BIO100 Ch1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Biology
The study of living things
Key Characteristics of biology
Order
responds to stimuli
Reproduction
Growth and Development
adaptation
Homeostasis
regulation
Energy processing
Order
Living things are very organized, from smaller structures that make up the bigger structures.
Order of structures
Atoms > molecules > organelles > cells > tissues > organs > systems
An example of responding to stimuli
Sunflowers facing the sun, pupil dilation in response to light conditions, leaves drooping when touched
Reproduction
The ability to create offspring; single cell organisms clone themselves, multicellular organisms have reproductive cells that contain DNA and passed on to the offspring.
Adaptation
“Fit” in to their environment EX: Heat resistant Archaea, Neck length in girrafes
Growth and development
genes that determine growth and development in living organisms, Grow characteristics to the of their parents
Regulation
internal processes that keep the organism functional EX: transport of nutrients
Homeostasis
Maintaining ideal internal conditions even with extreme environmental changes
Positive feedbaack loop
when stimuli is increased in response to change, driving the system further away from its original state EX: Labor contractions, sneezing
Negative feedback loop
reversing or reducing the magnitude of a change in response to a change EX: sweating, shivering
Energy processing
source of energy to run metabolic systems, chemical energy from food, solar energy from the sun
Diversity
variability in living things due to evolution
Evolution
a process of gradual change over a long period of time where new species come from old species
Taxonomy
A system used to organize and classify organisms by how similar they are

Levels of Taxonomy in Order
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Phylogeny
The study of relationships between organisms, traces the evolutionary history of organism
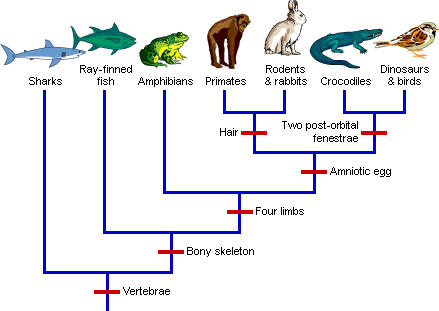
Phylogenetic Tree
A diagram the shows the evolutionary relationships between organisms based on similarities and differences
Three domains of life
Archaea: Unicellular Microorganism
Bacteria: Unicellular microorganism that are extremophiles
Eukarya: complex cellular organization, unicellular or multicellular
Nature of science
Knowledge about the natural world, concerns itself with material phenomena (matter and energy)
Scientific Method
Used to answer questions informed by science and reason using the following steps:
Observation
Question
Testable, falsifiable Hypothesis
Experimentation
Analysis
Reporting/summary
Independent Variable
the factor that is manipulated/changed in an experiment to observe its effects
Dependent Variable
the outcome/effect that is measured in response to changes in the independent variable
Consitancy
results are consistent when study is repeated under similar conditions
Representative Sample
A sample population that accurately reflects a large population, is diverse.
Control of variables
a other variables in an experiment that is minimized/controlled to minimize skewed results.
repeatability
a study that other researchers can replicate and can produce the same or similar results from.
Probability value (p value)
statistical measure of the results to see if they are significant or not
small p value
less than or equal to 0.05, significant effect or difference
large p value
more than 0.05, suggests there is no significance,