mechanisms of localization
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
biodistribution
body acting on radiopharmaceutical, may move and localize in organs, tissues, and compartments
then radioactivity does the work
what are the mechanisms of localization
active transport
simple diffusion/passive transport
ion exchange
physiochemical absorption
capillary blockade
phagocytosis
cell sequestration
compartmental localization
antigen-antibody complexation
receptor
chemotaxis
metabolism
active transport
cellular metabolic processes that result in organ or tissue concentrations above plasma levels, requires energy ("active" process)
Na+/K+ pump
active transporter that moves three Na+ out of a cell and two K+ into the cell against their respective concentration gradients
(not selective for K ions but for monovalent cations of certain ionic radius)
what are examples of active transport with radiodrugs
Tl201 and Rb82, iodine localization
potassium analogues
Thallium201, Rubidium82
how does uptake of Tl201 and Rb82 work?
uptake in cardiac cells directly proportional to perfusion and viability of the cells
positive (+) charge, hydrophilic (water-loving)
utilize Na+/K+ pump
what drug uses active transport for thyroid imaging
I123 sodium iodide
what is used for radioiodine therapy
liquid I131 in capsule
thyroid
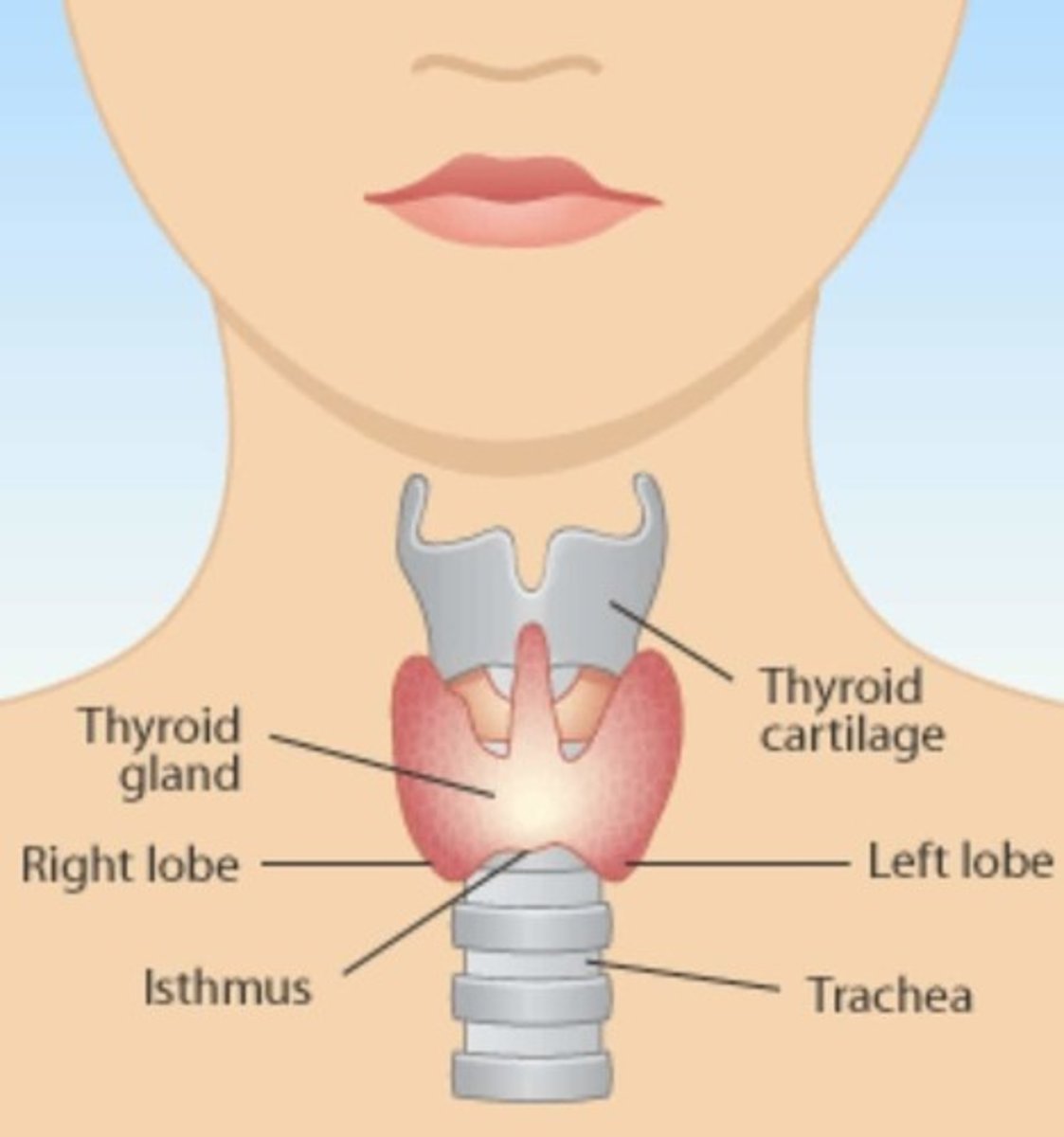
signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism
tiredness, depression, goiter, puffy face, slow heartbeat, dry skin, cold intolerance, weight gain, dry skin, heavy periods, constipation
signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism
nervousness, bulging eyes, goiter, rapid heartbeat, increased sweating, heat intolerance, weight loss, scant periods, frequent BM, warm palms, finger tremors
synthesis of thyroid hormone
1. trapping of iodine
2. oxidation of iodine
3.organification
4.condensation or coupling
5.release of T3 and T4
organification
binding of iodine with thyroglobulin molecule
what is used to trap iodide
iodide pump
what hormones require iodine for production
T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine)
TRH
thyrotropin releasing hormone
TSH
thyroid stimulating hormone
thyroid hormone regulation loop
1. hypothalamus releases TRH to pituitary gland
2. pituitary gland releases TSH to thyroid
3. thyroid gland releases thyroid hormone
4.circulating free T3 and T4
(T3 and T4 set off negative feedback loop)
T3 and T4 negative feedback loop
T3/T4 goes to hypothalamus & anterior pituitary gland and tells them to either secrete more or less TRH/TSH
iodine
I-
iodide
I2
difference between iodide and iodine
iodide is used in body for thyroid (bioavailable) , iodine is elemental form
I- shape
spherical shape
TcO4- shape
tetrahedral
what most closely resembles I in its biologic behavior
Tc99mO4- (pertechnetate)
where does pertechnetate localize
in thyroid, salivary glands, gastric mucosa and choroid plexus of brain
how does pertechnetate localize
like iodine but will not get trapped and turn into thyroid hormone
I123 is better for imaging overall, specifically functional imaging than sodium pertechnetate.
true
secretion (technically active transport)
transport out of glands or tissues
what is similar between sodium pertechnetate and iodine
size, allows both to be used for thyroid imaging
what drug uses tubular secretion for kidney imaging
Tc99m MAG-3 (mertiatide)
simple diffusion/passive transport
movement of substance from regions of higher concentration to lower concentration
perfusion
random movement of molecules with net effect of uniform concentration
radiopharmaceutical localization with perfusion
-many times coupled with retention mechanism
-passive diffusion gets radiodrug to areas of interest, something else causes it to stick
what imaging agents (4) use simple diffusion
brain imaging agents
cardiac imaging agents
kidney imaging agents
bone imaging agents
99mTc-DTPA uses simple diffusion in brain scans via
good cerebral blood flow, followed by clearing with no brain
99mTc-DTPA uses passive diffusion via kidney filtration driven by
pressure (hydrostatic or osmotic)
18F-FDG uses facilitated diffusion via
like a revolving door with escort, glucose transporters
can be inhibited due to limited # of doors
carrier-mediated
ion exchange
the exchange of ions of the same charge between an insoluble solid and a solution in contact with it, occurs at active bone growth/repair sites due to increased turnover of calcium and hydroxyl ions
what can be substituted for calcium ions
89Sr (Metastron)
223Ra (Xofigo)
what can be substituted for hydroxyl ions
18F (fluoride)
chemisorption
the binding of a species to a surface by chemical bonding forces, covalent and hydrogen bonding
what radiodrugs use chemisorption
99mTc labeled phosphate complexes
i.e. 99mTc-MDP, 99mTc-HDP, 153m Lexidronam)
absorption onto surface of hydroxyapatite crystals
what scan uses chemisorption
whole body bone scans
capillary blockade
upon IV injection, particles larger than RBC will become lodged in first capillary bed they encounter
99mTc MAA (macroaggregated albuminum)
uses capillary blockades for lung imaging
particle limit of MAA
200-800k particles per dose
what can be used to determine dimension of not less than 100 MAA particles
hemacytometer grid by optical microscopy
true
more than 90% (at least) MAA particles have 10-90um diameter range (Pulmotech)
true
90% within 10-70 um diameters for generic
no particle exceeds 150um
true.
ideal # of MAA particles in normal adult dose
350,000
what occurs if too few MAA particles are injected
statistical parameters may lead to false-positive results
what occurs if too many MAA particles are injected
unnecessary occlude pulmonary capillaries
phagocytosis
process by which phagocytes remove foreign particulate matter from blood circulation
engulf and ingest foreign particles
recognition and removal of small foreign particles in blood by the cells of reitculoendothelial (RE) system
biodistribution of RE cells
85% in liver
10% in spleen
5% in bone marrow
if shunt is suspected in heart, how many MAA particles should be used
50,000 or less
what uses phagocytosis to create scintillation image of liver
99mTc sulfur colloid
average size of 99mTc sulfur colloid
0.1 um
cell sequestration
process by which spleen recognizes and removes damaged red blood cells or cells near end of life
what method is used when injecting 99mTc into damaged red blood cells
cell sequestration
compartmental localization
when radiopharmaceuticals are introduced directly into the well-defined body compartments and remain there long enough for imaging to be performed
ventilation scans with 133Xe
example of compartmental localization
gastric emptying study with 99mTc sulfur colloid
example of compartmental localization
CSF study with In-111 DTPA
example of compartmental localization
antigen-antibody complexation
using labeled antibodies for the immunodetection and immunotherapy of a variety of diseases (particular oncologic nature)
monoclonal antibodies
a collection of identical antibodies that interact with a single antigen site
antibody
protein that acts against a specific antigen
antigen
protein that, when introduced in the blood, triggers the production of an antibody
90Y-Ibritumomab Tiuxetan (Zevalin)
uses antigen-antibody complexation to treat non-Hodgkins lymphoma (NHL)
monoclonal antibodies
a collection of identical antibodies that interact with a single antigen site
drawbacks of radiolabeled MoAb
-significant cross-reactivity with other antigens
-poor target-to-nontarget in vivo
-human antimouse antibody (HAMA) immune responses
receptor binding
changes in receptor concentration are thought to be related to certain disease states
drug receptors
specific cellular site that interacts with drug molecule mediating action
located in/on cells or within cell itself
affected by micromolar to nanomolar concentrations
selectively blocked by drug antagonists
111In-pentetreotide (OctreoScan)
radiodrug binds to somatostatin receptors on cell surfaces throughout the body
(no longer used)
DTPA conjugate of octreotide
Octreoscan
kit for prep of 111In-pentetreotide
octreotide
long-acting analog of human hormone somatostatin
NETSPOT
kit for prep of 68Ga-dotatate
68Ga-dotatate
binds to somatostatin receptors with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors
indicated for use with PET for localization
what is 68Ga-dotatate used for
localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETS) in peds and adults
Lutathera
177Lu Dotatate
What is 177Lu-dotatate used for?
neuroendocrine tumors treatment
theranostics
involves combining diagnostic imaging and therapy with same molecule which is radiolabeled differently or administered in other dosages
chemotaxis
movement of cell in response to chemical stimulus
when would imaging utilize radiolabeled white blood cells
infection
what are 3 molecules that are naturally occurring that are metabolic analogues
13N ammonia
11C flucose, fatty acid
15O water
foreign label incorporated metabloic analogues
18F-FDG (uses facilitated diffusion)
what is 18F-FDG used for
cancer imaging (mets, diagnosis)
brain imaging