LECTURE 24 - THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what are the 4 specialized subparts of the peritoneum? where is each found? what is the function of each?
-mesentery
encircles the small intestine (except the duodenum) and anchors them to the dorsal body wall
functions: houses blood vessels and prevents entanglement
-greater omentum
extends between the greater curve of the stomach and the transverse colon
functions: fat deposition, lubrication, cushioning, prevents spread of infection
-lesser omentum
extends between the liver and lesser curvature of the stomach
function: encloses/supports bile duct, hepatic artery, and portal vein
-mesocolon
attached to transverse colon
function: support the transverse colon
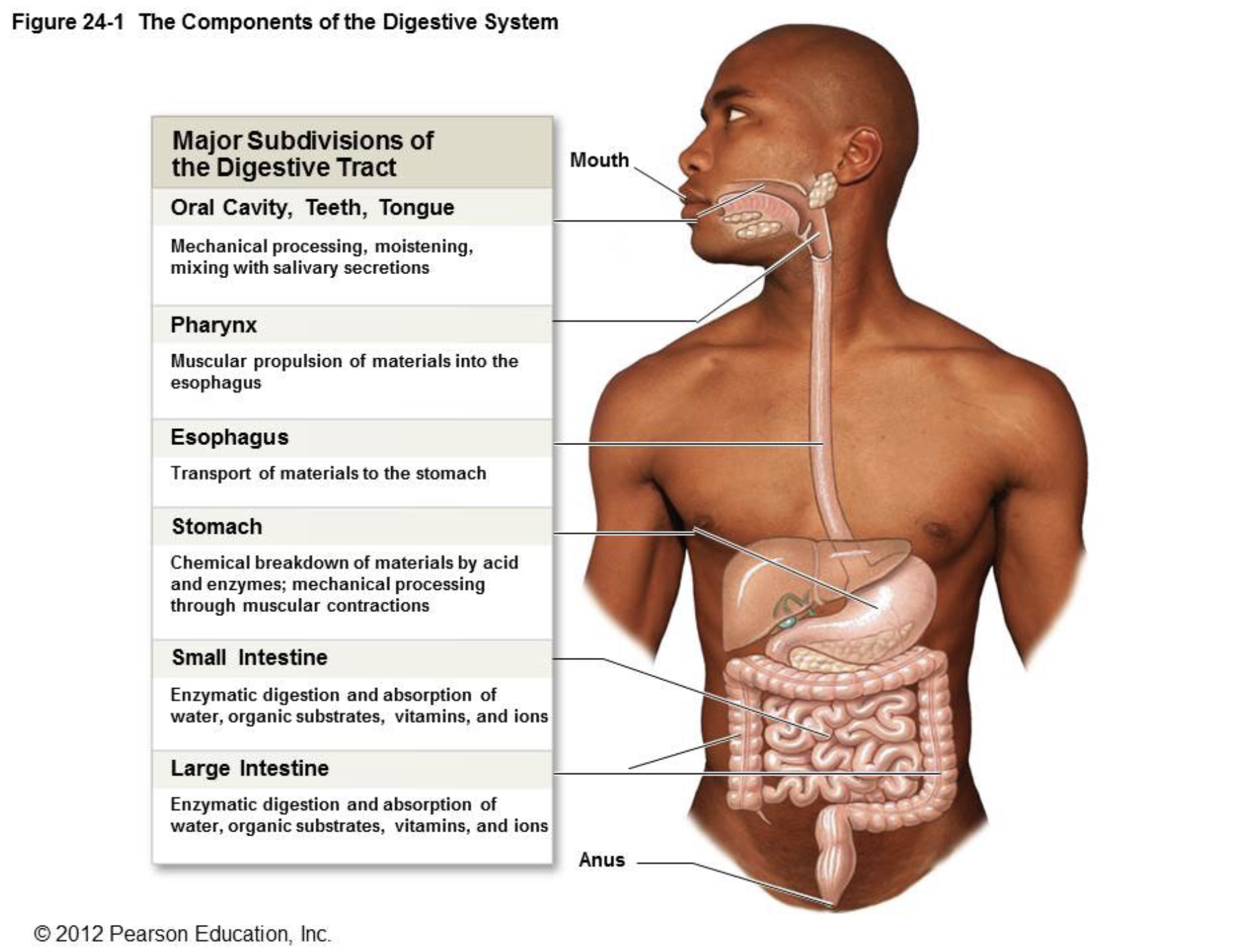
know the pathway through the GI tract. make sure to include the sub-regions of the small and large intestines.
Mouth (oral cavity)
histology: stratified squamous epithelium
Oropharynx —→ Laryngopharynx
histology: stratified squamous epithelium
Esophagus
histology: stratified squamous epithelium
Stomach
histology: simple columnar epithelium
Small Intestine
histology: simple columnar epithelium
Duodenum
Jejunum
ileum
Large Intestine
histology: simple columnar epithelium (no villi)
Cecum
Ascending Colon —→
Transverse Colon —→
Descending Colon —→
Sigmoid Colon —→
Rectum
histology: stratified squamous epithelium
Anus
internal sphincter —→ smooth muscle
external sphincter —→ skeletal muscle
what are the functions of the tongue and teeth?
-tongue
function: skeletal muscle for speech, mastication, swallowing, and taste
-teeth
function: organs of mastication
what are the main functions of the salivary glands/saliva? what molecule do the enzymes found in saliva digest?
functions: lubrication; primary carbohydrate digestion
breaks down starch or carbohydrates
what is the function of the esophagus? know the histology of the esophagus.
-function: initiates peristalsis to move food down to the stomach
-histology: lined with stratified squamous epithelium
upper 1/3 = voluntary (skeletal muscle)
lower 2/3 = involuntary (smooth muscle)
what is peristalsis?
wave like contractions
what molecules are absorbed in the stomach? what molecules are digested in the stomach?
absorbed: water, electrolytes, aspirin, and alcohol
digested: further digestion of carbohydrates and proteins
what is the histology of the lining of the stomach? how does this tissue help protect the stomach?
histology: lined with simple columnar epithelium
secretes mucus to protect the walls from acids
what is the function of the:
rugae
esophageal/cardiac sphincter
pyloric sphincter
gastric glands
-rugae
internal folds of mucosa
function: allow for the stomach to expands; increases surface area
-esophageal/cardiac sphincter
entrance to stomach
function: prevents backflow of acidic stomach contents
-pyloric sphincter
exit
function: controls entry of chyme into the small intestine
-gastric glands
function: secrete gastric juice
what do gastric glands secretes? what does this secretion break down/digest?
secretes gastric juice
composed of hydrochloric acid and enzymes for protein digestion
where does the majority of digestion and absorption occur?
the small intestine
primarily within the duodenum and jejunum
what are the 3 regions of the small intestine? which are suspended by the mesentery?
-duodenum: proximal
receives chyme from the stomach and digestive enzymes from the pancreas and liver
-jejunum: middle
-ileum: distal
-the jejunum and ileum are suspended by the mesentery
be able to diagram.