Philips Curve and Fed Model
1/13
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What causes inflation?
Excess demand, changed in cost of production, and the general public’s expectation of future inflation.
How is total inflation calculated?
total inflation = inflation expectations + demand-pull inflation + cost-push inflation
What are inflation expectations?
The rate at which average prices are anticipated to rise next year. Inflation expectations change slowly over time.
What is demand-pull inflation?
When excess demand pulls inflation above expectation, or when insufficient demand pulls inflation below expectation.
What is the Phillips Curve?
It creates a link between output gap and unexpected inflation.
How to graph the Philips Curve?
The y-axis is unexpected inflation. The x-axis is output gap. The curve is a line with a positive slope.
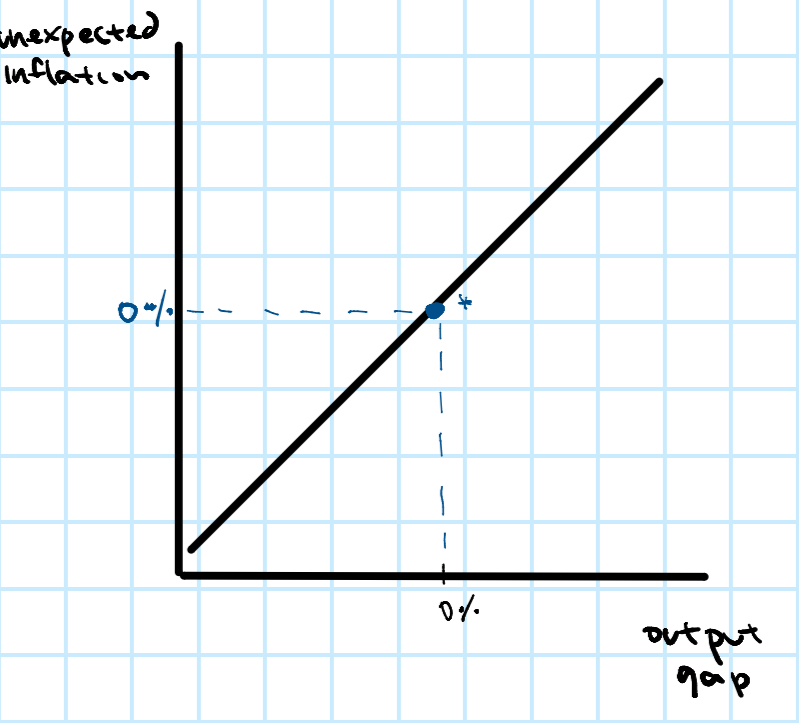
What is a movement along the Philips Curve caused by?
This is from a change in the output gap.
What is cost-push inflation?
Supply shocks: A change in production costs at a given output gap that leads to a change in price. (
What are the types of supply shocks?
Changes to input prices, changes to productivity, changes to the exchange rate.
What effect does cost-push inflation / supply shocks have on the Philips Curve?
It shifts the Philips Curve. Higher prices shifts up, lower prices shift down.
How does an increase to the exchange rate impact the Phillips Curve?
An increase to the exchange rate increases the value of the US $ (appreciates). This directly this decreases the price of foreign goods. Indirectly, it decreases the price of domestic goods through lower foreign input cost. This is a shift down in the Phillips Curve
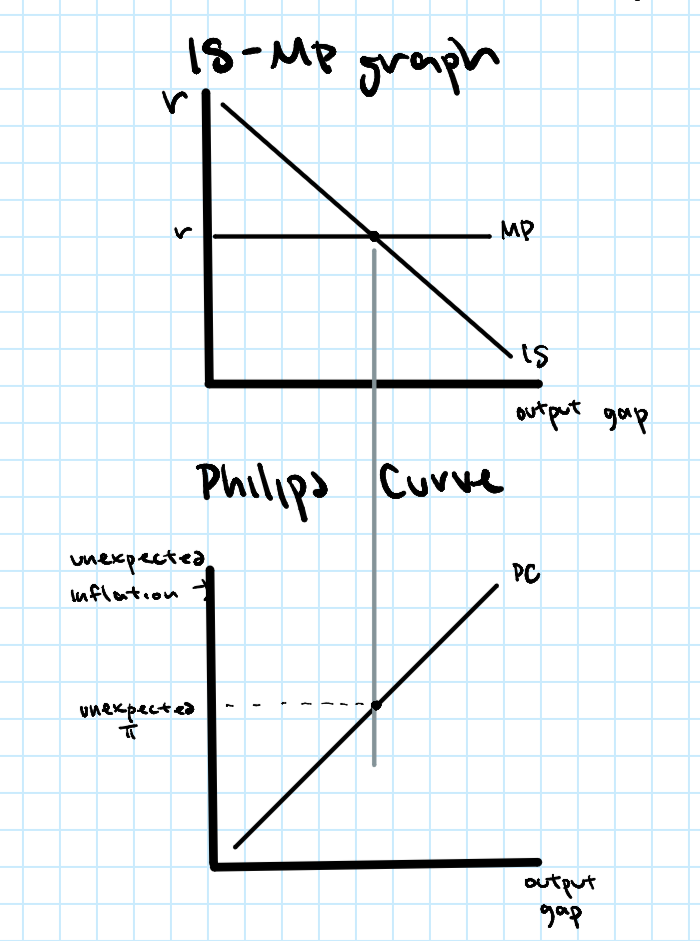
What is the Fed Model?
A framework that uses the IS curve, MP curve, and the Phillips Curve to link interest rates, the output gap, and inflation. It aims to predict what policy responses the Fed would make as a result.
How to graph the Fed Model?
The IS-MP graph stacked on top of the Phillips Curve. The IS-MP curve is first used to find the output gap. The PC is then used to asses the result on inflation.
What is the Federal Reserves dual mandate?
Achieve stable prices through managing inflation. Achieve maximum sustainable employment through manage the unemployment rate.