Resource Management
System Resources
System Resources involves identifying the resources that are required within a computer system.
A computer system has many important resources including
Primary memory (RAM): Temporary storage for data and instructions.
Secondary storage: Long-term storage for data when not in use.
Processor speed: Determines how fast a computer can execute instructions.
Bandwidth: Amount of data that can be transferred in a given time.
Screen resolution: Number of pixels displayed on screen.
Sound processor: Handles audio input and output.
Graphics processor: Processes visual data for display.
Cache: High-speed memory for frequently accessed data.
Network connectivity: Ability to connect to other devices or networks.
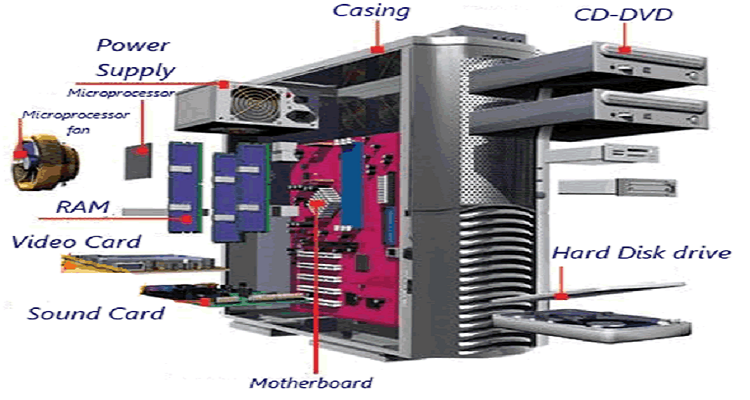
There are many types of computer systems
The IB exam requires you to evaluate the resources available in multiple computer systems
Mainframe:
Processor: High-performance, multiple CPUs.
Primary Memory: Large RAM capacity.
Secondary Memory: High-capacity storage drives.
Common Use: Large-scale data processing, critical applications.
Servers:
Processor: Powerful multi-core CPUs.
Primary Memory: High RAM for multitasking.
Secondary Memory: RAID arrays for data storage.
Common Use: Hosting websites, managing networks.
PCs:
Processor: Various CPUs based on usage.
Primary Memory: Moderate RAM capacity.
Secondary Memory: HDDs or SSDs.
Common Use: General computing tasks, gaming.
Sub-laptops:
Processor: Low-power CPUs for portability.
Primary Memory: Limited RAM for efficiency.
Secondary Memory: SSDs for fast storage.
Common Use: Lightweight computing on the go.
Cell phones:
Processor: Mobile-specific processors.
Primary Memory: Limited RAM for mobile apps.
Secondary Memory: Flash storage.
Common Use: Communication, apps, multimedia.
Tablets:
Processor: Mobile processors for tablets.
Primary Memory: Moderate RAM for apps.
Secondary Memory: Flash storage.
Common Use: Entertainment, browsing, productivity.
PDAs:
Processor: Low-power processors.
Primary Memory: Limited RAM for tasks.
Secondary Memory: Flash memory.
Common Use: Personal organization, basic computing.
Digital cameras:
Processor: Image processing units.
Primary Memory: Limited internal memory.
Secondary Memory: SD cards for storage.
Common Use: Capturing and storing images.
Another important topic the IB exam quizzes you on is the limitations of a range of resources within a specific computer system
This includes 3D graphics rendering and how single-processor computers are not able to render as well has multiprocessors with a GPU
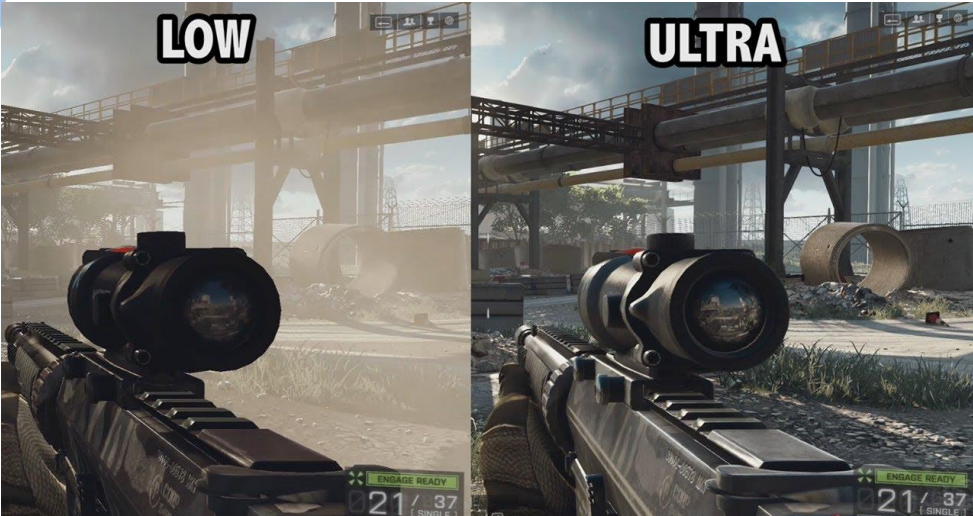

Consequences of limiting:
Primary memory: Slower performance, inability to run multiple programs simultaneously.
Secondary storage: Limited space for data storage and slower access to files.
CPU speed: Decreased processing power, slower execution of tasks.
CPU cores: Reduced multitasking capability, slower parallel processing.
Connectivity: Limited access to networks and slower data transfer speeds.
Resource management involves lots of problem-solving, and there is a list of limitations in the resources in a computer system. It’s important to familiarize yourself with these as well as the consequences involved
Remember to always answer these questions when in doubt:
If the processor is too slow?
If the processor has only one core?
If the amount of primary memory is limited?
If the amount of cache is limited?
Is network connectivity limited?
If user access is limited to a single user per device?
Some specific examples in the IB curriculum include:
Multi Programming system vs Single programming system
The only difference between these two is the fact that each system can run different sets of apps or programs (multiple vs one)
Multi User System
Multiple people can work on the same machine or network
Role of the Operating System
The operating system in IB Computer Science manages hardware resources, provides user interface, runs applications, and ensures system security.
You will also have to explain the role the operating system, managing memory, peripherals, and hardware interfaces
Functions of an operating system
Resource Management: Allocating resources like CPU, memory, and peripherals.
Process Management: Managing running processes and scheduling tasks.
Memory Management: Allocating and deallocating memory efficiently.
File Management: Organizing and accessing files on storage devices.
Security: Protecting system resources and data from unauthorized access.
User Interface: Providing a user-friendly interface for interaction.
Managing (primary) memory involves controlling the allocation and deallocation of memory resources for processes, ensuring efficient utilization, and preventing conflicts. It includes tasks like memory allocation, relocation, protection, and sharing.
Controls (peripheral) devices are devices that the OS manages by providing device drivers and handling input/output operations.
Hardware Interfaces are physical connections that allow devices to interact with each other.
the IB curriculum also requires you to understand multiple techniques that help you manage your resources in a computer system.
These include:
Scheduling: OS technique to manage CPU allocation to processes.
Policies: Rules set by OS for resource allocation and management.
Multitasking: OS ability to run multiple processes concurrently.
Virtual Memory: OS technique to manage memory by using disk space.
Paging: OS memory management technique to swap data between RAM and disk.
Interrupt: Signal to OS to handle events requiring immediate attention.
Polling: OS technique to check status of devices at regular intervals.
For the IB exam, you need to know when each technique is used and why it is used
You will also have to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of producing a dedicated operating system for a device.
Advantages:
Can optimize performance and resource allocation.
Can enhance security by reducing vulnerabilities.
Tailored features and functionalities can be designed for specific device requirements.
Disadvantages:
Limited compatibility with other devices
Higher development costs
Longer time to market
Maintenance challenges
Potential lack of support and updates
OTHER IMPORTANT TERMS TO KNOW FOR THE EXAM
Abstraction is the process that hides certain hardware details from users and applications
Drive Letters are alphabetic labels assigned to storage devices in Windows operating systems.
It helps users identify and access different disk drives
Such as hard drives, SSDs, and external storage devices.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is a virtual machine that enables a computer to run Java programs. It interprets Java bytecode and executes the instructions.
Java is an essential programming language, and many applications run with Java, so it's possible that most computers, even yours, have JVM installed.
Examples of popular apps that use Java
Minecraft
Spotify
Netflix
Many IDE’s