PSYCH1X03 - Problem Solving & Intelligence (PS&I)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit/Week 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
PS&I
Intelligence (Sternberg/Operational)
Cognitive ability to learn from experience, reason well, remember important information, cope with the demands of daily living
Analytic
Creative
Practical
No single operational definition
PS&I
Intelligence (Boring)
Intelligence is anything measured by an intelligence test
PS&I
Problem Solving
Reliable indicator of intelligence: Arc of Knowledge model
PS&I/Problem Solving
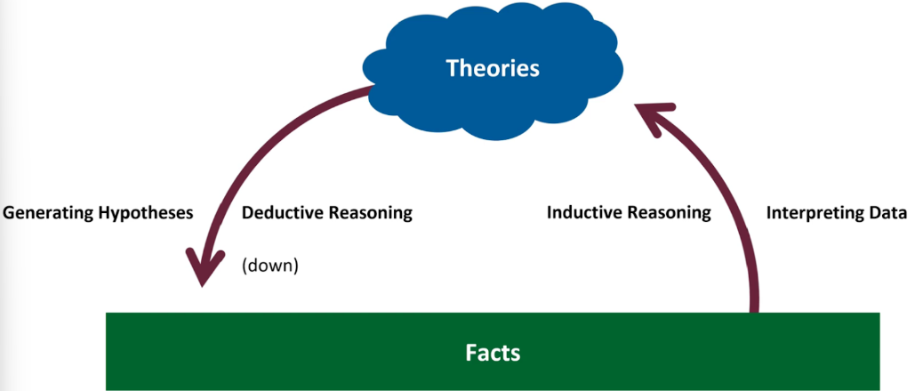
Arc of Knowledge
Model that guides scientific method
Deductive Reasoning
Inductive Reasoning
PS&I/Arc of Knowledge
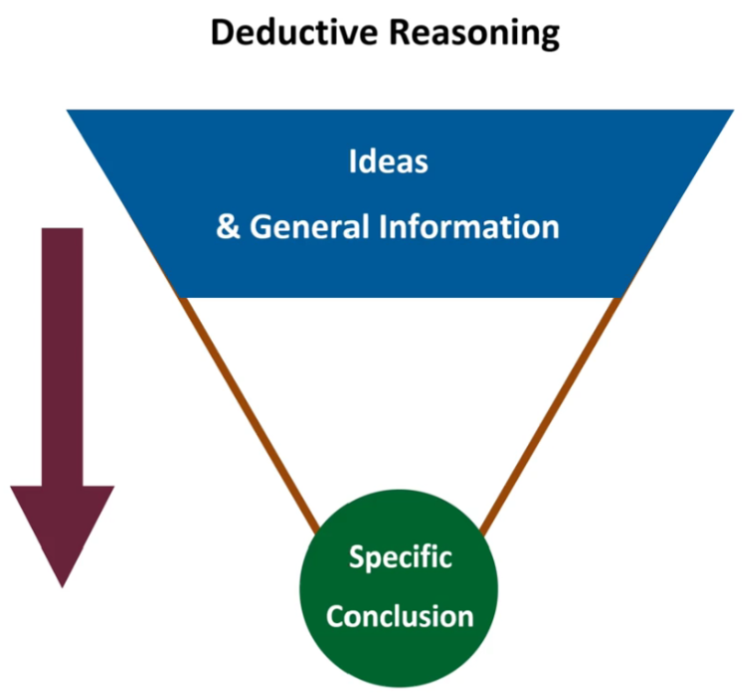
Deductive Reasoning
Theory down to fact
i.e. person is tidy → conclude desk is tidy too
PS&I/Arc of Knowledge
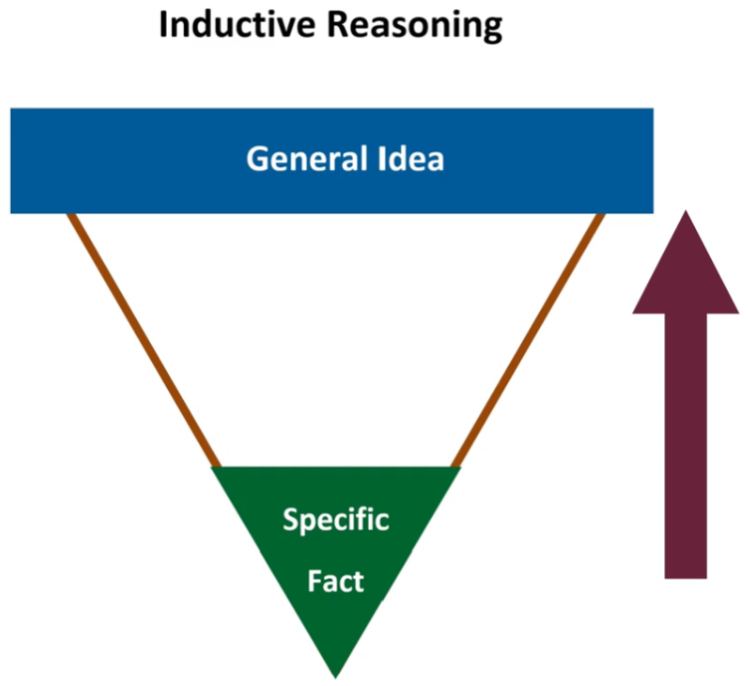
Inductive Reasoning
Fact up to theory
i.e. desk is messy → conclude person is messy too
PS&I
Insight Problems
Difficult problems that require restructuring/creative thinking of problem to solve
PS&I/Insight Problem
Functional Fixedness
Difficulty seeing alternative uses of common objects
PS&I
Well-defined Problem
Defined start position, rules, and end goal
Structured and theoretical
PS&I
Ill-defined Problem
Undefined start position, rules, and end goal
Real life
PS&I
Reliability
Reliable tests produce the same results over many trials. Important because intelligence is a static quality
PS&I
Validity
Valid tests accurately measures targeted trait. Important because want to measure intelligence, not ability to answer questions after training
PS&I
Intelligence Testing
Heavily controversial. Not all in history have been reliable or valid
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Galton
Reaction speed
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Binet
Children given multiple short tasks related to daily life. First valid intelligence test
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Stanford-Binet
Ratio between child’s mental age & true age = “IQ”
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Spearman
Single measure of generalized intelligence, called “g”
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Gardner
Multiple independent intelligence types, but no evidence
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Weschler (WAIS & WISC)
Standardized: mean = 100 & standard deviation = 15. Modern
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Hierarchical Intelligence
Independent intelligence types contribute to a general intelligence
PS&I/Intelligence Testing
Flynn Effect
Observation that raw IQ has been increasing. Due to increased quality of schooling, life, access to information, media, etc
PS&I
Twin Studies
Genes & environment are both important to intelligence
PS&I/Twin Studies
Identical Twins vs Fraternal Twins
Identical twins are more similar than fraternal twins
PS&I/Twin Studies
Fraternal Twins Same Home vs Fraternal Twins Different Homes
Fraternal twins in the same home are more similar than fraternal twins in different homes
PS&I/Textbook
Adoption Studies
Children are more positively correlated with biological parents (genetics) than adoptive parents (environment)
PS&I
Schema
Mental framework for interpreting information and the world
PS&I/Schema
Assimilation
New information becomes incorporated as part of schema
PS&I/Schema
Accommodation
Schema is modified to accommodate disagreeing new information
PS&I
Piaget’s Intellectual Development Theory
Children’s stages of schema development and change as they grow
Sensorimotor
Preoperational
Concrete operational
Formal operational
Super Preppy Cheetos From 7/11
PS&I/Piaget
Sensorimotor Stage
Child can intentionally engage with environment
Object permanence
0-2 years old
PS&I/Piaget/Sensorimotor
Object Permanence
Objects continue to exist when not visible
PS&I/Piaget
Preoperational Stage
Mastered object permanence, but is limited in skills
Egocentric
Seriation
Reversible relationships
Conservation
2-7 years old
PS&I/Piaget/Preoperational
Egocentric
Cannot understand another’s perspective
Piaget’s 3 mountain experiment

PS&I/Piaget/Preoperational
Seriation
Cannot logically order objects
PS&I/Piaget/Preoperational
Reversible Relationships
Cannot understand something is reversible
i.e. boy knows he has sister, doesn’t know she has brother
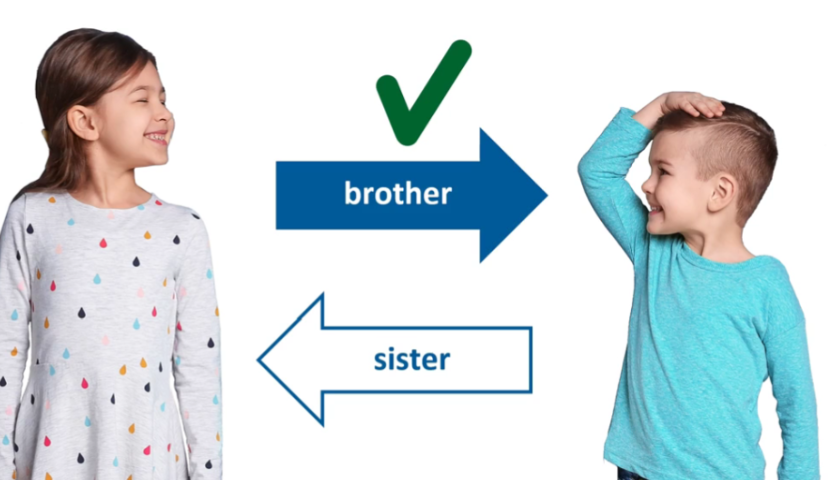
PS&I/Piaget/Preoperational
Conservation
Cannot reason with amounts of substances
i.e. liquid conservation; think taller glass instead of wider
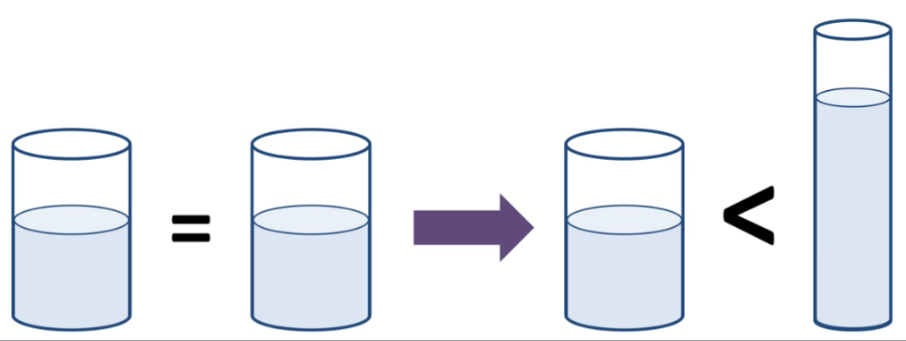
PS&I/Piaget
Concrete Operational
Limited by lack of abstract thinking & reasoning
7-12 years old
PS&I/Piaget
Formal Operational
Defined abstract thinking & reasoning
12+ years old
PS&I/Piaget
Criticisms
Decalage
Relies on language ability
PS&I/Piaget/Criticisms
Decalage
Children tend to develop skills out of order
PS&I
Bias
Tendency to favour something over another
PS&I/Bias
Confirmation Bias
Seeking information that directly supports our hypothesis
PS&I
Heuristics
Mental shortcuts for fast and usually accurate decisions. Prioritizes saving mental resources
PS&I/Heuristics
Availability Heuristic
Decisions based on most available information
Judge frequency
Relies on ease of memory
Errors occur factors influence example availability
PS&I/Heuristics
Representative Heuristic
Make assumptions on example based on prototype
Judge probability
Relies on resemblance
Errors occur because not all are the same
PS&I
Neural Encoding
Process that makes learning more endurant
PS&I
Bounded Rationality
Cognitive limitations that prevent humans from being completely rational
PS&I/Bounded Rationality
Anchoring
Bias caused by arbitrary initial information
i.e. first seeing expensive wine, and then seeing cheaper wine as reasonable option
PS&I/Bounded Rationality
Framing
Bias caused by way information is presented; frame something as positive vs negative
i.e. Opt-in vs opt-out for organ donation