center for arts and sciences, math
developments in europe
middle ages: fall of rome before renaissance
- eastern roman empire became byzantine empire
- western europe: collapsed entirely but christianity remained strong
european feudalism: land divided
feudalism: european hierarchy social system of middle ages
king: power over whole kingdom
nobles: had power over sections of kingdom in exchange for loyalty to king
vassals: lesser lords with land that could be divided into estates called manors
peasants/serfs: worked the land
emergence of nation states
at the end of middle ages, feudalism declined
germany: reigning family of emperors died out, where merchants and tradespeople became more powerful
england: english nobles rebelled against king john and forced him to sign magna carta (limited the power of the monarchy, established the principle of the rule of law, and protected the rights of individuals against authority)
france: in 12th century england occupy many parts of france with revolts
- hundred years’ war (1337-1453): conflict between england and france over french throne, unified france as england withdrawal
spain: queen isabella of castile and ferdinand of aragon married to unite spain in a single monarchy and forced all residents to convert to christianity —> this is called the spanish inquisition
russia: taken over by tartars (eastern mongols) under genghis khan in 1242 until russian prince ivan III expanded his power in 1400s and became ivan the terrible ruler
developments in asia
song dynasty (960-1279)
confucianism justified subordination of women (men head of house) - foot binding: women’s feet bound after birth to keep them small
neo-confucianism: buddhist ideas about soul, filial piety (obey parents), loyalty to superio
neo-confucianism vs. confucianism:
confucianism: focuses on ethics, social harmony, and proper conduct.
neo-confucianism: incorporates metaphysical and cosmological elements, emphasizing self-cultivation and moral perfection.
ming dynasty (1368-1644): after brief period of mongol dominance
religion: influenced by nestorianism, manichaeism, zoroastrianism, islam, and especially buddhism in its two forms
mahayana: peaceful + quiet existence apart from wordly values
chan or zen: meditation and appreciation of beauty
japan
relatively isolated from external influences outside asia for many years
feudal japan (1192)
emperor
shogun (chief general)
daimyo: owners of larger pieces of land, powerful samurai
loyalty, courage, honor
lesser samurai (vassals)
peasants and artisans
women had little rights
india
delhi sultanate: islamic invader kingdom in delhi
islam took over northern india - clash between islam monotheism and hinduism polythesim
islam rulership brought in farming improvements
southeast asia
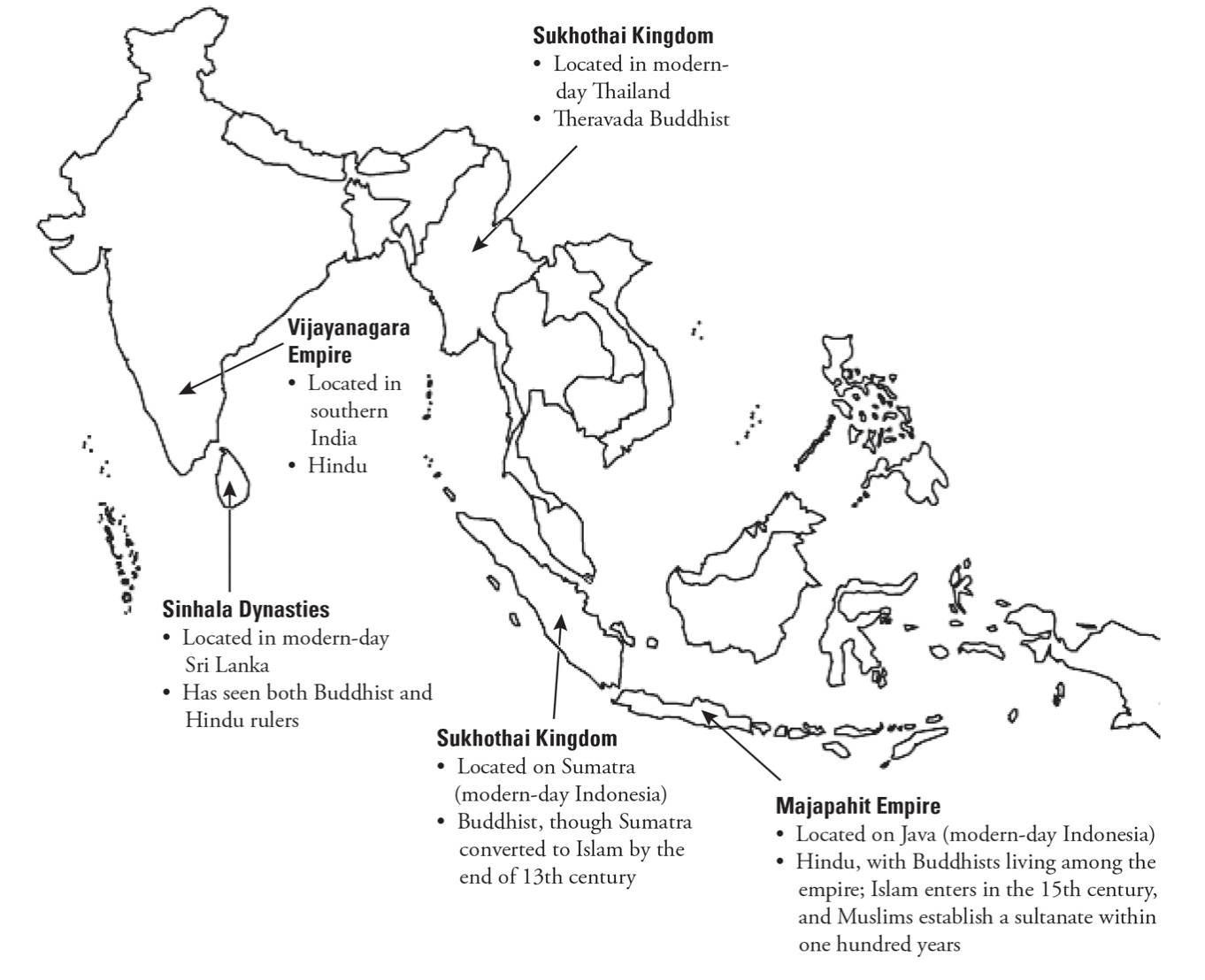
khmer empire (9th-15th century): hindu empire in cambodia, laos, thailand
developments in africa
islamic empire spread to north africa in 7th to 8th centuries
explosion of trade began
hausa kingdoms: series of state system kingdoms off niger river
islam region, achieved economic stability + religious influence through long trade
political + economic decline in 18th due to internal wars
developments in americas
3 main civilizations in central + south america: maya, incas, aztecs
aztecs: trade + sacrifice
arrived in mexico in mid 1200s
tenochtitlan: capital city
strict army, expansionist policy
empire of 12 million people with trade, many people ensalved
women were subordinate but could inherit property
inca: my land is your land
expansionist - army, unified language, system of roads
many peasants
capital of cuzco had almost 300000 people in late 1400s
women more important, could pass property to daughters
polytheistic religion with human sacrifice - sun god was most important
people mummified after death
military very important
unit 2: networks of exchange
crusades (11-14th century): military campaigns by european christians to convert muslims and non christians, combat religious questioning
urbanization
trade led to growth of urban culture - cities usually around trade routes
silk route cities were the most populous
the rise and fall of the mongols
set of tribes + clans that were superb horseman + archers
gengis khan: unified tribes in mongolia to expand authority over other societies - first invaded china in 1234
mongol empire: pacific ocean to eastern europe
kulbai khan: genghis khan’s successor - ruled china
members of mongol society could not rebel in fear of being killed
overall impact:
great diffusers of culture
the mongols stopped russia from developing to maintain control over the region and prevent any potential threats to their empire.
world trade, global awareness
mali and songhai
mali had a lot of gold that islamic traders were interested in
mansa musa: mali ruler who built capital of timbuktu and expanded kingdom beyond ghana
sonni ali: songhai ruler that conquered region in west africa
chinese technology
song dynasty: system built on merit + civil service exam
improved transportation
business practices
improved literacy with printed books
silk road
china to mediterranean cultures in early days of roman empire
cultural exchange through travellers stopping at trade towns - kashgar, samarkand
silk, porcelain, paper, religion, good, military technologies
unit 3: land-based empires
major european developments:
the renaissance
as trade increased, people moved to cities and flow of money
humanism: focus on personal accomplishment, happiness, and life on earth instead of goal of salvation
people could afford art again
inventions: johannes gutenberg invented printing press - made books easy to produce and affordable
protestant reformation
catholic church was one of the most powerful organizations in middle ages
indulgences could be bought to reduce time in purgatory
nobles + peasants frustrated by church’s exploitation
martin luther: german monk who purblished his list of complaints against the church - proposed salvation was directly given through god, not through the church
pope leo X: excommunicated luther
luther’s ideas led many other to come forward
lutherans: luther’s followers - separated from catholic church
calvinism - john calvin: only a few people would be saved by god, great influence in scotland + france
catholic reformation
a movement within the catholic church in response to the protestant reformation. It aimed to address corruption, reaffirm catholic doctrine, and establish new religious orders
council of trent: reinstated pope authority, reestablished latin as only language in worship
caused wars
scientific revolution
expanded education led to world discoveries
copernican revolution: nicolaus copernicus - discovered earth revolved around sun and rotated on its axis
galileo: built off copernicus’ theory, put under house arrest by catholic church
scientific method: shift from reasoning being most reliable to scientific method (theory, documentation, others experimenting)
european rivals
spain+portugal
spain became very powerful, supporting exploration, expansion of spanish language + culture
england
henry VIII never succeeded in having male heir, daughter elizabeth became queen
elizabethan age: expansion, exploation, colonization in new world
muscovy company: first joint stock company - british easy india comp
france
unified under strong monarchy after hundred years war
france almost constantly at war to increase empire
gunpowder empires:
gunpowder empires were ottoman, safavid, and mughal empires in the middle east and south asia. they rose in the 15th-16th centuries, using gunpowder technology to expand their territories. they were known for their military strength, centralized governments, and cultural achievements
ottoman empire (turkey) - founded by osman bey as mongol fell
invaded constantinople in 1453 and ended byzantine empire
ottomans were islamic
devshirme: enslaved christian children, turned them into warriors called janissaries
mughal empire (india) - founded by babur
united india with religious tolerance
silver was commonly used currency
hindus + muslims lived side by side
safavid empire(persian)
tolerated non muslims
japan
shoguns ruled japan in 16th century, but christian missionaries came in and took control of nagasaki - westernization
tokugawa shogunate (edo period) - strict government that instituted a rigid social class model
moved capital of japan to edo (tokyo)
national seclusion policy: prohibited japanese from traveling abroad and prohibited most foreigners
unit 4: transoceanic interconnections
the encomienda system
spanish implemeted hierarchical colonial society as they took over new world
structure:
peninsulares: spanish officials governing colonies
creoles: spanish born in colonies to spanish parents (educated + wealthy)
mestizos: those with european/native american ancestry
mulattos those with european/african ancestry
native americans
viceroys: governors of each of 5 regions of new spain - established encomienda system (system of forced labor of the natives and african slaves)
african slave trade
slaves brought to new world to work on plantations and mines
europe exploited system of slavery in africa
demand of slaves in europe increased
slaves were forced onto ships, chained below deck, endured brutal middle passage
the columbian exchange
transatlantic transfer of animals, plants, diseases, people, technology, ideas among europe, americas, africa
never had so much moved across ocean
transfer of food products caused pop increase in europe, asia, africa
2 key products: sugar (plantations appeared all over spanish colonies), silver (minig also in spanish colonies) - both used significant forced labor
mercantilism: theory that creating a favorable balance of import + export was best - this led to europe’s intense colonialism to match their import demand
unit 5: revolutions
the enlightenment
divine right: church allied with strong monarchs, monarchs believed they were ordained by god to rule - people had moral obligation to obey
mandate of heaven in china - had to rule justly in order to be appreciated in heaven
philosophers of the age:
thomas hobbes: government should preserve peace/stability
john locke: men born equal, mankind is good and rational - revolting is justified if government doesnt not equalize everyone
jean jacques rousseau: all men are equal, society orgnized according to general will of people
voltaire: idea of religious toleration
montesquieu: separation of powers among branches of government
david hume: lack of empirical evidence casts doubt on religion
adam smith: an “invisible hand” will regulate economy if left alone
mary wollstonecraft: women should have political rights including voting and holding office
enlightenment revolutions in the amercas and europe
american revolution
british defeated france over american territory - seven years war
americans revolting against british rulership
revenue act, stamp act, tea act, intended to raise funds for british government
colonists opposed these laws and battled british troops shortly after
boston tea party: colonists dumping imported tea in harbor to protest
thomas paine: wrote common sense, encouraging colonists to form a better government than the monarchy - declaration of independence was signed
france joined forced with americans in 1777 and defeated the british in 1781 and american democracy was created
french revolution
france running out of money from monarch spending, wars, droughts
louis XVI wanted to raise taxes
first estate: clergy
second estate: noble families
third estate: everyone else
third estate was being shut out of new constituion - formed national assembly out of protest and peasants stormed the bastille shortly after
declaration of the rights of man - adopted by national assembly and caused big changes in french gov
napoleon overthrew directory
haitian revolution
france enslaved many haitians, who revolted successfully, led by pierre toussaint l’ouverture
industry + imperialism
industrial revolution in britain related to imperialism
industrial countries gained power to exploit colonies
industrial revolution: spread through europe, japan, us
new advancements
spinning jenny: spinning vast amounts of thread
cotton gin: invented by eli whitney - massive amounts of cotton quickly
steam engine - james watt
telegraph - communication with great distances
lightbulb
major developments in medicine and science, theory of natural selection
unit 6: consequences of industrialization
european imperialism in india
india had luxuries to europeans - tea, sugar, silk, salt, jute
india vulnerable to external powers after wars in mughal empire and religious conflict
france + england battled in seven years war for colonial superiority and britain won
british east india company: joint stock company - had exclusive british trade rights in india
britain started taking over mughal empire territory + setting up administrative regions through empire
sepoy mutiny: indians who worked for british as soldiers were called sepoys