your mom definitions unfinished
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
:(
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Chemical reaction
A reaction that involves the creation of new substances
Conservation of mass
The scientific law that mass cannot be created or destroyed
Reactant
A substance that starts a chemical reaction
Product
A substance formed in a chemical reaction
Word equation
A representation of a chemical reaction using words
Physical change
A change in physical properties of a substance that doesn’t alter its chemical composition
Chemical change
A change that alters the chemical composition of a substance, resulting in new substances
Equation
A representation of a chemical reaction
Electrolysis
A decomposition reaction using electricity
Endothermic
A reaction that absorbs energy in the form of heat
Exothermic
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat
Alkali
A base that is dissolved in water
Caustic
Able to burn or corrode through organic matter through chemical action
Concentration
The amount of a substance in a volume of solution
Corrosive
Highly reactive and destructive to another substance
Neutralise
To make something chemically neutral
pH
A measure expressing the acidity or alkalinity of a solution
Indicator
A substance that changes hue based on how basic or acidic a substance is
Carbonate
A substance containing the elements carbon and hydrogen
Neutralisation reaction
A reaction involving an acid and a base to produce water and a salt
Strong acid
An acid that ionises completely in water
Weak acid
An acid that partially ionises in water
Ionises
The removal of electrons from ions or atoms
Metal carbonate
A compound containing metal, carbon and oxygen
Antacids
Calcium carbonates that release carbon dioxide by burping to neutralise stomach acid
Combustion
A reaction that involves burning in the presence of oxygen to release heat
Hydrocarbon
A compound made up of only hydrogen and carbon
Oxidation
A reaction taking place in the presence of oxygen
Soot
A black form of carbon formed by incomplete combustion
Transform
To change from one form to another
Complete combustion
A combustion reaction that occurs with adequate oxygen present
Incomplete combustion
A combustion reaction that occurs with inadequate oxygen present
Respiration
The chemical reaction occurs in cells to release energy
Alloy
A mixture of two or more metals
Degrade
To wear down a substance
Dissociate
To split apart into ions
Insoluble
Unable to be dissolved
Ionic compound
A compound made up of metal and non-metal ions
Precipitate
An insoluble product
Compound
A substance made up of two or more elements chemically bonded together
Mixture
Two or more substances that are not chemically bonded and can be separated
Element
A pure substance
Passivating metal
A chemical treatment for metal that enhances its ability to resist corrosion
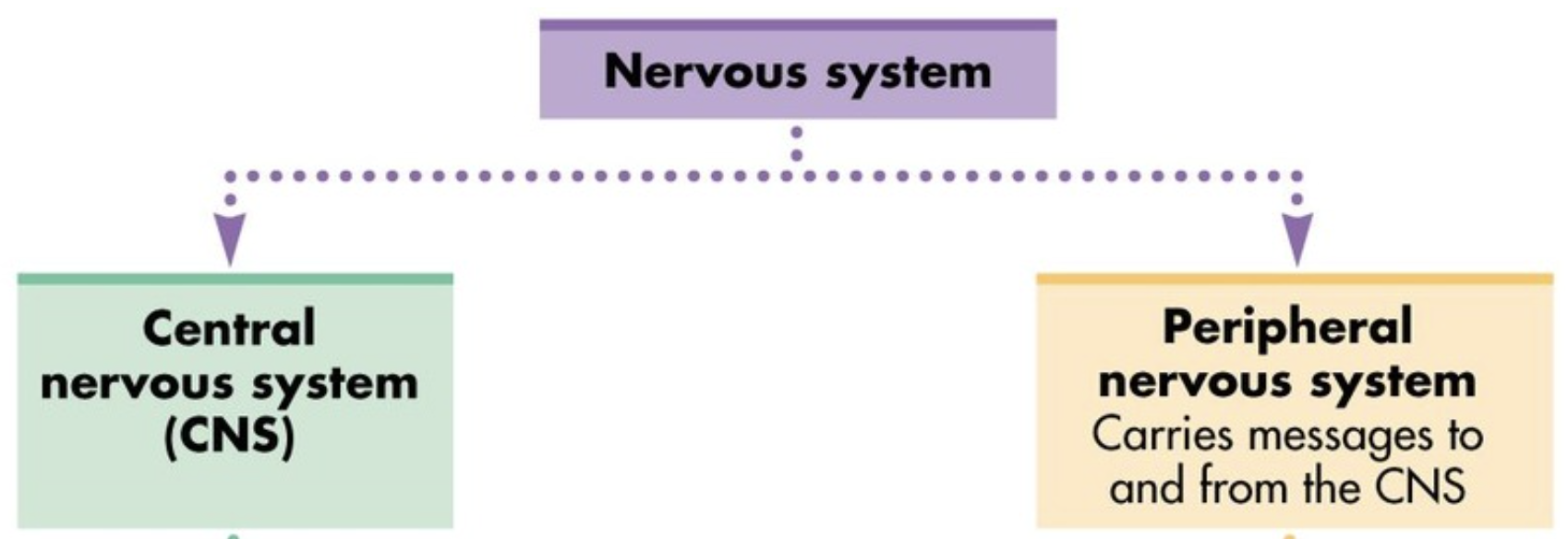
The nervous system:
A network of cells and fibres that transmit fast messages within the body
Central nervous system
A network consisting of the brain and spinal cord that controls the body’s activities and functions
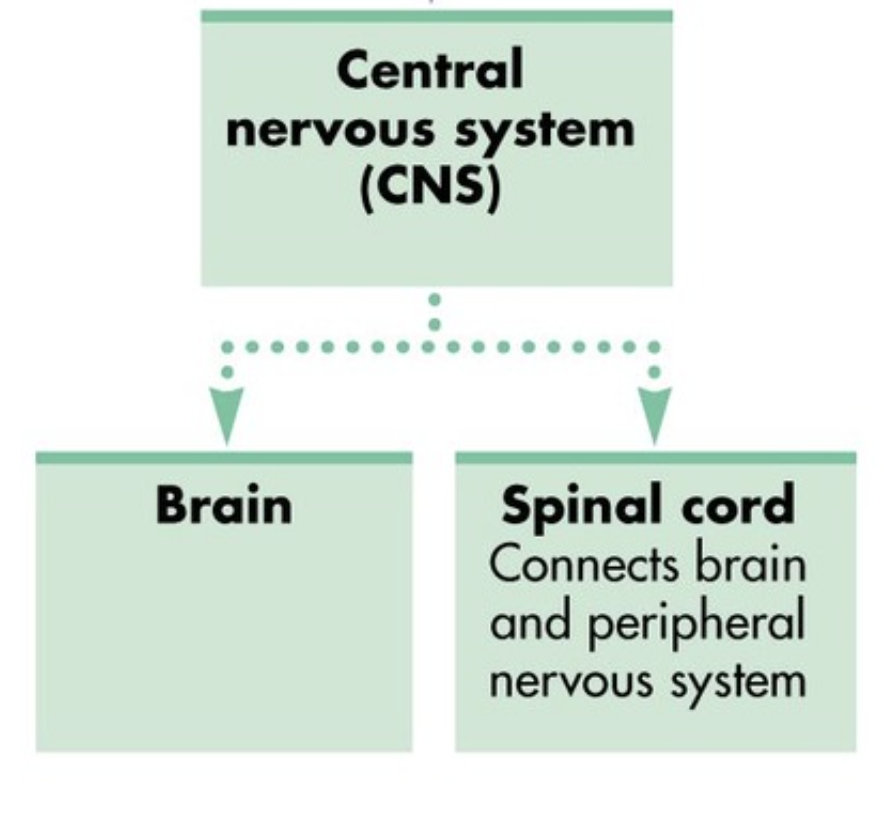
Spinal cord
Connects the brain and peripheral nervous system
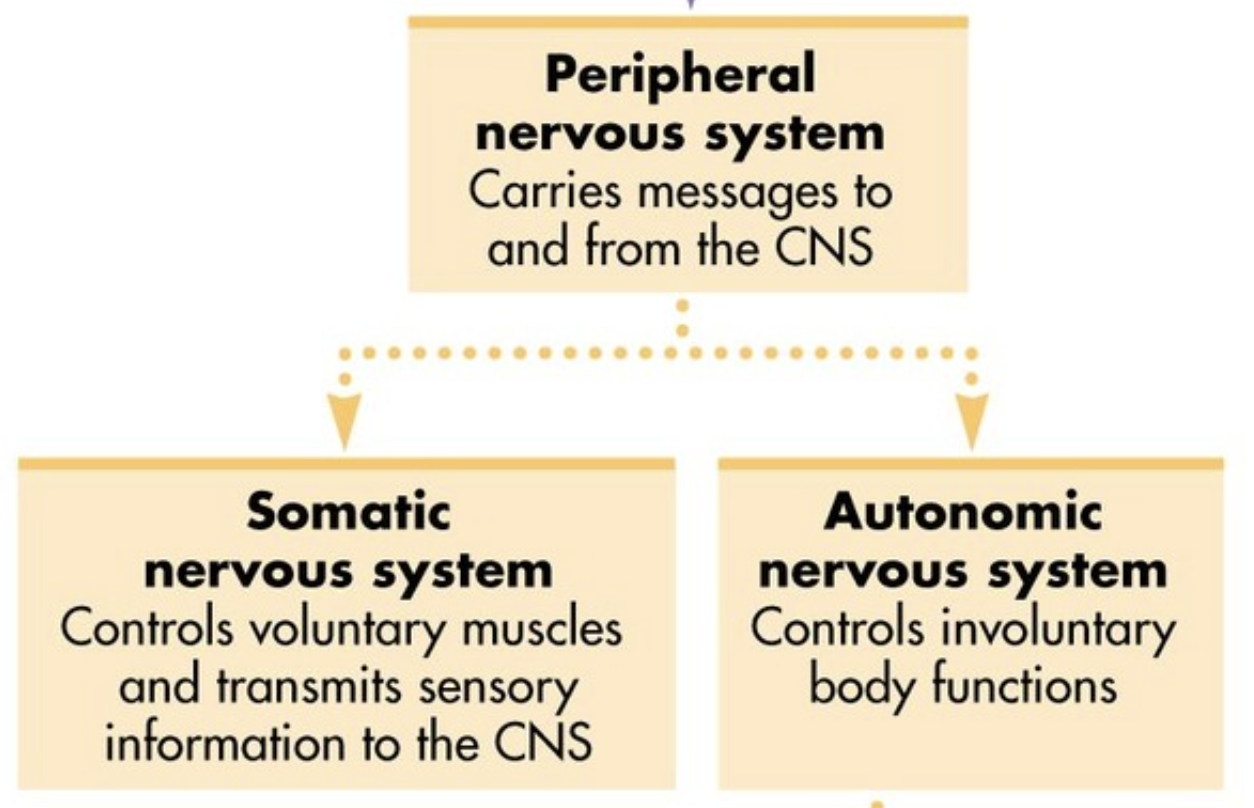
Peripheral nervous system
Carries messages to and from the CNS
Somatic nervous system
Controls voluntary muscles and transmits sensory information to the CNS - Voluntary
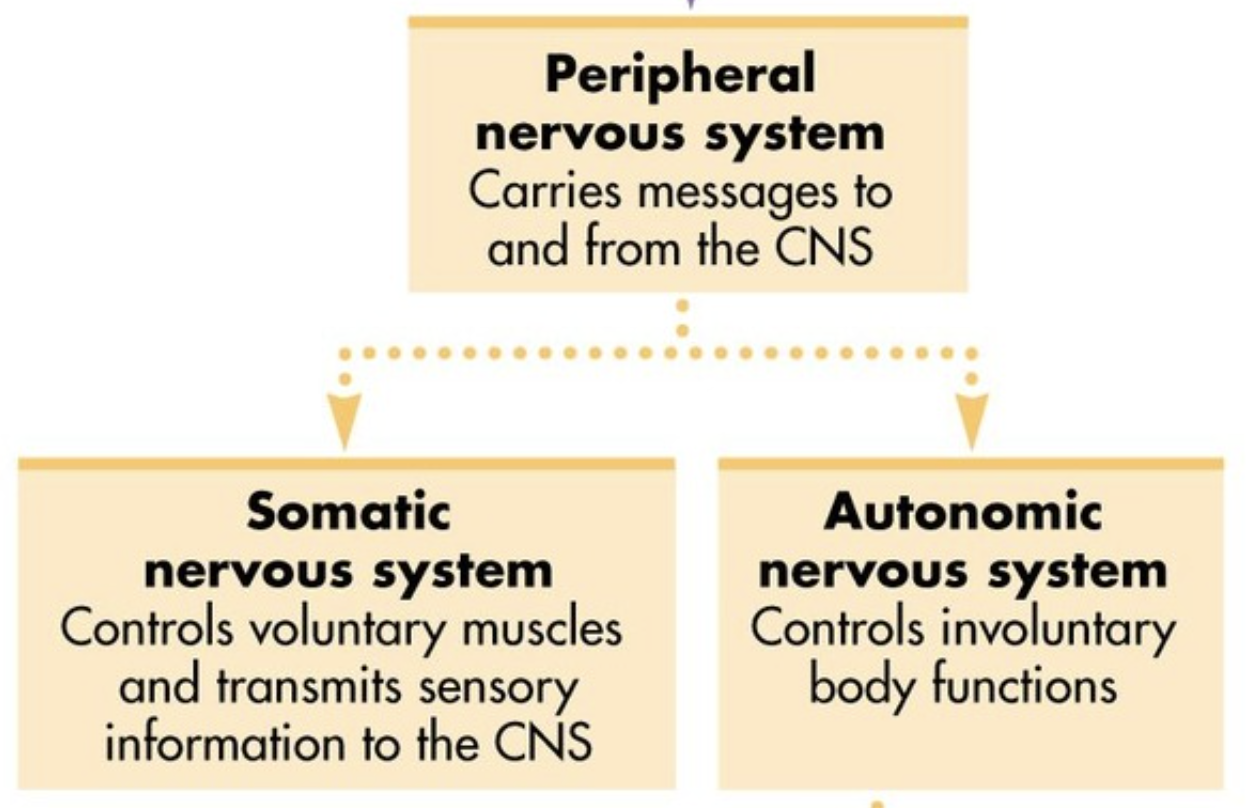
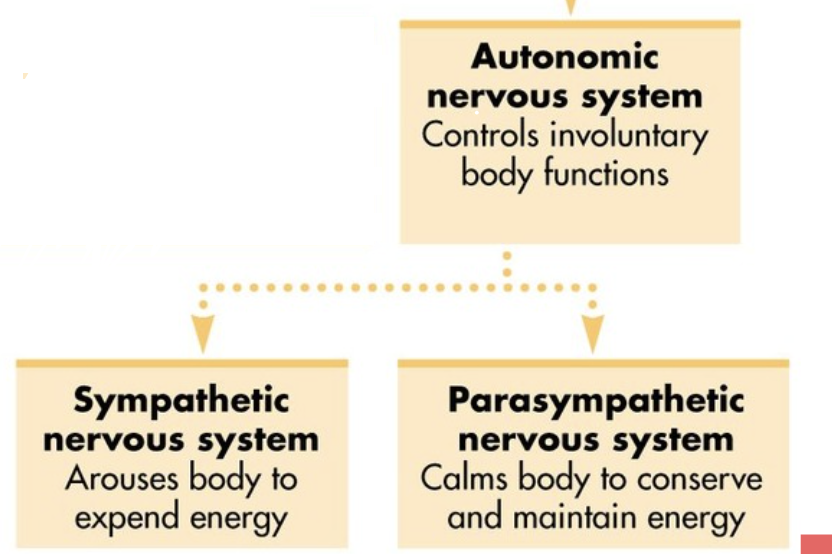
Autonomic nervous system
Controls involuntary bodily functions - Involuntary
Sympathetic nervous system
Prepares the body for stressful situations through arousal - Fight or flight
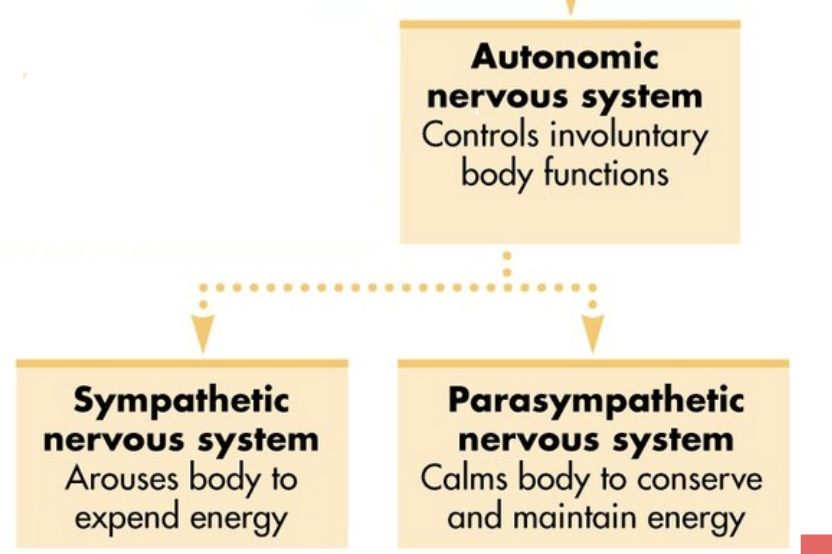
Parasympathetic nervous system
Relaxes the body after stressful situations - Rest and digest
Axon terminals
1 - The end of the axon that releases neurotransmitters
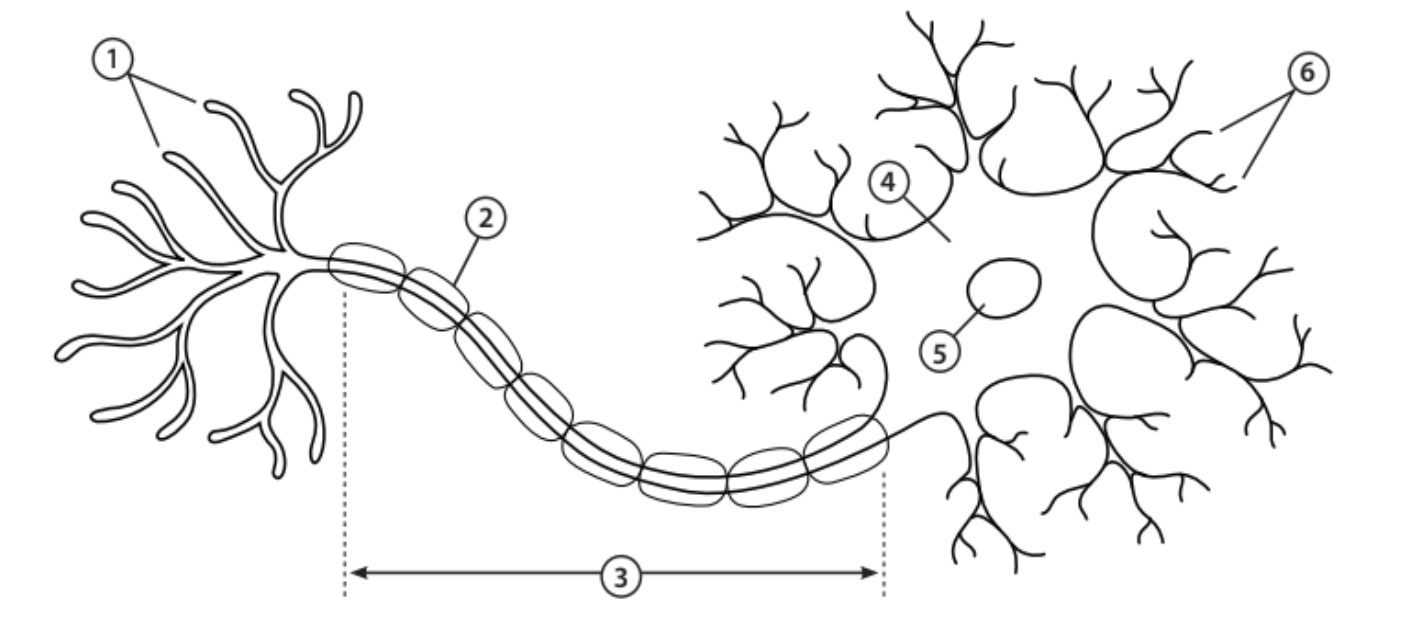
Myelin sheath
2 - Covers the axon and works as insulation to keep electrical signals within the cell
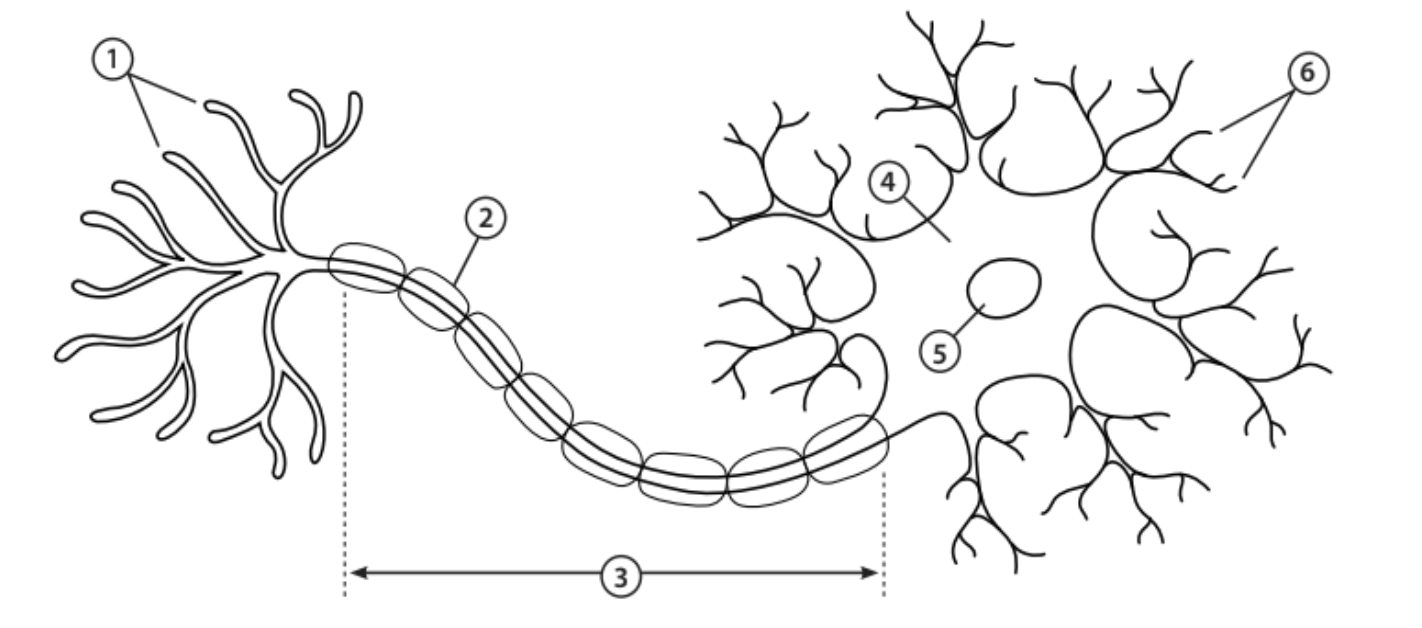
Axon
3 - A nerve fibre that transfers electrical impulses signals from the cell body to the next neuron
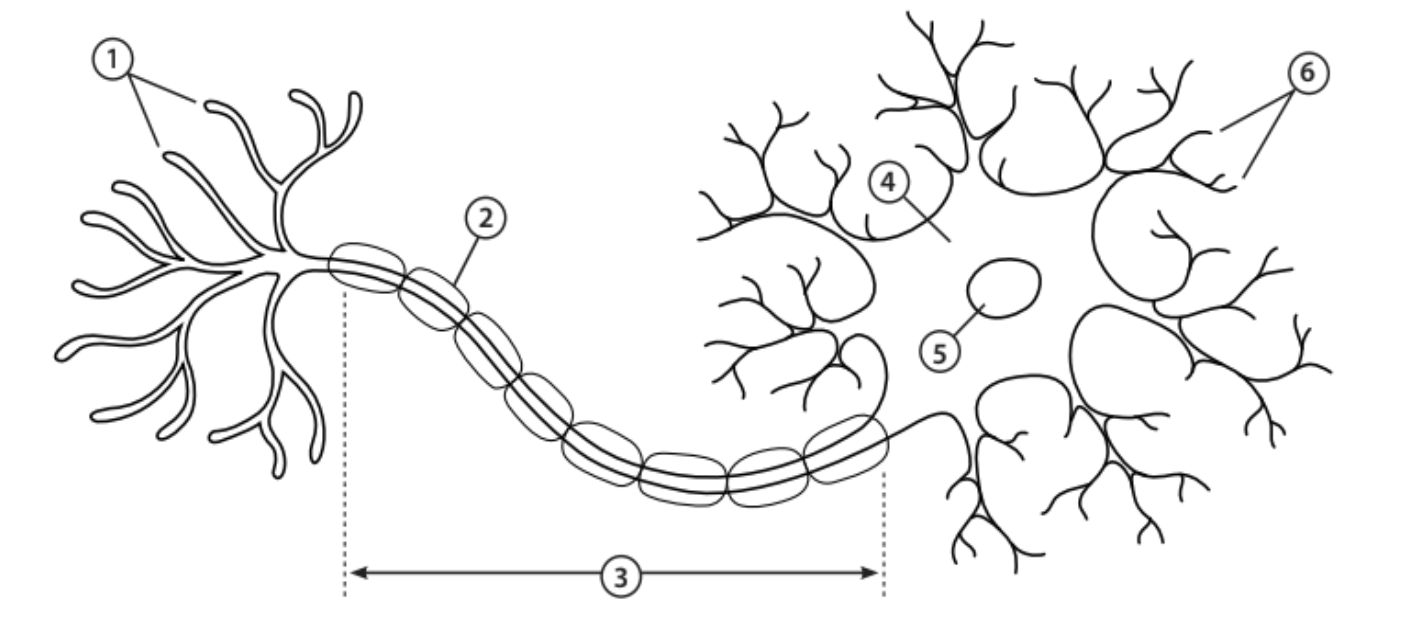
Cell body
4 - Contains most of the cells organelles
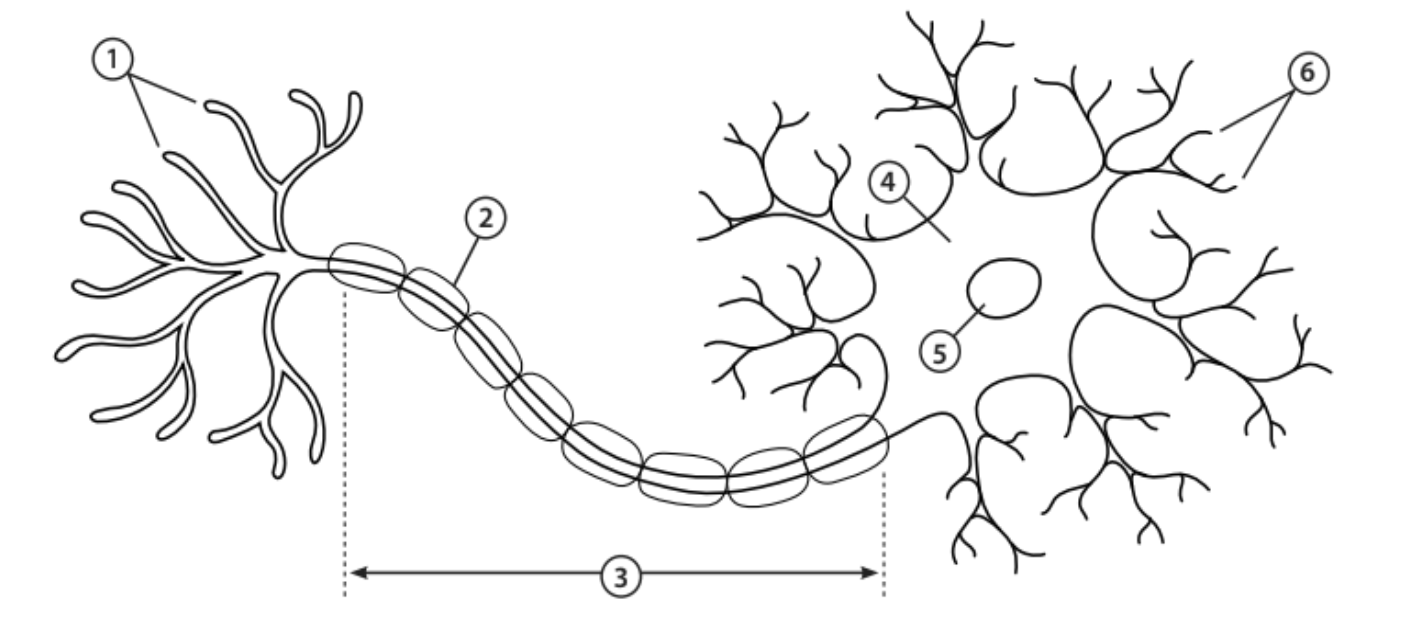
Nucleus
5 - An organelle that contains the cell’s DNA
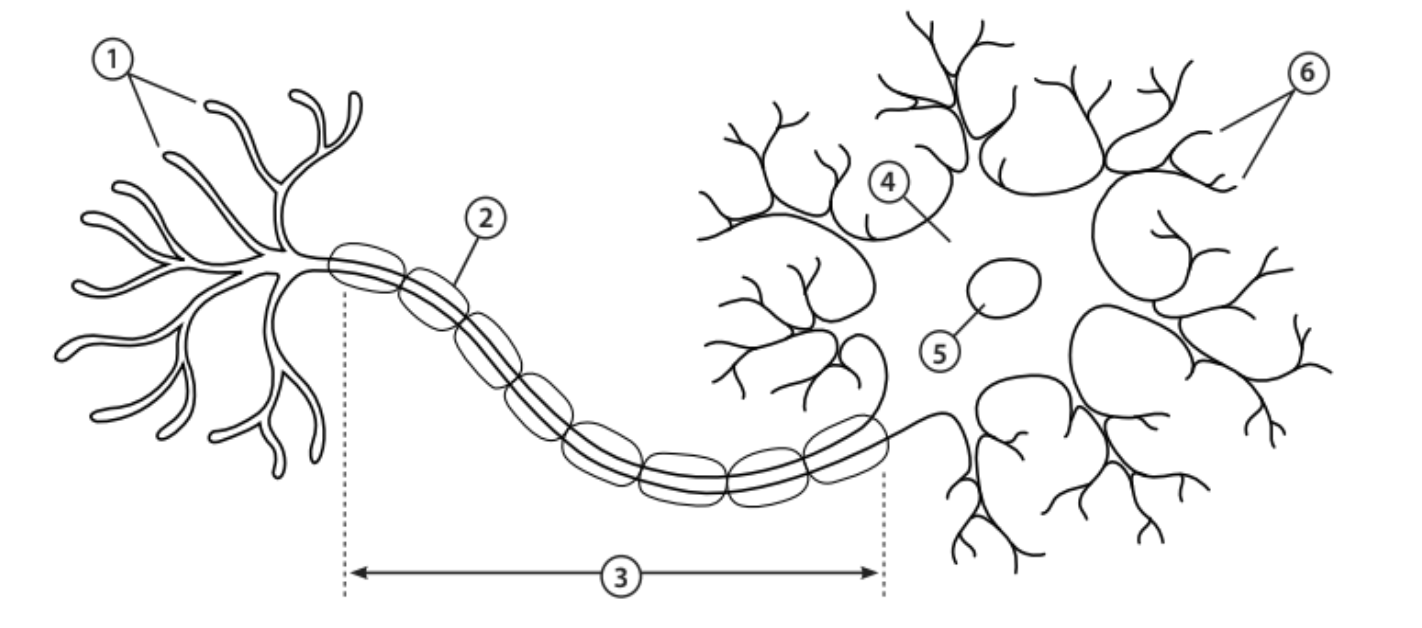
Dendrites
6 - Tree-like structures that receive electrical impulses from neighbouring neurons
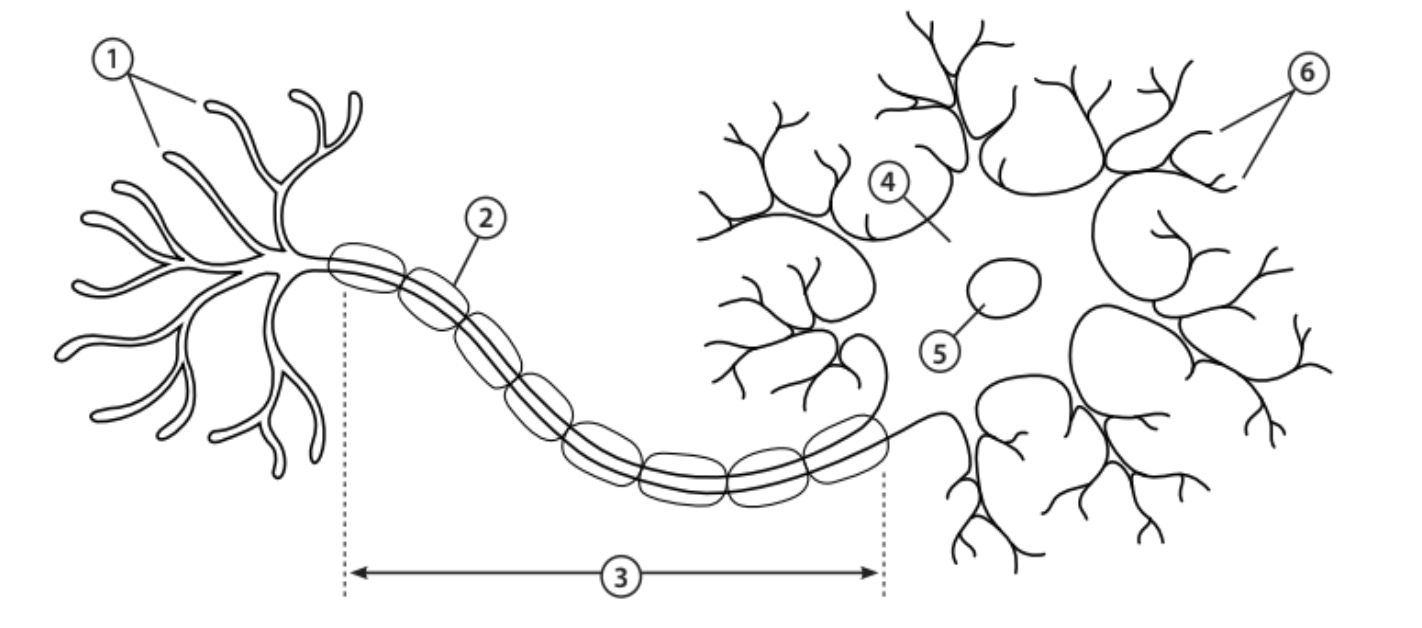
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that trigger an electrical response in the neighbouring neuron
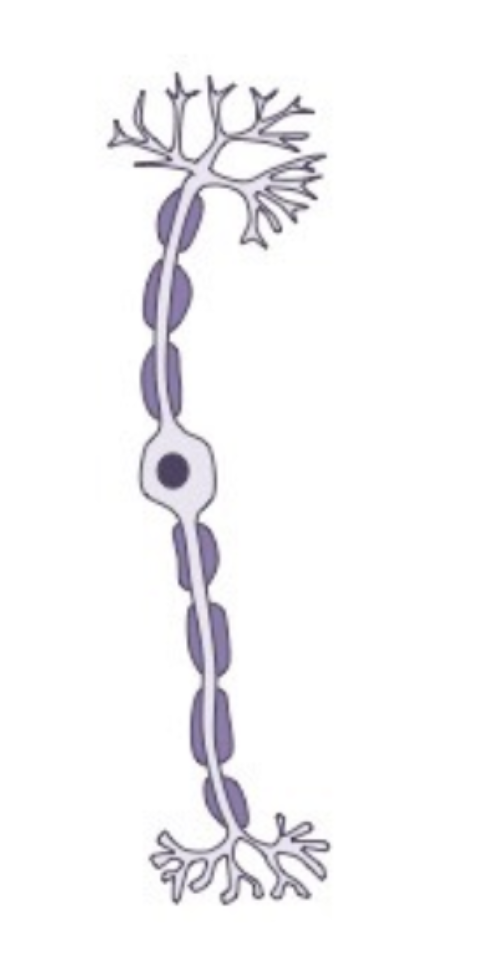
Sensory neuron
A nerve cell that carries sensory information to the central nervous system
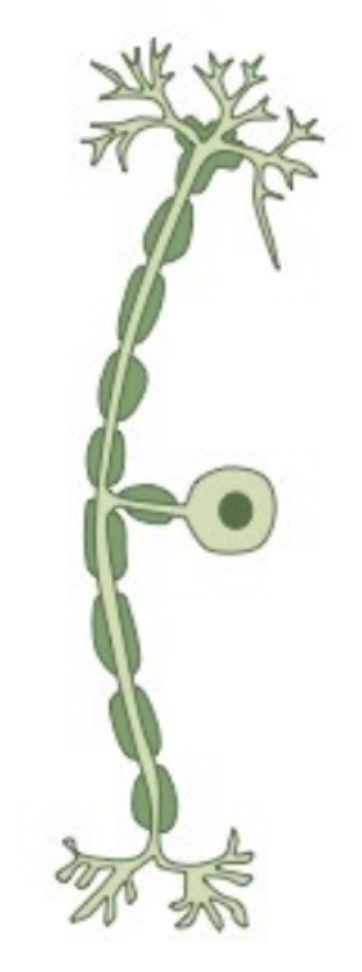
Motor neuron
A nerve cell that carries signals from the CNS to the muscles to trigger voluntary movements
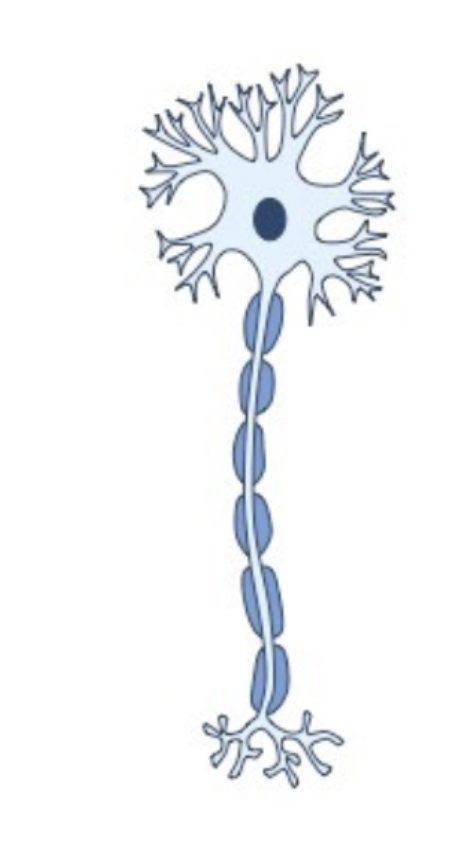
Interneuron
A nerve cell that connects other neurons with the CNS to process information between them
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
Cerebral cortex
The outermost layer of the brain
Cerebral hemispheres
The division of the left and right hemispheres
Longitudinal fissure
The groove that separates the hemispheres
Corpus callosum
The band of nerve tissue that connect the left and right hemispheres
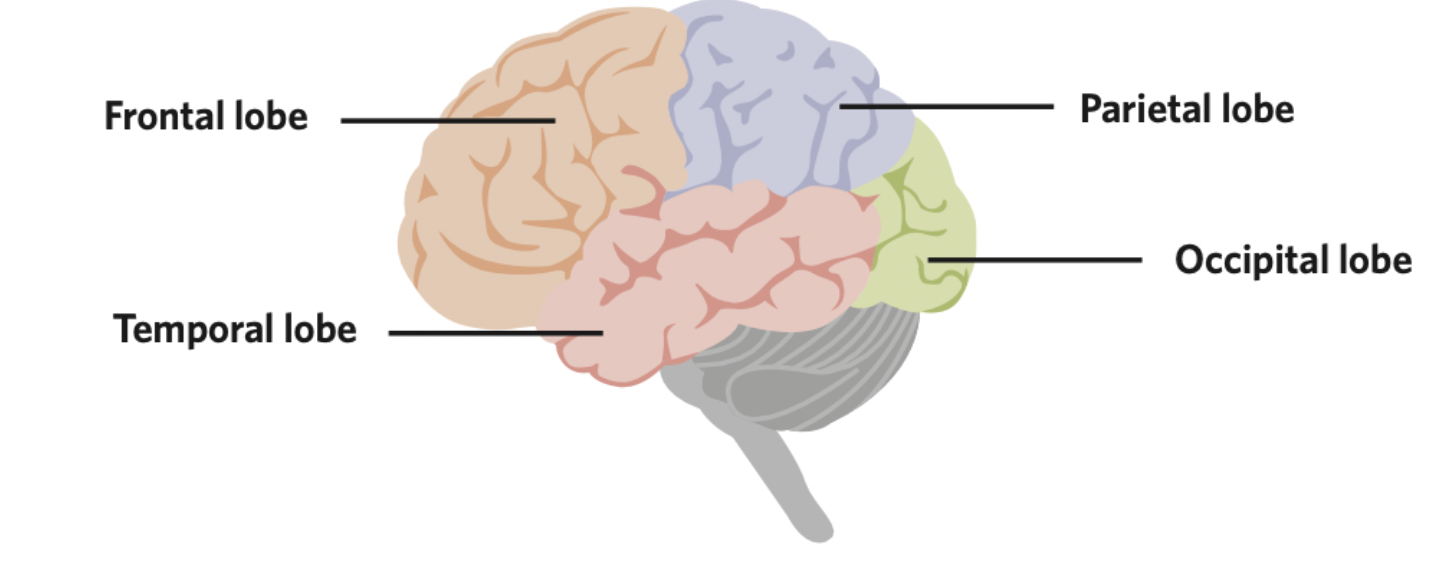
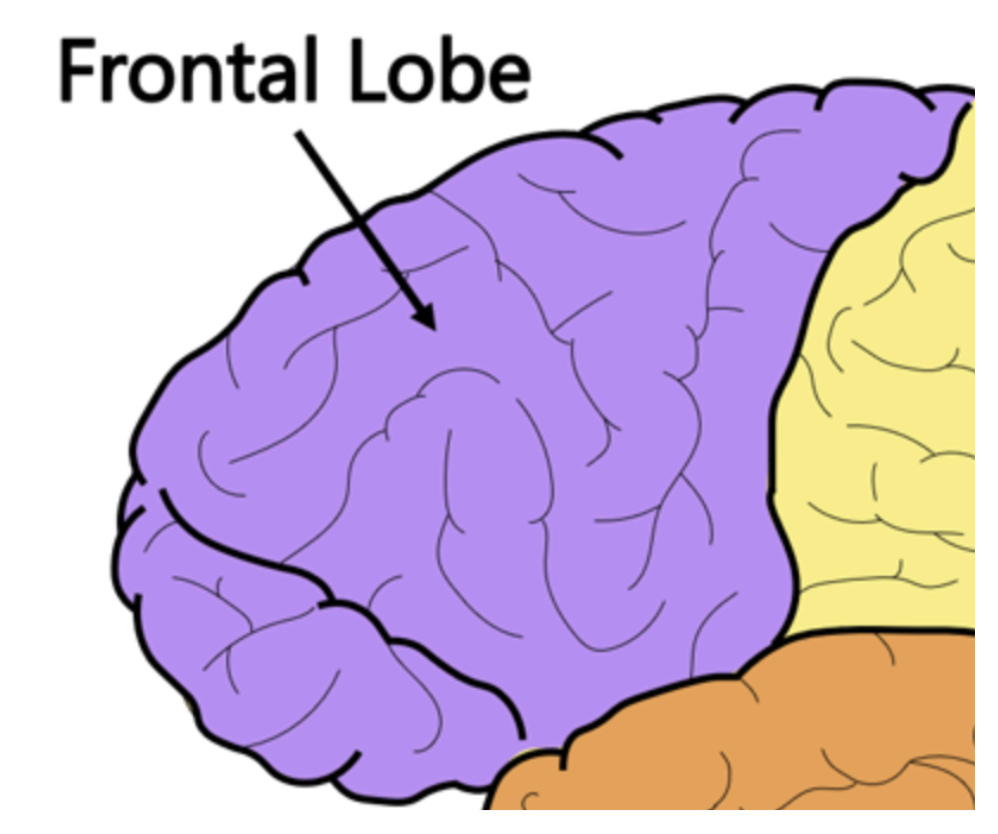
Frontal lobe
The largest lobe in the cortex responsible for problem solving, judging, personality, emotions and organizing
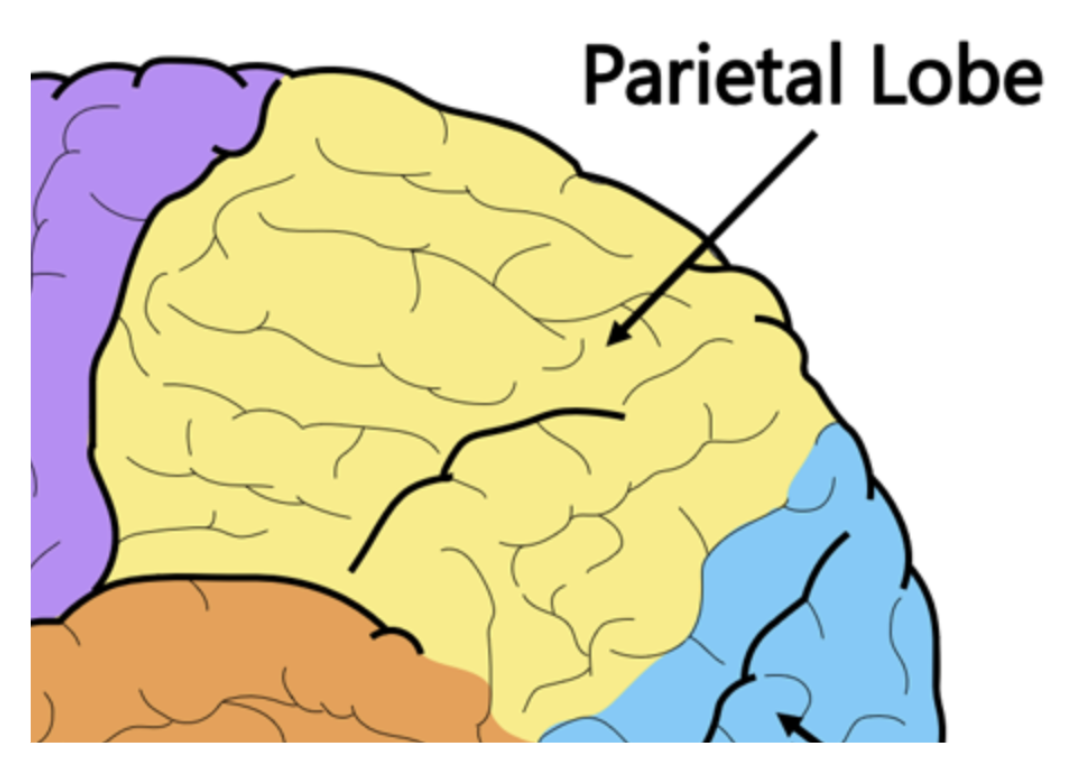
Parietal lobe
The lobe that receives sensory information from the body and skin to perceive sensory sensations
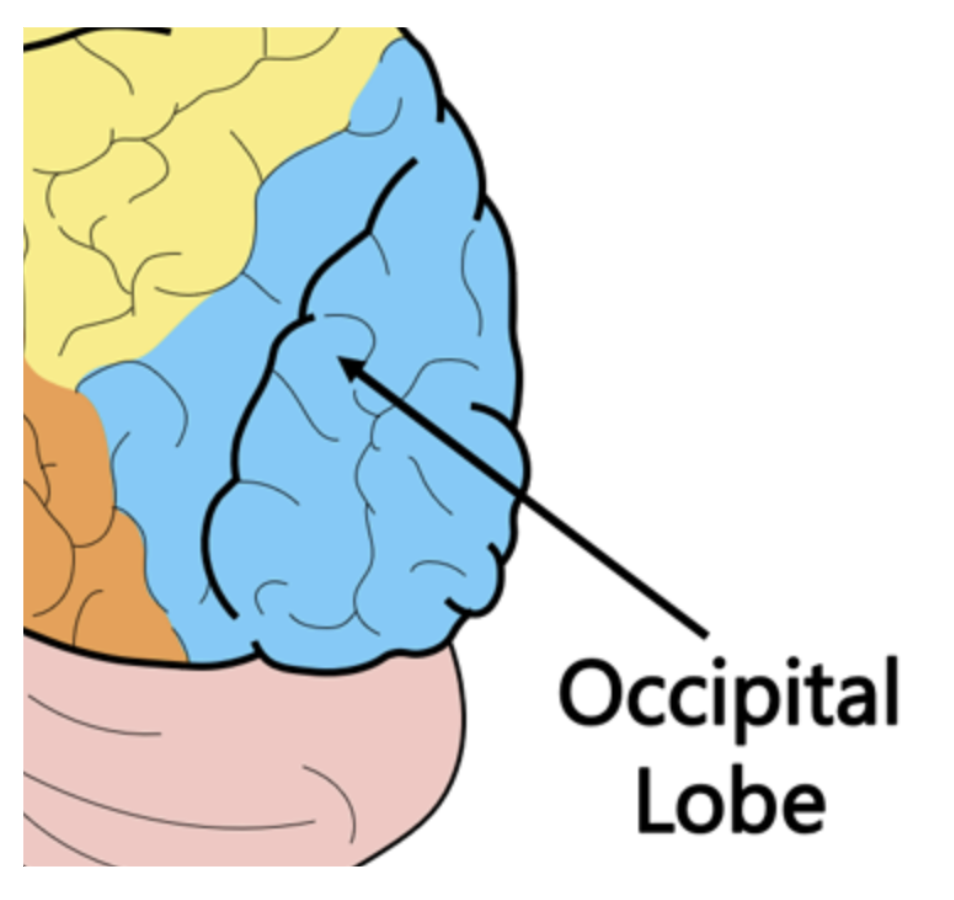
Occipital lobe
The lobe that interprets visual information from outside the body
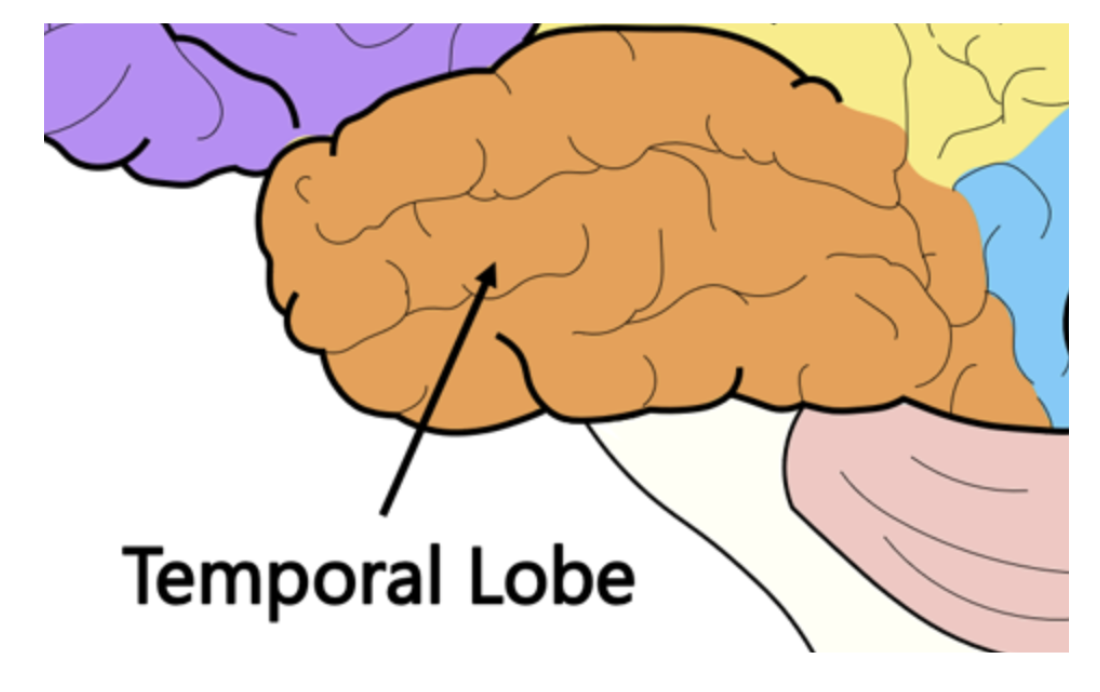
Temporal lobe
The lobe that processes auditory information
Hemispheric specialisation
The concept of the cerebral hemispheres having inverted functions
Cerebellum
Responsible for voluntary movements and motor skills like balance and posture
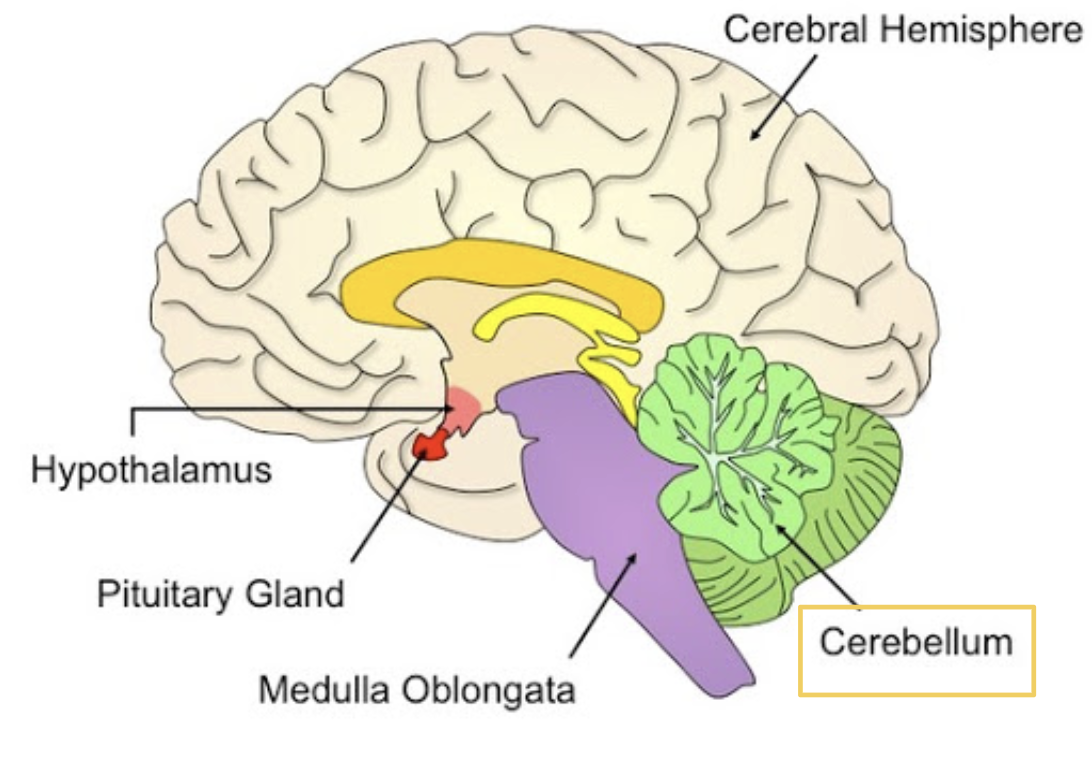
Brainstem
The part of the brain that connects the brain and spinal cord
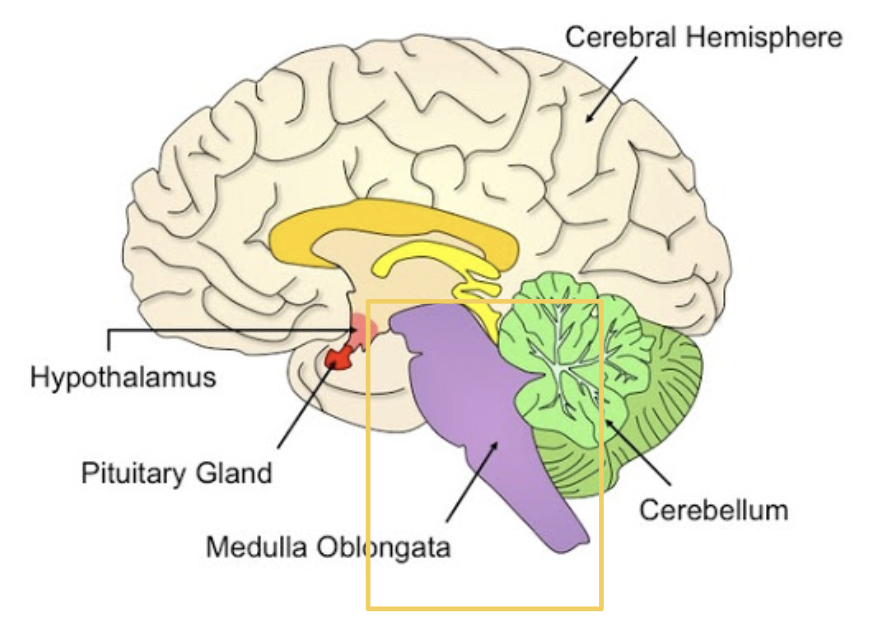
Medulla oblongata
Responsible for autonomic functions and regulates all vital organs
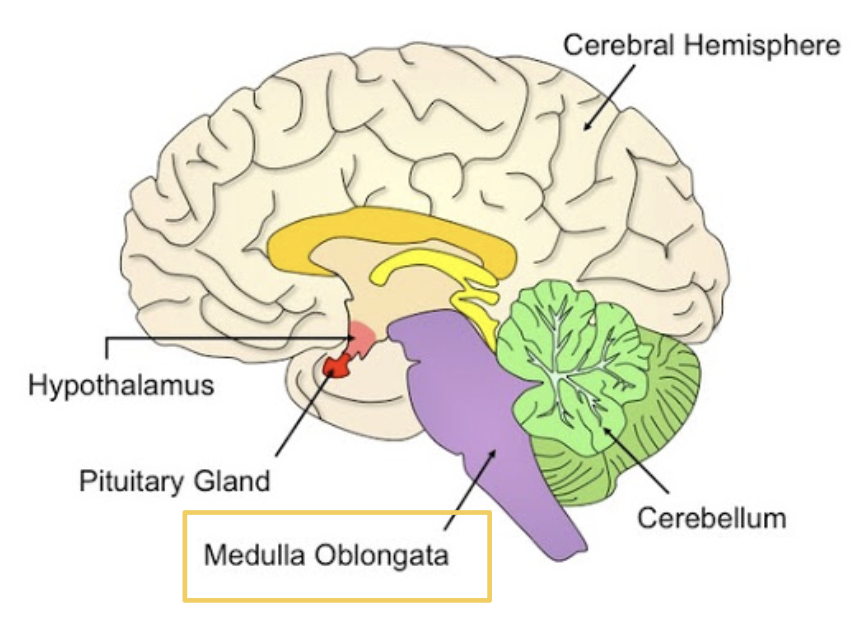
Hypothalamus
Responsible for controlling emotions and motivated behaviours and regulates homeostasis
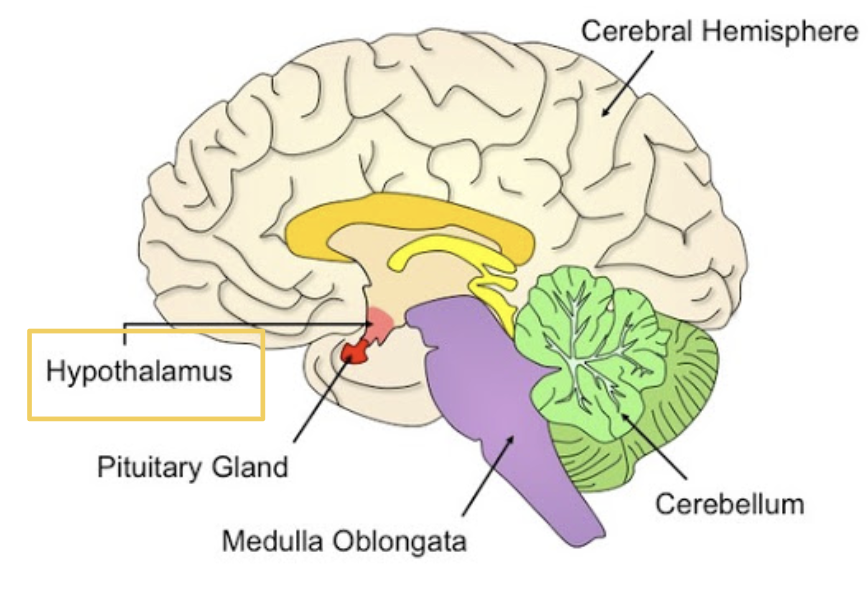
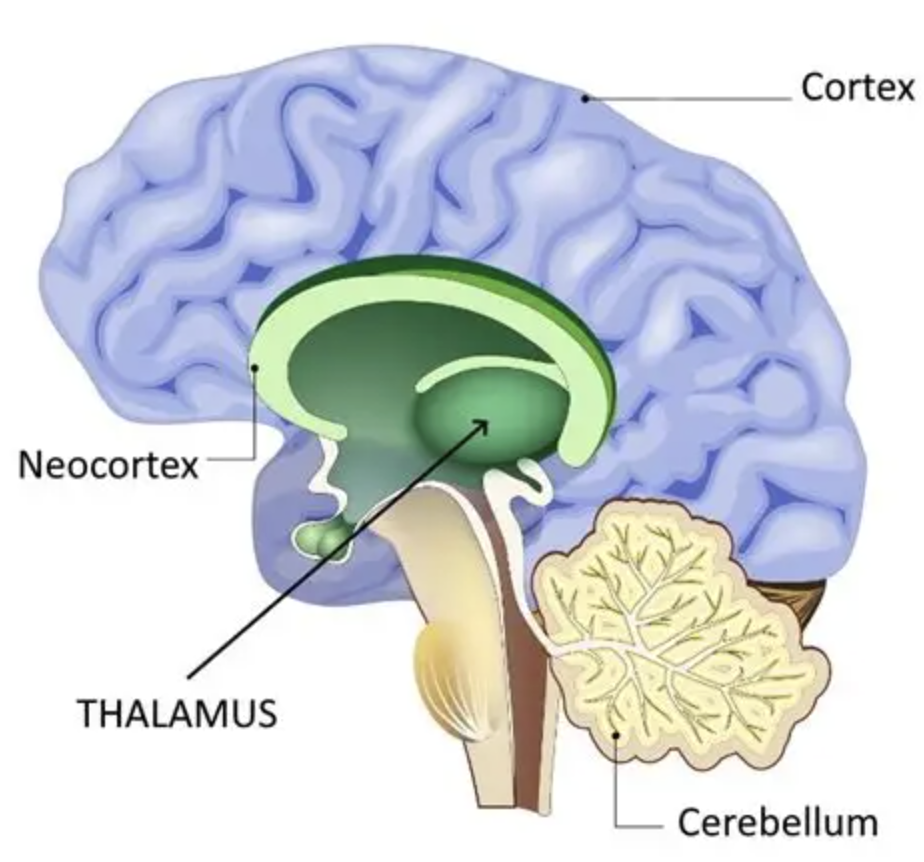
Thalamus
Filters information from all sensory receptor sites (except the nose) to send to the relevant area for processing
Sensory stimuli
Raw information detected from the five senses
Gland
A tissue in the body which secretes hormones
Hormone
A chemical molecule that triggers cellular response
Homeostasis
The regulation of the body’s internal environment
Negative feedback
A type of regulation that responds to a change in conditions by initiating responses that will counteract the change to maintain a stable state
Positive feedback
A type of regulation that amplifies or enhances the initial changet to achieve a specific outcome
Synapse
The space between two neurons where signals are transmitted
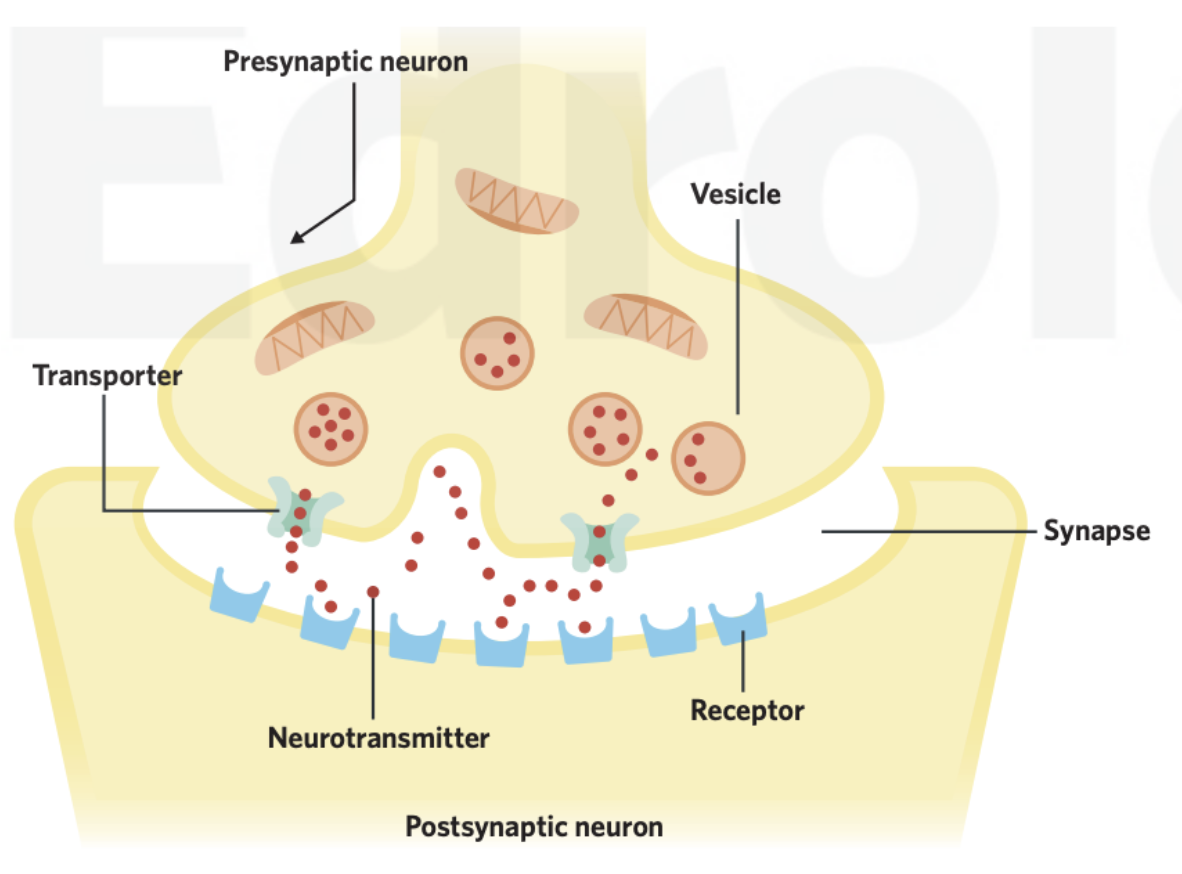
Receptors
Specialised cells and organs that detect change
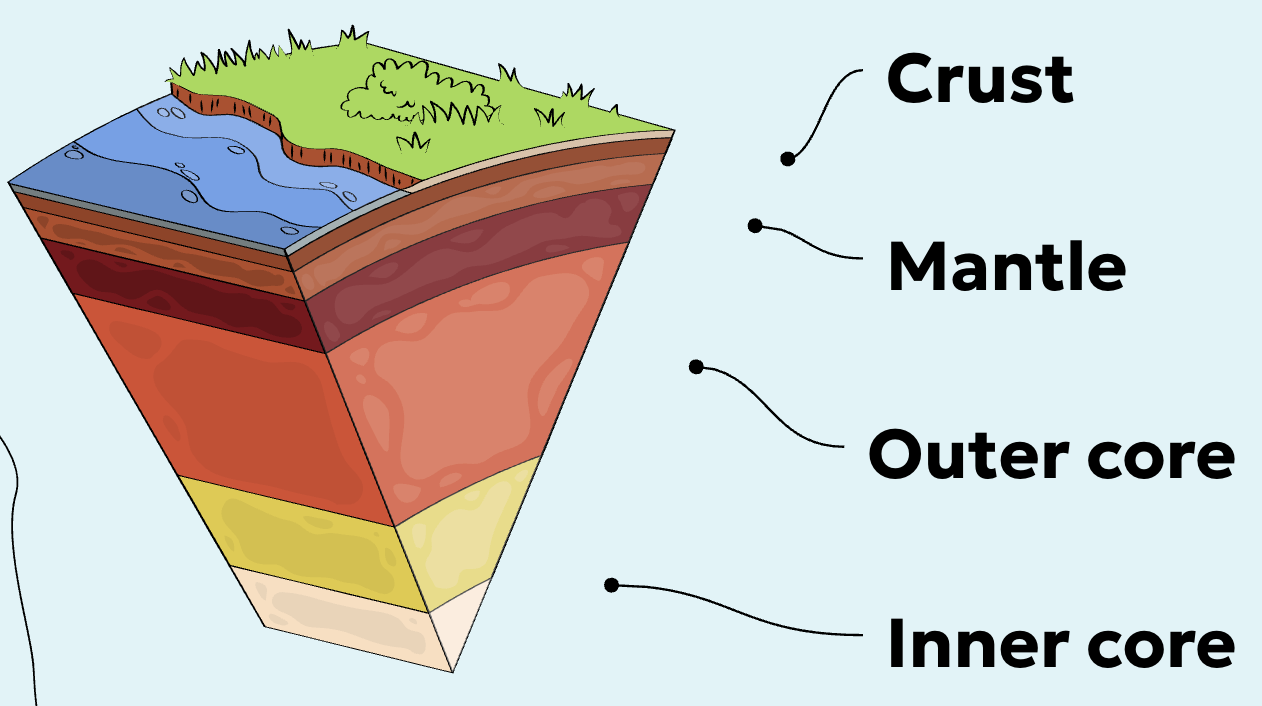
Crust
Earth’s hard thin outer layer
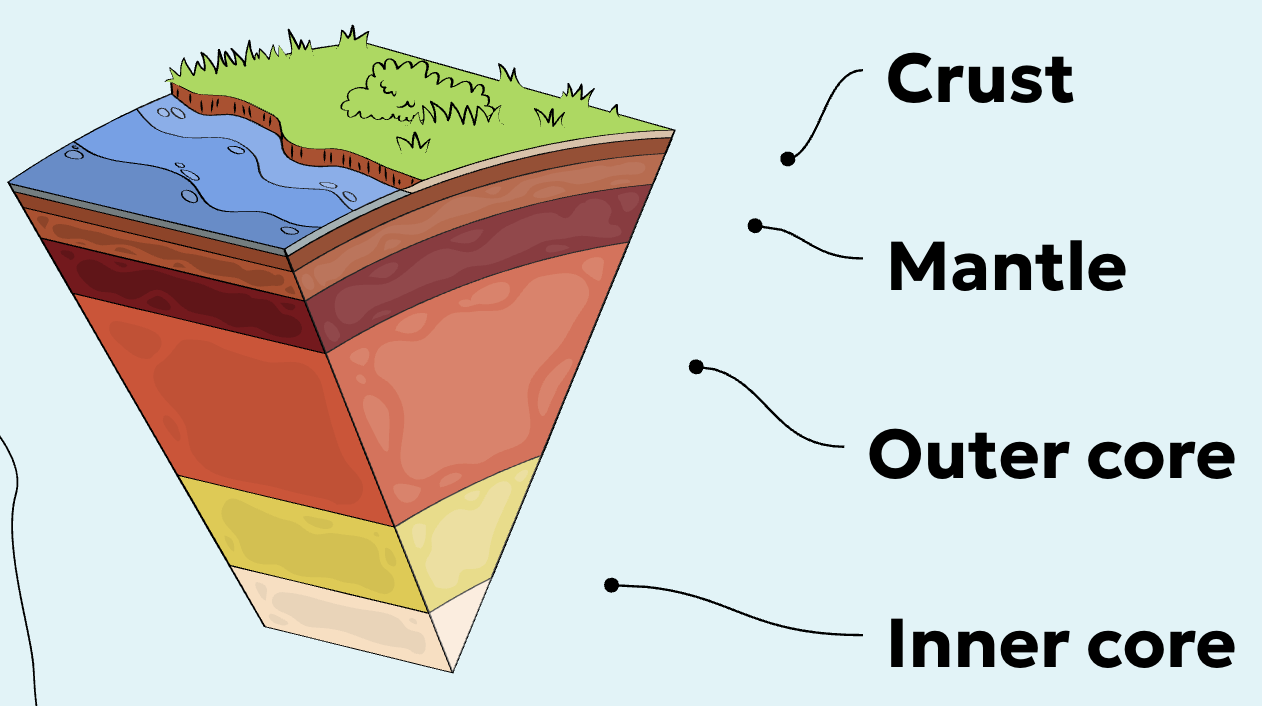
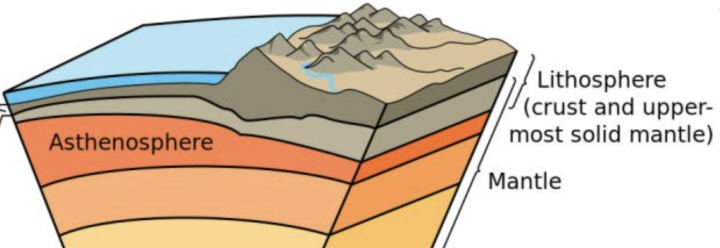
Mantle
Earth's middle layer
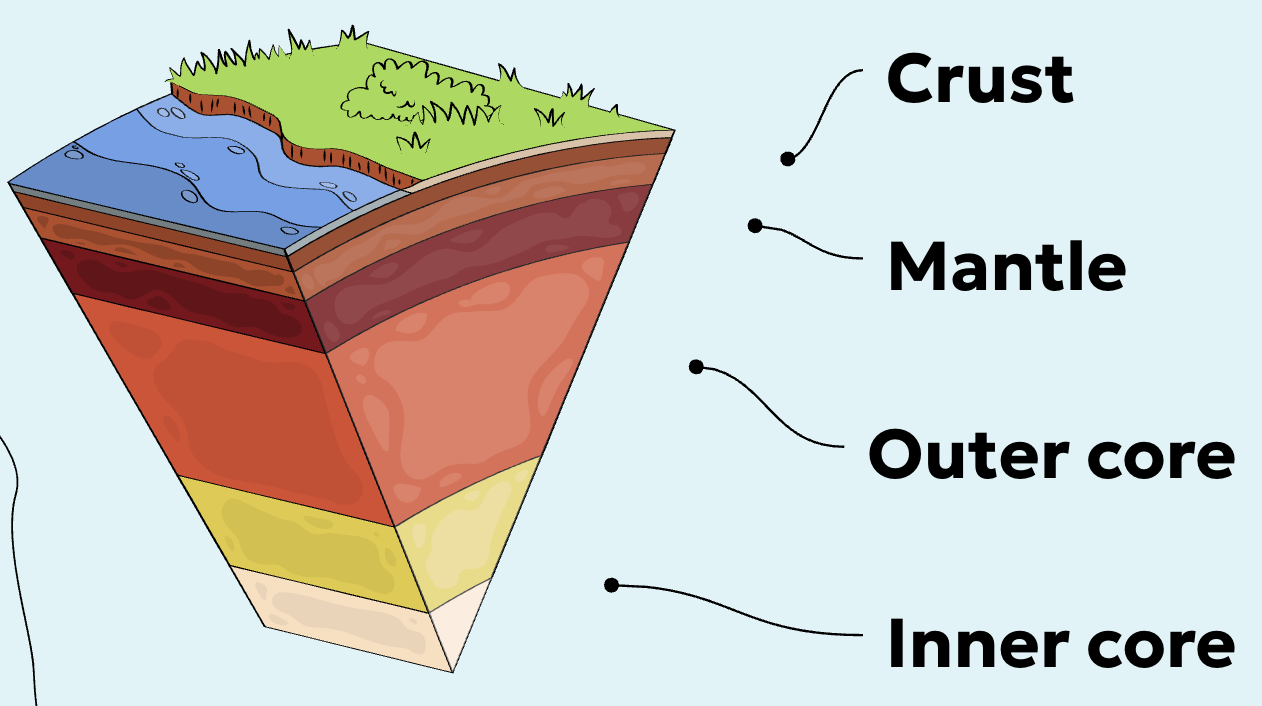
Outer core
Central liquid nickel and iron layer
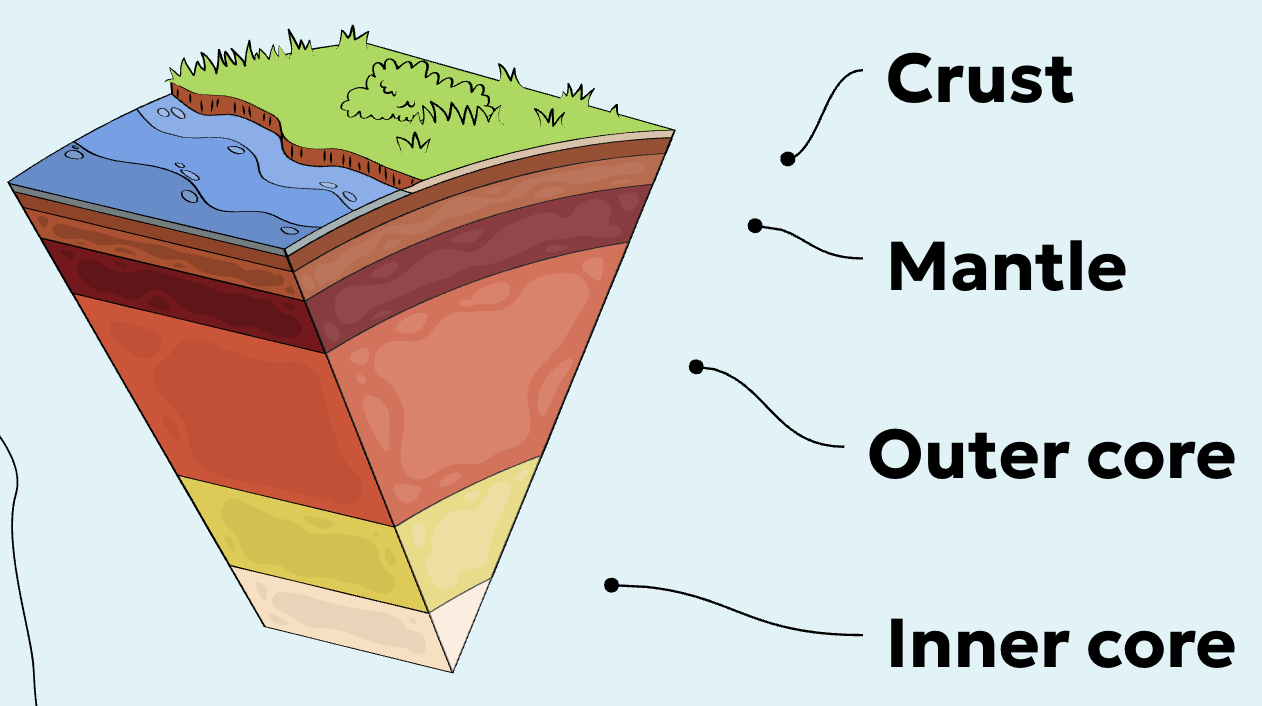
Inner core
Central solid nickel and iron layer
Lithosphere
Earth’s rigid outer layer divided into 15 plates
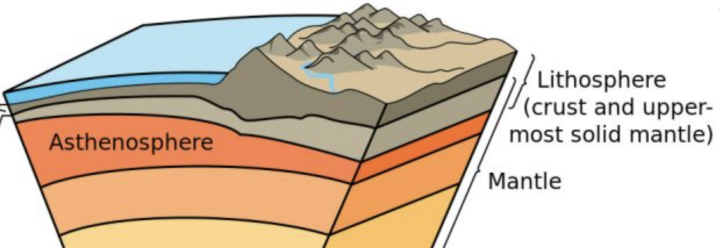
Asthenosphere
Thin zone of mantle beneath the lithosphere
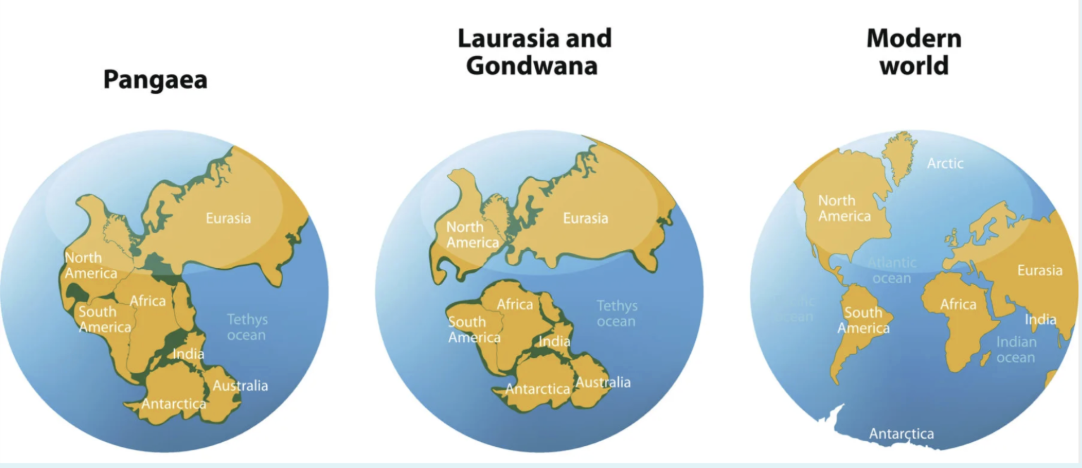
Continental drift
The movement of continents
Tectonic plate
A section of Earth's lithosphere
Mid-ocean ridge
A long chain of mountains below the ocean
Rift valley
A valley formed when a continent is being pulled apart
Subduction
When a plate submerges beneath another
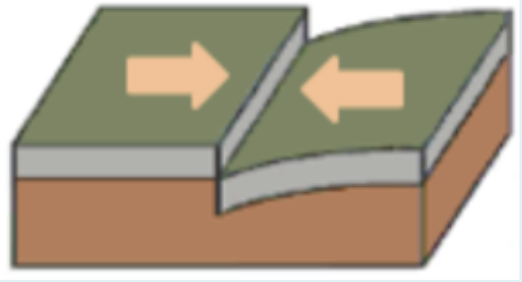
Convergent boundary
When two plates move towards each other - →←
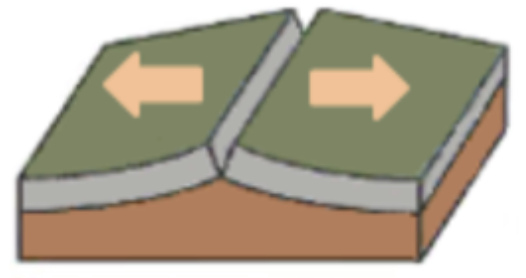
Divergent boundary
When two plates move away from each other - ←→
Transform boundary
When two plates slide past each other - ↑↓
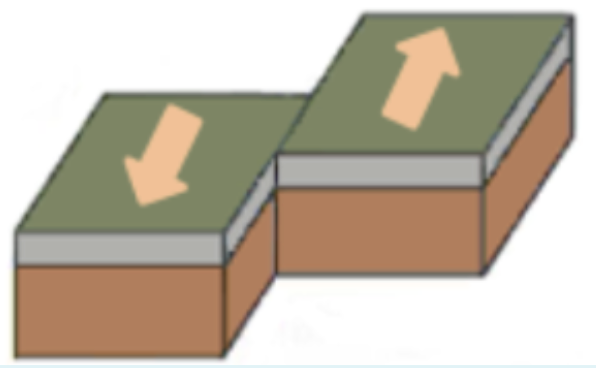
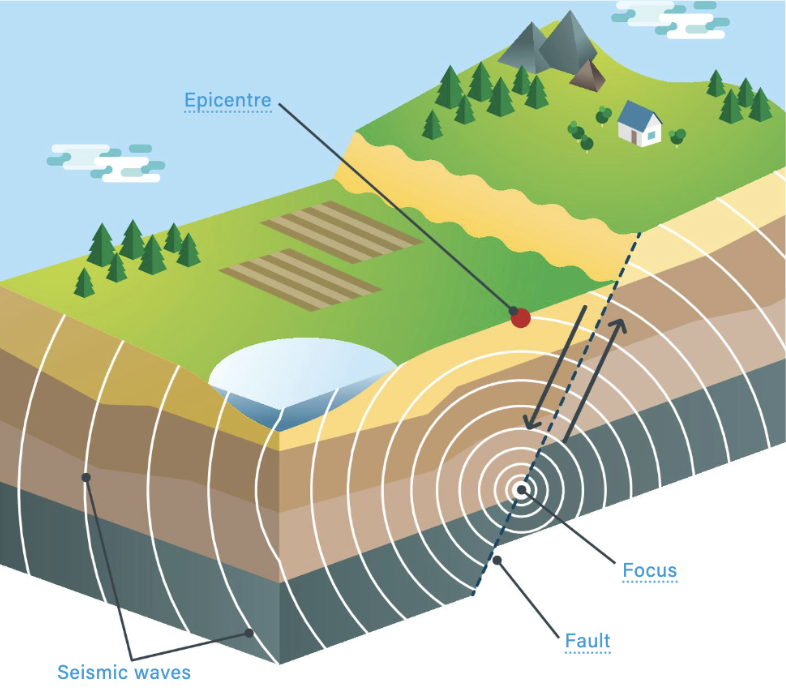
Fault
A break in the Earth’s surface
Fold mountain
A mountain formed by the folding of continental crust