Substitution and Elimination Reactions
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Which reactions use only one step?
Sn2 and E2
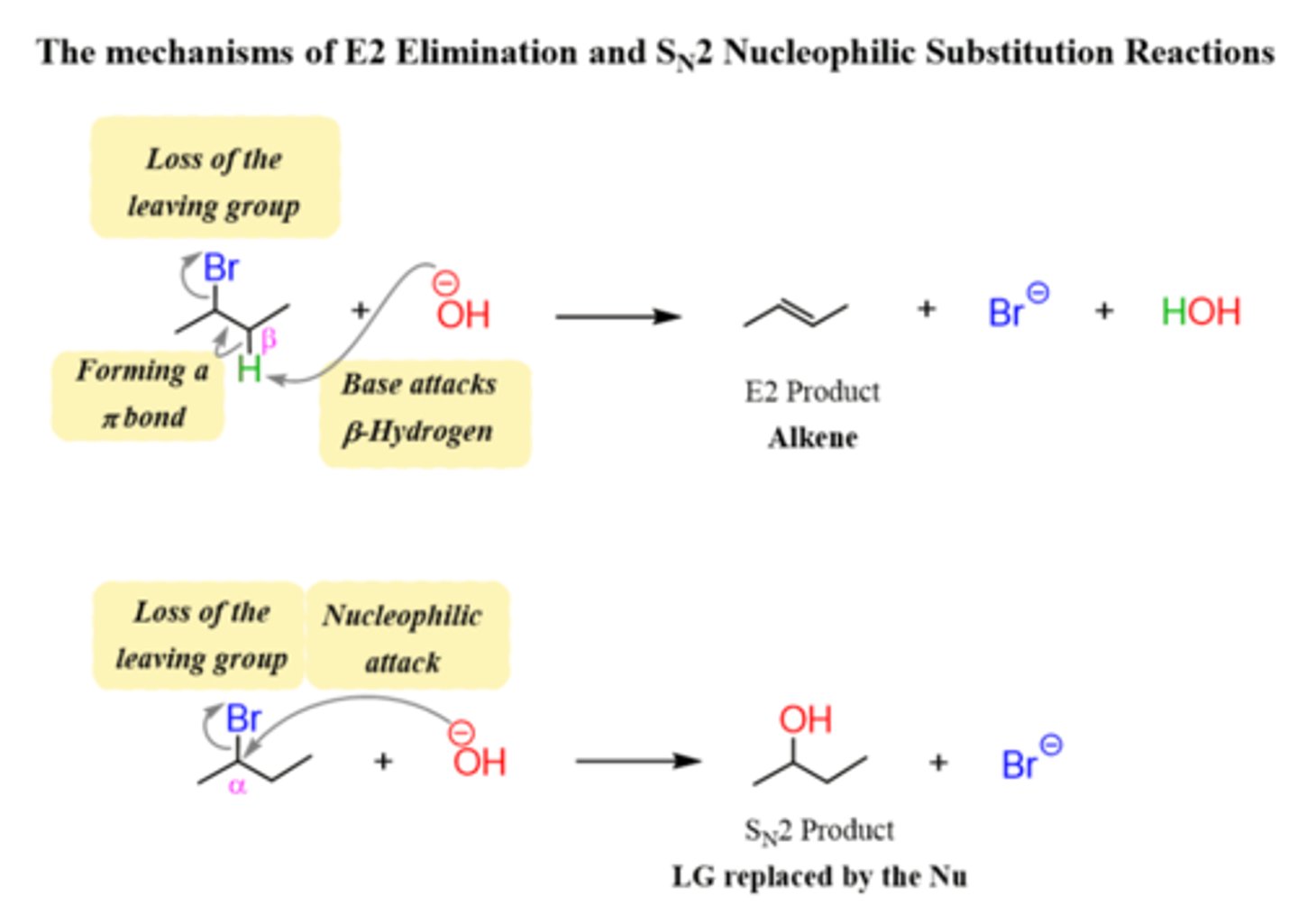
Which reactions require two steps? and why?
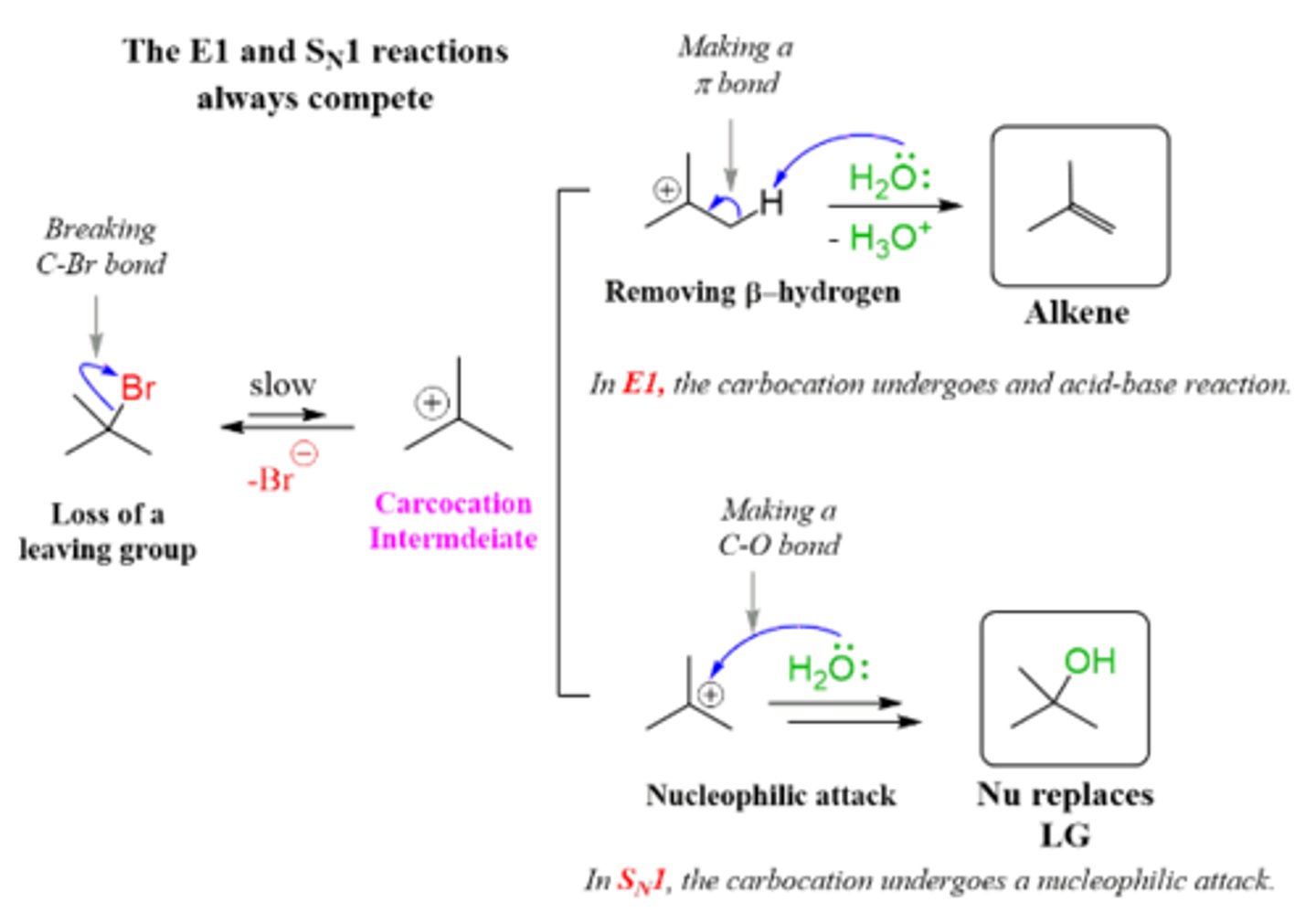
Sn1 and E1. There is a carbocation intermediate that occurs once the leaving group leaves which allows for a rearrangement of a alkyl or hydrogen this leads to a more stable rearrangement of the carbocation before the nucleophile attacks.
Which reactions do best in cooler temperatures?
Sn1 and Sn2
Which reactions do best in warmer temperatures?
E1 and E2
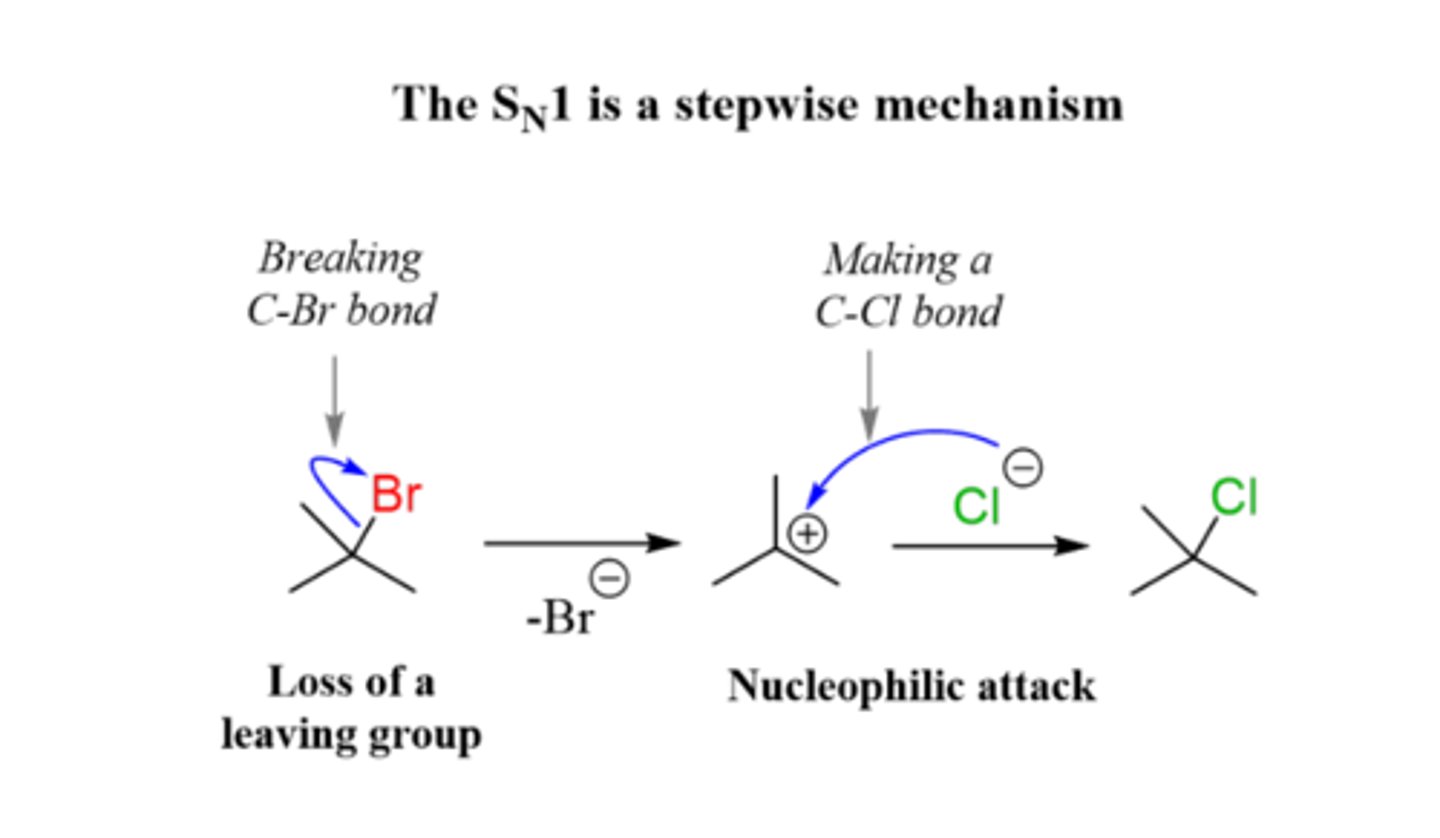
List the steps of an Sn1 reaction mechanism.
1. Leaving group leaves and a carbocation intermediate is formed
(alkyl or hydride shift may take place)
2. Nucleophile attacks
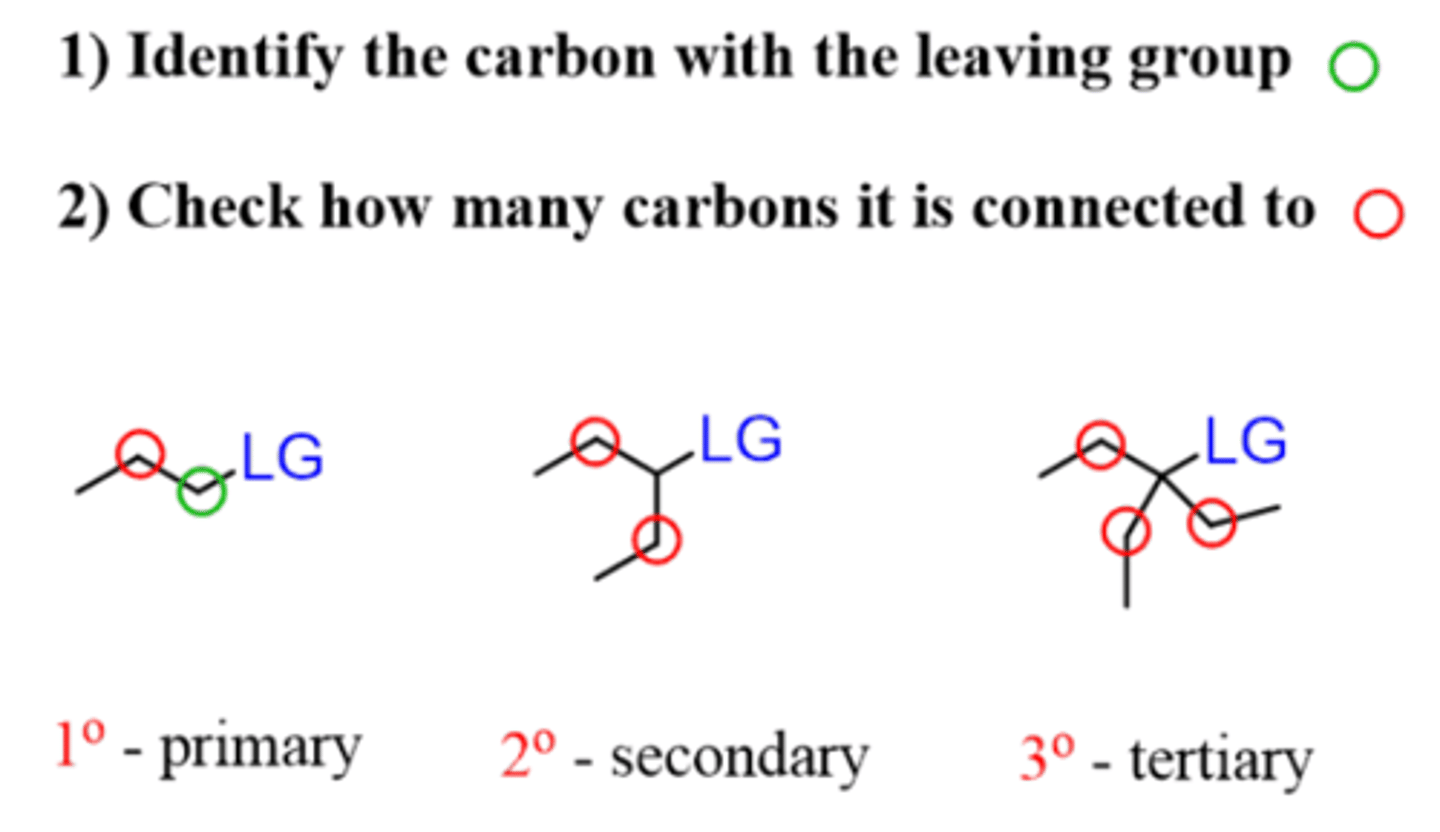
Which substrates work best for an Sn1 reaction?
Tertiary or secondary
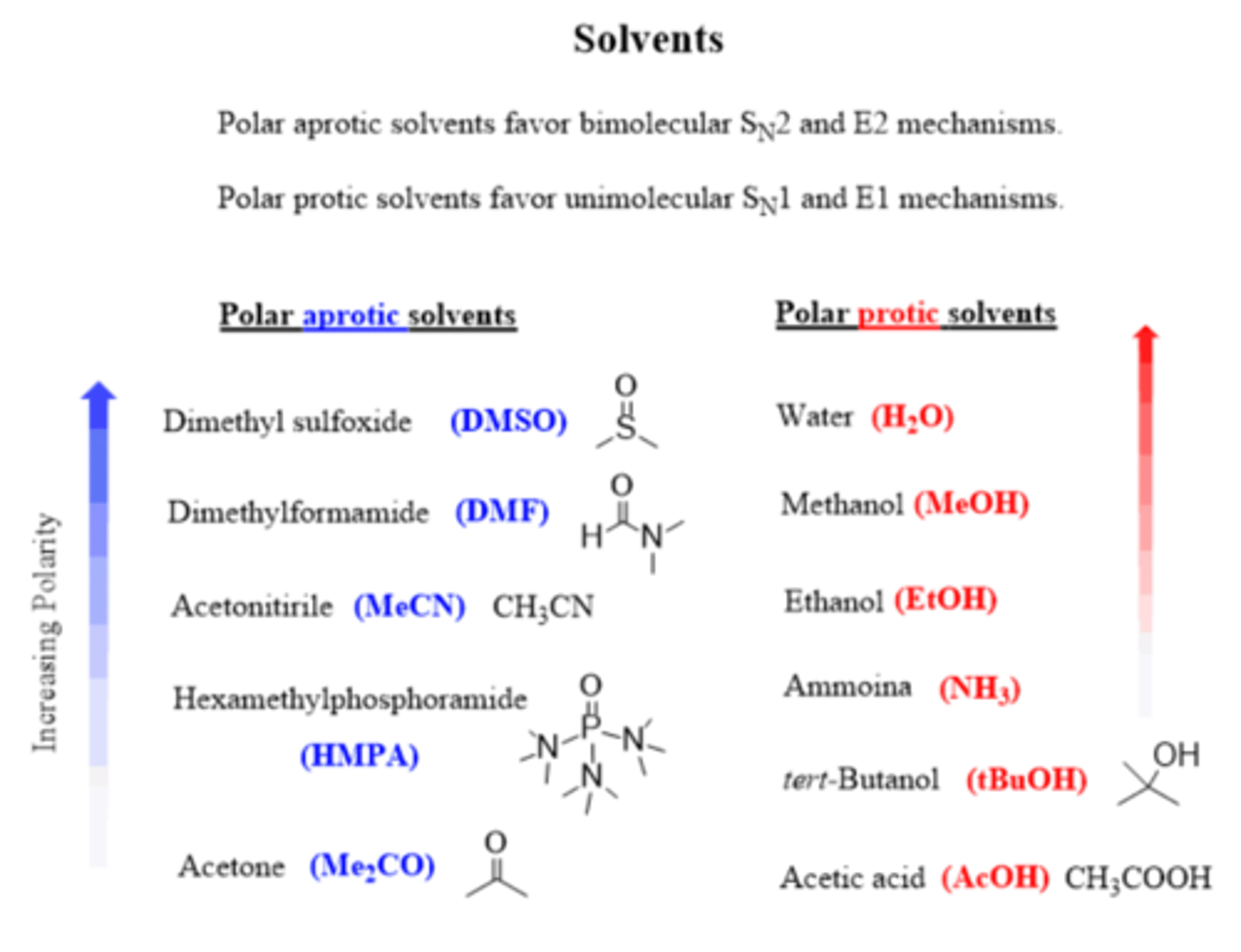
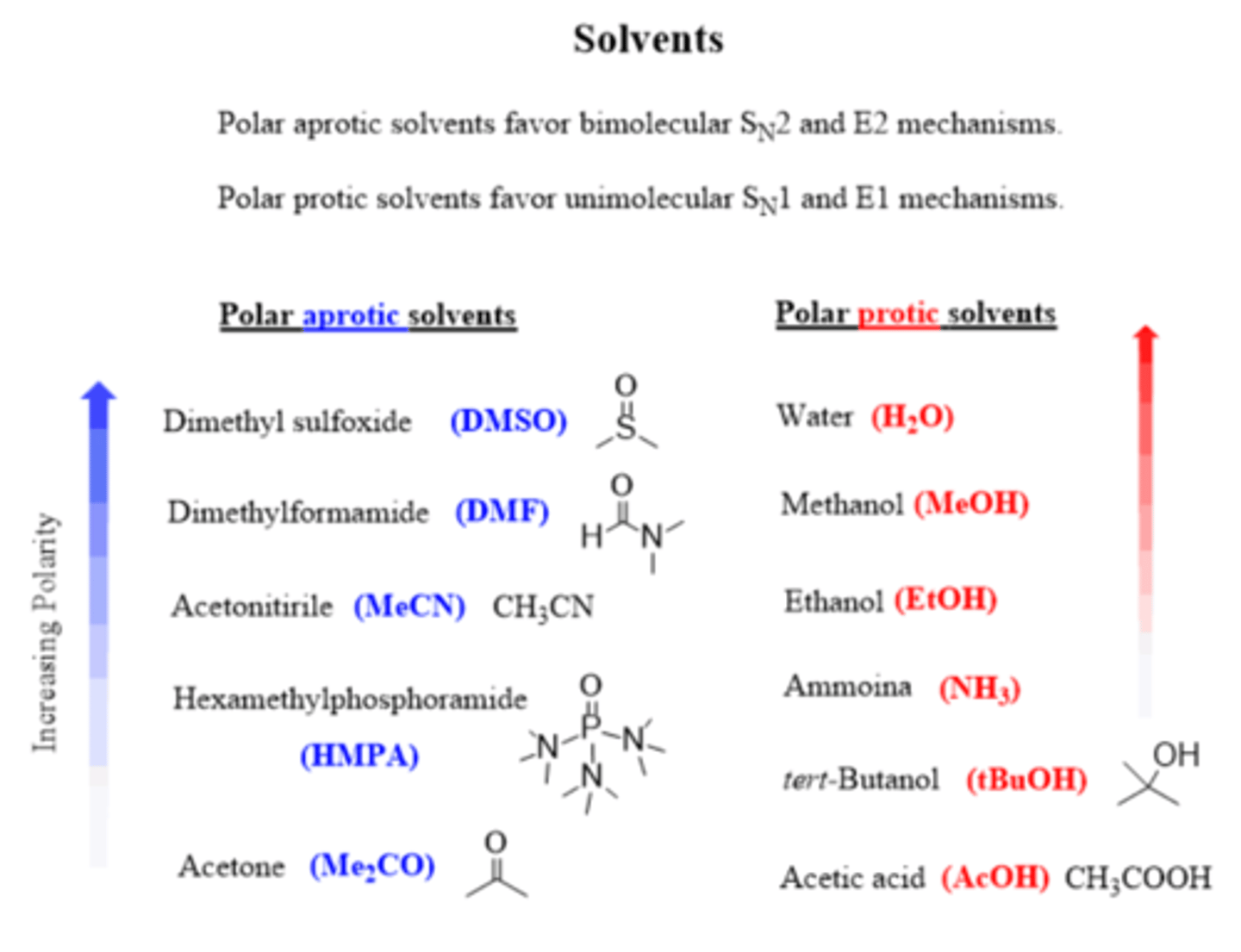
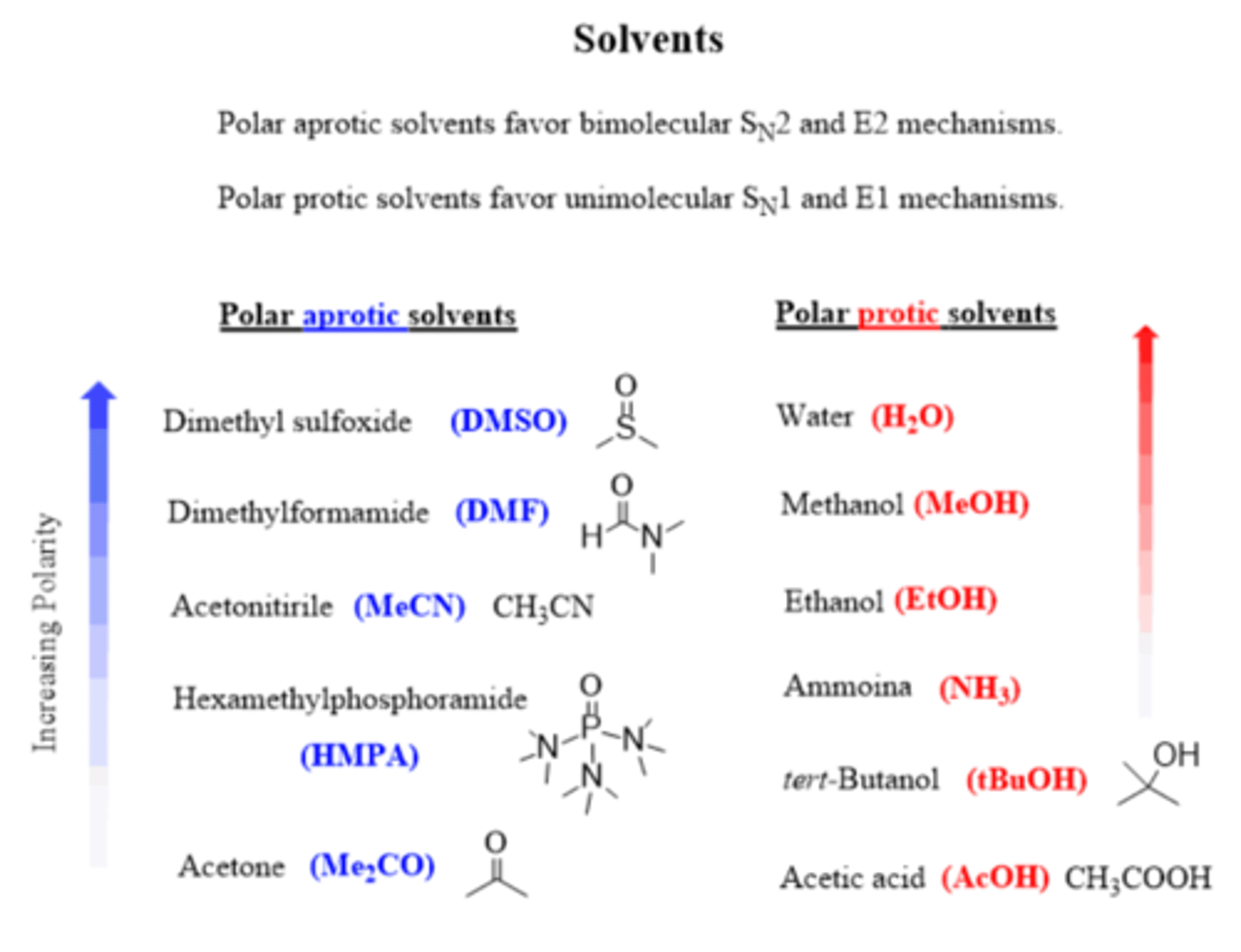
What kind of solvents work best in an Sn1 reaction?
Polar protic (H2O, alcohol ROH, Carboxylic acid RCOOH)
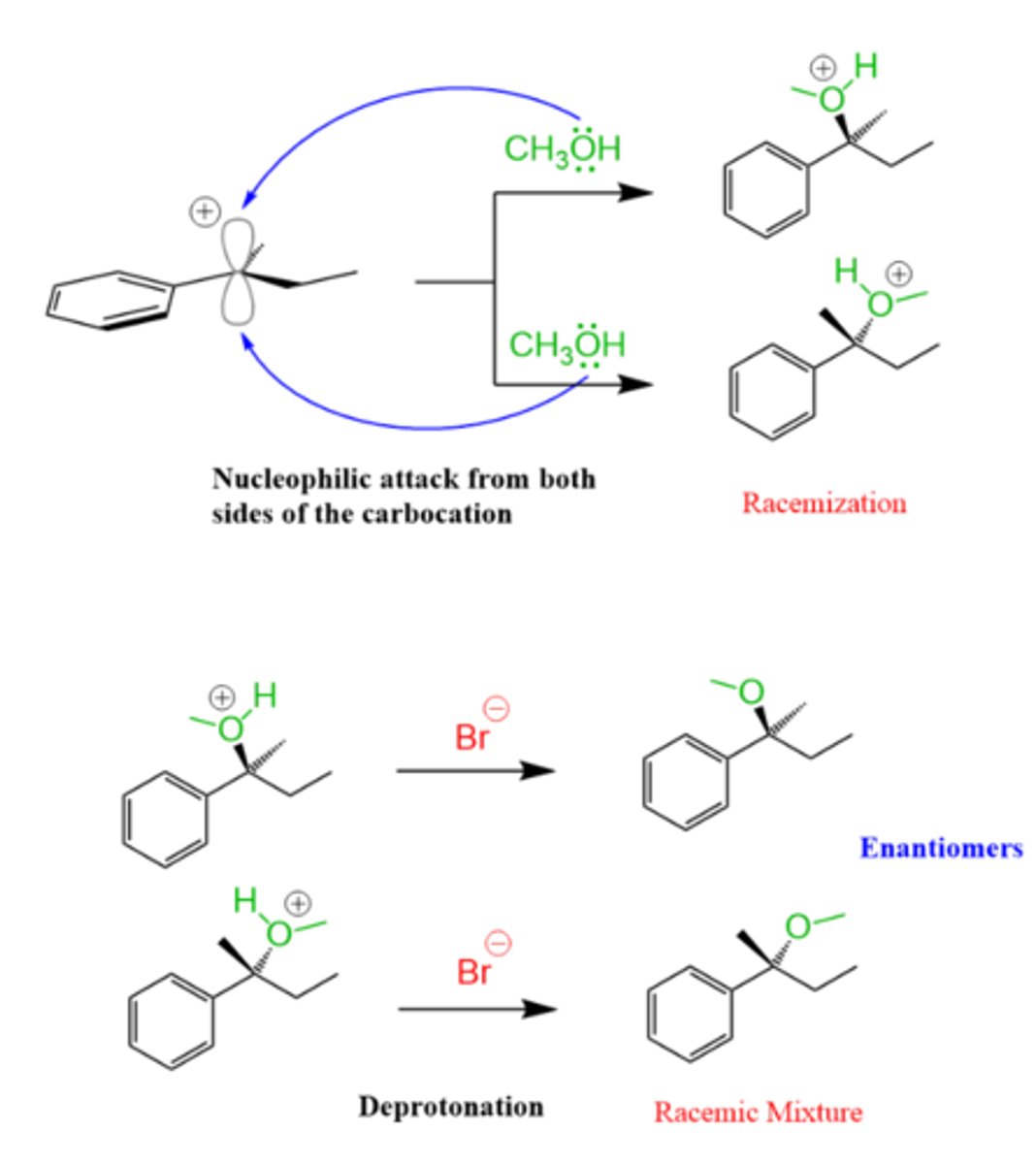
What is the end product of an Sn1 reaction?
Racemic mixture
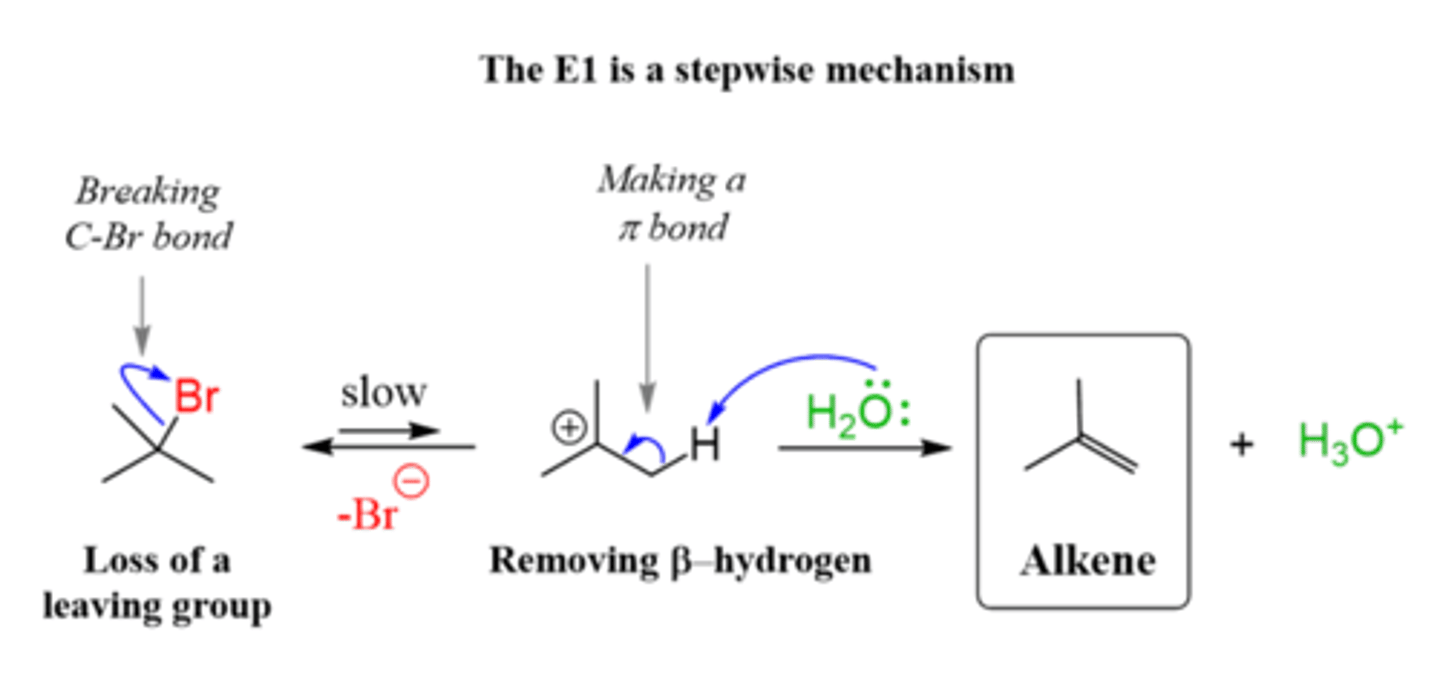
List the steps of an E1 reaction mechanism.
1. Leaving groups leaves creating a carbocation intermediate.
(alkyl or hydride shift)
2. Hydrogen on beta carbon is removed and a double bond is formed between the alpha and beta carbon
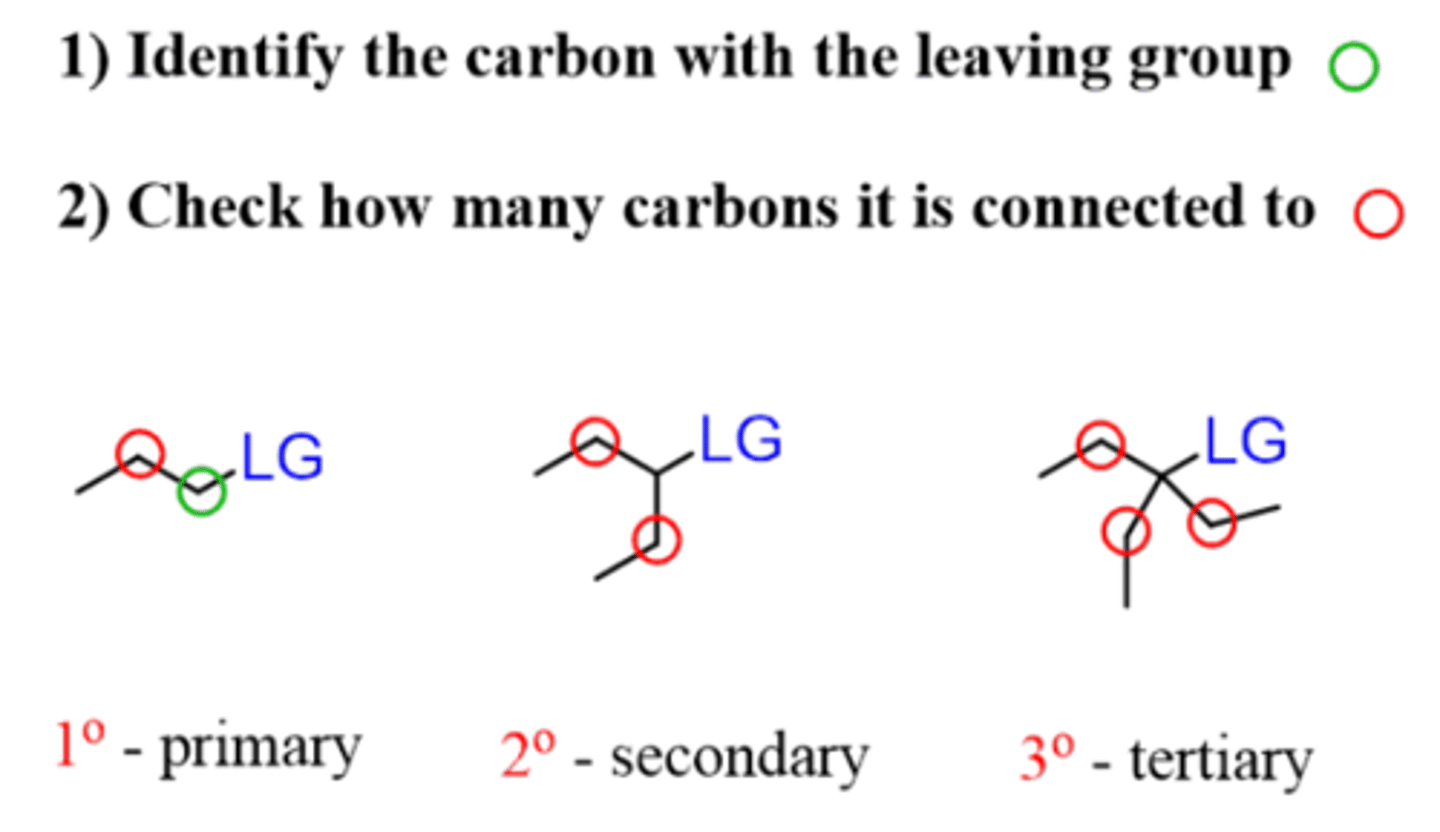
Which substrates work best for an E1 reaction?
Tertiary or secondary
What kind of solvents work best for an E1 reaction?
Polar protic (H2O, alcohol ROH, carboxyiic acid RCOOH)
What is then end product of an E1 reaction?
mainly trans but cis as well
If choosing between an E1 or Sn1 reaction for a substrate, what is the determining factor?
The temperature of the reaction, cold for Sn1 and hot for E1.
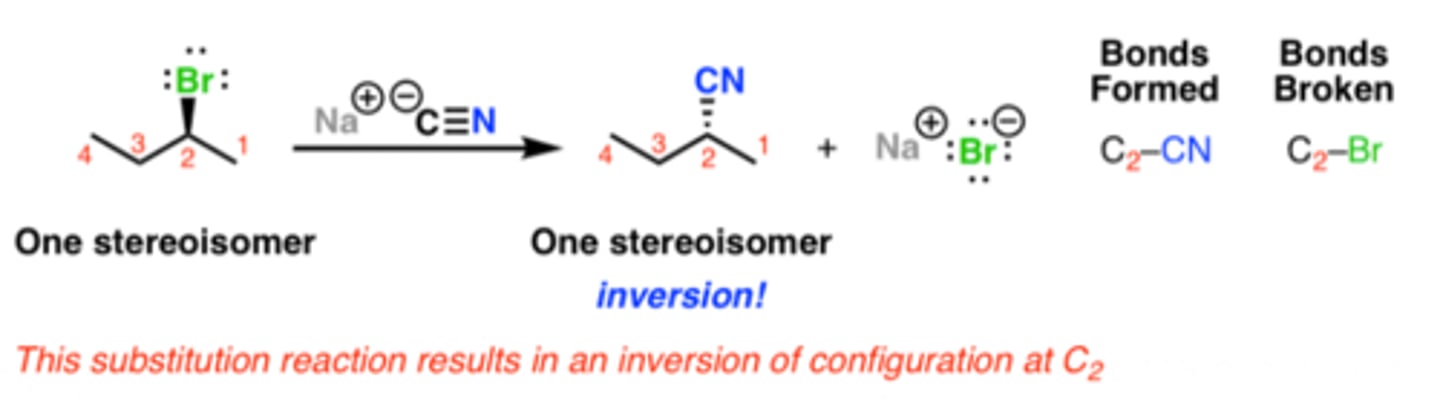
List the steps of an Sn2 reaction mechanism.
1. Leaving group leaves and nucleophile backside attack
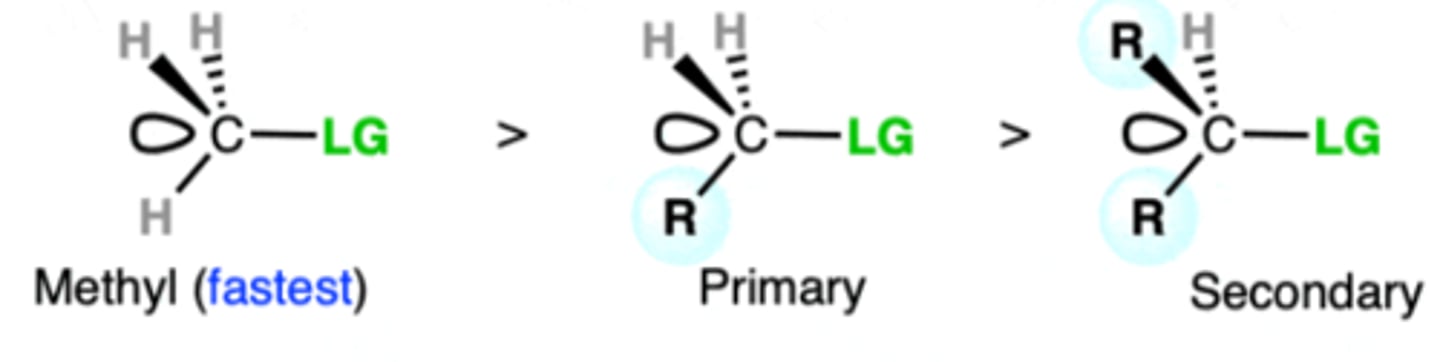
Which substrates work best for an Sn2 reaction?
Methyl (CH3), primary, and secondary (if using strong nucleophile (I-, CN-, OH-) and leaving group (Cl-, Br-, I-, OTs-)
What kind of solvents work best for an Sn2 reaction?
Polar aprotic (DMSO, DMF, HMPA, acetone)
What is the end product for an Sn2 reaction?
Inversion
List the steps of an E2 reaction mechanism.
1. Leaving group leaves, hydrogen on beta carbon removed and double bond formed between alpha and beta carbon.
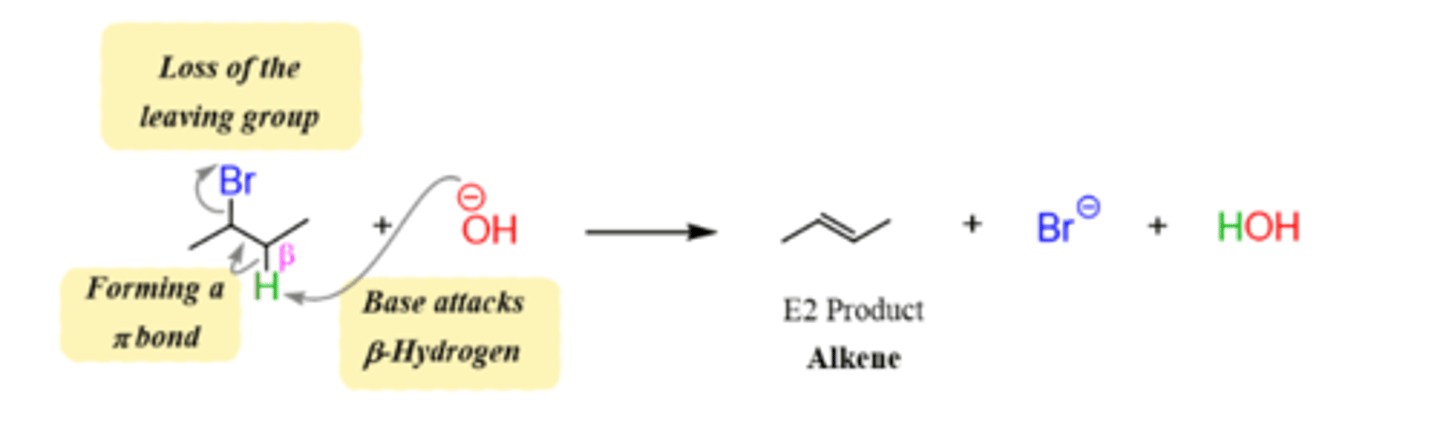
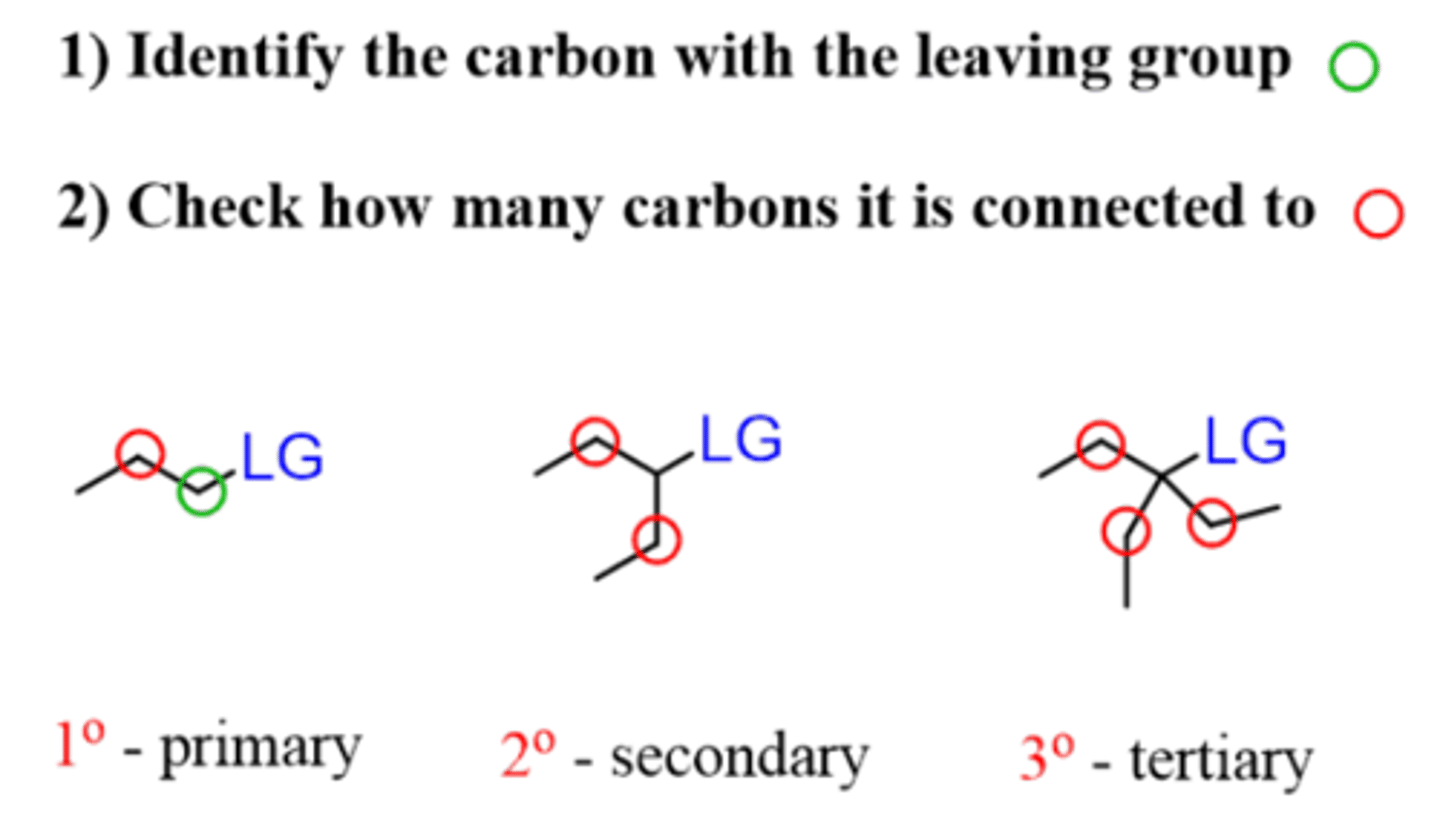
Which substrates work best for an E2 reaction?
Primary, secondary, and tertiary
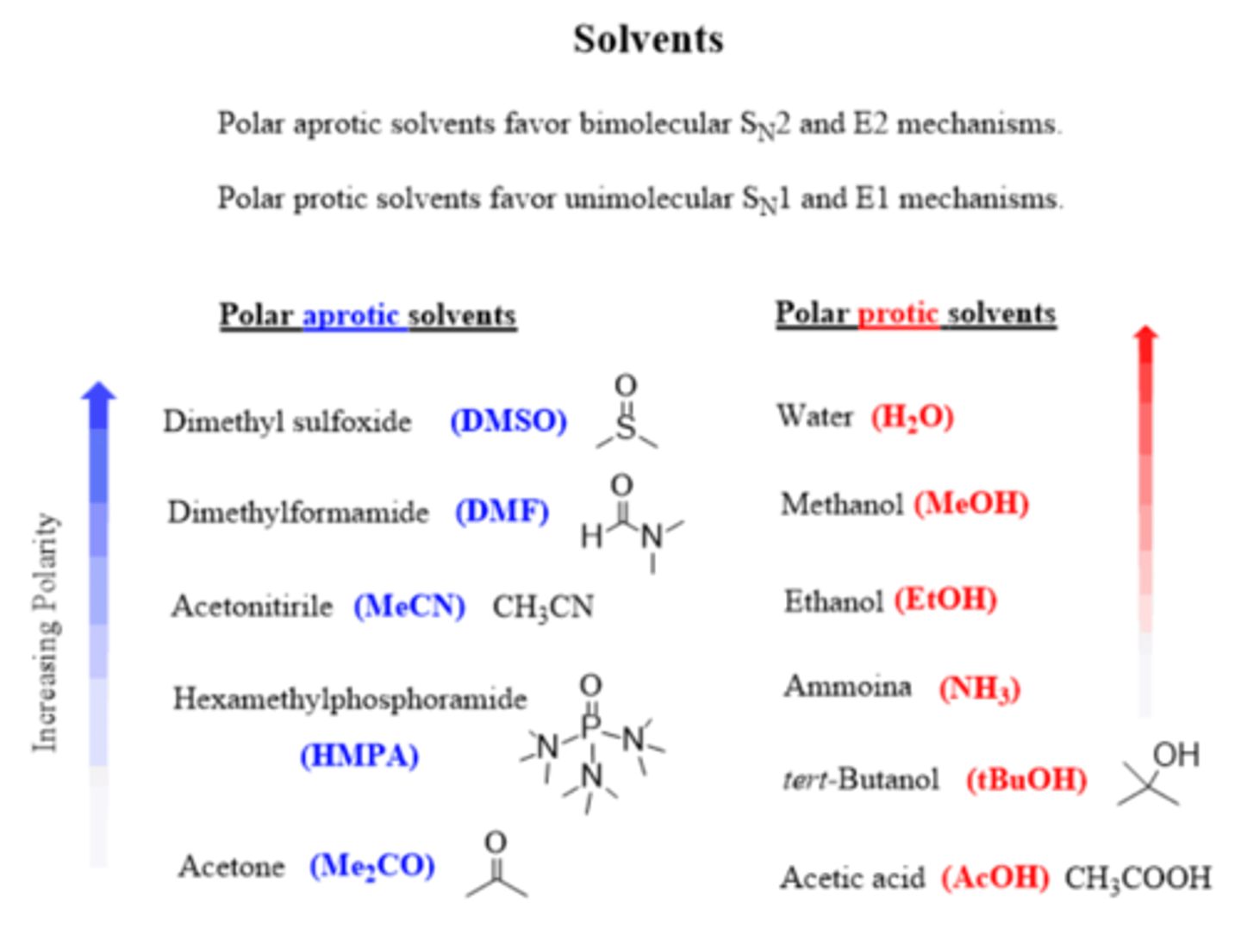
What solvents work best for an E2 reaction?
Polar aprotic ( DMSO, DMF, HMPA, acetone)
What is the end product of an E2 reaction?
Trans major, cis formed as well
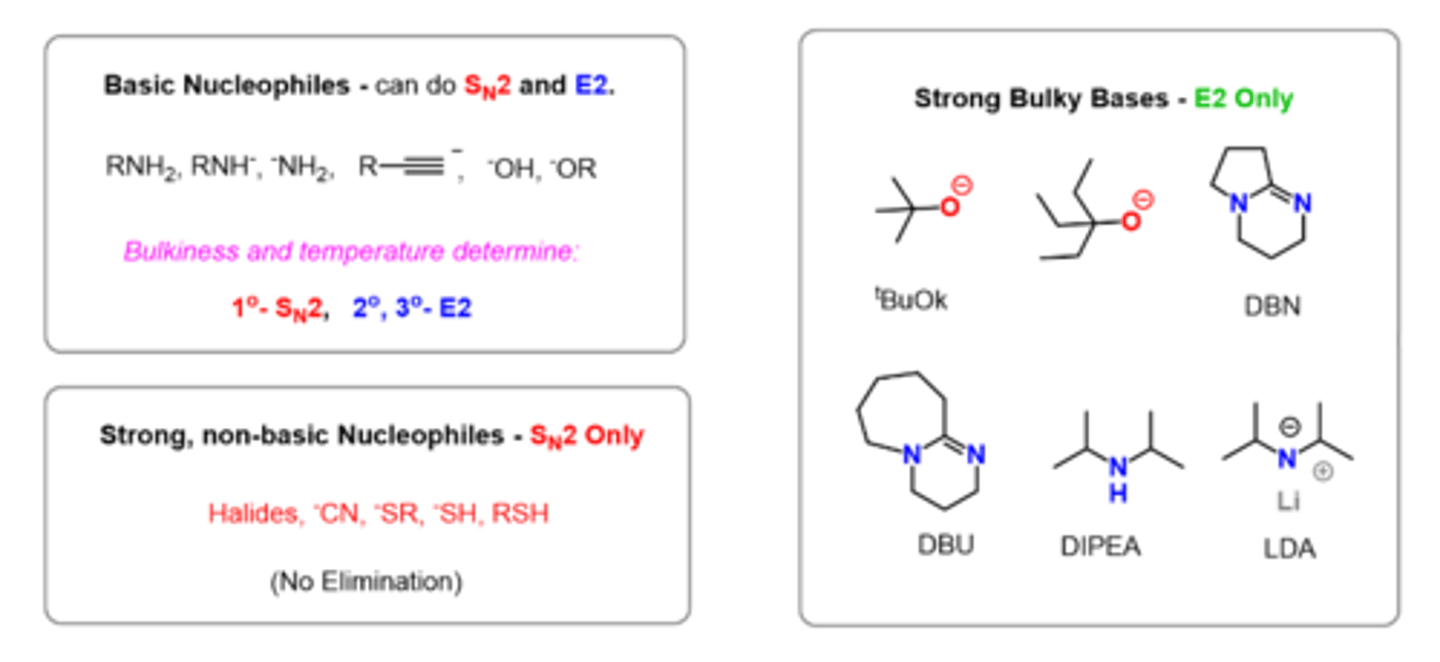
Strong nucleophiles and weak bases produce?
Sn2
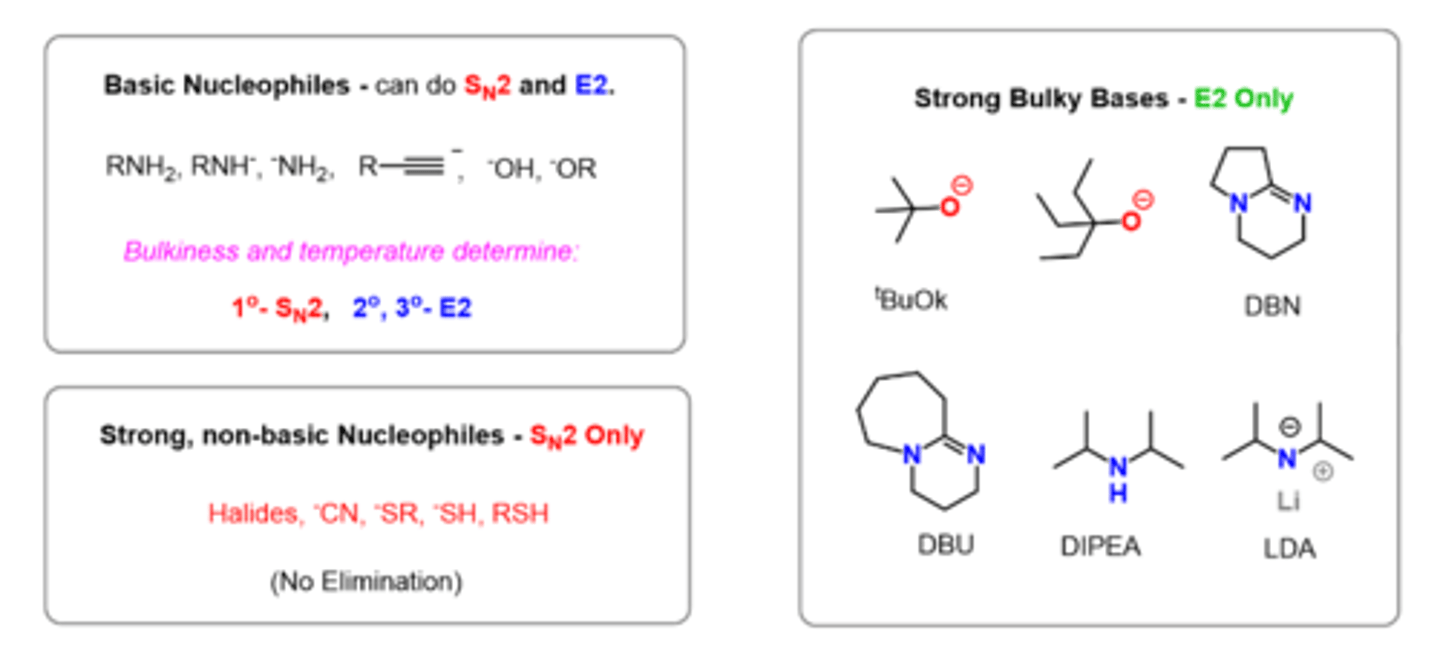
Weak nucleophiles and strong bases produce?
E2
References
1. The E2 Reaction Mechanism. Chemistry Steps. Published September 9, 2017. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/the-e2-mechanism/
2. E1 Reaction Mechanism and E1 Practice Problems. Chemistry Steps. Published September 9, 2017. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/the-e1-mechanism/
3. The SN1 Reaction Mechanism and SN1 Practice Problems. Chemistry Steps. Published November 19, 2019. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/the-sn1-nucleophilic-substitution-reaction/
4. The Role of Solvent in SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 Reactions. Chemistry Steps. Published September 9, 2017. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/sn1-sn2-e1-e2-effect-of-solvent/
5. When Is the Mechanism SN1 or SN2? Chemistry Steps. Published September 9, 2017. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/when-is-the-mechanism-sn1-or-sn2/
6. Ashenhurst J. The SN2 Reaction Mechanism - Master Organic Chemistry. Master Organic Chemistry. Published July 4, 2012. https://www.masterorganicchemistry.com/2012/07/04/the-sn2-mechanism/
7. Gevorg DS. SN2 vs E2. Chemistry Steps. Published July 26, 2025. Accessed November 23, 2025. https://www.chemistrysteps.com/sn2-vs-e2/