gr12b term 1 quiz 1 bio - sponges and cnidarians
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what phylum are sponges in? wh?
porifera, because they have pores
how are sponges simple organisms?
they have no tissues, no organs, and most lack symmetry
can sponges regenerate?
yes, if u break one down into individual cells, they will reform a new sponge
sponges - body structure
composed of two layers of independent cells with a jelly-like substance in between
osculum
a sponge’s mouth-like opening
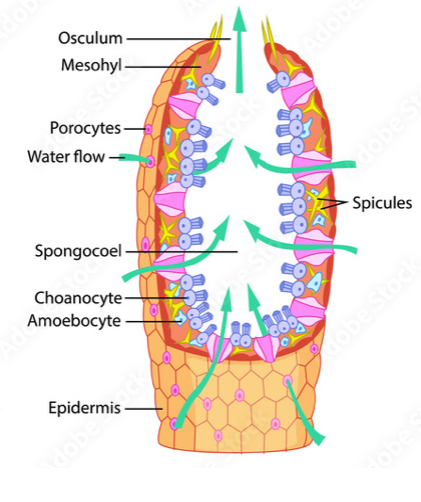
sponges - feeding and digestion
they are filter feeders, they obtain food by filtering small particles out of water, food particles cling to the cells and digestion of nutrients take place within individual cells
sponges - movement
sponges are free-swimming as larvae, but are sessile as adults (stay in 1 place)
sponges - support
within the jelly-like substance between sponge’s two cell layers are archaeocytes, which are amoeba-like cells that secrete spicules, which is the support structures
demospongiae
sponges that have spicules composed of spongin fiber, silica, or both
calcarea
sponges that have spicules composed of calcium carbonate
hexactinellida
sponges that have spicules of silica joined together to form a netlike skeleton
how do sponges respond to stimuli?
they dont have a nervous system, but they have epithelial-like cells that detect external stimuli, such as touch or chemical signals, they respond by closing their pores
how do sponges reproduce?
some asexually, most sexually
how do sponges reproduce asexually
fragmentation - when it breaks into two pieces and forms into two new organisms
budding - grows from a small outgrowth on the parent
gemmules - cells protected by spicules
how do sponges reproduce sexually ?
eggs remain within the organism, sperm is released into the water, the zygote develops into a free-swimming larvae after fertilization
sponge ecology
food for some tropical fish and turtles
form habitats for a variety of worms, fishes, shrimp, and symbiotic green algae
spongin fiber sponges are used for household scrubbing / cleaning
potential use in pharmaceuticals
what phylum do cnidarians belong to?
cnidaria
contains jellyfish, sea anemones, and contain abt 10000 species, mostly marine
cnidarians - body structure
one body opening, most hv 2 layers of cells
cell layers organized into tissues:
outer layer - protection
inner layer - digestion
exhibit radial symmetry
cnidarians - feeding nd digestion
tentacles are armed with stinging calls called cnidocytes containing nematocysts, a capsule that holds a coiled tube containing poision and barbs
nematocysts work like tiny harpoons in response to touch or chemical stimuli, one of the fastest cellular processes in nature
after capture by nematocysts, nd tentacles, prey is brought to the mouth
inner cell layers surrounds the gastrovascular cavity, where cells release digestive enzymes, undigested materials are ejected through the mouth
cnidarians - response to stimuli
have a nerve net that conducts impulses to and from all parts of the body, causing contractions of muscle-like cells in the two cell layers
cnidarians - reproduction
have 2 body forms :
polyp - tube shaped with a mouth surrounded by tentacles
medusa - umbrella shaped with tentacles hanging down
cnidarians - diversity
split into 4 classes :
hydroids: both polyp and medusa stages, many form colonies
jellyfishes: medusa is dominant, float near the surface of the ocean
sea anemones and coral: polyp stage is dominant
cnidarian ecology
mutualism is common in cnidarians
habitat for fishes
recreational pleasure to humans from visiting coral reefs
medical use