Anatomy of Vision & Ocular Exam
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is special about dog and cat orbit?
Do not have a bony orbit like horses and humans fo
Optical canal
CN II
Orbital fissure
CN III
CN IV
CN V (ophthalmic)
CN VI
Rostral alar foramen
CNV (maxillary)
What opens the eyes
-skeletal muscle: levator palpebrae
-smooth muscle with sympathetic control: mullers muscle
What closes the eyes
Skeletal muscle: orbicularis oculi
What produces liquid tears?
Lacrimal gland 65-70%
Third eyelid 30-35%
What are the tunics of the globe?
Fibrous, vascular, nervous
Fibrous tunic
Cornea and sclera
Vascular tunic
Iris, ciliary body, choroid
Nervous tunic
Retina and optic nerve
Why is the cornea clear?
-regularity of collagen fiber
-low cellularity
-lack of blood and lymph vessels
-relatively dehydrated
What does the cornea do?
bends light as it enters the eye
What is the anterior chamber?
Aqueous humor filled space between the cornia and the lens. Aqueous humor maintains its shape and carries nutrients to the space
What does the iris do?
Sphincer and dilator muscles for the pupils
What does ciliary body do?
Creates aqueous humor and its muscles help to focus the lens by pulling down on it
What is the vitreous?
Gel structure between lens and retina that is attached via tiny ligaments = can have tears or detachment
What are the photoreceptors?
-rods: dim light, movement, contrast
-cones: color and detail, dogs have blue and yellow-green
What is the tapetum?
Reflective layer of chorid
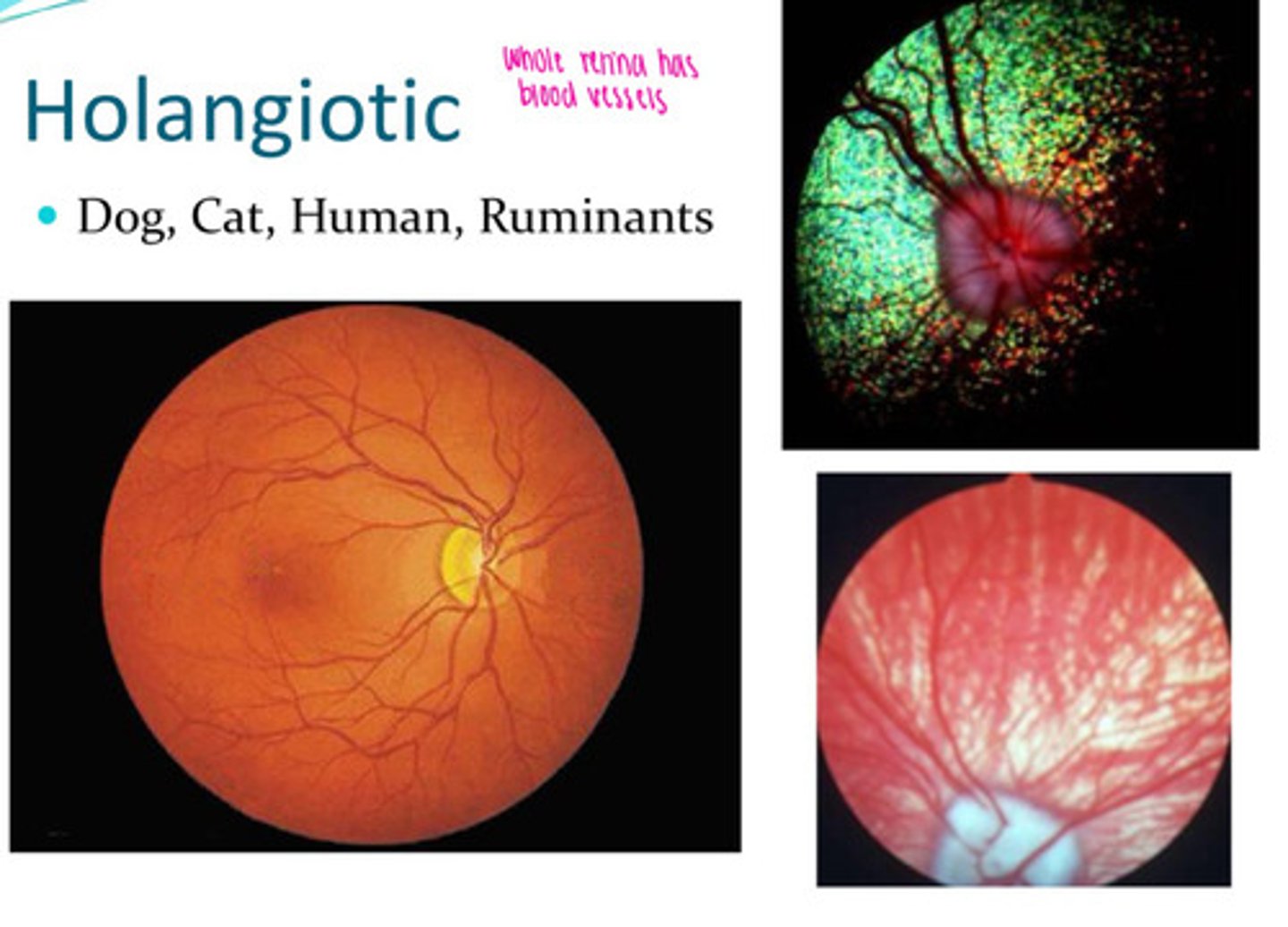
Holangiotic tapetum
Whole retina has blood vessels. Dogs, cats, humans, ruminatns
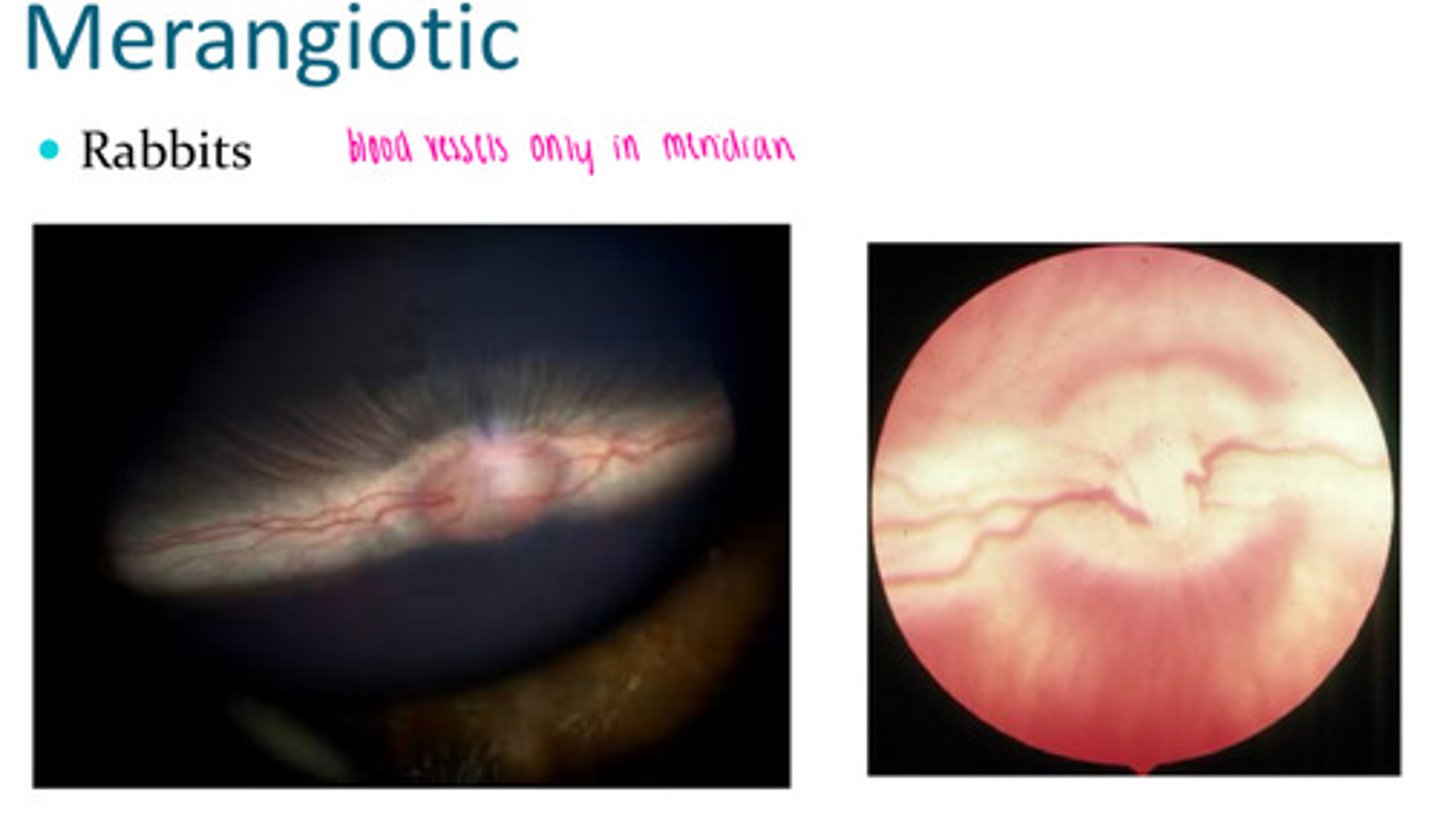
Merangiotic tapetum
Rabbits have this. Only blood vessels in the meridian
Paurangiotic tapetum
Equine and elephants. Blood vessels come from behind and within = stars of winslow
CN II
-optic n
-vision
-afferent PLR
CN III
-oculomotor n
-dorsal, ventral, medial rectus, ventral oblique, levator palpebrae superiorus
-efferent PLR
CN IV
-trochlear n
-dorsal oblique
CN V
-trigeminal n
-sensory to skin, globe cronea
-mm of mastication
CN VI
-abducent n
-lateral rectus, retractor bulbi
CN VII
-facial n
-orbicularis oculi (blinking)
-parasympathetic fibers to lacrimal gland
CN VIII
-vestibulocochlear n
-nystagmus, head tilt
Sympathetic enervation to the eye
-pupil dilation
-control of mullers muscle
-rigidity to extraocular muscles
Equine eye exam
-sedation: alpha 2 and opioid
-nerve blocks: auriculopalpebral upper eyelid motor, frontal upper eyelid and cornea sensation
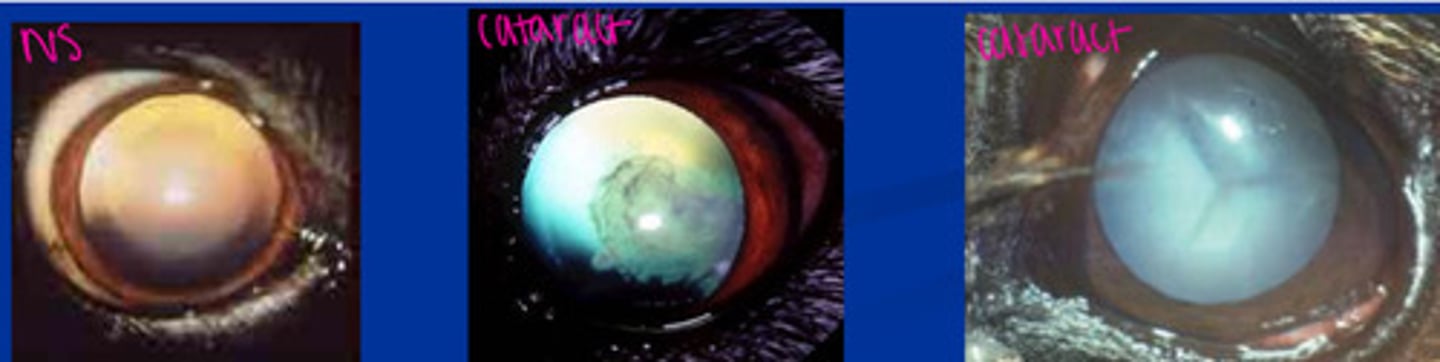
Cataracts vs NS
First need to dilate with tropicamide 1%.
NS: hazy appearance, can see the lens
Cataract: completely blocks light
When do you not dilate the eye?
Increase in IOP or questionable lens position
What do we evaluate in the anterior chamber?
Flare within thin bright light indicated inflammation and leakage of proteins
Persistent pupillary membrane
Birthmark from cornea and iris not splitting — rarely a concern
Neovascularization (rubeosis irides)
Iris inflammation from uveitis
Synechia
-iris sticking to other structures
-anterior = cornea
-posterior = lens
Schirmer teat test
Normal 15mm in 60 seconds
Fluorescein stain tests
-Jones tests: nasolacrimal duct patency
-Seidels test: leaking aqueous
Tonopen
-requires propaocaine
-angled to any surface of eye is okay
Tonovet
-does not require proparocaine
-must be straight against the eye because it uses a vector calculation
Normal IOP
8-25mmHg, no more than 3-5mmHg discrepancy between eyes
IOP elevated
Glaucoma
IOP decreased
Uveitis and old age