PHA6112 LAB: NUCLEIC ACIDS PRE & POST LAB
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Nucleic acids
Biomolecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction
False: DNA stores; RNA synthesizes
T or F: RNA stores the information while the DNA synthesizes the proteins
proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids
The proteins produced in the cell are needed to make other ______, _______, _______, and ______.
Nitrogen heterocyclic base and Pentose sugar
What are the 2 parts of a nucleoside?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
2 Types of Nucleic acid
nucleotides
These are polymers consisting of long chains of monomers called _______.
Nitrogen heterocyclic base, Pentose sugar, and Phosphate residue
What are the 3 parts of nucleotide?
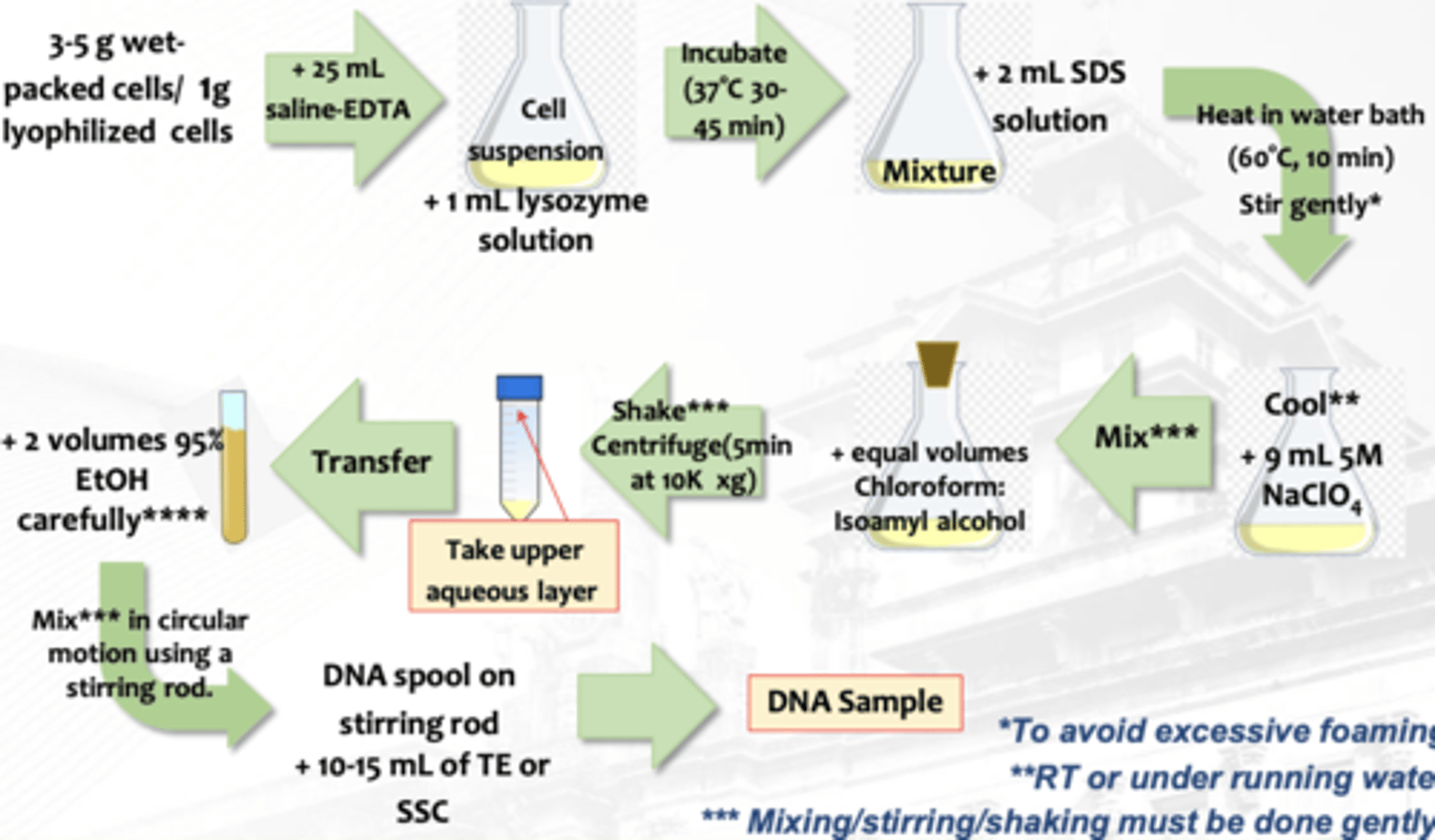
Isolation of Microbial DNA
What isolation is this?
Isolation of Plant DNA
What isolation is this?

Isolation of DNA from Onion
What isolation is this?

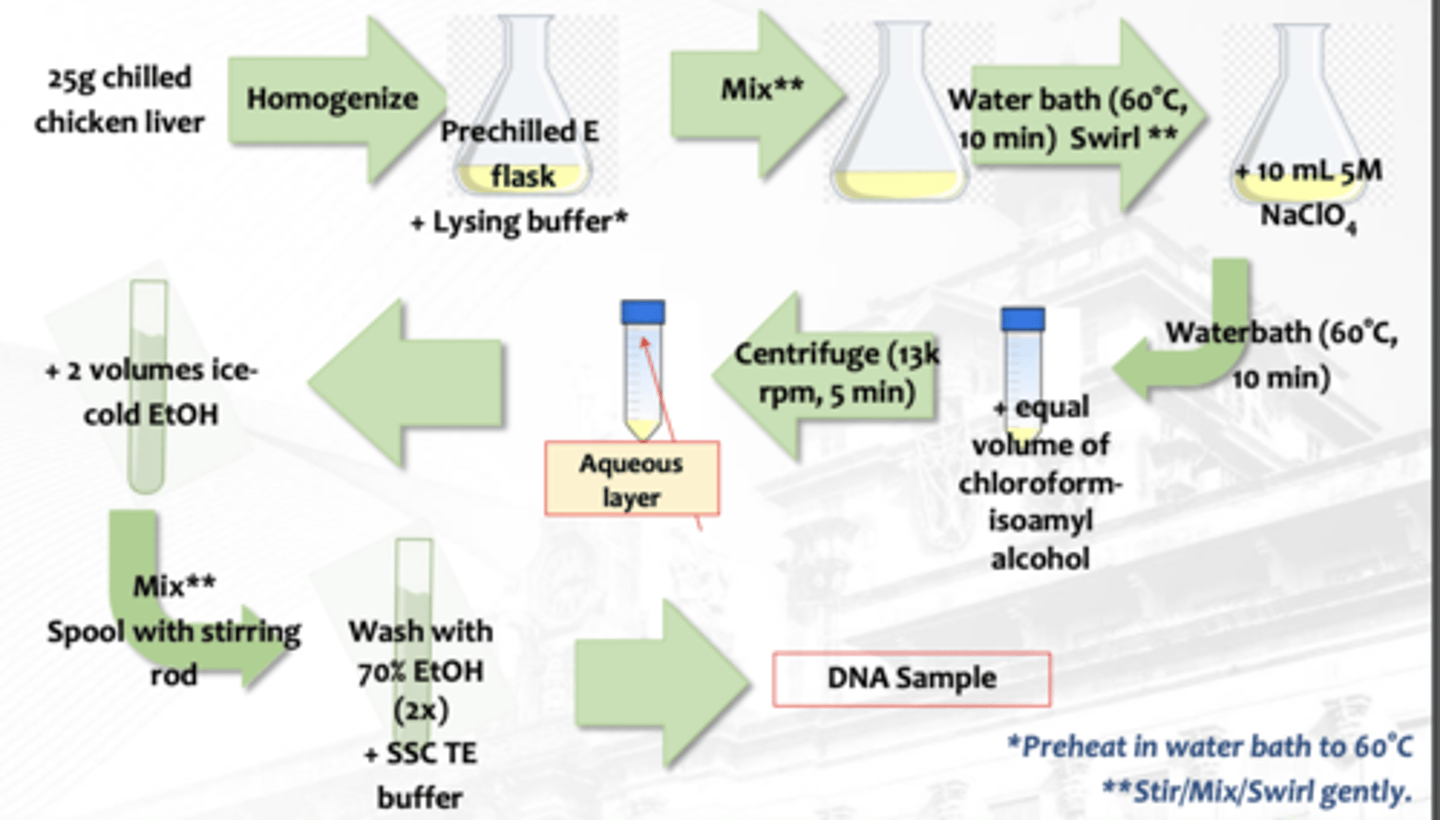
Isolation of DNA from Animal Tissue
What isolation is this?
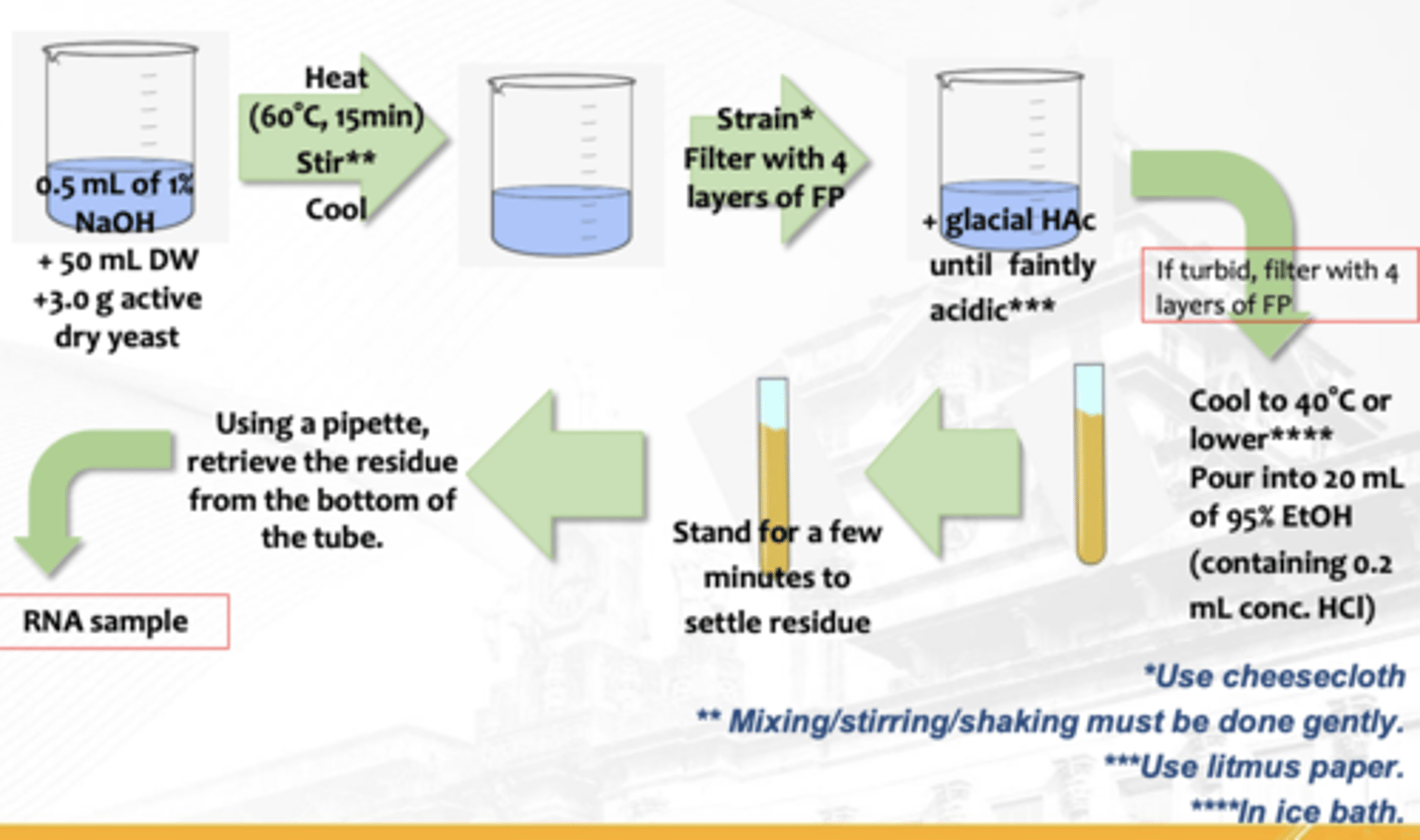
Isolation of RNA from Yeast
What isolation is this?
Acid Hydrolysis of DNA
Test for Deoxyribose Test for Phosphate Test for Purines
Test for Pyrimidines
Alkaline Hydrolysis of RNA
Test for Ribose
Test for Phosphate
Test for purines
Test for Pyrimidine
Test for Ribose: Bial's Orcinol Test
Reagent: Orcinol in HCL (yellow solution
Positive result: blue-green coloration
Test for Deoxyribose: Diphenylamine or Dische (1930) test
Reagent: diphenylamine in conc. H2 SO4
Positive result: : blue complex/compound (λmax = 595 nm)
Test for Phosphates
Reagent: Sulfuric acid, conc. HN03, and 10% (nh4)mOo4
Positive result: yellow crystalline precipitate
Test for Purines: Murexide Test
Reagent: NA solution, conc. HN03, 10% KOH
Positive result: red residue
Adenine and guanine
What are the two derivatives of the test for purine?
Test for Pyrimidines
Reagent: NA solution, bromine water, Ba(OH)2 solution
Positive result: purple color due to Ba2+ salt of dialuric acid
True
T or F: Test for pyrimidines detects U and C
False: Negative for T
T or F: Test for pyrimidine is negative for G
True
T or F: Each nucleotide unit is made up of nitrogen heterocyclic base, pentose sugar, and phosphate residue.
Deoxyribose
The pentose sugar in DNA contains what?
Ribose
The pentose sugar in RNA contains what?
Pyrimidine
6-membered heterocyclic bases
Purine
Fused 6- & 5-membered rings for its heterocyclic bases
Pyrimidine
Heterocyclic base that contains cytosine, uracil, and thymine
Purine
Heterocyclic base that contains adenine and guanine
RNA
Uracil is found in ____.
DNA
Thymine is found in ___.
Cytosine
A pyrimidine base that contains an amine group
Thymine
A pyrimidine base that contains a methyl group
Guanine
A purine base that contains a carbonyl group
tissues containing cells with high nuclear volume/cytoplasmic volume ratio
choice of sample in isolation of DNA
Bacillus subtilis or Escherichia coli
Microbial DNA sample source in isolation of DNA
meristematic region of any plant & yellow onion
Plant DNA sample source in isolation of DNA
spleen, liver, thymus and pancreas (vs brain and muscle tissues - lower concentration)
Animal DNA sample source in isolation of DNA
1. Homogenization
2. Dissociation and denaturation/precipitation of nucleoprotein
3. Purification of NA
general principle and steps in the isolation of DNA
homogenization
lysis or disruption of cell membrane and organelle membranes releases the nucleoprotein (DNA-histone complex) into a medium in which it is soluble and protected from degradation
Mechanical disruption
homogenization using homogenizer, blender, mortar and pestle, cut into small/fine pieces or mashed, mincing, grinding, sonication
Chemical
homogenization using detergents & chaotropic agents
n-butanol, ethanol, guanidinium chloride, lithium perchlorate, lithium acetate, magnesium chloride, phenol, 2-propanol, sodium dodecyl sulfate, thiourea, and urea
examples of detergents & chaotropic agents
to inactivate nucleases
why is denaturation of enzymes performed?
salt, alcohol (isopropyl alcohol or ethanol)
reagents used in dissociation and denaturation/precipitation of nucleoprotein
T
T or F: it is difficult to isolate DNA in an intact and undamaged form because of its large and fragile nature
F (drastic changes in conditions are avoided or minimized)
T or F: Isolation should be conducted where drastic changes in conditions (experimental factors affecting DNS) are observed
isolation of microbial DNA
Target for extraction is the disruption of bacterial cell wall and the inactivation of enzymes
EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)
in the isolation of microbial DNA, it is used as chelating agent for divalent cations (Mg++) for the metals present in DNases. This inactivates the enzyme.
Lysozyme
in the isolation of microbial DNA, it is used to cause lysis of bacterial cells by hydrolyzing the peptidoglycan present in cell walls. This disrupts the bacterial cell wall to let the DNA be in solution
plant DNA
One of the most difficult DNAs to isolate
• Structure of the plant cell - hard, rough, solid cell wall because of peptidoglycan, pectin, cellulose and chitin.
• Component of the plant cell - secondary metabolites such as polysaccharides, phenols etc.
reasons why plant DNA is difficult to isolate
CTAB (Cetyl trimethylammonium bromide)
in the isolation of plant DNA, it is a cationic detergent used to separate polysaccharides during purification of DNA samples from plants
NaCl
in the isolation of plant DNA, it removes proteins that are conjugated to the DNA. Proteins are kept dissolved in the aqueous portion which prevents alcohol from precipitating it along with DNA.
0.15 M NaCl, 5% SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate), 0.15 M sodium citrate, 1 mM EDTA
components of homogenizing solution
0.15 M NaCl
component of homogenizing solution that precipitates nucleoproteins (salting-out)
5% SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate)
component of homogenizing solution that breaks ionic interaction between protein and nucleic acid
0.15 M sodium citrate and 1 mM EDTA
component of homogenizing solution that Chelate Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions (cofactors)
dissolves nucleic acids
Heating at 60°C
retards nuclease activity
Cooling in ice bath
denatures protein
Papain or meat tenderizer 6%
precipitates DNA and RNA
Ice-cold 95% EtOH
Precipitates DNA only
Ice-cold 100% iPrOH
5 M Sodium chloride
Lysing buffer: osmosis in the cell
Tris HCl
Lysing buffer: buffer
0.5M EDTA
Lysing buffer: chelates the metals in the DNAses
5% SDS
Lysing buffer: disrupts cell membrane and nuclear envelope
Chloroform
denature the proteins and lipids to maintain separation of organic and aqueous phases
Isoamyl alcohol
prevents foaming
F (Large cytoplasmic volume)
T or F: RNA is single-stranded NA found in high concentrations in tissues with low cytoplasmic volume
T
T or F: RNA isolates are easily damaged by shearing
T
T or F: RNA is very vulnerable to digestion by ribonucleases (endogenous and exogenous)
F (higher UV absorption)
T or F: RNA has lower UV absorption at 260 nm than DNA
T
T or F: Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae) has low nuclear-cytoplasmic volume ratio
T
T or F: RNA concentration is high in the cytoplasm
F (4% RNA by weight)
T or F: Saccharomyces cerevisiae is 10% RNA by weight
Heating with dilute NaOH;
Glacial acetic acid (pH 4-5);
Ethanol with concentrated HCl;
Alcohol (EtOH) and ether (organic solvents);
TE Buffer;
SSC (Standard Saline Citrate) Solution
processes and reagents involved in Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
Heating with dilute NaOH
Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
—Separates RNA from proteins
—Extracts RNA and water-soluble proteins
—Inactivates nucleases (RNase)
Glacial acetic acid (pH 4-5)
Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
Separates nucleic acids associated with proteins and other interfering substances
Ethanol with concentrated HCl-
Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
precipitates RNA
Alcohol (EtOH) and ether (organic solvents)
Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
Removes lipids
TE Buffer, SSC (Standard Saline Citrate) Solution
Isolation of RNA from Yeast (S. cerevisiae)
preserves the integrity of DNA by maintaining the pH of the solution
260, 280, and 230 nm
What are wavelengths in measuring absorbance of nucleic acids? (3)
A260/280
relative measure of NA/protein content
1.8-2.0
range of relative measure for good quality NA
1.8
relative measure of pure DNA
indicates increased contamination by protein
what does a relative measure of x < 1.8 indicate?
indicates increased contamination by RNA or denature DNA
what does a relative measure of 1.8 < y indicate?
A = ԑbc
formula for Beer-Lambert's Law
Produces brown-black solid
visual positive result of Acid hydrolysis
F (not complete for RNA)
T or F: Alkaline (basic) Hydrolysis is not complete for DNA
Alkaline (basic) Hydrolysis
what type of hydrolysis creates a mixture of 2' and 3'- nucleotides
F (DNA is not readily hydrolyzed by dilute alkali)
T or F: RNA is not readily hydrolyzed by dilute alkali