BIO Lab Meiosis Understand how traits are inherited Quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Question 1 : Before the fertilization process, higher eukaryotes have to produce reproductive cells (gametes). Through which
type of cell division are the reproductive cells produced?
a. Meiosis
b. Mitosis
c. Binary fission
d. Budding
a. Meiosis
Question 2 : What would happen if organisms produced reproductive cells through mitosis instead of meiosis?
a. The chromosome number o f that species would double with each generation
b. There would be no difference
c. The offspring would always have a syndrome
d. Individuals in the next generation would have a bigger body mass compared to their parents
a. The chromosome number o f that species would double with each generation
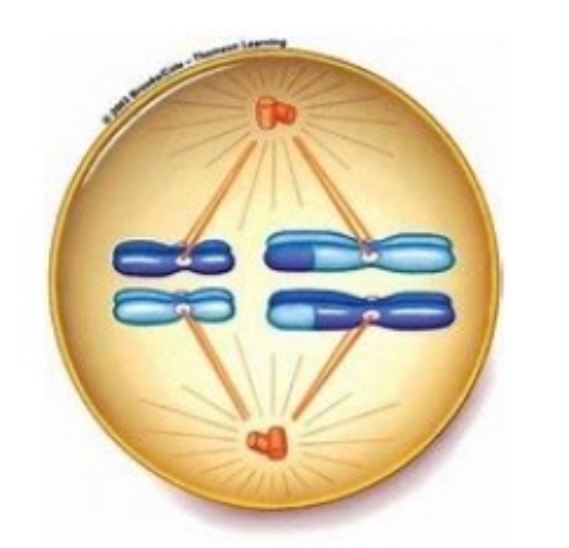
Question 3: Which phase are the cells currently in?
a. Metaphase II
b. Anaphase II
c. Telophase II
d. Metaphase I
d. Metaphase I
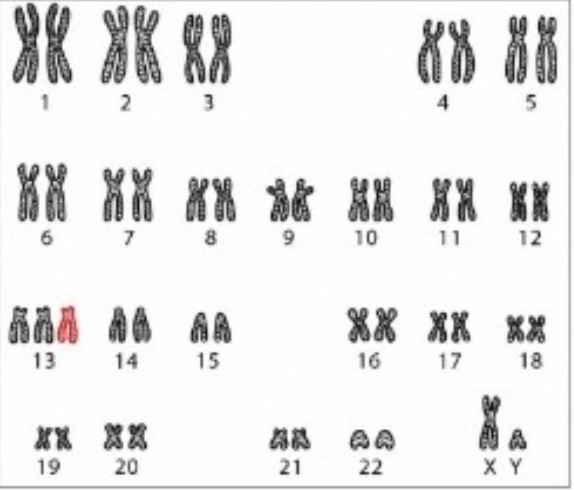
Question 4: Based on the image analysis, do you think that the baby would have any chromosome abnormality?
a. Yes, he would have a trisomy 13
b. Yes, he would have a trisomy 21
c. Yes, he would have monosomy
d. No, he would be a healthy baby
a. Yes, he would have a trisomy 13
Question 5: Individuals with the appropriate number of chromosomes are called euploid. What is the correct term to describe an organism that has an unusual number of chromosomes?
a. Diploid
b. Triploid
c. Mutaploid
d. Aneuploid
d. Aneuploid
Question 6: Aneuploidy and chromosomal structural rearrangement are examples of inherited genetic disorders. During which process do the chromosomes behave abnormally for these type disorders to arise?
a. Meiosis
b. Fertilization
c. Copulation
d. Mitosis
a. Meiosis
Question 7: Errors in meiosis are the cause of chromosomal abnormality. What is an error that occurs when pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis?
a. Nondisjunction
b. Translocation
c. Deletion
d. Duplication
a. Nondisjunction
Question 8: Ovum and sperm are gametes. Unlike somatic cells (the rest of the cells in our body), they only contain a single set of chromosomes, therefore they are considered as what type of cells?
a. Haploid
b. Diploid
c. Zygote
d. Homologs
a. Haploid
Question 9: What is the union of two gametes from two individual organisms called?
a. Fertilization
b. Ovulation
c. Recombination
d. Inoculation
a. Fertilization
Question 10: Unicellular organisms such as bacteria depend on asexual reproduction. Why is sexual reproduction so common in higher multicellular organisms such as humans?
a. Because a sexual population can grow faster than an asexual population
b. Because it requires less energy
c. Because it produces offspring that are identical to the parents
d. Because it creates genetic variation in the population
d. Because it creates genetic variation in the population
Question 11: Mitosis and meiosis are both involved in reproduction. While asexual reproduction only involves mitosis, what does sexual reproduction involve?
a. Both mitosis and meiosis
b. Mitosis
c. Meiosis
d. None
a. Both mitosis and meiosis
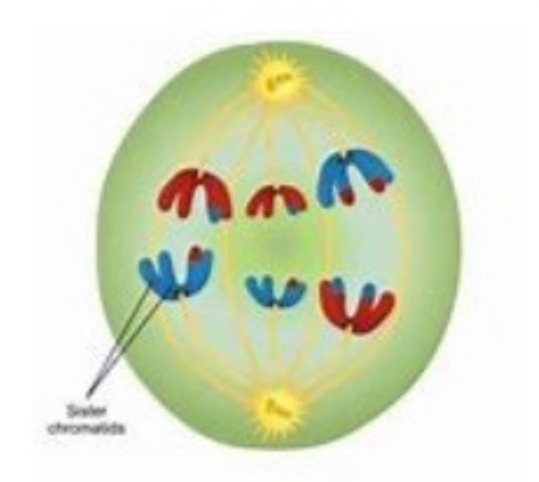
Question 12: Which stage of meiosis is the cell on the right side currently in?
a. Anaphase II
b. Metaphase II
c. Prophase II
d. Telophase II
a. Anaphase II
Question 13: What are the individual chromosomes that are inherited from each of the parents called?
a. A homologous pair
b. DNA
c. Chromosomes
d. Sister chromatids
a. A homologous pair
Question 14: What happens to homologous chromosomes during interphase?
a. They replicate
b. They separate
c. They become fragmented
d. They elongate
a. They replicate
Question 15: In meiosis a diploid cell divides twice yielding four haploid daughter cells. What separates in meiosis I.1?
a. Homologous chromosomes
b. Sister chromatids
c. Old and new chromosomes
d. Parent and daughter DNA
a. Homologous chromosomes
Question 16: During which phase of meiosis does the synapsis and crossing over event occur?
a. Prophase I
b. Prophase II
c. Metaphase I
d. Metaphase II
e. Telophase II
f. Anaphase I
g. Anaphase II
a. Prophase I
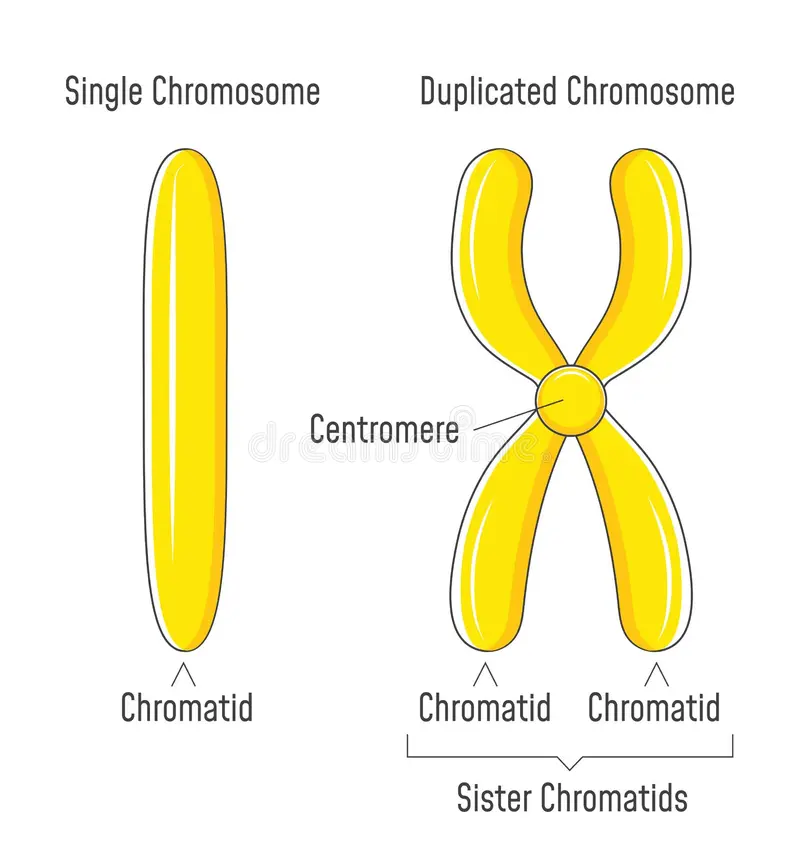
Question 17: What is box 'D' connected to?
a. Sister chromatids✓
b. Centromere
c. Homologous chromosome
d. Unduplicated chromosome
a. Sister chromatids✓
Question 18: In order to yield haploid cells, what separates in meiosis II?
a. Sister chromatids
b. Homologous chromosomes
c. Male and female chromosomes
d. Parent and daughter DNA
a. Sister chromatids
Question 19: Homologous chromosomes (tetrads) align at the midline of the cell during ________________.
a. Prophase II
b. Metaphase I
c. Metaphase II
d. Telophase II
b. Metaphase I
Question 20: During _____________________, the homologous chromosome pairs separate, but the individual chromosome, each consisting of two sister chromatids remain intact.
a. Anaphase I
b. Metaphase II
c. Telophase II
d. Prophase II
a. Anaphase I