Atoms and Bonding
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is a valence electron?
Electron located in the outermost shell, participating in chemical bonding by being shared, lost, or gained by an atom to become more stable
What are the 3 forms of primary bonding?
• Ionic
• Covalent
• Metallic
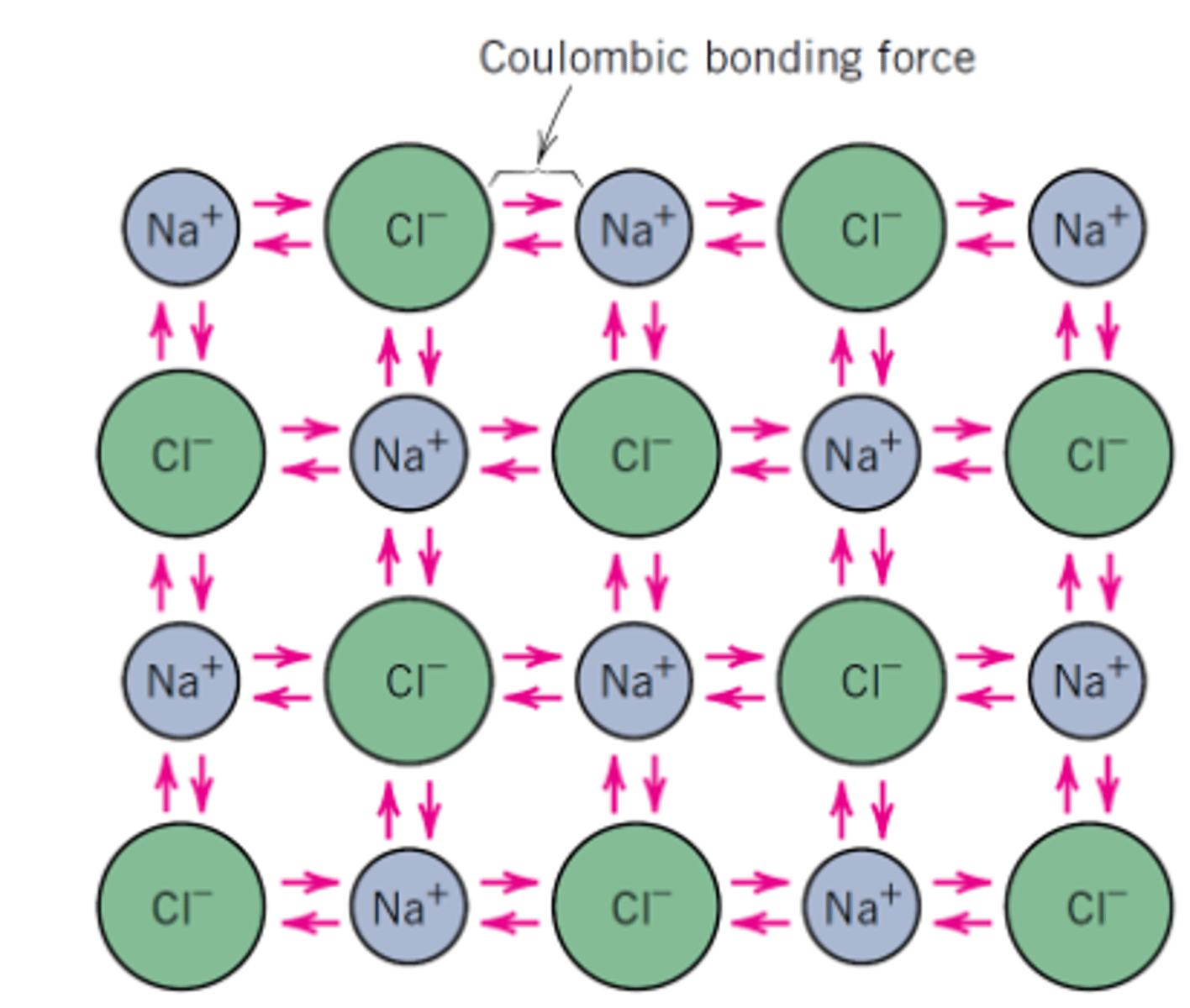
Ionic Bonding
Electrons are transferred between atoms; creates charged particles (ions)
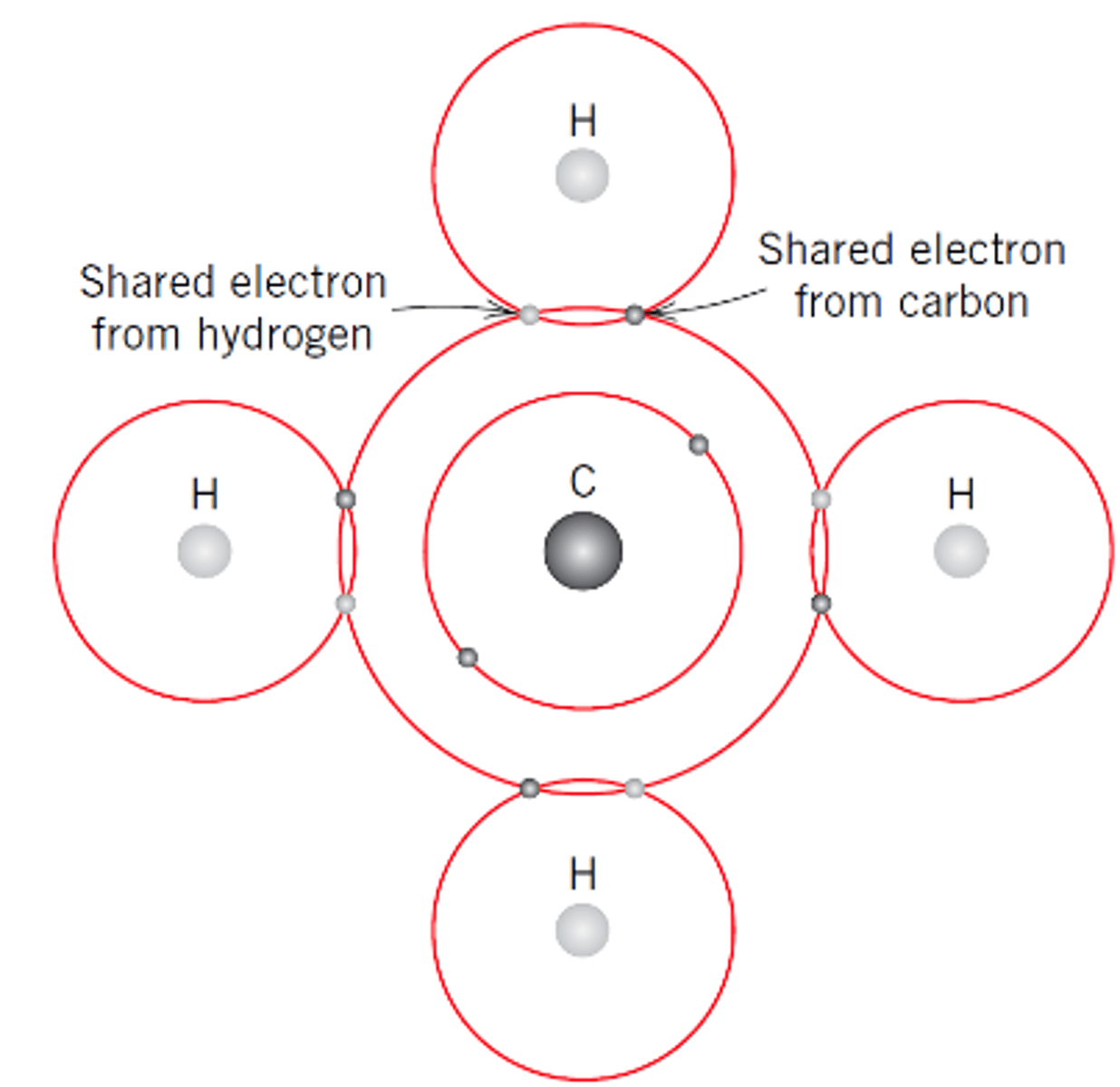
Covalent Bonding
Electrons are shared between atoms and firmly localised between them
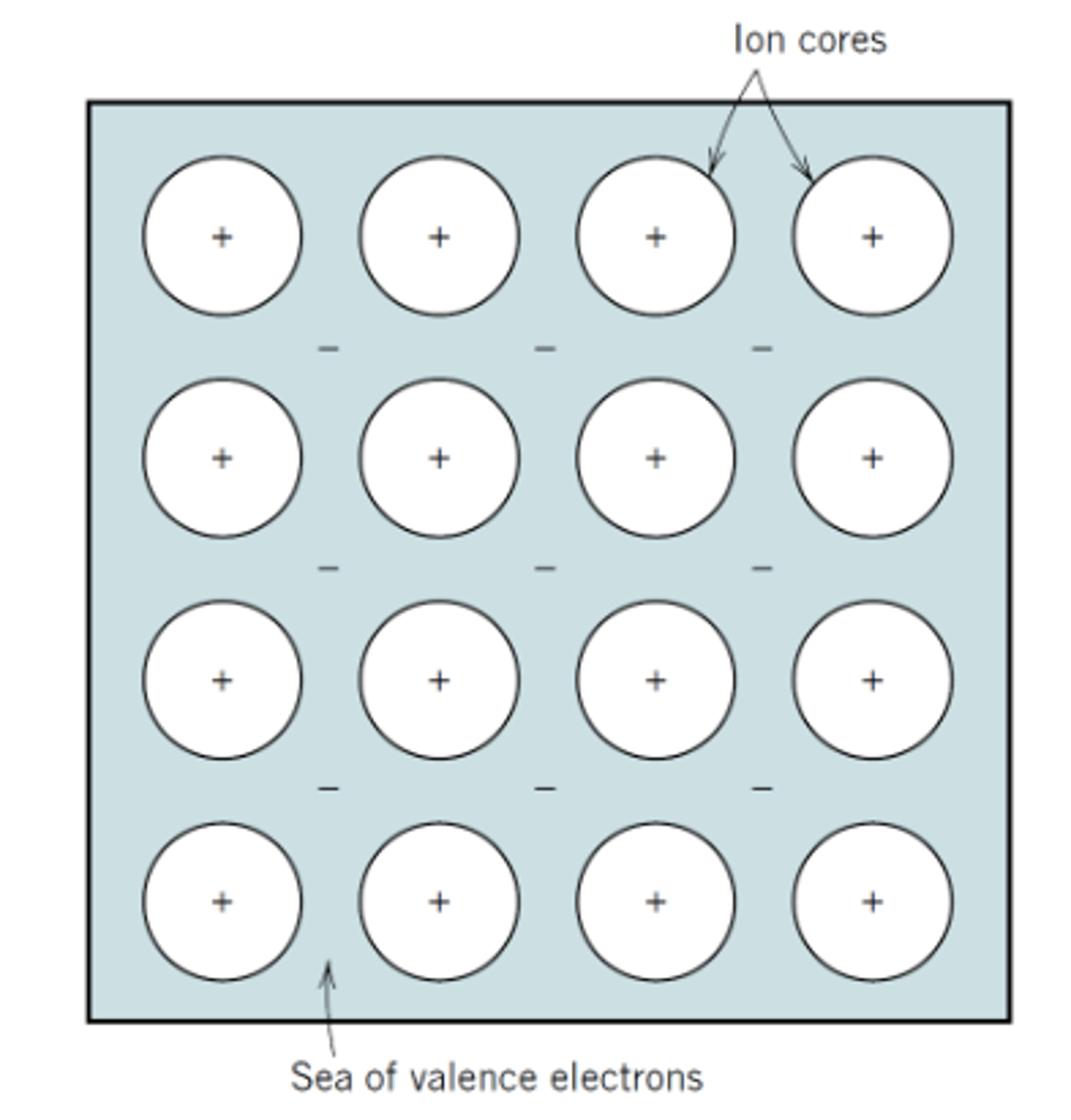
Metallic Bonding
Electrons are shared between atoms but delocalised over a large distance
What are the 2 forms of secondary bonding?
• Fluctuating dipoles
• Permanent dipoles
What are fluctuating dipoles? (Van der Waals)
Constantly changing regions of slight positive/negative charge within an atom/molecule caused by the movement of electrons
What are permanent dipoles?
Separation of positive and negative charge within a molecule, caused by the unequal sharing of electrons in a covalent bond. This asymmetry creates a slightly positive (δ+) end and a slightly negative (δ-) end, making the molecule polar (i.e. hydrogen bonding)
Properties of Metals (Metallic bonding)
• Electrical and thermal conductivity
• Ductile and strong
• Various melting points
• May form alloys
• Magnetic
• Shiny
Properties of Polymers (Covalent, Van der Waals, H-bonding)
• Electrical and thermal insulation
• Low density
• Low melting point
• Low strength
• Flexible
If a materials electrons are bound, what effects will it have on its properties?
The material will provide electrical and thermal insulation
What are intrachain (or intramolecular) bonds?
Hold atoms within a single molecule or polymer chain (generally stronger/more stable than interchain bonds)
What are interchain (or intermolecular) bonds?
Weaker forces that hold separate molecules or chains together
What causes a material to have a lower melting point, less strength and more flexibility?
Having strong intrachain bonds, but weaker interchain bonds
Properties of Ceramics (Ionic or covalent bonding)
• Electrical and thermal insulation
• Hard and brittle
• High melting point
• Environmental resistance
• Always compounds
If a materials bonds are stronger, what effects will it have on its properties?
• Higher melting temperature
• Higher modulus