Rubella (German Measles)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is another name for Rubella?
German measles, 3-day measles (think, "I know a German named "Ella," and we were married in 3 days)
The source of measles disease?
The source of measles disease is the rubeola virus, which is a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA virus from the Paramyxoviridae family
What are the two types of rubella?
Rubella (German measles) and congenital rubella syndrome
How is Rubella spread?
Rubella is spread through respiratory droplets and through the placenta in congenital rubella syndrome
What are the clinical manifestations of rubella?
- URI prodrome with low-grade fever, malaise, and lymphadenopathy (posterior auricular, occipital)
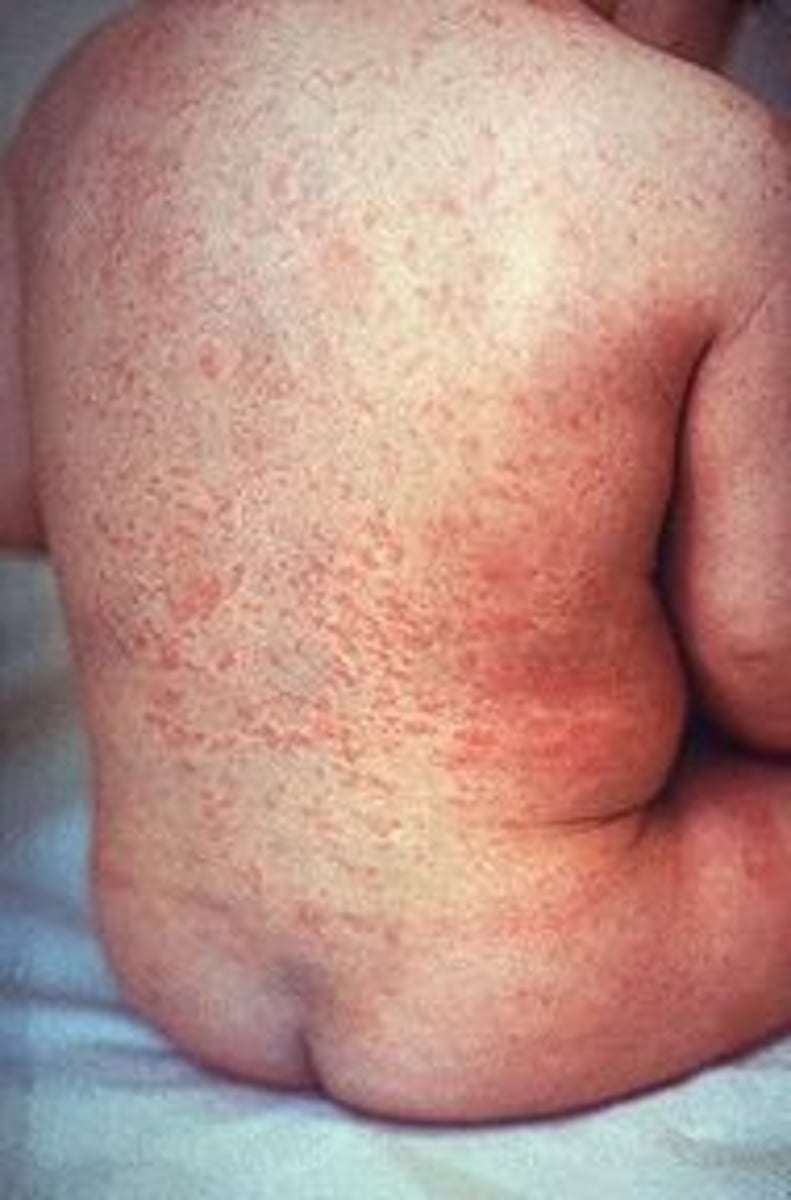
- Pink/light red nonconfluent maculopapular rash that starts on the face spreads to the trunk/extremities and LASTS 3 DAYS (compared to 7 for measles). It spreads more rapidly and does not coalesce or darken like measles
- Forchheimer spots: small red macules or petechiae on soft palate
- Photosensitivity and joint pains
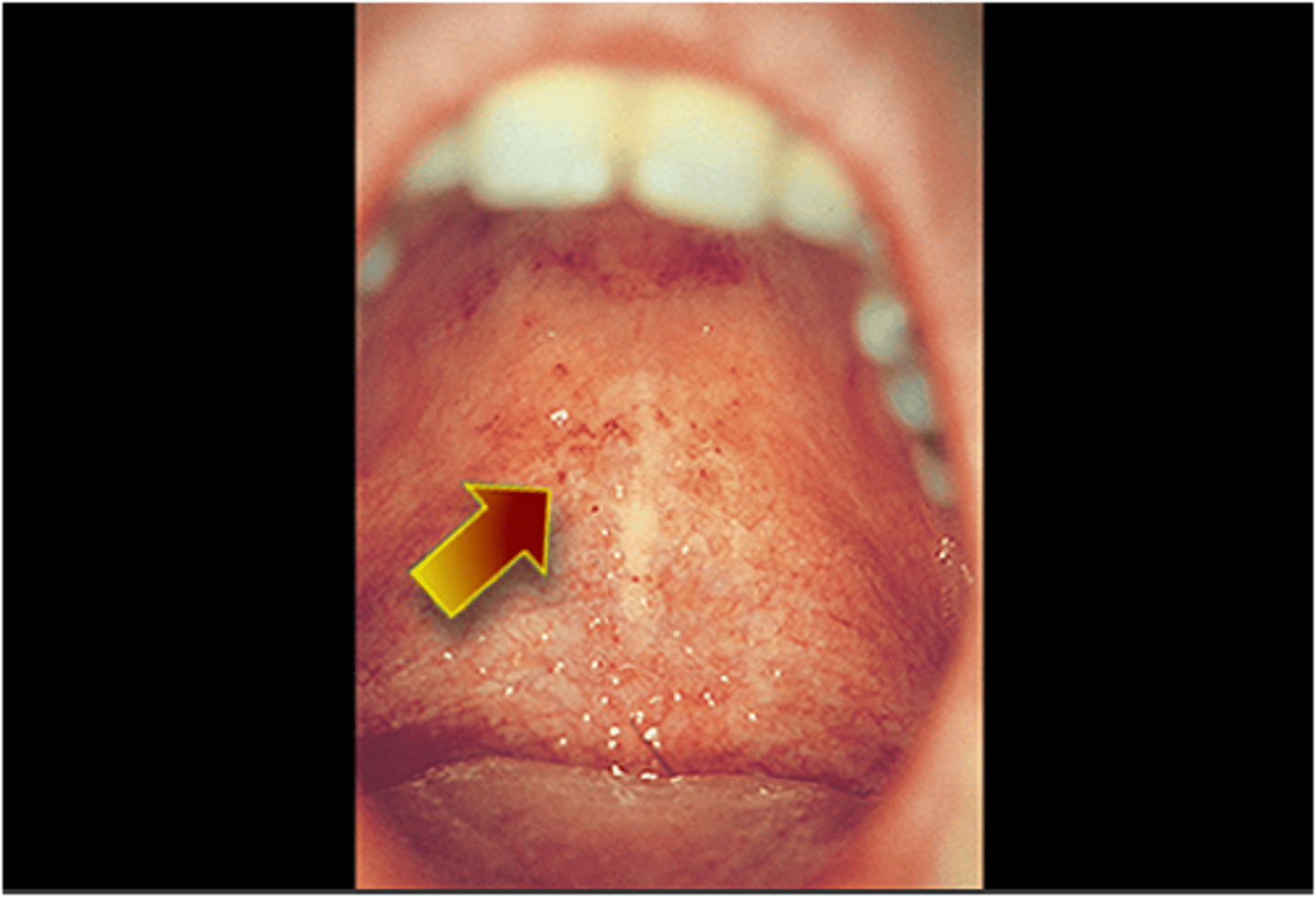
What are Forchheimer spots?
Forchheimer spots are small, red petechiae that appear on the soft palate and uvula during the prodromal phase of rubella (German measles). They are not pathognomonic but can help differentiate rubella from other viral exanthems
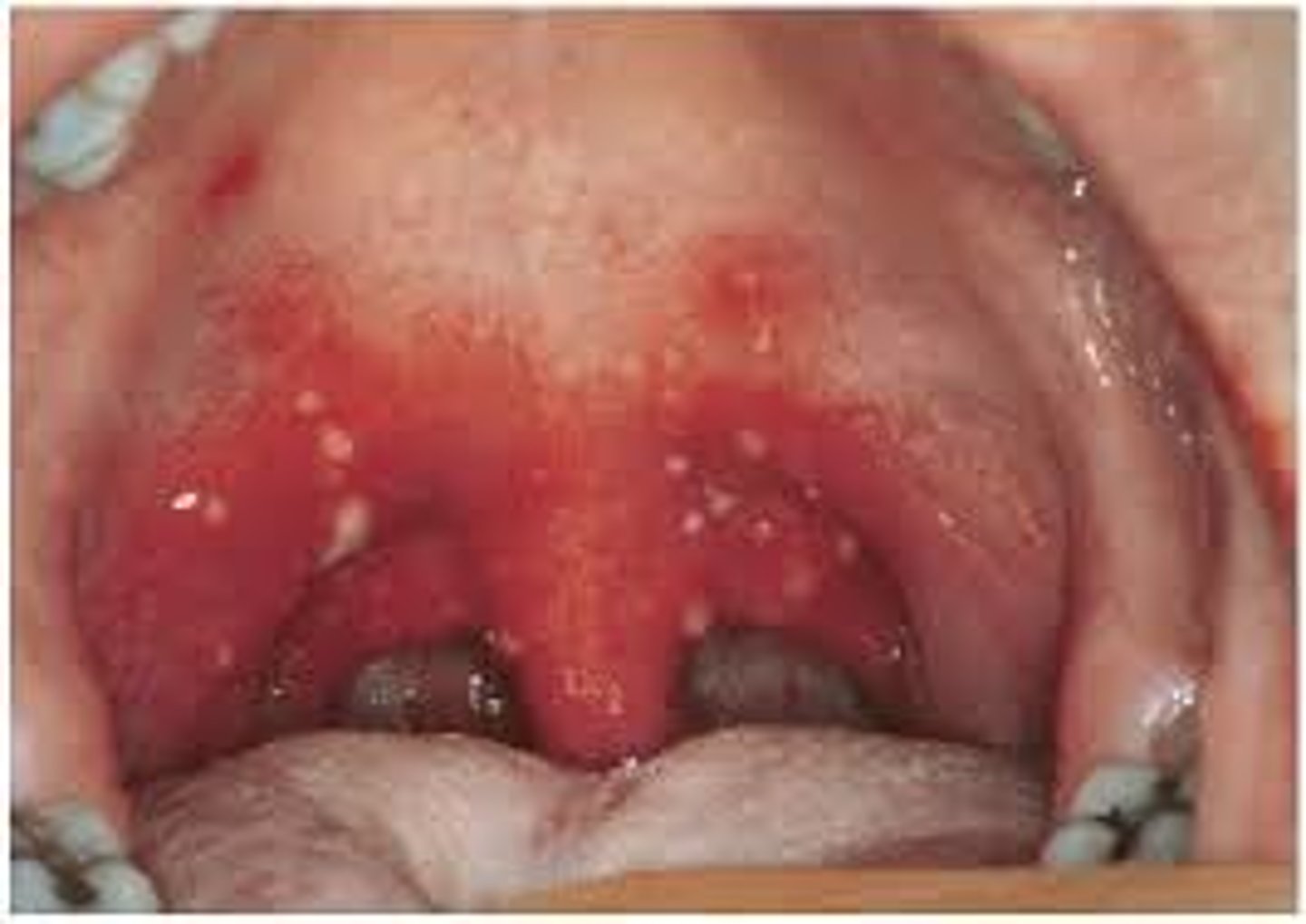
What are Nagayama spots?
Nagayama spots are erythematous papules on the soft palate and uvula, commonly seen in roseola infantum (exanthem subitum), caused by human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6). They typically appear during the febrile phase or shortly before the onset of the rose-colored maculopapular rash.
Name the three congenital defects as a result of rubella?
Neonates born with congenital Rubella syndrome commonly have a triad of symptoms:
1. sensorineural hearing loss, or deafness
2. eye abnormalities such as cataracts and retinopathy, or damage to the retina
3. congenital heart disease such as Patent Ductus Arteriosus, which is when the blood vessel that connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta during fetal development fails to close after birth.
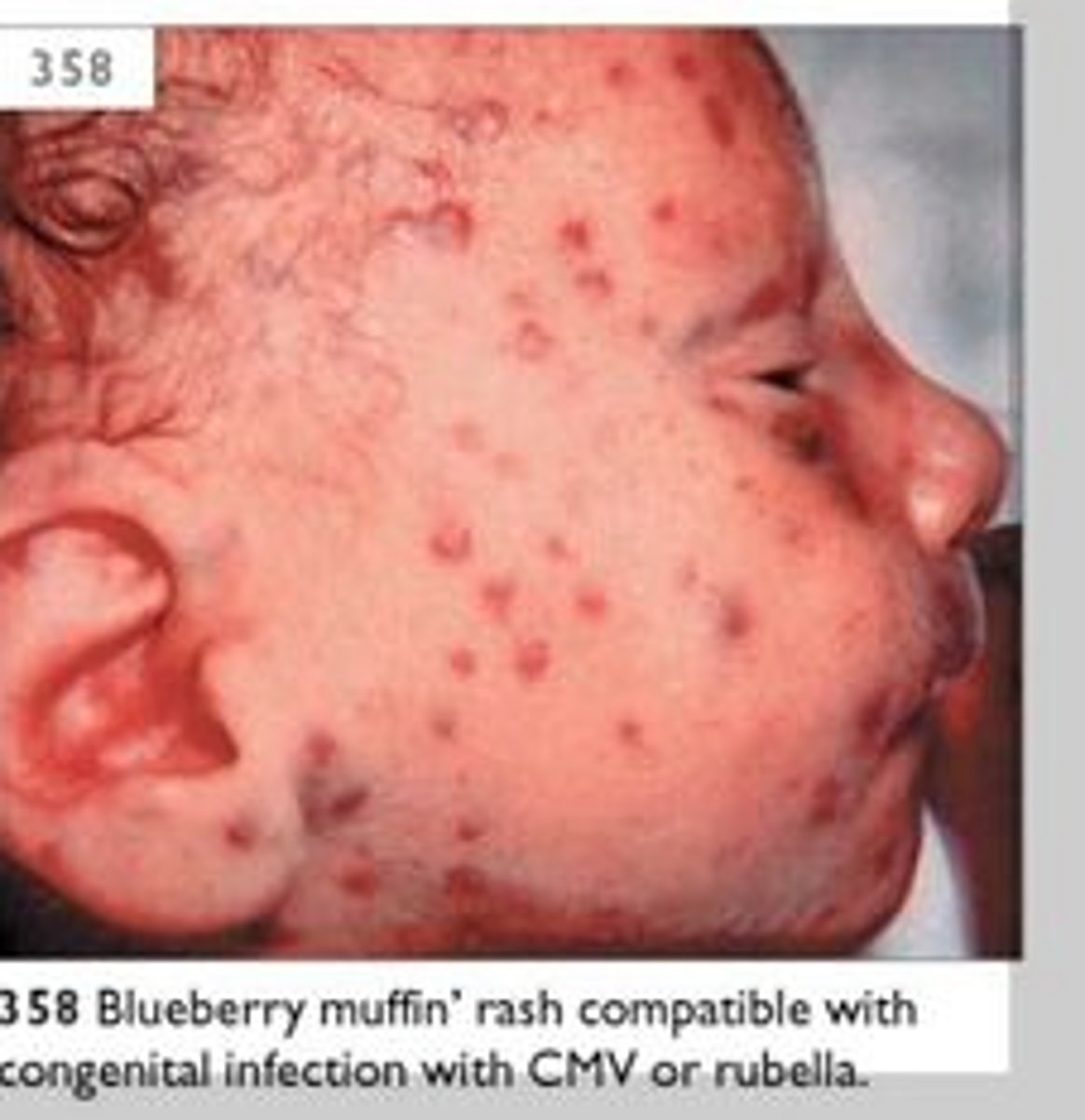
What is a blueberry muffin rash in a baby?
Pediatricians initially coined the term blueberry muffin baby to describe cutaneous manifestations observed in newborns infected with rubella during the American epidemic of the 1960s. These children had generalized hemorrhagic purpuric eruptions that, on histopathology, showed dermal erythropoiesis producing red or purple spots on the skin that look like a "Blueberry Muffin" - Since then, congenital infections comprising the TORCH syndrome (toxoplasmosis, other, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes) and hematologic dyscrasias have classically been associated with blueberry muffin-like lesions.
How do you diagnose Rubella?
Rubella is often diagnosed clinically, can do rubella IgM antibodies via immunoassay. The presence of these antibodies along with, or a short time after, the characteristic rash confirms the diagnosis.
How do you manage a patient with rubella?
Supportive - antipyretics and fluids
What is the prognosis of rubella?
Less complications than rubeola (measles) however can be teratogenic if mother gets rubella in first trimester
CDC recommends all children get two doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine when?
CDC recommends all children get two doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine, starting with the first dose at 12 through 15 months of age, and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age.