Chapter 11: DNA/Gene Synthesis and Repair
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Erwin Chargaff
The scientist who discovered that there are equal proportions of base pairs AT and GC
secondary structure
Early data provided clues to DNA secondary structure
sugar-phosphate
Early chemists knew the structure of nucleotides and that DNA has a _________-__________ backbone.
Chargoff's Base Pair Rule
The base pair rule that %A=%T and %G=%C
Rosalin Franklin, Maurice Wilkins
______ ______ obtained images of DNA using X-ray crystallography, an idea first broached by ______ ______.
True
(T/F) Scientists build on eachother's ideas
hydrogen bonds
two strands of the DNA is held together by ______ bonds between pyrimidines and purines
True
(T/F) DNA is antiparallel. Meaning one strand runs 3 to 5 while te other 5 to 3.
exterior
The sugar phosphate backbone faces: interior or exterior?
interior
The nitrogenous base pairs face the: interior or exterior?
nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.

phosphate, hydroxyl
DNA strands are directional. One end has an unlinked 5' ____________ (P) group, while the other ends has an unlinked 3' ___________ (OH) group.
Pyrimdines
thymine, cytosine, uracil
Purines
Adenine, Guanine
Thymine
Adenine binds with _____
Cytosine
Guanine binds with _____
Conservative
DNA replication is semi-_________ because one strand is from the parent while the other is daughter strand
Origin of replication
In DNA replication, a bubble forms when DNA synthesizes, this area is known as the "________ __ _____________"

1) Unwinding
2) Priming the leading strand
3) Building the leading strand
4) Priming and building the lagging strand.
There are 4 stages of DNA Replication
1) Un________
2) Priming the _________ strand
3) Building the _________ strand
4) Priming and building the _________ strand
DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication
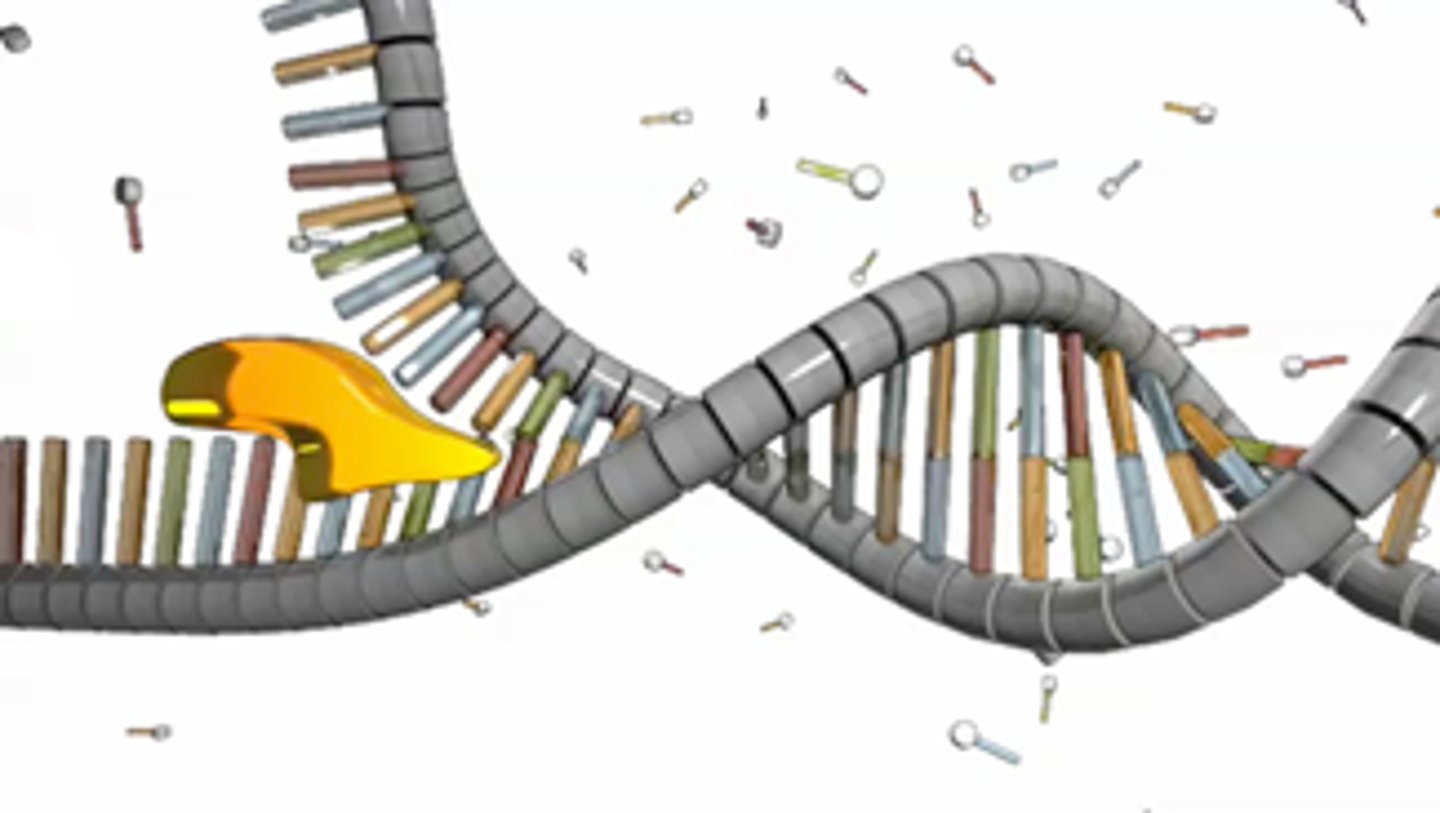
Topoisomerase
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands

RNA Primase
An enzyme that creates an RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication.

DNA polymerase III
synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction
Lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.

single-strand DNA-binding proteins
SSBPs: attach to separated strands to prevent them from closing
Leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
Okazaki fragment
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
Ligase
final binding of sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA during synthesis and repair
Replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.
TACGTA
What's the matching strand?
ATGCAT