Lab Practical 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What does “anaerobic” mean?
without oxygen
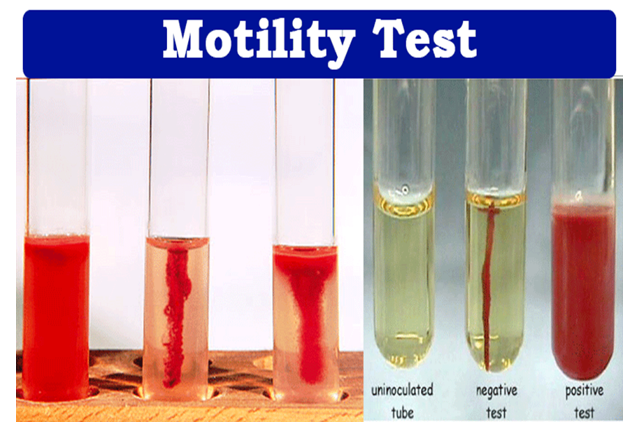
What are we going to use fluid thioglycollate medium to indicate?
the presence/absence of oxygen
How will we make a jar anaerobic?
we place a hydrogen generator packet in the jar, along with a catalyst. The hydrogen reacts with the oxygen in the car.
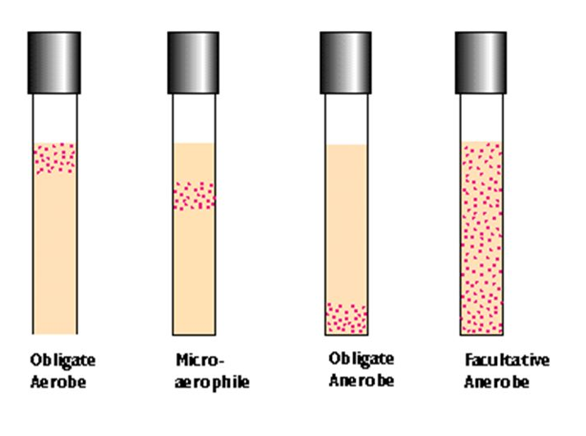
Define each of the following and state the location of the most growth for each in thioglycollate medium: obligate anaerobe, obligate aerobe, facultative anaerobe, aerotolerant anaerobe, microaerophile
obligate anaerobe: cannot grow when O2 is present, grows in the bottom half of the tube
obligate aerobe: grows only when O2 is available, grows within the red zone at the top of the tube
facultative anaerobe: grows best when O2 is available, but also grows without it, growth all the way through the tube with the most growth within the red zone at the top of the tube
aerotolerant anaerobe: grows equally well with or without O2, even growth all the way through the tube
microaerophile: grows only if small amounts of O2 are available, just below the red zone near the top of the tube
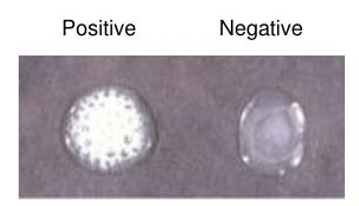
What does the oxidase test tell us about bacteria? Describe what a positive and negative result looks like.
it tells us whether or not the bacteria make oxidase, an enzyme essential for aerobic respiration.
Positive test (oxidase positive) - the reagent turns blue/purple within 15 seconds
Negative test (oxidase negative) - yellow or no color within 15 seconds
catalase breaks down ___(1)_____, producing ____(2)_____ and ____(3)_____.
(1) hydrogen peroxide
(2) oxygen
(3) water
how can one tell if catalase is acting on its substrate?
bubbles
phenol red broth is a differential media. what does a color change in a phenol red broth indicate about a bacterium that has been growing in it?
it indicates whether or not the bacterium has enzymes necessary to ferment the sugar in the tube
Phenol red broth contains a pH indicator called phenol red, which indicates a pH change when it changes color. State the color of the broth under the following conditions:
Neutral pH ____
Acidic pH ____
Alkaline pH ____
Neutral pH = red
Acidic pH = yellow
Alkaline pH = pink
what is a Durham tube? what does it collect?
a tiny tube that sits upside down in the phenol broth tubes. It collects gas
what two products may be produced during fermentation of simple carbohydrates? how is each identified in the fermentation test? can you have one without the other?
acid and gas; acid turns phenol red, yellow; gas collects in the Durham tube so you can see a bubble there; yes, you can have one without the other
name 3 simple carbohydrates that can be added to media for biochemical testing
glucose, sucrose, lactose
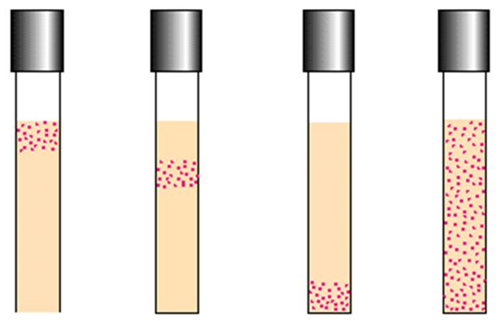
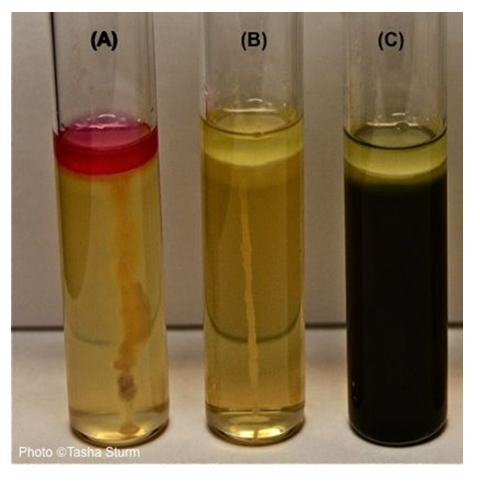
label the oxygen requirements for each thioglycolate medium
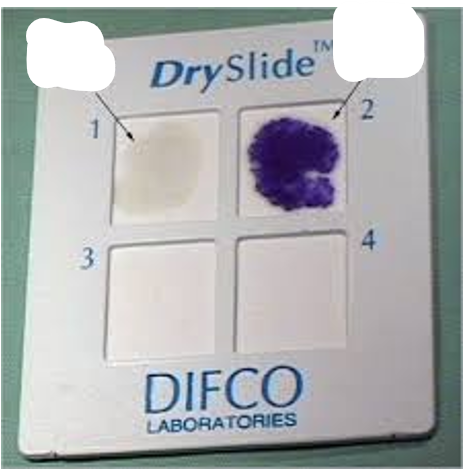

which is oxidase positive and oxidase negative


which is catalase positive and catalase negative
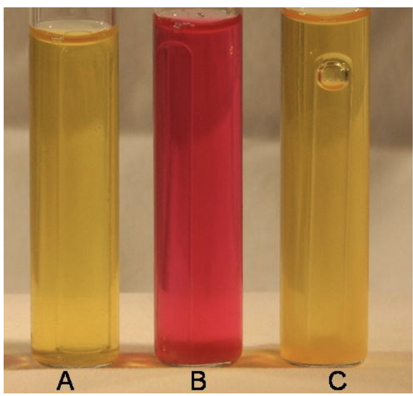
what are the results of each tube
A - turned yellow, so it ferments sucrose, but there is no gas bubble so it produces acid only
B - stayed red, no gas bubble, does not ferment sucrose
C - turned yellow and there is a gas bubble, so it ferments sucrose with both acid and gas production
disinfectant
chemical agent used on inanimate objects to lower the level or number of microbes on the surface
antiseptic
chemicals used on living tissue to decrease the number of microbes
antimicrobial agent
a general term for drugs, chemicals, or other substances that either kill or slow the growth of microbes
what is an antibiotic
a drug used to treat bacterial infections
what is a narrow spectrum antibiotic
an antibiotic effective against a restricted number of bacteria
ex: penicillin G, amoxicillin
what is a broad spectrum antibiotic
an antibiotic effective against a wide range of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
-cidal
to kill
static
to inhibit
a disinfectant must _________ the pathogen while in contact with them
kill
list two types of bacterial cells that are more resistant to disinfectants
endospore-formers (bacillus, clostridium)
acid-fast bacteria (mycobacterium)
why is antimicrobial susceptibility testing done
to determine which antibiotics will be most effective against a specific infection
what is the name of the antimicrobial susceptibility test also known as the filter paper disk agar diffusion method
the kirby-bauer test
what is the filter paper disks of the kirby-bauer test
antibiotic
what kind of agar is used in the kirby-bauer test
mueller-hinton agar
what is streaked onto the agar plate in the kirby-bauer test
a lawn of bacteria
where are the filter paper disks placed in the kirby-bauer test
on top of the bacteria on the agar plate
what happens to the antimicrobial agent in the disk after it contacts the agar in the kirby-bauer test
it diffuses away from the disk in all directions
after incubation, what does one look for on the plates in the kirby-bauer test
zone of inhibition around the disk
what does R mean interpretation? how is it determined
Resistant
compare the width of the zone of inhibition to the standardized table of antibiotics
what does S mean interpretation? how is it determined
Susceptible
compare the width of the zone of inhibition to the standardized table of antibiotics
name a broad spectrum antibiotic
ampicillin
name a narrow spectrum antibiotic
penicillin G
amoxicillin
what is enriched media? give examples
allows many types of bacteria to grow - even fastidious bacteria
ex: blood agar, chocolate agar
what is differential media? give examples
allow you to distinguish one group of bacteria from another after they have grown on the media
ex: mannitol salt agar, blood agar
what is selective media? give examples
allow some types of bacteria to grow and not others
ex: mannitol salt agar
describe the characteristics of staphylococci
gram-positive spheres growing in irregular clusters; catalase-positive; salt-tolerant
where is S. epidermidis normally found? does it cause any diseases? if so, what?
skin and mucous membranes
it doesn’t normally cause any disease
where is S. saprophyticus normally found? does it cause any diseases? if so, what?
it is found only infrequently on our bodies
it is associated with urinary tract infections in women from ages 16 -21
where is S. aureus normally found? does it cause any diseases? if so, what?
skin, internal nares, vagina
diseases - TSS (toxic shock syndrome), food poisoning, scalded skin syndrome, pneumonia, meningitis, sinusitis, otitis media, abscesses
what does hemolysis do
destroy red blood cells
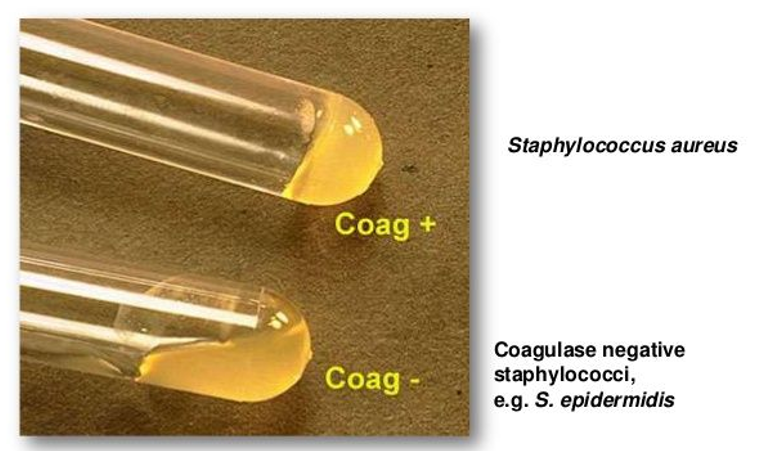
what does coagulase do
coagulate plasma
what does leucocidin do?
destroys white blood cells
what does hyaluronidase do?
destroys connective tissue (“spreading factor”)
what does staphylokinase do?
dissolves fibrin clots
what does enterotoxin do?
affects the digestive system (produced in food, not the body)
what staph species produces hemolysins, coagulase, gelatinase, leucocidin, hyaluronidase, staphylokinase, and enterotoxin?
staphylococcus aureus
what does mannitol salt agar (msa) select for? what ingredient is present in msa that causes it to be selective?
msa selects for salt-tolerant bacteria (like staph)
9.5% salt
how is msa differential? what does it differentiate between? what ingredients are present in msa that cause it to be differential?
it distinguishes mannitol fermenters form mannitol nonfermenters
msa contains mannitol and an acid-base indicator
s. aureus colony color on blood agar
yellow
s. epidermis colony color on blood agar
white
s. saprophyticus colony color on blood agar
white or yellow
s. aureus type of hemolysis on blood agar
beta
s. epidermidis type of hemolysis on blood agar
gamma
s. saprophyticus type of hemolysis on blood agar
gamma (usually)
s. aureus coagulase (+ or -)
+ (forms a clot)
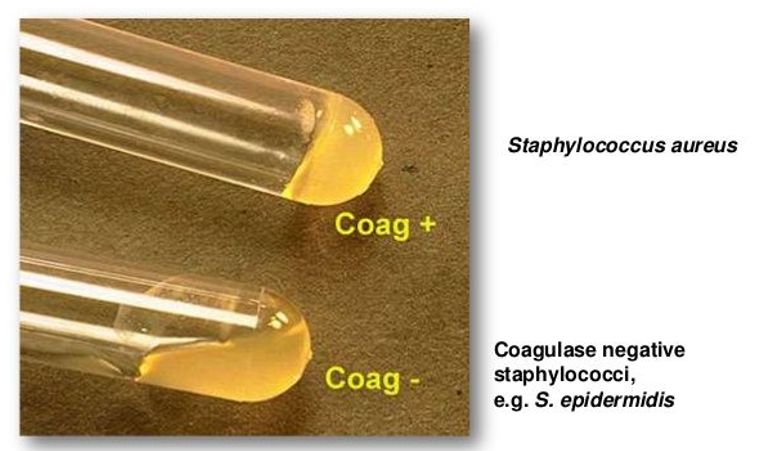

s. epidermidis coagulase (+ or -)
-
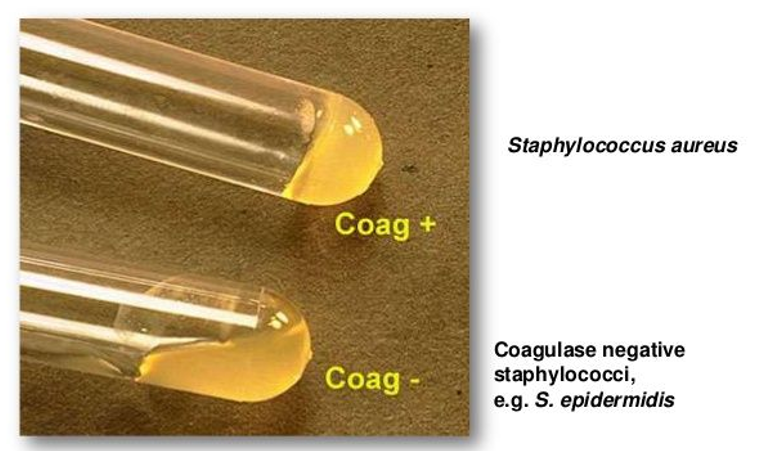

s. saprophyticus coagulase (+ or -)
-

s. aureus mannitol fermentation (+ or -)
+
s. epidermidis mannitol fermentation (+ or -)
-
s. saprophyticus mannitol fermentation (+ or -)
varies +/-
s. aureus novobiocin (S or R)
S
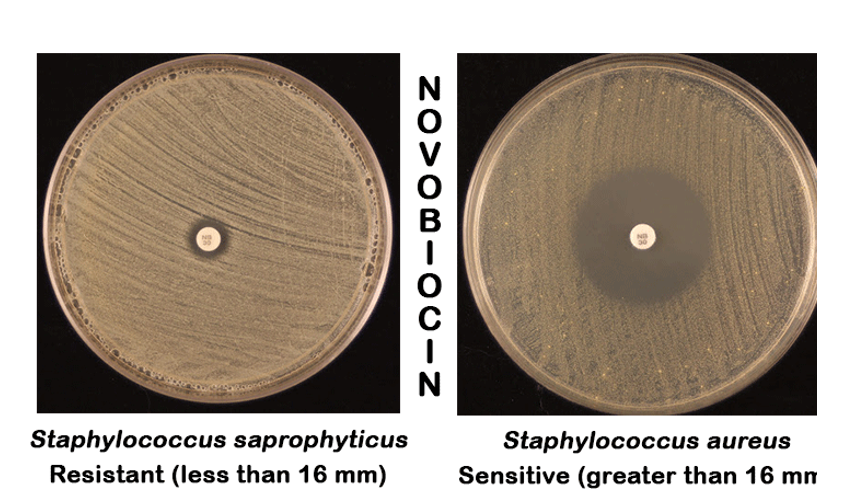
s. epidermidis novobiocin (S or R)
S
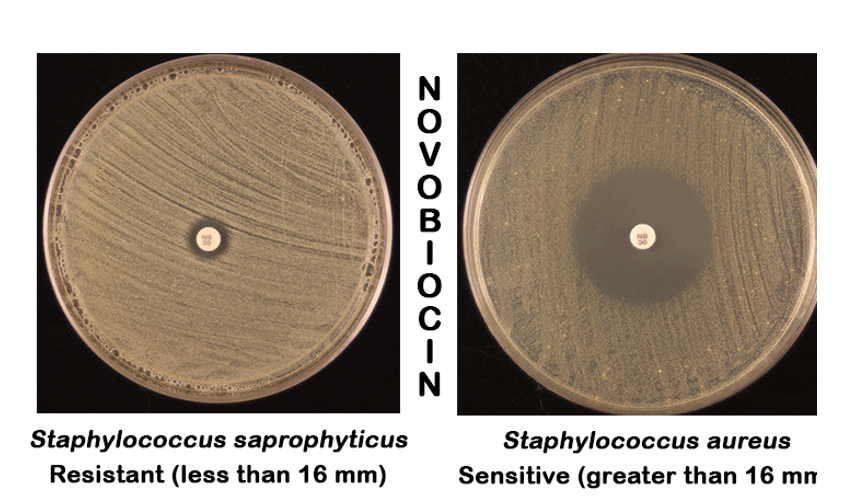
s. saprophyticus novobiocin (S or R)
R
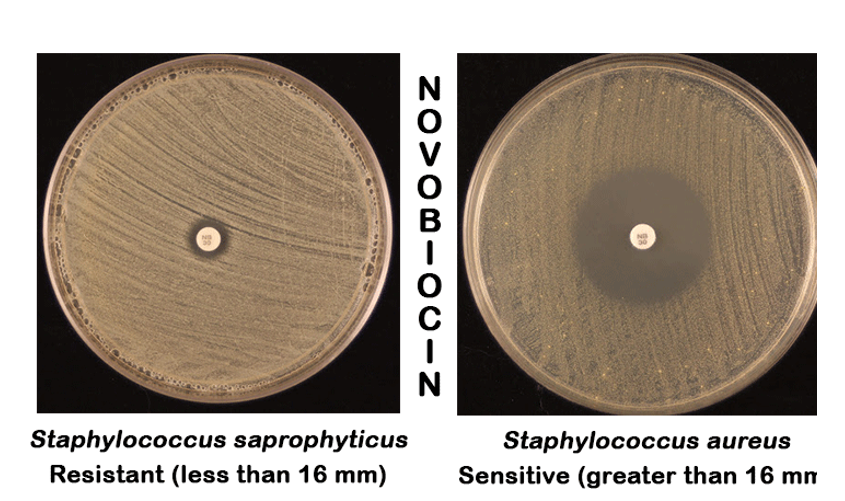
describe the members of the genus streptococcus
gram-positive spheres arranged in chains; catalase negative
what does fastidious mean?
these bacteria need enriched medium to grow on
what type of media do strep need to grow on?
enriched (blood agar plates)
substances that destroy red blood cells are called _______
hemolysins
one way strep are classified is by the type of hemolysis they produce on blood agar. describe the following:
alpha hemolytic strep
beta hemolytic strep
gamma strep
alpha hemolytic strep: BAP turns red to green because they incompletely break down hemoglobin
beta hemolytic strep: BAP clears to colorless because they completely break down hemoglobin
gamma strep: no change
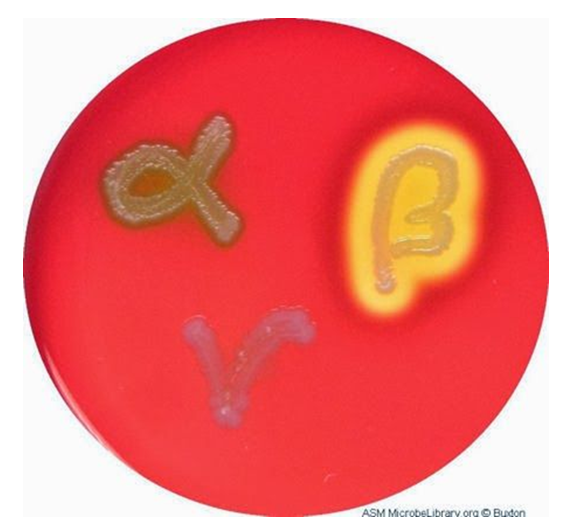

which group causes disease? list several of the diseases that are caused by a member of this group
beta hemolytic (streptococcus pyogenes)
diseases caused include toxic shock syndrome, strep throat, scarlet fever, and rheumatic fever
a second way strep can be classified is by the type of carbohydrate antigens present in their cell wall. what is an antigen?
any substance that causes antibodies to be produced by the body; it reacts only with its specific antibody
how are these strep named?
Group A, Group B, ….. Group T
Human pathogens belong to which group?
Group A
describe the Enterobacteriaceae
gram-negative nonsporing rods, facultative anaerobes
name three species of the Enterobacteriaceae that are pathogens. name the disease that each causes
klebsiella pneumoniae - causes pneumonia
shigella dysenteriae - causes shigellosis (bacillary dysentery)
salmonella typhi - causes typhoid fever
how do these pathogens differ from the non-pathogenic forms?
the pathogens do not ferment lactose, but the non-pathogenic forms do ferment lactose
do all E. coli normally cause disease?
no
what are MacConkey and EMB agar selective for
gram-negative rods
what do MacConkey and EMB agar differentiate?
lactose fermenters from non-lactose fermenters
phenylalanine is broken down into ______________ when bacteria that produce phenylalanine deaminase are grown in culture
phenylpyruvic acid
in the phenylalanine deaminase test, a reagent called ferric chloride is added after incubation. what does a positive reaction look like (color)?
green

name a genus in Enterobacteriaceae that is phenylalanine deaminase positive
proteus
urea is hydrolyzed into ______ and _______
carbon dioxide and ammonia
name the exoenzyme studied in the urea hydrolysis exercise
urease
name one genus of bacteria that can hydrolyze urea
proteus
after incubation, how can you tell if a urea slant was inoculated with urease-positive organism or a urease-negative organism?
urease-positive organism turned urea slant pink
urease-negative organism didn’t
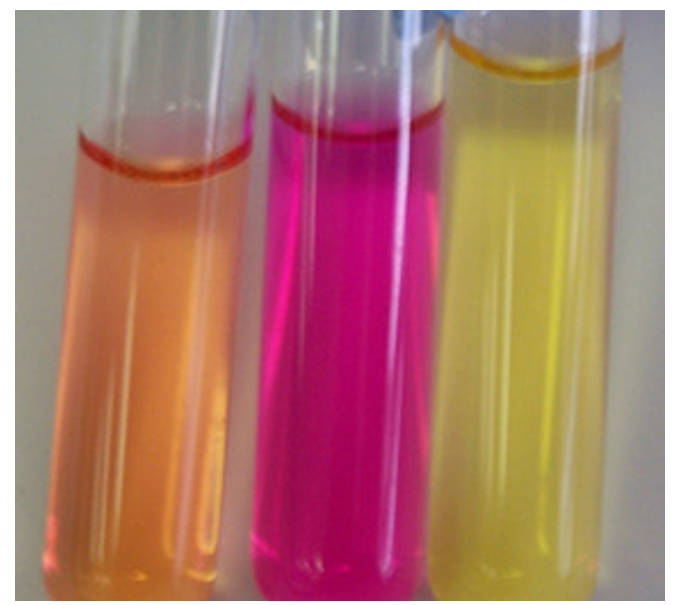

name the indicator that was added to the urea slant before inoculation
phenol red
this indicator is ______ in a solution below pH 8.4 and _______ above pH 8.4
yellow/orange, red/pink
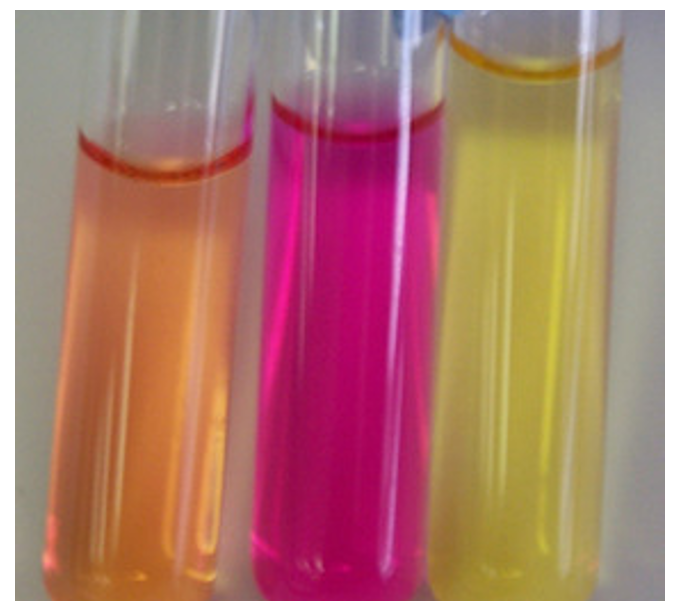

we will be working with “SIM” medium. In the acronym what does each letter stand for
S stand for sulfide
I stands for indole
M stands for motility
name the enzyme responsible for sulfide production
cysteine desulfurase or thiosulfate reductase
after incubation, how can you tell if a SIM tube has been inoculated with an organism positive for sulfide production?
the SIM medium turns black
Name a genus in Enterobacteriaceae that is positive for sulfide production
salmonella, shigella, proteus
In the presence of tryptophanase, tryptophan breaks down into _______________ plus ammonia.
indole
What does Kovac’s reagent indicate?
the presence of indole
After incubation, how can you tell if a SIM tube had been inoculated with an indole-positive organism or an indole-negative organism?
if you get a red color after adding Kovac’s reagent, its indole-positive