Ch #8: Communicable Diseases
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Communicable Diseases - Definition
Caused by an infectious agent (like a virus or bacteria) and can transmitted from one source to another
Communicable Diseases - Transmission Types
Person to person
Animal to person
Person/Animal indirectly via reservoir
… helps distinguish between infectious and noninfectious diseases?
Laws and regulations
Disease Transmission - Human Reservoir Definition
Person to person disease transmission without intermediaries
Ex:
STDs
Measles
Mumps
Streptococcal infection
Many respiratory pathogens
Disease Transmission - Animal Reservoir Definition
Animal to animal disease transmission with humans as incidental hosts
Disease Transmission - Environmental Reservoir Definition
Plants, soil, and water that house diseases
Ex: Fungal agents
Disease Control - Definition
Preventative measures, advocating for those affects, protecting the well-being of uninfected persons, and controlling communicable diseases in populations and groups
Disease investigation requires a … approach?
Systematic
Disease Control - Systematic Approach
#1) Identify people who may be infected
#2) Determine the source of infection and means of transportation
#3) Identify others who are at risk
#4) Prevent further transmission
#5) Monitor the response
Disease Control - Nurse’s Role in Systematic Approach
Review the information → Report what needs to be reported and follow guidelines
Clarify if disease is suspected or lab-confirmed
Review the case definition and disease information
Use disease-specific questionnaire when available
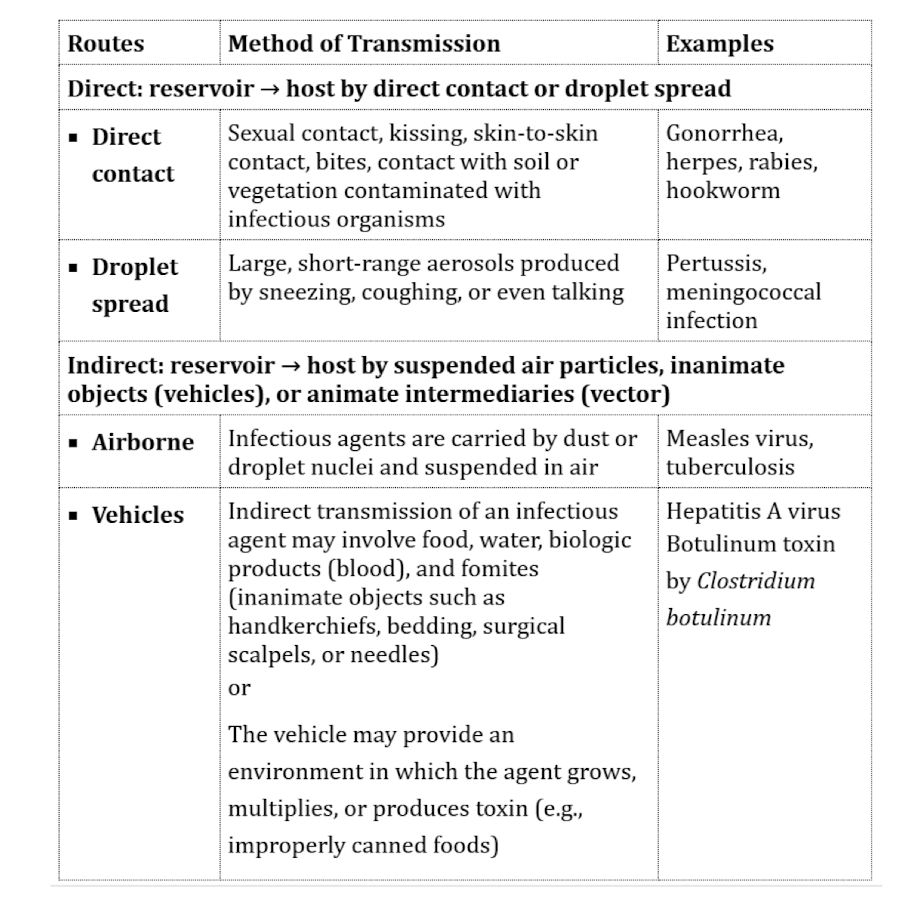
Modes of Transmission - Definition
How a disease is passed from one source to another
Modes of Transmission - Direct Examples
Person to person
Animal to person
Modes of Transmission - Indirect Examples
Reservoirs → Ex: Contaminated water
Modes of Transmission - Vector Definition
Living organisms that transmit infectious diseases
Modes of Transmission - Vector Examples
Insects → Ex: Mosquitos
Animals → Ex: Rats
Modes of Transmission - Mechanical Transmission to Vector
Infectious organism that does NOT multiple within the vector
Vector Ex: Flies
Modes of Transmission - Biological Transmission to Vector
Infectious organism multiplies within the vector
Vector Ex: Mosquitos and ticks
Modes of Transmission - Food/Water Illness Definition
Microorganism contamination of food that results in illness
Caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites
Modes of Transmission - Food/Water Illness Tranmission Process
Occurs at the source through:
#1) Unsanitary handling
#2) Improper storage
Modes of Transmission - General Info
Influenza - Definition
Acute communicable viral disease of the respiratory tract
Influenza - S/S
Fever
Headache
Myalgia
Prostration
Coryza
Sore throat
Cough
Influenza - Types
A = Severe and widespread
B = Milder
*Are other ones, but these are the two biggest ones
Influenza is typically … and happens in the … months. As a result, … is given based on WHO surveillance?
Seasonal → Winter months
Annual vaccine
COVID - Transmission
Respiratory droplets
Contaminated surfaces
COVID - High Risk Groups
Older adults
Immunocompromised or underlying health conditions
Pregnant individuals
COVID - Protection
Vaccines
Boosters
Testing
Pandemic Prevention
IMMUNIZATIONS
High Risk Groups → Healthcare workers and personal care providers, children under 5 y/o, adults over 65 y/o, pregnant women, and those with chronic diseases
Pandemic Lessons
Exposed underprepared health systems and societal inequities
Severe outcomes highlighted health disparities
Pneumonia - General Info
Pulmonary infection causing inflammation of the lungs
High Risk Groups = Infants, older adults, and immunocompromised or those with chronic diseases
S/S = Fever, pleural pain, dyspnea, productive cough, and tachypnea
Protection = Pneumococcal vaccine
Hepatitis - Definition
Serious liver disease caused by viral hepatitis infection
Hepatitis A (HAV) - Spread
Spread through oral-fecal contact
Highly contagious
Hepatitis A (HAV) - S/S
Fever
Malaise
Anorexia
Nausea
Abdominal discomfort
Jaundice
Hepatitis A (HAV) - Protection
Inactivated hepatitis A vaccine
Hepatitis B (HBV) - Spread
Spread through blood or body fluids
Acute and chronic disease
Hepatitis B (HBV) - S/S
Fatigue
Anorexia
Abdominal pain
Nausea
Jaundice
Hepatitis B (HBV) - Protection
Hepatitis B vaccine
Hepatitis C (HCV) - Spread
Spread through contact with infected blood
Hepatitis C (HCV) - S/S
Asymptomatic, but can lead to liver disease
Hepatitis C (HCV) - Protection
NO vaccine
Testing and medical treatment are key!
HIV - Definition
Retrovirus attacking the immune system
AIDS - Definition
Severe, life threatening condition representing late clinical stage of infection with HIV
HIV/AIDS - High Risk Groups
Gay and bisexual males
Black/African American
Hispanic/Latin American
HIV/AIDS - Causes
Unprotected sex
Sharing drug injection equipment
HIV/AIDS - Protection
PrEP and PEP
PrEP = Preexposure Prophylaxis
PEP = Postexposure Prophylaxis
HIV/AIDS - Rx
Antiretroviral Therapy → To reduce viral load and transmission risk
TB - Definition
Infection caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis that primarily affects the lungs
TB - High Risk Groups
HIV positive
Young age
Close contact
Comorbidities
Residence in high-risk settings
Latent TB - Definition
In the body, but no S/S
Without S/S, can not spread it!
Will have a positive TB skin or blood test
Multidrug Resistant TB - Definition
TB that is resistant to first-line drugs like isoniazid or rifampin
Caused by noncompliance to therapy
TB - Screenings
Mantoux Tuberculin Skin Test )TST)
Blood Tests (IGRAs)
TB - Dx
Presence of acid-fast bacilli in sputum
Confirmation by culture revealing MTB
TB is being targeted via the … blueprint?
Global Plan to End TB 2023-2030 Blueprint
Focus = Prevention, screening, treatment, and patient-centered care
How are HIV and TB connected?
HIV increases the risk of developing TB
*HIV patients may not react to TB skin test due to autoimmune response of the HIV
One major issue with TB and managing cases is …?
Medication compliance
Chlamydia - General Info
#1 most reported STD
Usually NO S/S
Rx = Antibiotics and no sex during treatment
Gonorrhea - General Info
#2 most reported STD
S/S = Purulent drainage, painful urination, and mild vaginal discharge
Concerned about antimicrobial resistance when Rx
Syphilis - General Info
#3 most reported STD
Has 4 distinct stages
Syphilis - Complications
Fetal death
Premature birth
CNS complications
Genital Herpes - General Info
Cause = HSV-1 and HSV-2
S/S = Systemic, bilateral lesions, fever, malaise
Rx = NO cure, but can take antiviral meds to reduce duration
STD - High Risk Groups
Underrepresented groups
Low-income populations
Those with less access to medical services
STD - Prevention
Promote healthy sexual behaviors
Strengthen community capacities
Increase access to quality services
Bioterrorism - Definition
Deliberate release of biologic agents to cause harm
Bioterrorism - Examples
Anthrax
Smallpox
Mpox (Monkeypox)
Anthrax - Definition
Acute bacterial disease affecting skin or respiratory tract
Anthrax - General Info
Inhalation is nearly ALWAYS fatal
Disseminated through US mail
Vaccine available and stored in Strategic National Stockpile
Smallpox - Definition
Disease caused by the variola virus that was eradicated in 1980
Smallpox - Spread
Spread via direct and close contact
Smallpox - S/S
Fever
Rash
*Contagious until the last scab falls off
Smallpox - Rx
Vaccine and antivirals → For a potential reemergence
Monkeypox - General Info
Disease caused by orthopoxvirus genus
S/S = Flu-like symptoms, rash, and fluid-filled blisters
Spread through close contact, contaminated items, and infected anims
Vaccine and antivirals for high risk groups
Measles - Causes
Rubeola virus
Measles - Transmission
Airborne
Direct contact
*Can get it from just being in the same room where a person with measles has been
Measles - S/S
PROMINENT RASH
Early → 4-7 days after exposure
Runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, small white spots inside the cheeks
When do Measles S/S usually start?
10-14 days after the exposure
Most people who get measles die from … related to the disease?
Complications!
Measles - Complications
Blindness
Encephalitis
Severe diarrhea and dehydration
Ear infections
Severe breathing problems → Includes pneumonia
Rubella is also known as … and it is caused by …?
“German Measles”
Caused by rubivirus
Rubella - General Info
Spread through direct or droplet contact from nasopharyngeal secretions
Humans are only natural hosts
Spikes in late winter and early spring
Pertussis is also known as … and is caused by …?
“Whooping Cough”
Caused by Bordatella Pertussis
Pertussis - General Info
Human disease
Spread through respiratory or airborne droplets
Rx = Antibiotics and postexposure prophylaxis (PEP)
Polio - General Info
Is an enterovirus → Are transient inhabitants of the GI tract and are stable at acidic pH
Enters the mouth and multiplies in oropharynx and GI tract
Rx = NO CURE → Children get 4 doses of the vaccine to prevent against
HPV - General Info
Caused by papillomaviridae
Very common infection
Spread through intimate skin to skin contact
HPV vaccine at ages 11-12 y/o
Foodborne Illnesses - Timeline
Infection = 12 hours to several days after ingestion of infected food
Intoxication = Minutes to hours after ingestion
Salmonellosis - General Info
Caused by salmonella bacteria that lives in the intestines of people and animals
Grows best in warm weather and unrefrigerated
Spread through eating contaminated food/water or touching animals, animal feces, and places where animals live
Leading cause of foodborne illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths
S/S = Diarrhea, abdominal pain/cramps, fever, N/V
Escherichia Coli - General Info
Most forms are harmless and a part of the general GI tract, but some cause infection
Spread through contaminated food/water or contact with animals, environments, or other people
Major reservoir for E. Coli is …?
Cows

Lyme Disease - Definition
Bacterial infection spread to people through the bite of a blacklegged tick
Caused by Borrelia Burgdorferi
In Lyme Disease, the tick must be attached for more than … to transmit an infection?
24 hours
Where is Lyme Disease most common?
Forested areas

Lyme Disease - S/S
Fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint aches
Swollen lymph nodes
ERYTHEMA MIGRANS (EM) RASH → Looks like a bullseye
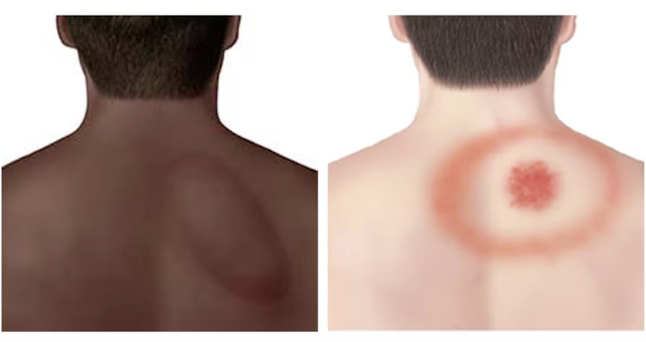
Lyme Disease treatment is all based on what …?
S/S are present!
Lyme Disease - Rx
EM Rash → Doxycycline (Amoxicillin) for 14 days
Neurological Lyme Disease → Doxycycline (Amoxicillin) for 21 days
Lyme Carditis
Mild → Doxycycline (Amoxicillin) PO for 21 days
Severe → Ceftriaxone IV for 21 days
Diseases of travelers are … and …?
Malaria
Zika
Malaria - General Info
Caused by Plasmodium parasite species
Categorized as uncomplicated or severe/complicated
Severity and duration can depend on species of malaria parasite and immunity level
S/S = Fever, chills, sweats, headache, N/V, myalgias, and malaise
Dx = Blood smear, PCR, and antigen
Get risk assessment prior to travel
Zika Virus - General Info
Spread through Aedes species mosquitos
Can also spread perinatal, in utero, sexual, and blood or lab exposure
Main concern is congenital infection → Pregnancy!
S/S = 80% asymptomatic
Complications = Rare → Guillian-Barre, encephalopathy, myelitis, uveitis, and thrombocytopenia
Rabies - General Info
Caused by lyssavirus
Spread via animal bit or scratch → Carried in saliva or mucus and spreads through the broken skin
Fatal in not treated!
S/S = Myalgias, weakness, fever, headache, anxiety, confusion, agitation, and hallucinations
Once S/S present, are always ALWAYS fatal
Primary Prevention - Two Approaches
Education
Immunizations
Primary Prevention - Education Focus
Health promotion/prevention methods
Use a health equity lens
Primary Prevention - Health Equity Principles for Education
Identify intended audience
Determine education level
Consider culture, race, and ethnicity
Pretest materials for attractiveness, comprehensibility, and persuasiveness
Give material at appropriate reading level
Avoid dehumanizing language
Avoid saying terms with violent connotation