N10-009 Networking Concepts
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
OSI Model
Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application (Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away)
LAN
Local Area Network
Subnet
Stands for subnetwork, a logical or physical subdivision of a larger network
Router
connects 2 or more LANs to internet
Switch
Connects computers in LAN
Firewall
Safeguards computers and networks against unauthorized access
Proxy
Gateway between users and internet
NAS
Network attached storage
SAN
Storage access network
AP
Access Point
IDS
Intrusion Detection System
IPS
Intrusion Prevention System
Load Balancer
Distributes traffic across servers
CDN
Content Delivery Network
QoS
Quality of Service
TTL ( Time to Live)
A mechanism for limiting the lifetime of data on a network or in a system
Network Security List
set of security rules applied to all devices on a subnet
Network Security Group
Set of security rules applied to a group of network devices
Internet Gateway
Allows inbound and outbound connections between private subnets and public networks
Network Address Translation (NAT) gateway
Allows outbound connections from a private subnet to public network services while shielding it from inbound connections from outside.
How does a VPN work?
First, the computer connects to the internet using local DHCP.
Then, the VPN client software creates a virtual NIC (vNIC) on the local computer (endpoint 1).
Then it makes a connection with the VPN server at the office (endpoint 2).
Then it makes a virtual direct cable from the vNIC to the office.
NFV
Network Function Virtualization
VPC
Virtual Private CLoud
SaaS
Software as a Service
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service
PaaS
Platform as a Service
Direct Connect
On-premises infrastructure connects to a provider’s network, bypassing the public internet
Internet Protocol (IP)
IPv4 and IPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
Used for ping packets
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Connection oriented, SYN-ACK handshake
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
Connectionless, best-effort
IPv4 address
32-bit number, consisting of four decimals from 0 to 255 separated by periods. e.g. 192.168.1.1
IPv4 loopback/localhost
127.0.0.1
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)/link-local
169.254.x.x
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
CIDR IPv4 addresses have a prefix; e.g., “/24“ in “10.150.23.58/24“ denotes a 255.255.255.0 subnet mask
802.11 Standards
for wi-fi communication
802.3 standards
for wired ethernet networks
Transceiver
combined transmitter and receiver of signals
form factor
hardware specifications
TIA/EIA-568A
1. White/green
2. Green
3. White/orange
4. Blue
5. White/blue
6. Orange
7. White/brown
8. Brown
TIA/EIA-568B
1. White/green
2. Orange
3. White/orange
4. Blue
5. White/blue
6. Green
7. White/brown
8. Brown
Single-mode vs. multimode
It is referring to optic fiber and it either allows one or multiple light modes to propagate.
DAC
Direct attach copper
Coaxial
F-type, BNC
BNC
Bayonet Neill-Concelman
Twinaxial/twinax
Has two inner conductors instead of one as in coaxial
Twisted pair
RJ45, (RJ)11
(RJ)11
Registered Jack
STP/UTP
Shielded/Unshielded twisted pair
Fiber optic
SC, ST, LC, FT, MT,RJ
SC
Subscriber Connector
ST
Straight Tip
LC
Local Connector
FC
Fibre Channel
Plenum-rated
Fire Resistant cable; compare with riser-rated, non-plenum rated, and PVC
UTP Categories
CAT1 - up to 1MBps
CAT2 - up to 4Mbps
CAT3 - up to 10Mbps
CAT4 - up to 16Mbps
CAT5 - up to 100Mbps
CAT5e - up to 1Gbps
CAT6 - up to 10Gbps
CAT6a - up to 10Gbps
CAT7 - up to 10Gbps
SFP
Small form-factor pluggable
QSFP
Quad small form-factor pluggable
MPO
Multi-fiber push on
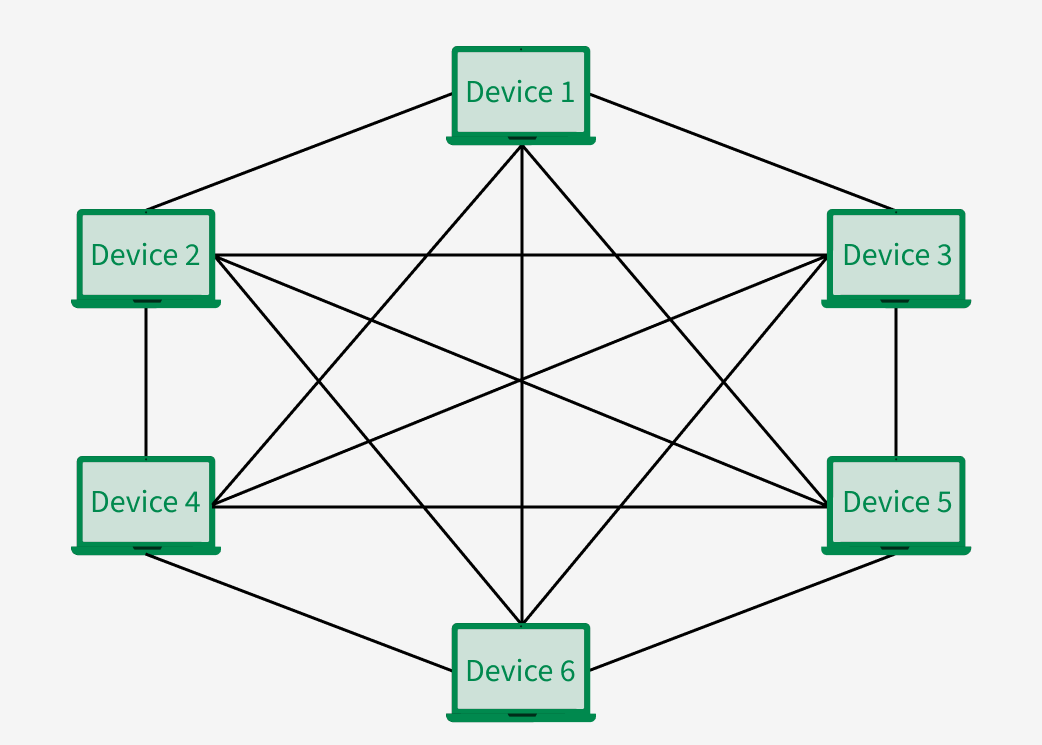
Mesh Topology
A network configuration where every device is interconnected with every other device, providing multiple route for data to travel.
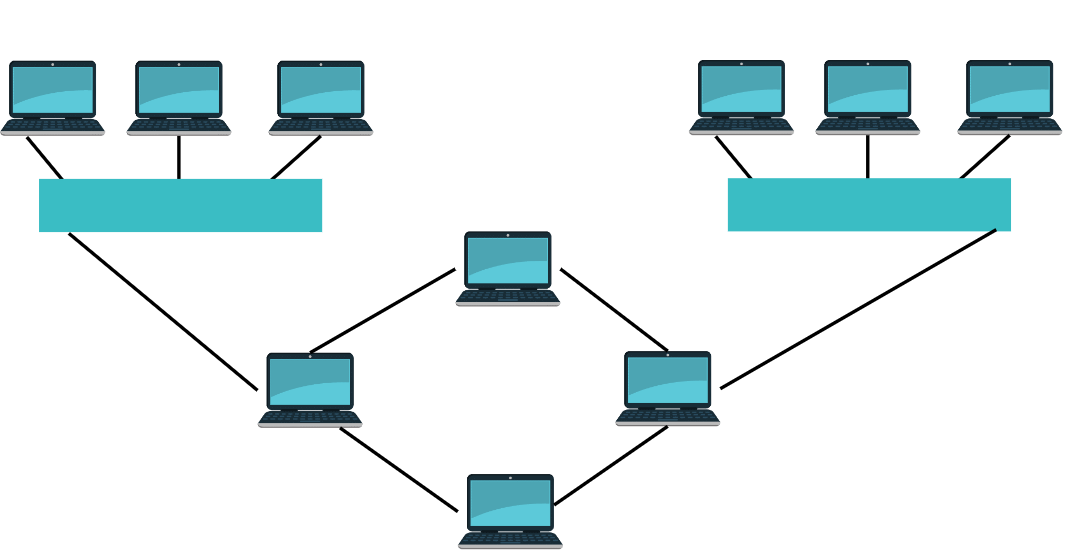
Hybrid Topology
A network topology that combines two or more different network topologies. It can be a combination of bus topology, ring topology and mesh topology
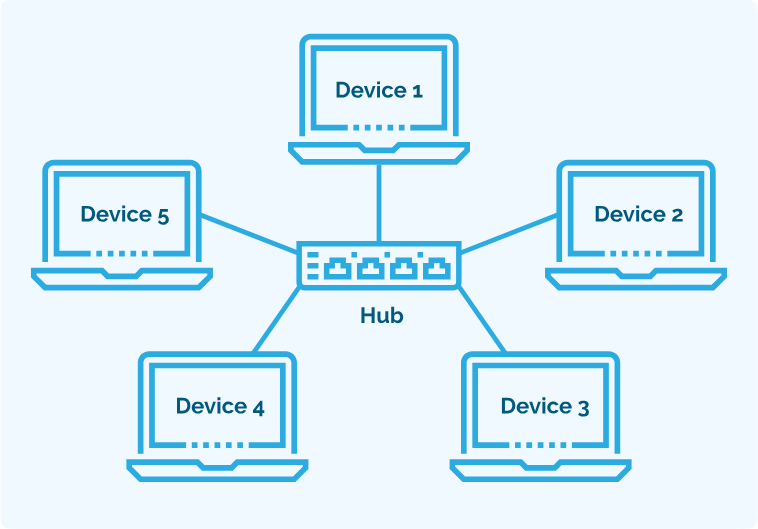
Star/hub and spoke Topology
A network topology type where each individual component is physically linked to a common central node, such as a switch or hub. A star network may comprise either wired or wireless connections. The central node functions as a server, while connected network components are clients, every one of which uses the server as an intermediary.
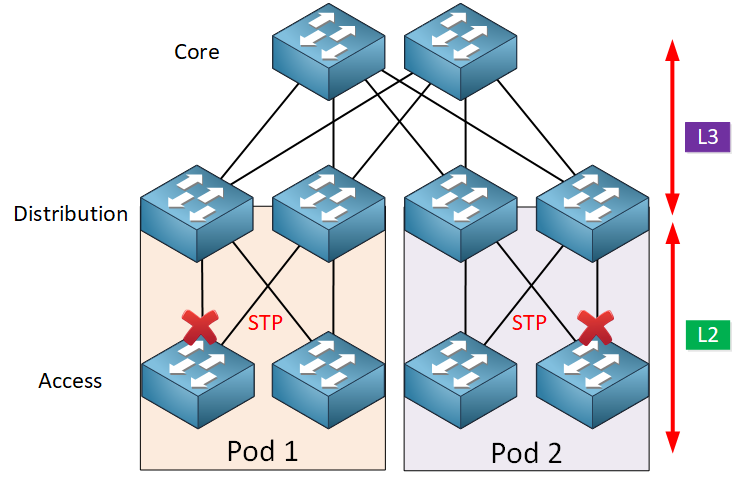
Spine and Leaf Topology
A two-tier network architecture where leaf switches connect directly to end-user devices, and spine switches form the network's core by interconnecting all leaf switches in a full-mesh pattern
Point to Point Topology
a type of topology that works on the functionality of the sender and receiver. It is the simplest communication between two nodes, in which one is the sender and the other one is the receiver.
3 tier Hierarchical model
Core, Distribution, Access
Collapsed core
Combine core and distribution layers
North-south
Traffic moving between a private network and the outside world
East-west
Traffic moving within an organization’s internal network
RFC1918
IP addresses set aside for private networks
VLSM
Varliable Length Subnet Mask
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
CIDR IPv4 addresses have a prefix; e.g., “/24“ in “10.150.23.58/24“ denotes a 255.255.255.0 subnet mask
IPv4 address classes
• Class A: 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
• Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
• Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
• Class D: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
• Class E: 240.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
SD-WAN
Software-defined wide area network
SDN
Software-defined networking
IaC
Infrastructure as Code
SASE
Secure Access Secure Edge
SSE
Security Service Edge
VXLAN
Virtual Extensible Local Area Network
ZTA
Zero Trust Architecture
DCI
Data center interconnect
GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation
IPSec
Internet Protocol Security
AH
Authentication Header
ESP
Encapsulating Security Payload
IKE
Internet Key Exchange
Traffic Types
Unicast, Multicast, Anycast