Week 4: Intro to Protostomes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
coelom
internal body cavity between gut and body wall
acoelomate
no body cavity (platyhelminthes)
pseudocoelomate
partially lined body cavity (nematodes and rotifers)
coelomate
body cavity completely lined with mesoderm (bryozoans, brachiopods, humans)
Clade Platyhelminthes characteristics
flatworms, acoelomate, hydrostatic skeleton, bilateral symmetry, incomplete digestive tract, monoecious
flame cells (protonephridia)
osmoregulatory and excretory cells
"Turbellaria"
flatworm, uses chemoreceptors to find prey
Clade Trematoda
parasitic flukes (flatworms), uses hooks and suckers, monoecious
liver fluke life cycle
sexual adult stage in humans, asexual larval stage in snails
Clade Cestoda
flatworm, parasitic, microvilli for absorption, have scolex and proglottids
scolex (tapeworm)
posessed hooks and suckers for attachment only
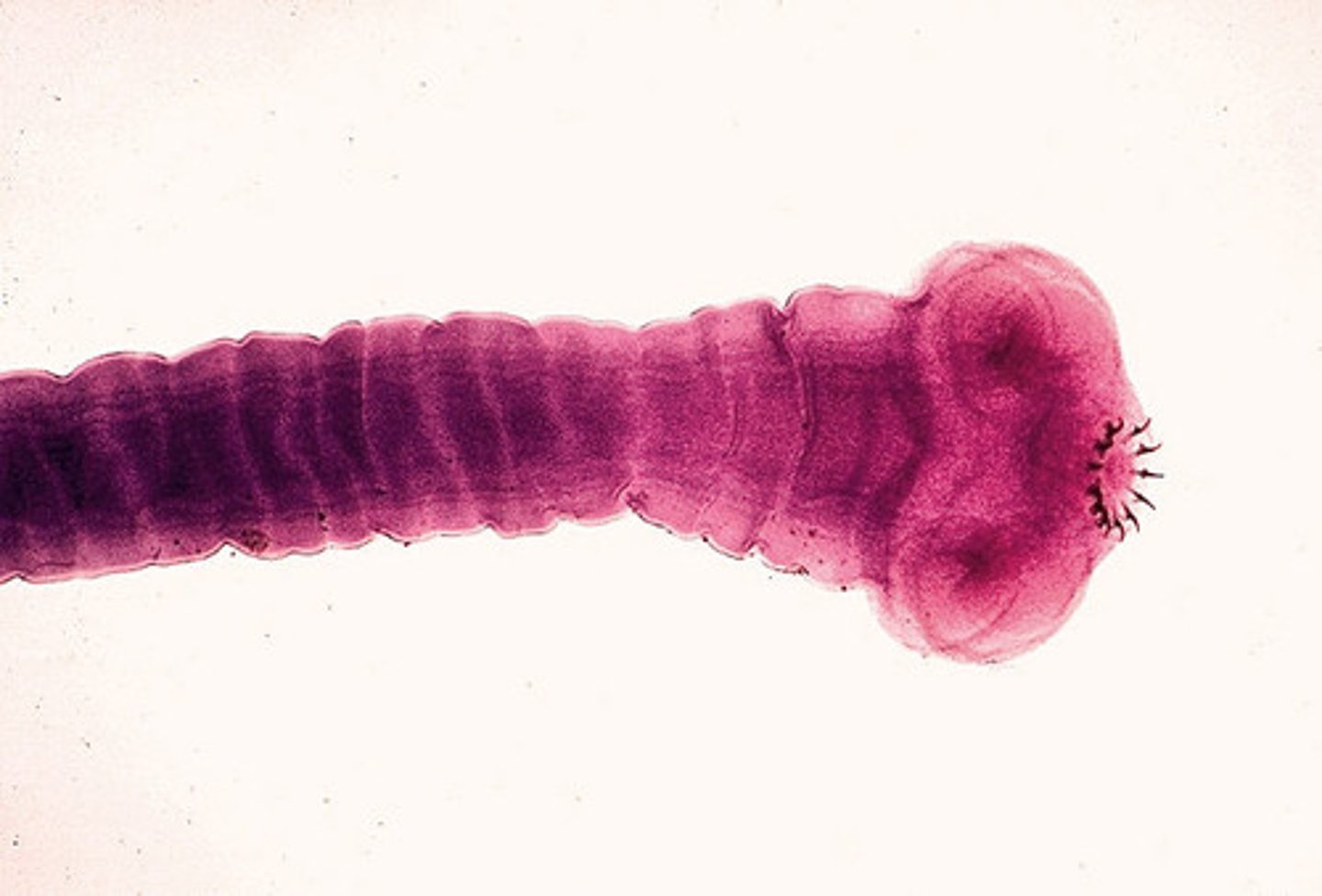
proglottids (tapeworm)
segments that contain gonads
Clade Rotifera
pseudocoelomate, complete digestive tract
rotifer: corona
enables locomotion, collects food
rotifer: mastax
grind food
rotifer: foot
attach to substrate
Clade Bryozoa
moss animals, coelomate, colonies of interconnected zooids
bryozoa: funiculus
connects the zooids
bryozoa: lophophore
ciliated crown of tentacles surrounding mouth
Clade Brachiopoda
lamp shells, coelomates, dorsal and ventral shell
Clade Nematoda
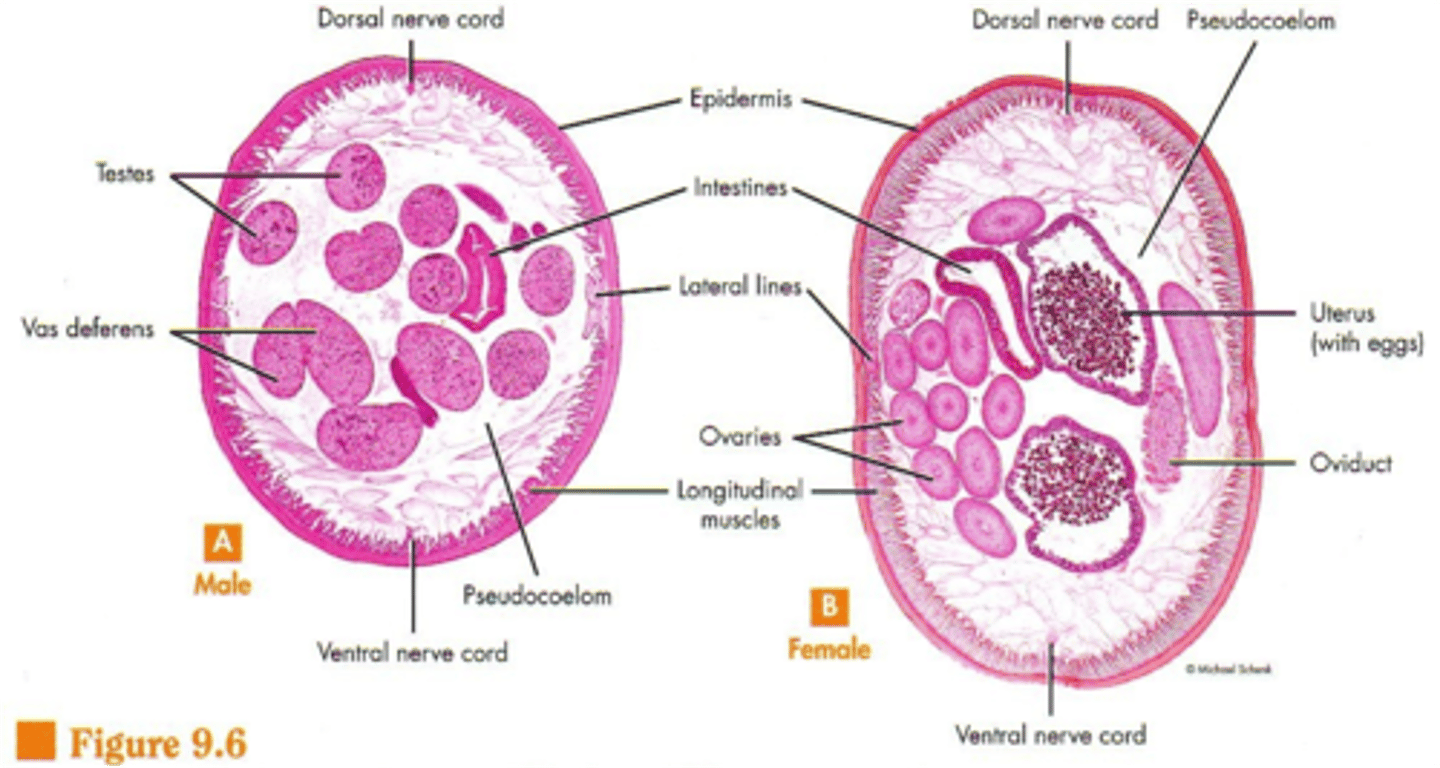
in Clade Ecdysozoa, roundworms, pseudocoelomate, bilateral symmetry, complete digestive system, hydrostatic skeleton, dioecious, longitudinal muscles only
how to determine Ascaris sex
female: both ends straight, two reproductive strings inside
male: posterior hook, one reproductive string
ascaris cross section
female has uterus filled with eggs, male has many testes