Lecture 1: Introduction to causality and potential outcomes framework
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What are the different prediction and causal inference algorithms?
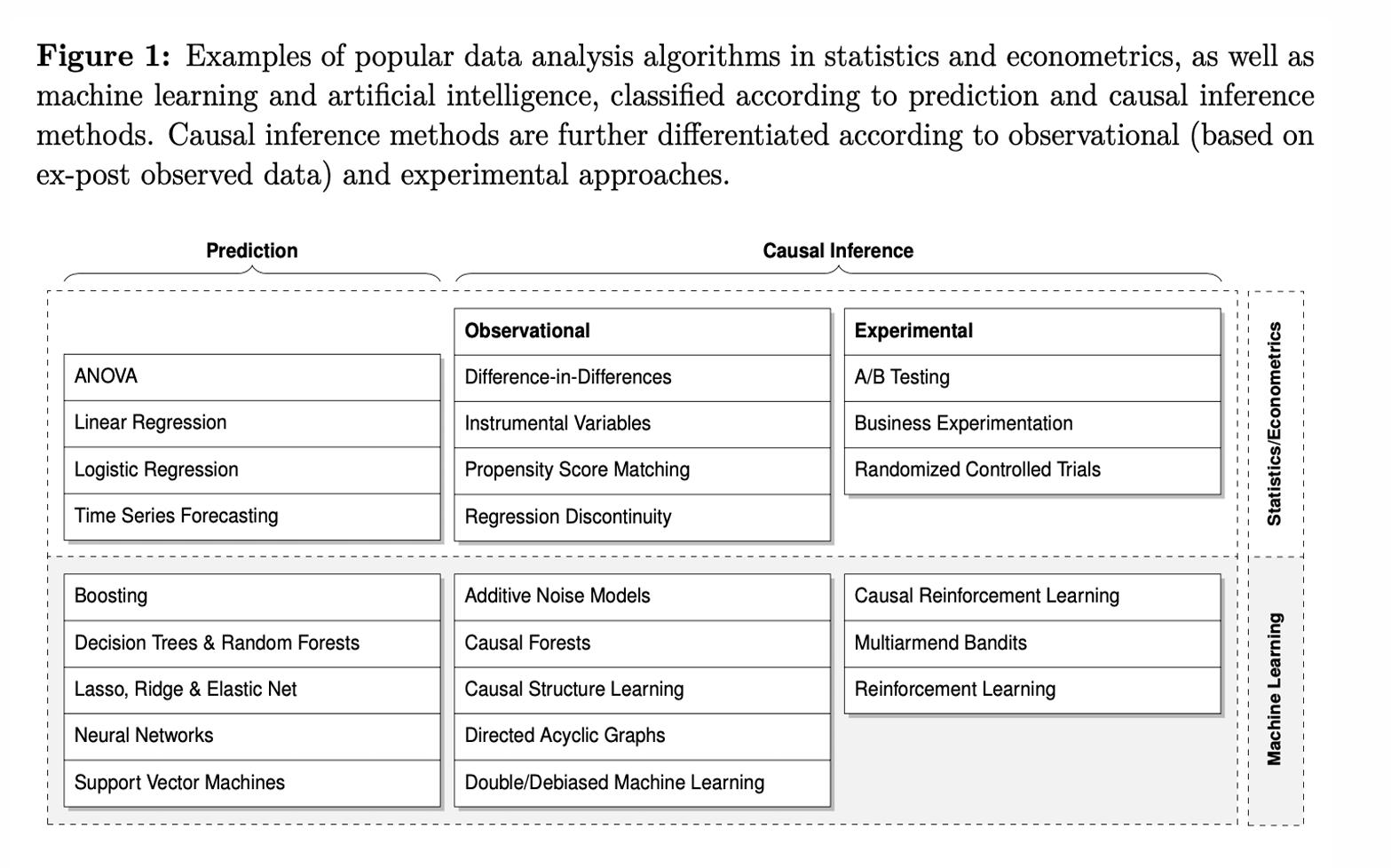
What do we mean by a traditional prediction?

What do we mean by causal inference?


Provide an example of this


What is the issue with this example?
Angela can’t exist both with D=0 and with D=1



What is the ‘would have been’ formally known as?
Counterfactual
What is the logic behind assessing the counterfactual?

When does the OLS regression work well?

What is the issue with running experiments and what should we do instead?

What is the purpose of the model?
Model is our idea of what we think the process is that generated the data

Write an OLS regression for this example


What do we want to estimate and what will β1 estimate?


Why might we see β1 > 0?

What is often the relationships between causality and correlation?

Why might opera and lifespan be related?
Reasons outside of directly lifespan and opera such as health status, wealth, when they started watching opera, etc.

How can we find an answer to this?

What do we mean by identification?

How does identification relate to causal inference?

How can we remove other sources of variation from the original variable of interest?

How can we isolate just the variation we are interested in?

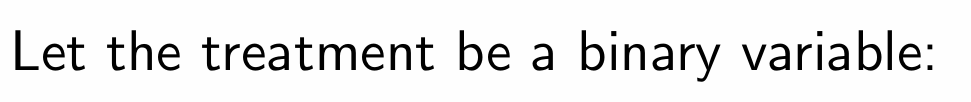
Write the notation for treatment in the potential outcomes framework example


Write the notation for the potential outcomes


i.e. what is represented by Y0 and Y1?

Why are there only two possible outcomes?

What are the differences between potential and realised outcomes?

What is the individual treatment effect and how do we denote it?

What is the switching equation and how do we denote it?

What is the fundamental problem of causal inference?

What is the average treatment effect (ATE) and how do we denote it?
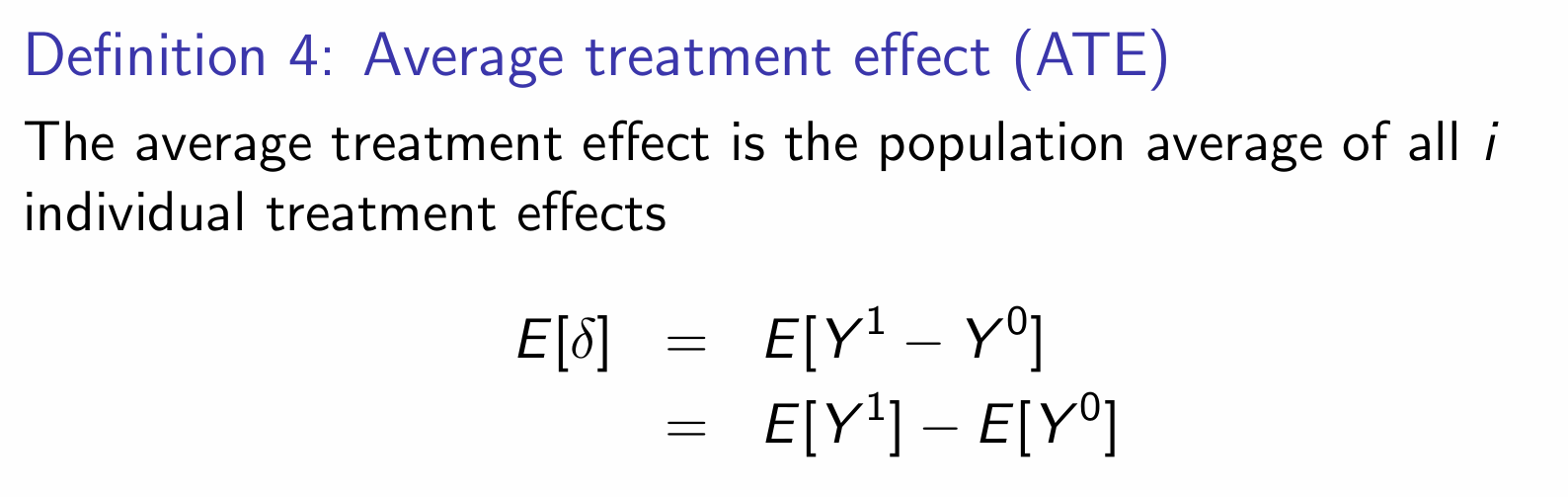
Aggregate parameters based on individual treatment effects are what?
Summaries of individual treatment effects
Why can’t we calculate the ATE for our treatment example?
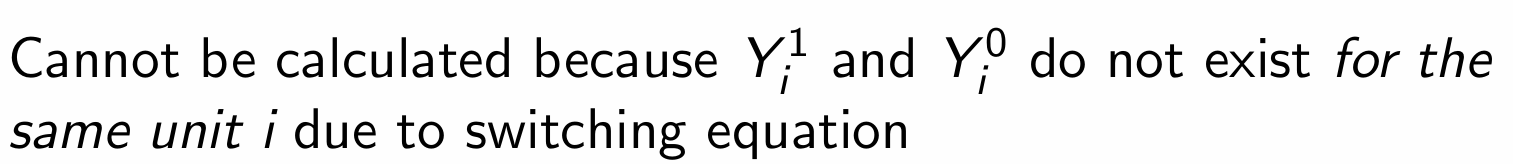
What is the average treatment effect on the treated (ATT) and how do we denote it?

Why can the ATT not be calculated for the treatment example?
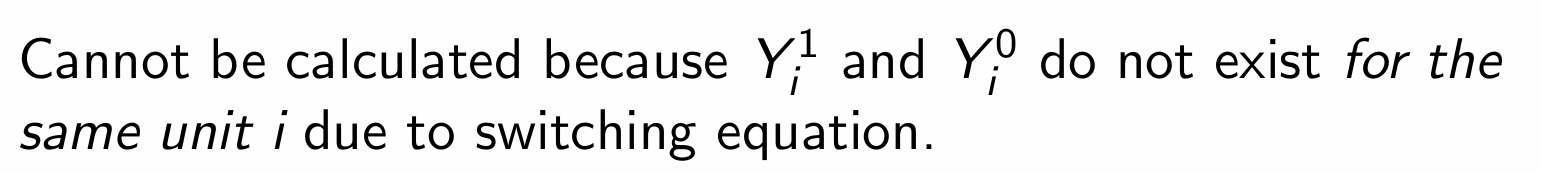
What is the average treatment effect on the untreated (ATU) and how do we denote it?

Why can the ATU not be calculated for the treatment example?
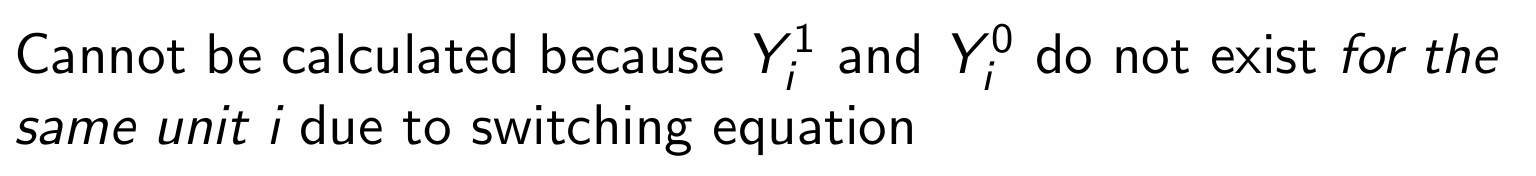
What is one way we can estimate average causal effects?
Randomisation
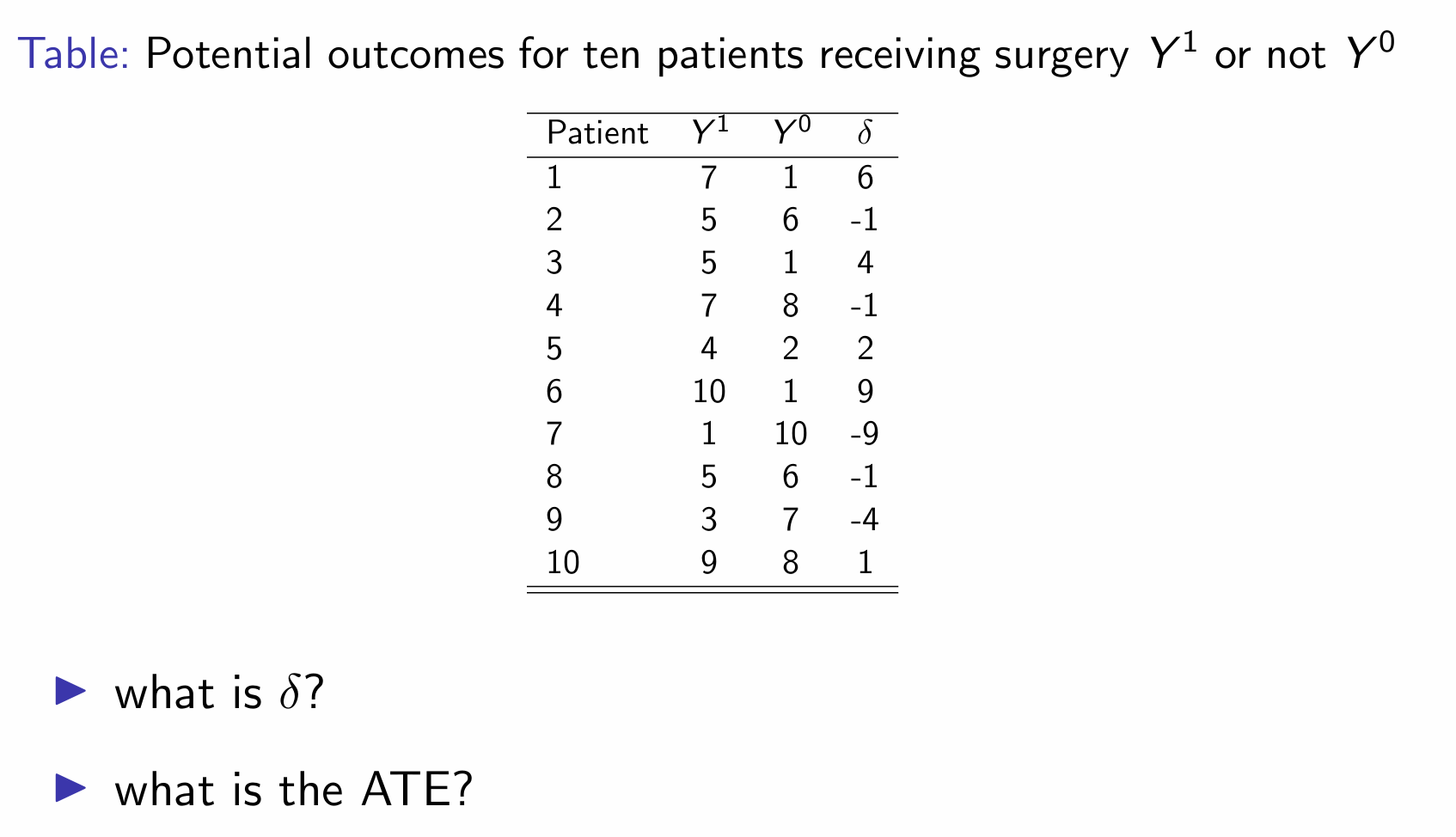
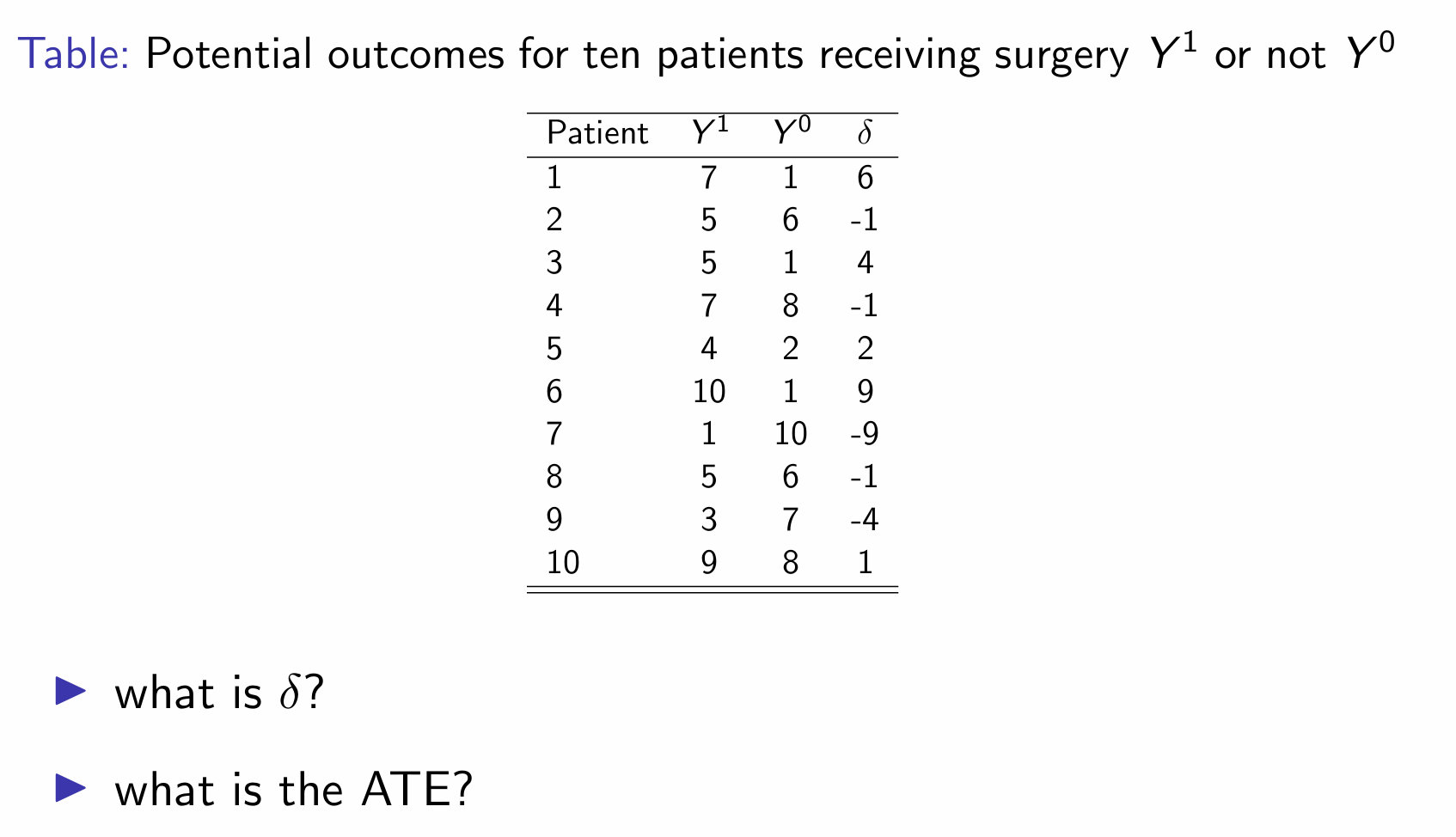
δ is the individual treatment effect (calculate Y1-Y0)
E[Y1] - E[Y0] = 5.6 - 5.0 = 0.6

ATT = (6+4+2+9+1)/5 = 4.4
ATU = (-1-1-9-1-4)/5 = -3.2
ATE = pATT + (1-p)ATU = (0.5 × 4.4) + (0.5 x -3.2) = 0.6
What is the simple difference in mean outcomes (SDO) and how do we denote it?

Is SDO a causal parameter?

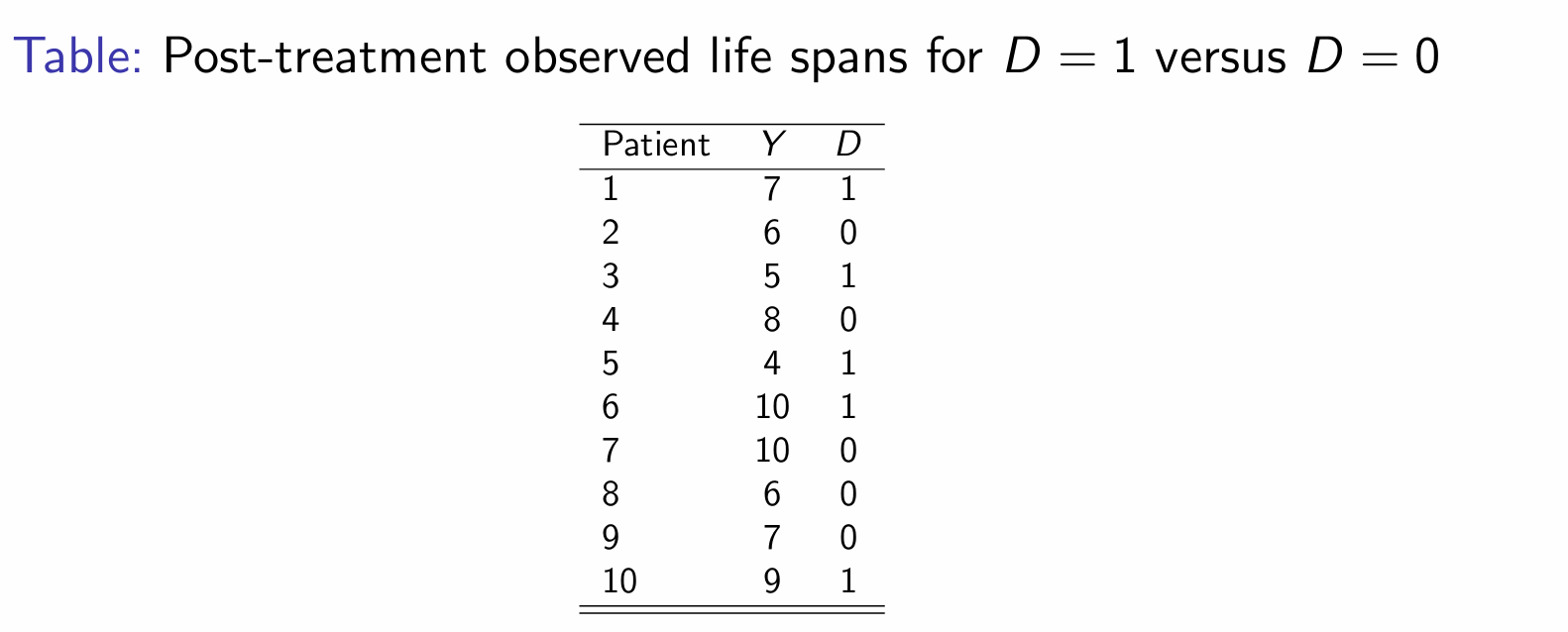
Calcuate the SDO for the treatment example. What does the outcome suggest?

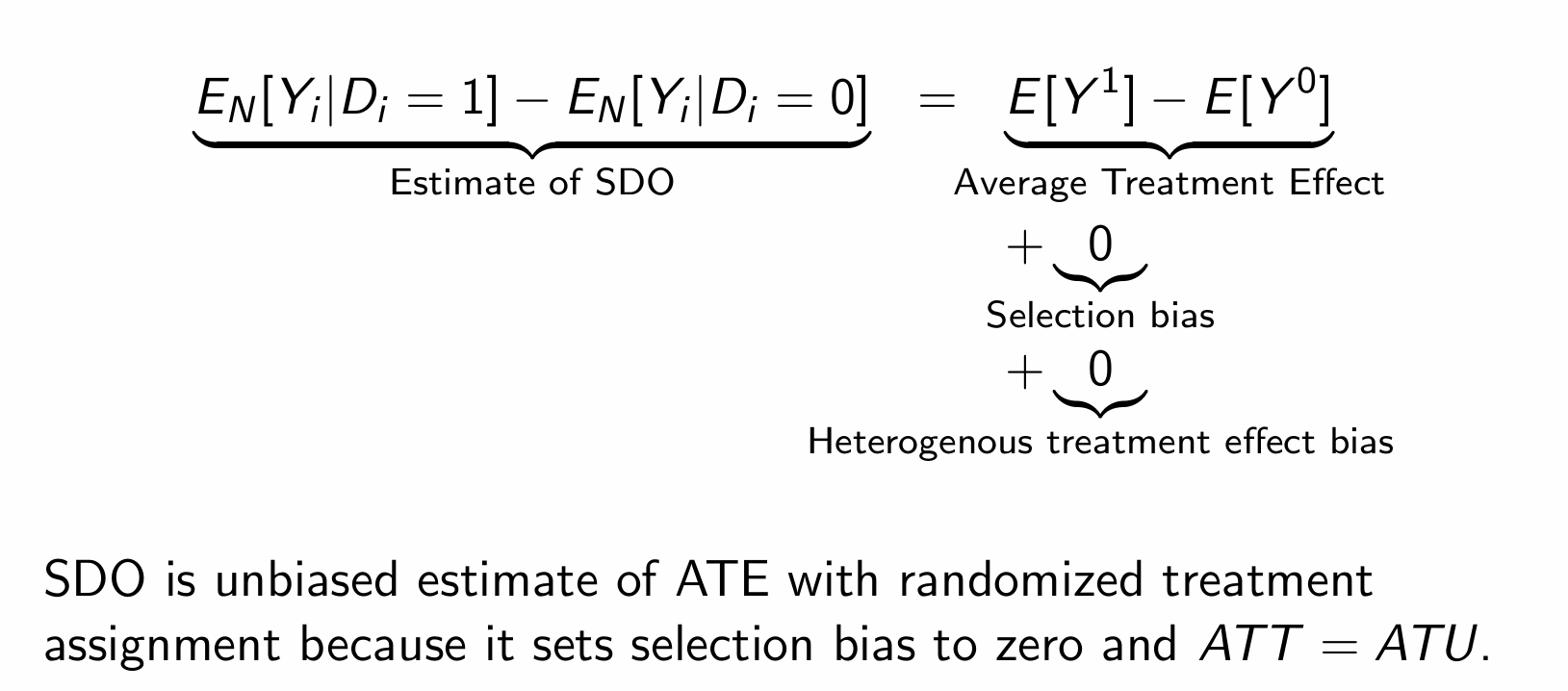
How does the SDO equate to the ATE and other biases?
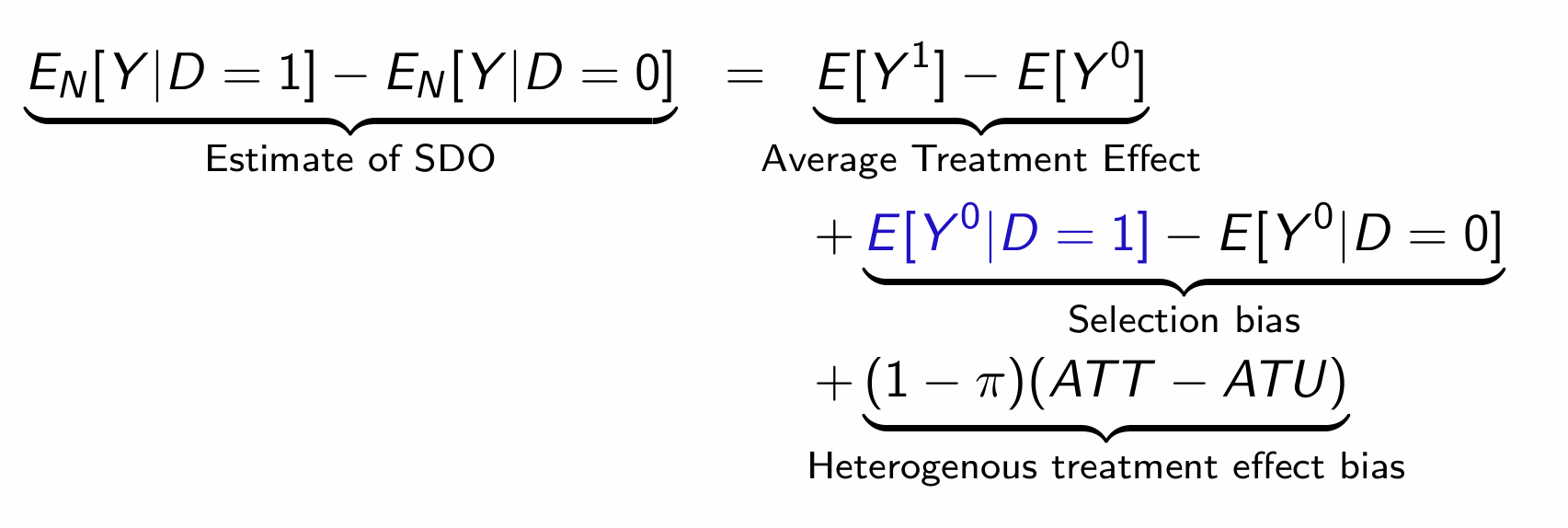
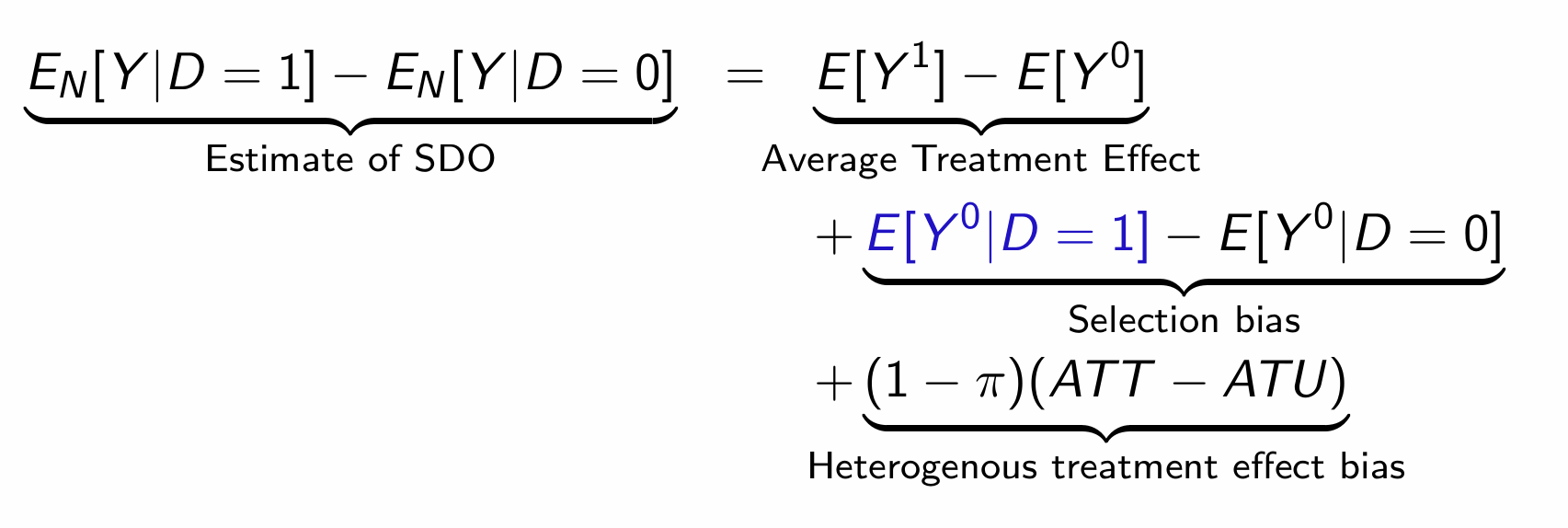
Find the values for the RHS in the treatment example
Assuming we use the theoretical table:
ATE = 0.6, Selection bias = -4.8, heterogenous treatment effect bias = 3.8

What is selection bias and what is the source of it?

What is difference between exogeneity and endogeneity in treatment example?

Two extreme examples of a treatment assignment mechanism are what?

Where does the bias come from?

In causal inference, selection bias is caused by different mean potential outcomes by treatment status. What are the different selections that can be made?

What are the impacts of the three selection biases on the ATE?

What is the goal of casual inference?

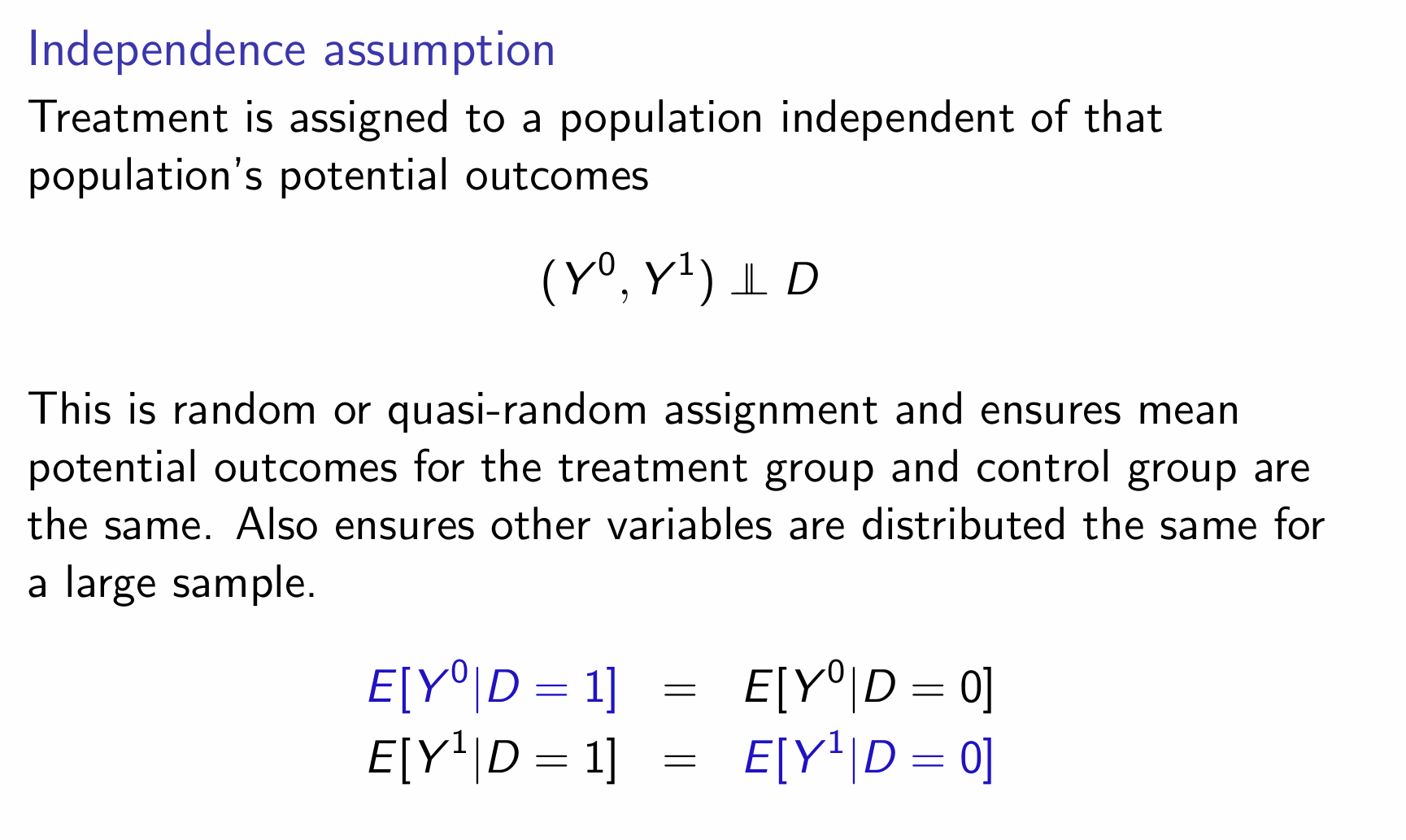
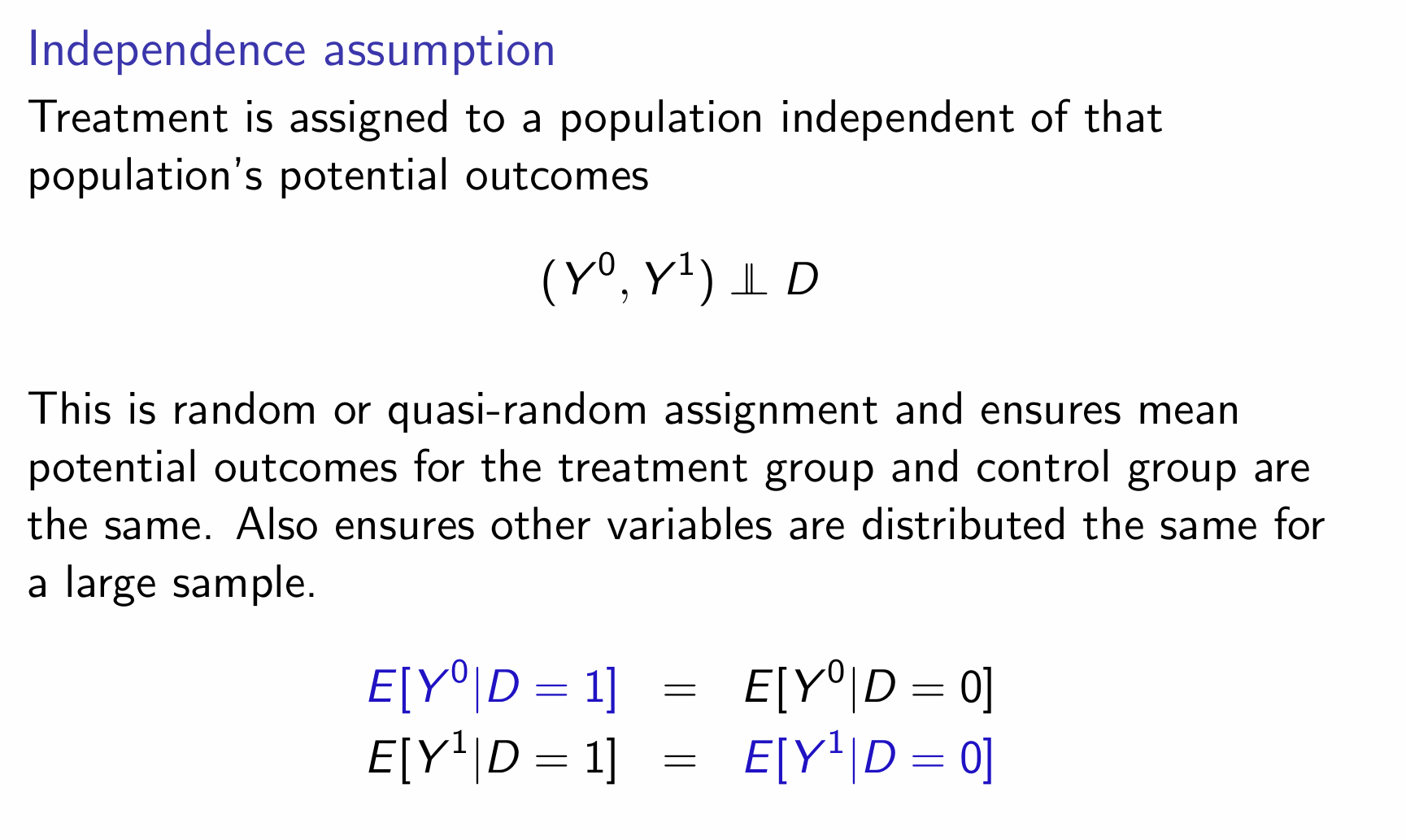
What is the independence assumption and how do we denote it?
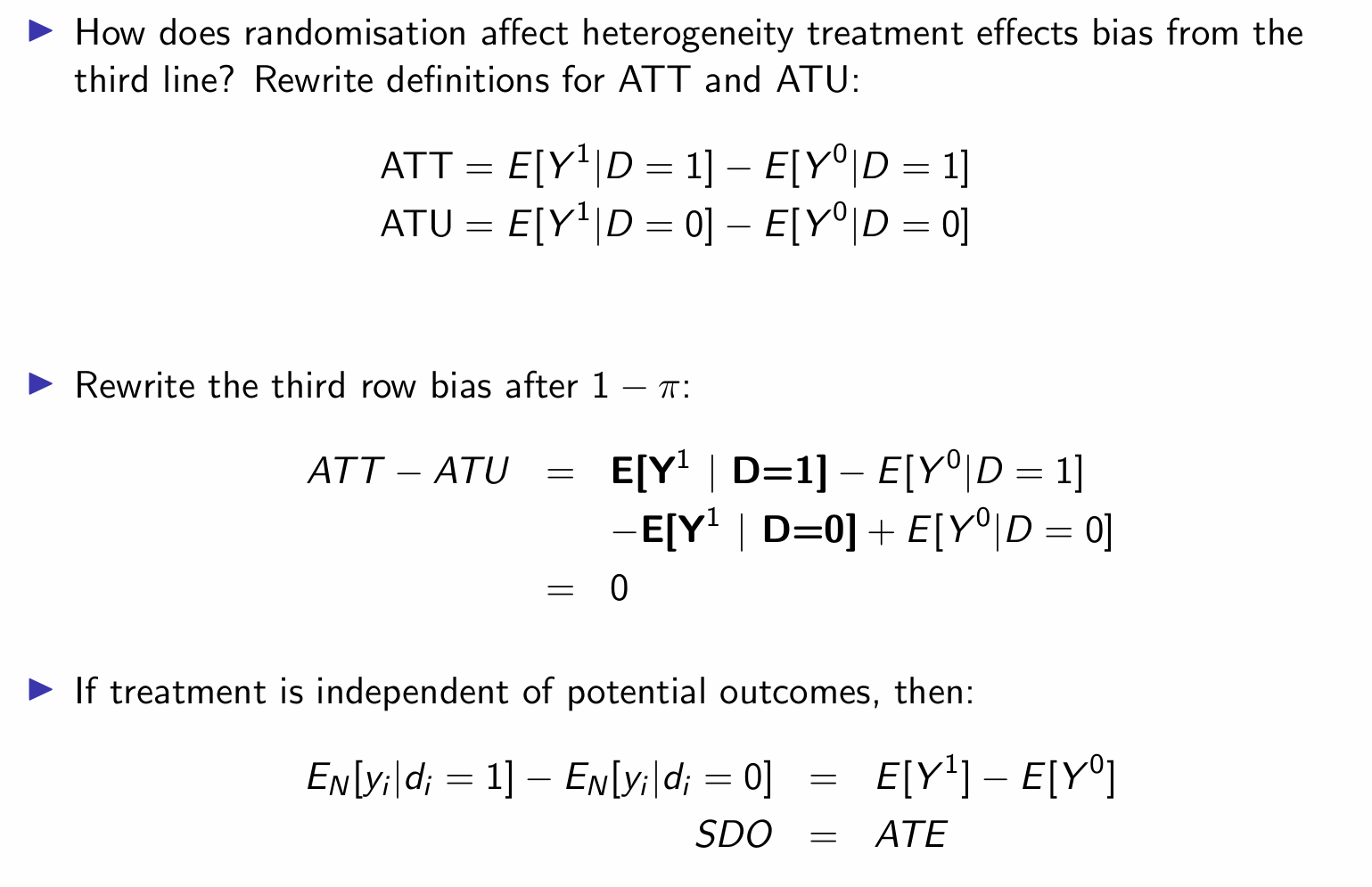
How can we use random assignment and the independence assumption to zero out the selection bias?

How can we use random assignment and the independence assumption to zero out the heterogenous treatment bias?
With the independence assumption, how does the SDO relate to the ATE?
How do we obtain stable aggregate parameters?

What does SUTVA stand for and what does it mean?



How might we mitigate the treatment spill overs?


Provide an example and how it could be violated for stability

How can the scale of the causal effect impact the stability of treatment effects?

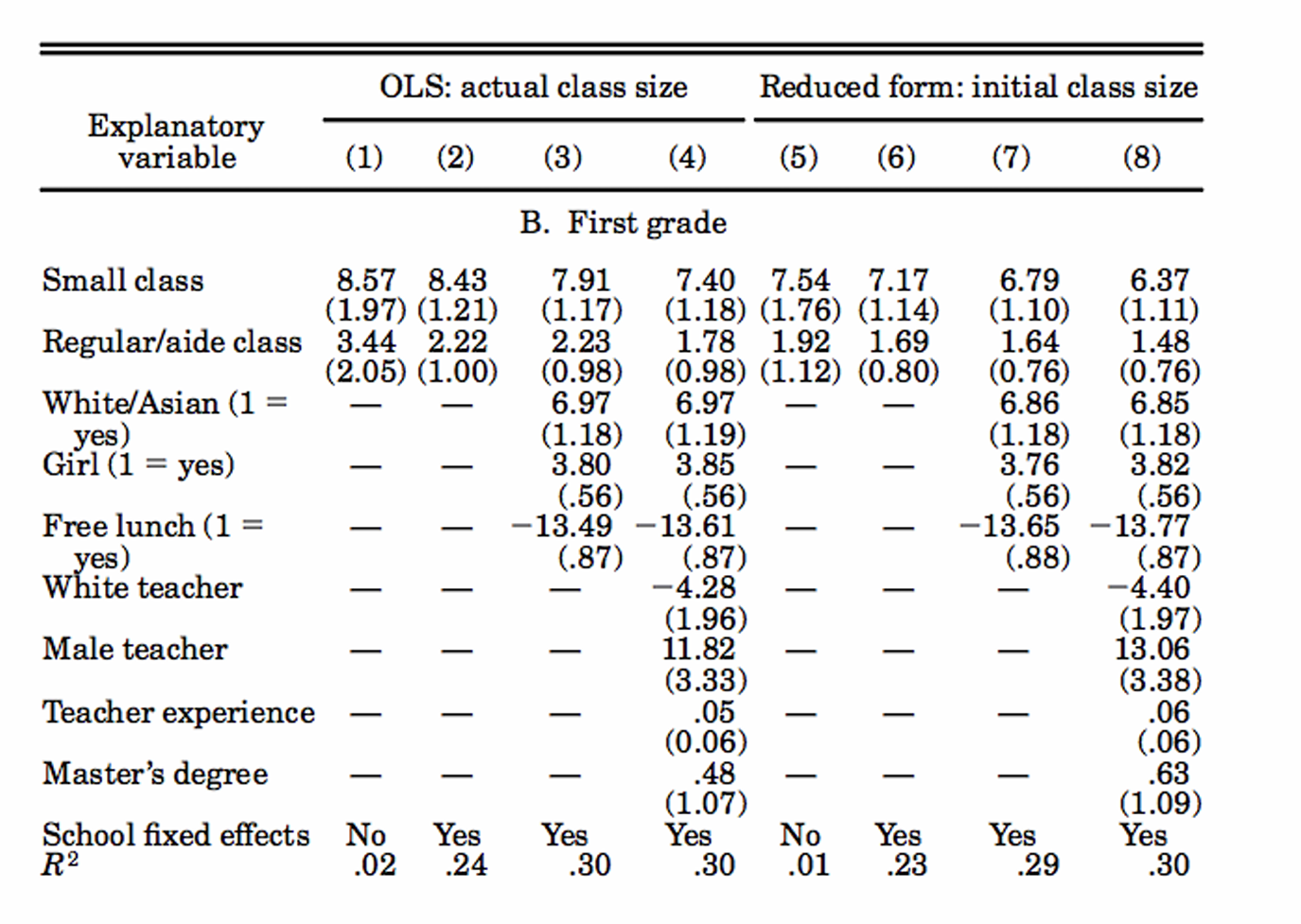
Provide a summary of the Krueger (1999) Project STAR experiment

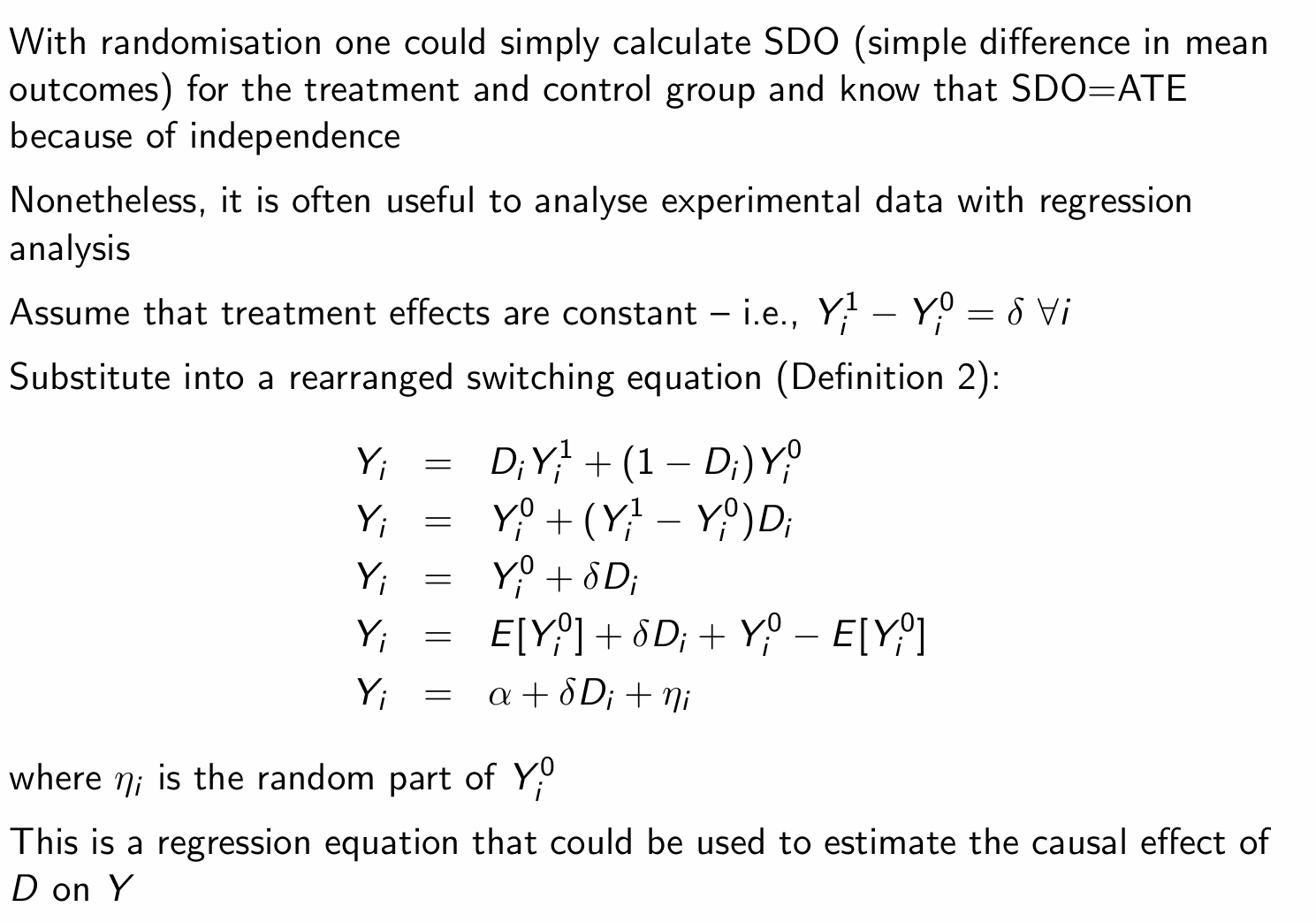
How can the switching equation and the assumption of constant treatment effects be used to form a regression equation?
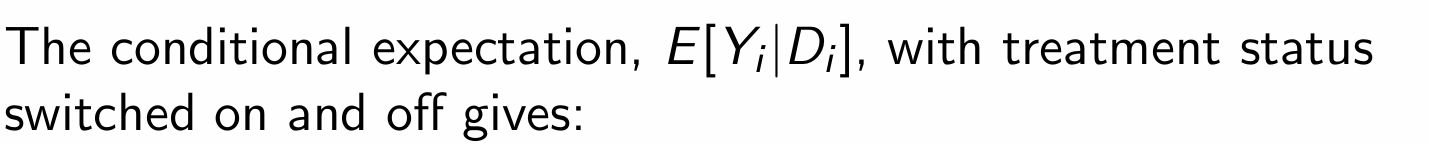
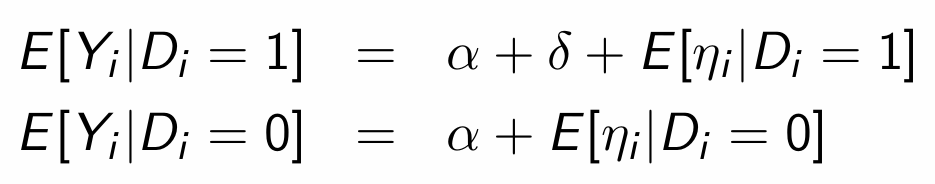
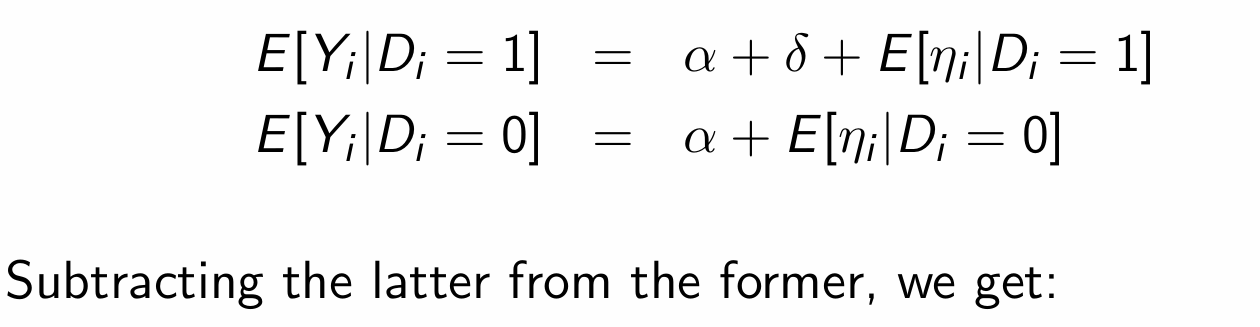
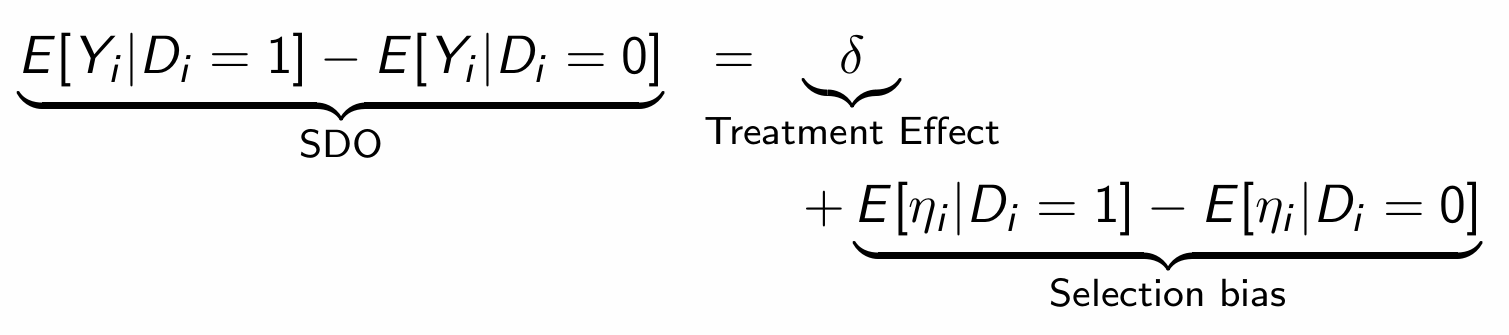

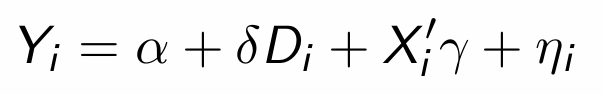


What was the econometric model that Krueger used?
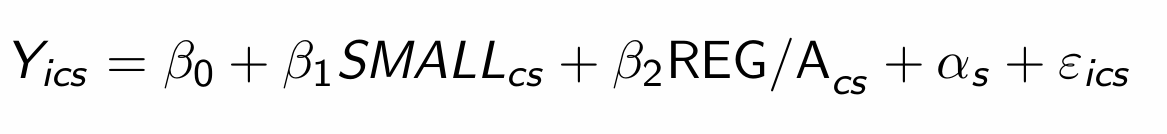
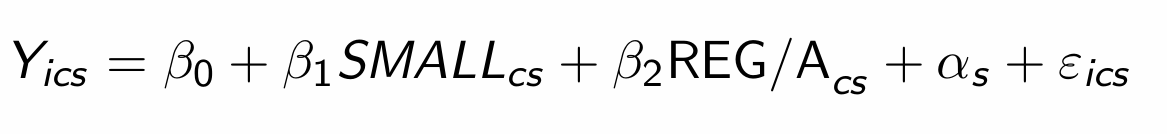
What does each parameter mean?

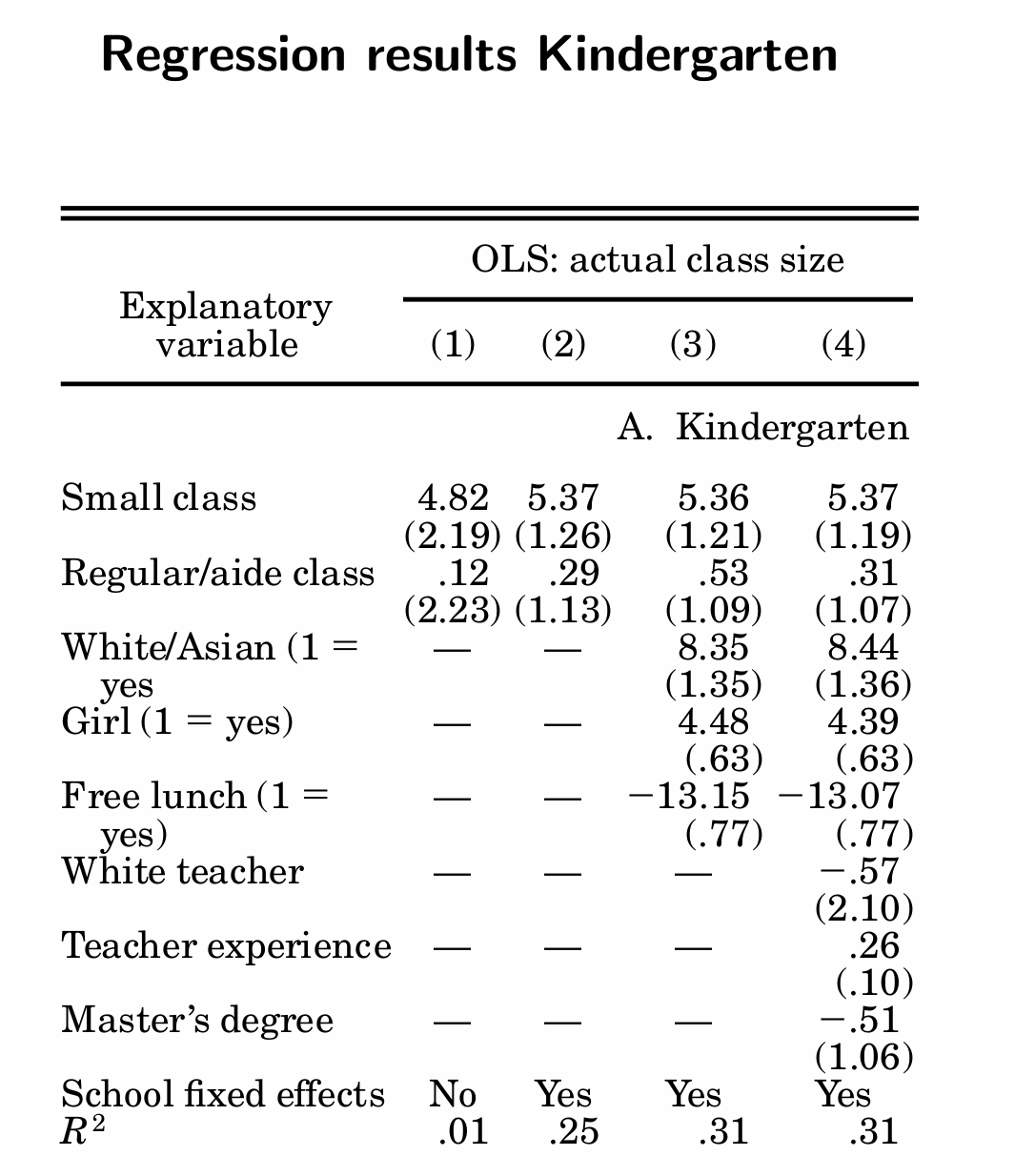

What is attrition and why is it a common problem in randomised experiments?

Is attrition random in Krueger’s experiments and how does he address attrition?

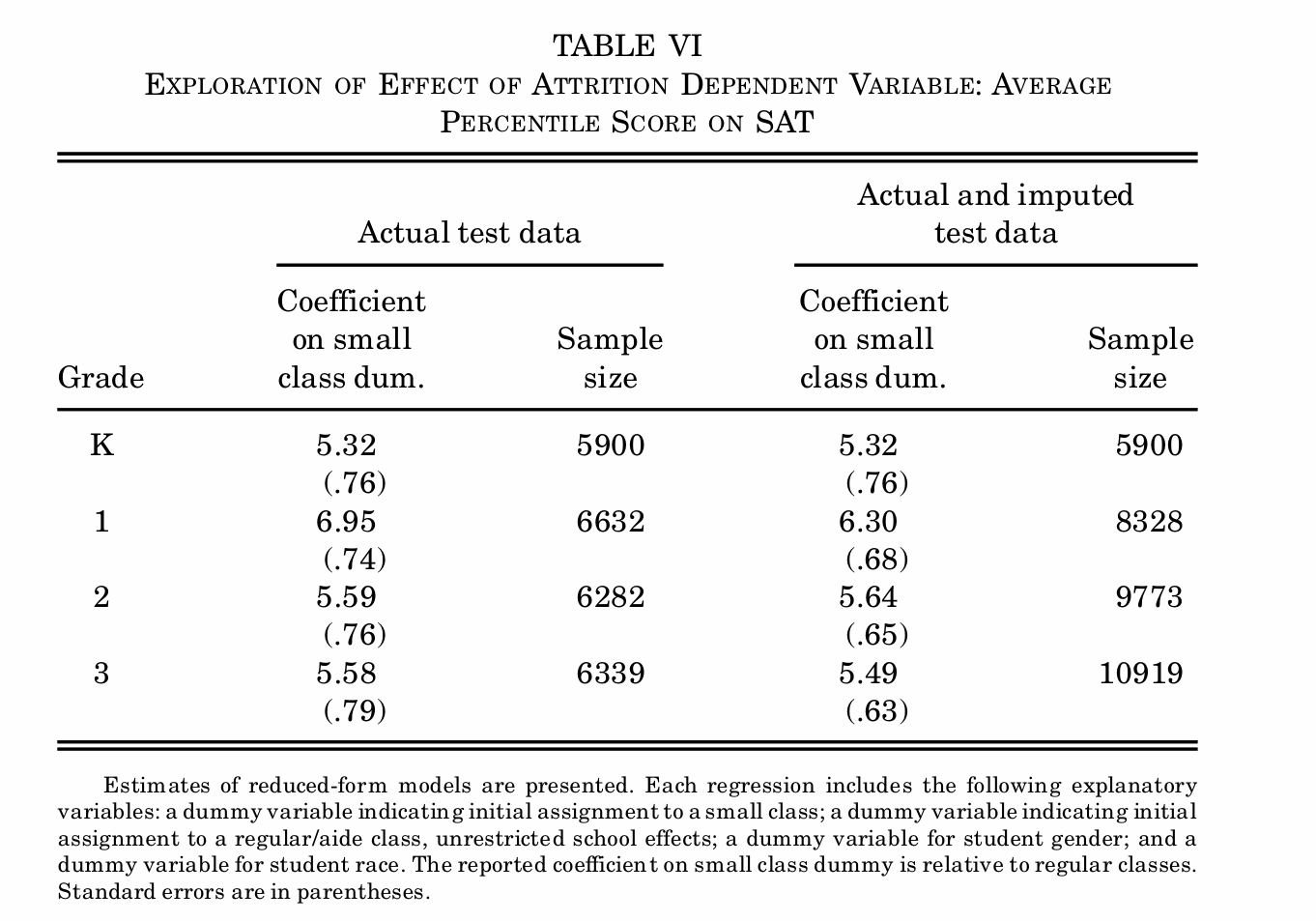
What is the impact of non-random attrition on these results?
Hardly biases the results
Why is students switching classrooms following the random assignment a problem?

How could you address the issue of switching classrooms?