Module 3 Quiz 2 - All Vocab
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cherstnuts roating ern arn opern fieeee
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Carbohydrate
organic molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen; major source of energy; 3 main types - monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
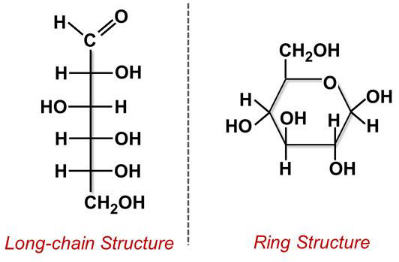
Monosaccharide
“simple sugars”; simplest form of carbs; typically contain 5 or 6 carbon atoms; basic building blocks for complex carbs; exs. glucose, fructose (fruit sugar), galactose
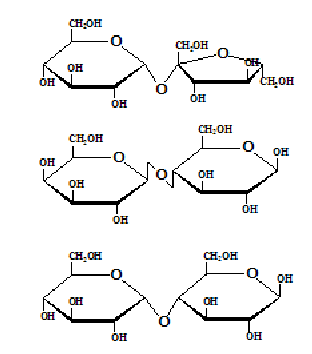
Disaccharide
carbs made via chemically joining 2 monosaccharides; must be broken down for absorption in the body; exs. sucrose (table sugar: glucose + fructose), lactose (milk sugar: glucose + galactose), maltose (malt sugar: glucose + glucose)
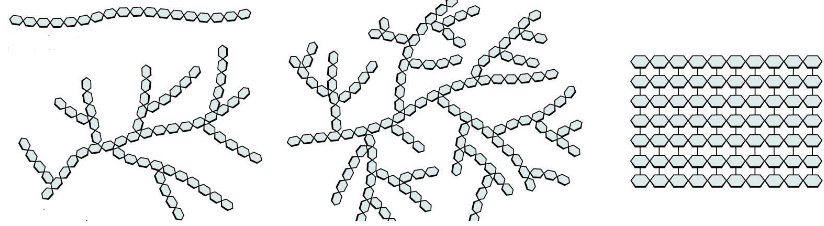
Polysaccharide
complex carbs made up of long monosaccharide chains (usually glucose); must be broken down for absorption in the body; exs. starch, glycogen, cellulose
Protein
large, complex organic molecules made up of long amino acid chains; important for tissue and organ structure, function & regulation; act as hormones for metabolism regulation, enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions, muscle fibers, & structural components; must be broken down into amino acids for body absorption
Polypeptide
long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds; make up proteins which typically consist of one or more chains
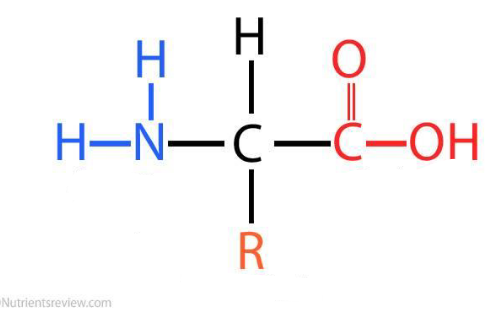
Amino acid
simplest building blocks of proteins ; consist of an amine group (holds nitrogen), a carboxyl group (acidic group), & an R group (side chain, differentiates the amino acid)
Lipids
“fats”, “oils”; store long-term energy, provide insulation for organs, help maintain body temperature; chemical exs. triglycerides & steroids (cholesterol); food exs. butter, cream, oils, etc.
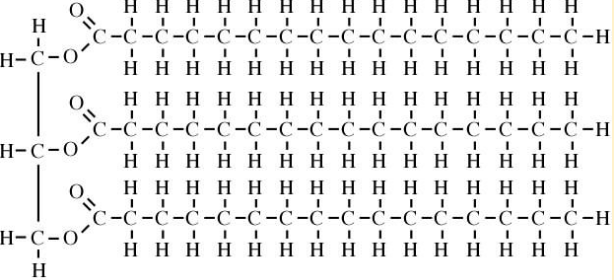
Triglyceride
lipid molecule; made up of 1 glycerol bound to 3 fatty acids; major forms of fat storage; can be saturated or unsaturated
Saturated fats
fats typically solid at room temp; carbon connected solely by single bonds in fatty acid chains; found in animal fats - butter, meat; linked to health issues - atherosclerosis
Unsaturated fats
fats typically liquid at room temp; have one or more double bonds between carbon in fatty acid chains; found in plant oils - olive oil, canola oil; considered healthier than the alternative
Glycerol
simple molecule with 3 carbon atoms each attached to a hydroxyl group; where fatty acids attach to form triglycerides
Fatty acids
long chains of carbon & hydrogen atoms; can be saturated or unsaturated; attach to glycerol to form triglycerides
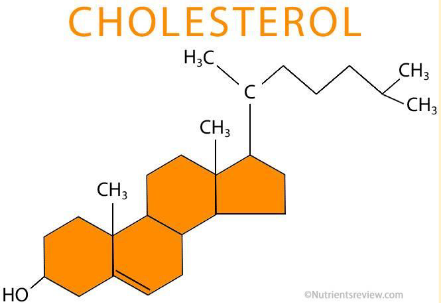
Cholesterol
steroid lipid that helps stabilize cell membranes & serve as bases for certain hormones; body can produce it, consuming too much can cause atherosclerosis
Steroid molecule
class of lipids that have 4 fused carbon rings; include cholesterols & hormones; exs. estrogen & testosterone
Nucleic acids
large organic molecules carrying genetic information; consist of DNA & RNA; store & transmit genetic info needed for protein synthesis & heredity
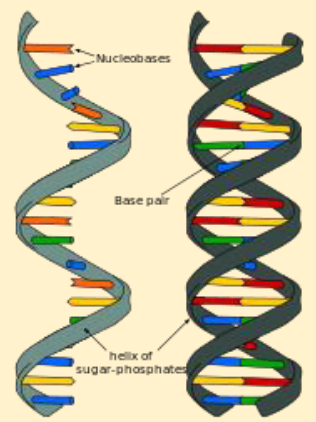
DNA
AKA “deoxyribonucleic acid”; nucleic acid that carries genetic blueprint; stores instructions needed to build & maintain an organism; made up of nucleotides; nucleotide form: phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine)
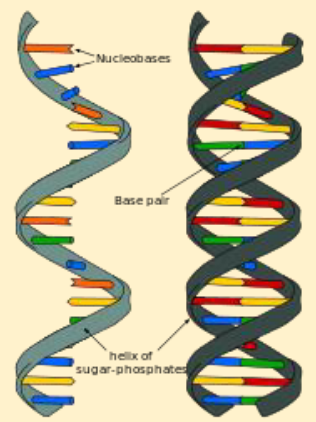
RNA
AKA “ribonucleic acid“; nucleic acid that carries out the instructions of the genetic blueprint; made up of nucleotides; nucleotide form: phosphate group, ribose sugar, nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil)
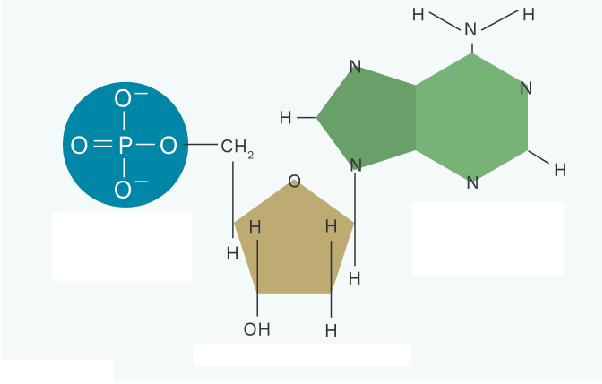
Nucleotide
link together to form long chains of nucleic acids; general form; phosphate group, sugar (ribose/deoxyribose), nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine/uracil)
Enzymes
proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed or changed in the process; help break down food, build molecules, & carry out many other vital functions
Salivary amylase
enzyme found in saliva; breaks down starches into simpler sugars in the mouth
Lysozymes
enzymes that help protect the bdoy by breaking down cell walls of certain bacteria which kills them; found in saliva, tears, & mucus
Pepsin
enzyme that helps digest proteins by breaking them into smaller peptides; found in the stomach
Pancreatic amylase
enzyme that continues breaking down starches into simple sugars: produced by pancreas & found in small intestine
Lipase
enzyme that helps break down fats (lipids) into smaller molecules like fatty acids & glycerol
Trypsin
enzyme that helps break down proteins into smaller peptides; targets basic amino acids; produced by pancreas & found in small intestine
Chymotrypsin
enzyme that helps break down proteins into smaller peptides; targets aromatic amino acids; produced by pancreas & found in small intestine
Carboxypeptidase
enzyme that breaks down proteins by removing amino acids one at a time from the carboxyl (end) side of the chain
Aminopeptidase
enzyme that breaks down proteins by removing amino acids one at a time from the amino (beginning) side of the chain
DNA and RNA Nucleases
enzymes that break down DNA & RNA molecules by cutting them into smaller pieces during digestion or cellular processes
Lactase
enzyme that breaks down lactose (sugar in milk) into simpler sugars (glucose & galactose)
Sucrase
enzyme that breaks down sucrose (table sugar) into simpler sugars (glucose & fructose)
Maltase
enzyme that breaks down maltose into simpler sugars (2 glucose)
Hydrochloric acid
strong acid that breaks down food, kills bacteria, & provides the acidic environment for enzymes like pepsin to work; found in stomach
Bicarbonate
substance that neutralizes stomach acid as food moves into small intestine → creates safe environment for digestive enzymes to work; produced by pancreas
Bile
fluid that helps break down fats into smaller droplets —→ easier for enzymes to digest in small intestine; produced by liver
Salivary glands
mouth glands that produce & secrete saliva which helps moisten food for easier swallowing; 3 main sets: parotid, submandibular, sublingual
Incisors
front teeth used for cutting food
Canines
pointed teeth used for tearing & shredding food
Molars
large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth used for crushing & grinding food
Esophagus
muscular tube connecting the throat (pharynx) to the stomach; transports swallowed food through peristalsis (involuntary muscle contractions)
Stomach
muscular organ that stores food & uses acids + enzymes to chemically break down food into usable form for the body
Gastric juice
digestive fluid that contains hydrochloric acid & enzymes, secreted by stomach
Cardiac (esophageal) sphincter
ring of muscle between the esophagus & stomach that controls food passage; prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus
Pyloric sphincter
ring of muscle at stomach exit, controls the flow of partially digested food into small intestine
Small intestine
long, narrow tube where most digestion & nutrient absorption occurs
Large intestine
wide, shorter tube that absorbs water from undigested food & forms solid waste (feces) for elimination
Liver
large organ that produces bile
Gall bladder
small organ that stores & concentrates bile produced by liver, releases it into small intestine for fat digestion
Villi
tiny, finger-like projections lining the small intestine; increase surface area for better nutrient absorption
Peristalsis
involuntary, wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract
Hepatic portal circulation
blood vessel system that carries nutrient-rich blood from digestive organs to the liver for processing before they enter the general bloodstream
Non-specific Immune Response
AKA “innate immune response”; natural, built-in body defenses against pathogens without specific targets; immediate or very quickly block or destroy pathogens; consists of skin, mucous membranes, WBCs that generally attack pathogens, inflammation, complement proteins
Specific Immune Response
AKA “adaptive immune response”; targets & defends against specific pathogens; takes longer to activate but provide long-lasting protection; consists of lymphocytes (T Cells & B Cells), antibody production, memory cells
Skin
outer protective layer of the body; physical barrier against pathogens; consists of the epidermis (outer layer), dermis (inner layer), & the sweat + oil glands
Mucous membranes
layers of epithelial tissue lining body openings; produce mucus which traps bacteria, viruses, etc. & filters to prevent pathogens from entering the body; contain antibodies & immune cells to defend against infections
Defensive white blood cells
AKA “leukocytes”; immune cells that protect the body against infections & foreign invaders; consists of non-specific: neutrophils, monocytes, basophils, eosinophils & specific: lymphocytes
Phagocytes
“cellular vacuum cleaners”; WBCs that engulf & digest harmful particles; remove pathogens & debris from the body; include neutrophils & monocytes (macrophages)
Monocytes
WBCs that move through the bloodstream, enter tissues, & develop into macrophages; act as phagocytes
Inflammatory response
non-specific response to injury or infection; consists of swelling, redness, heat, & pain; happens due to blood vessels dilating which allows immune cells & fluid to enter the affected tissue that fight off pathogens & start healing
Antimicrobial proteins
proteins that help fight & destroy pathogens like bacteria & viruses; 2 major types: complement proteins, interferons
Interferon
protein produced by virus-infected cells; helps protect nearby healthy cells by interfering with the virus’s ability to spread & multiply; activates other parts of immune system
Opsonization
process where immune proteins attach to the surface of a pathogen → easier for WBCs to recognize & destroy pathogen
Complement proteins
proteins that mark pathogens for destruction (opsonization), cause pathogens to burst, & trigger inflammation to attract immune cells
Sebum
oily substance secreted by sebaceous skin glands; help keep skin & hair soft; slightly acidic nature helps prevent bacterial growth on skin
Sebaceous gland
small skin gland that produces & secretes sebum into hair follicles & onto skin surface
Sweat gland
skin gland that produces sweat which helps cool the body, remove waste, & contain salts + enzymes that kill bacteria on the skin
Leucocytes
“WBCs”; help body fight infections & protect against diseases
Neutrophil
WBCs that defends body by engulfing & digesting pathogens through phagocytosis
Macrophage
WBCs that engulf & destroy pathogens, dead cells, & debris to protect the body & clean infections
Basophil
WBCs that release histamine which causes blood vessels to dilate & play a key role in inflammation
Eosinophil
WBCs that mainly defend against parasitic worms by releasing enzymes that kill or irritate parasites
Lymphocytes
WBCs that play a role in specific immune response; consists of T cells & B cells; help produce antibodies to fight specific pathogens
B cells
lymphocytes that produce antibodies to specifically target & neutralize pathogens
T helper cells
lymphocytes that activate other immune cells & coordinate immune response against pathogens
Antigen
parts of pathogens that trigger immune response; targets that immune cells recognize & respond to by producing specific antibodies
Antibody
AKA “immunoglobulins”; proteins produced by B cells that recognize & bind to specific antigens; help immune system identify & neutralize pathogens
Immunity
ability of the body to resist & fight off infections & diseases
Active immunity
body creates its own antibodies & immune cells after exposure to pathogen; long-lasting protection; exs. vaccination & infection
Passive immunity
body receives antibodies from another source; temporary protection; exs. injection & mother-to-child transfer
Natural immunity
protection body develops after being directly exposed to pathogen; infection
Artificial immunity
protection body gains through medical intervention; vaccination
Humoral immune response
process in which the body produces specific antibodies to fight a pathogen; macrophage engulfs pathogen → macrophage presents pieces of pathogen to T cells → T cells pass info to B cells → B cells transforms into plasma cells & travel throughout bloodstream to release specific antibodies
Plasma cell
specialized WBCs developed from B cells; produce & release tons of antibodies into bloodstream
Cytotoxic t cell
WBCs that identify & destroy infected cells & cancer cells
IgM (Immunoglobulin M)
type of antibody; pentameter (consists of 5 y-shaped antibody units joined together); good at agglutinating (clumping) antigens
IgG (Immunoglobulin G)
type of antibody; most abundant in the blood; recognize & bind to specific antigens, help neutralize pathogens & enhance their removal
IgA (Immunoglobulin A)
type of antibody; found on surface of mucous membranes; protects these areas by binding to pathogens & preventing entry into the body
IgD (Immunoglobulin D)
type of antibody; primarily attach to B cells & help stimulate them to differentiate (change) into plasma cells
IgE (Immunoglobulin E)
type of antibody; binds to mast cells & basophils, triggers histamine & other chemicals involved in allergic reactions or inflammation to release
Primary immune response
the body’s first reaction to a new antigen; immune system recognizes pathogens & starts producing specific antibodies & memory cells to fight it; takes time to develop but prepares body for faster defense if exposed again
Secondary immune response
body is exposed to the same antigen again; memory cells quickly produce antibodies to neutralize pathogen; faster & stronger immune reaction
Agglutination
AKA “clumping”; process where antibodies cause antigens to clump together → easier for immune system to identify & remove pathogens
Neutralization
when antibodies bind to a pathogen or its toxin & blocks its ability to infect cells or cause harm
Precipitation
when antibodies bind soluble antigens & cause them to form easily removable solid complexes
Autoimmune diseases
disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks & damages the body’s own cells & tissues with antibodies & immune cells
Systematic lupus
autoimmune disease; immune system does the self-attack thing and inflammation spreads across the body; damage to skin, heart, kidneys, & liver
Type 1 diabetes
autoimmune disease; immune system attacks & destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas → lack of insulin & high blood sugar
Rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disease; immune system attacks joint lining → inflammation, pain, swelling, & joint damage that can lead to deformity
Graves’ disease
autoimmune disease; immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland which leads to the overproduction of thyroid hormones → weight loss, anxiety, & nervousness (hyperthyroidism)