Physics - Magnetism, Electromagnets
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a magnet
any material or object that produces a magnetic field. They have a north and south pole
What are the two poles of a magnet?
North pole (N) and South pole (S).
What happens when opposite poles of magnets are near each other?
They attract.
What happens when the same poles of magnets are near each other?
They repel.
Can you separate a magnet's poles?
No. Cutting a magnet gives two magnets, each with a north and south pole.
What is a magnetic field?
The space around a magnet where magnetic forces can be felt.
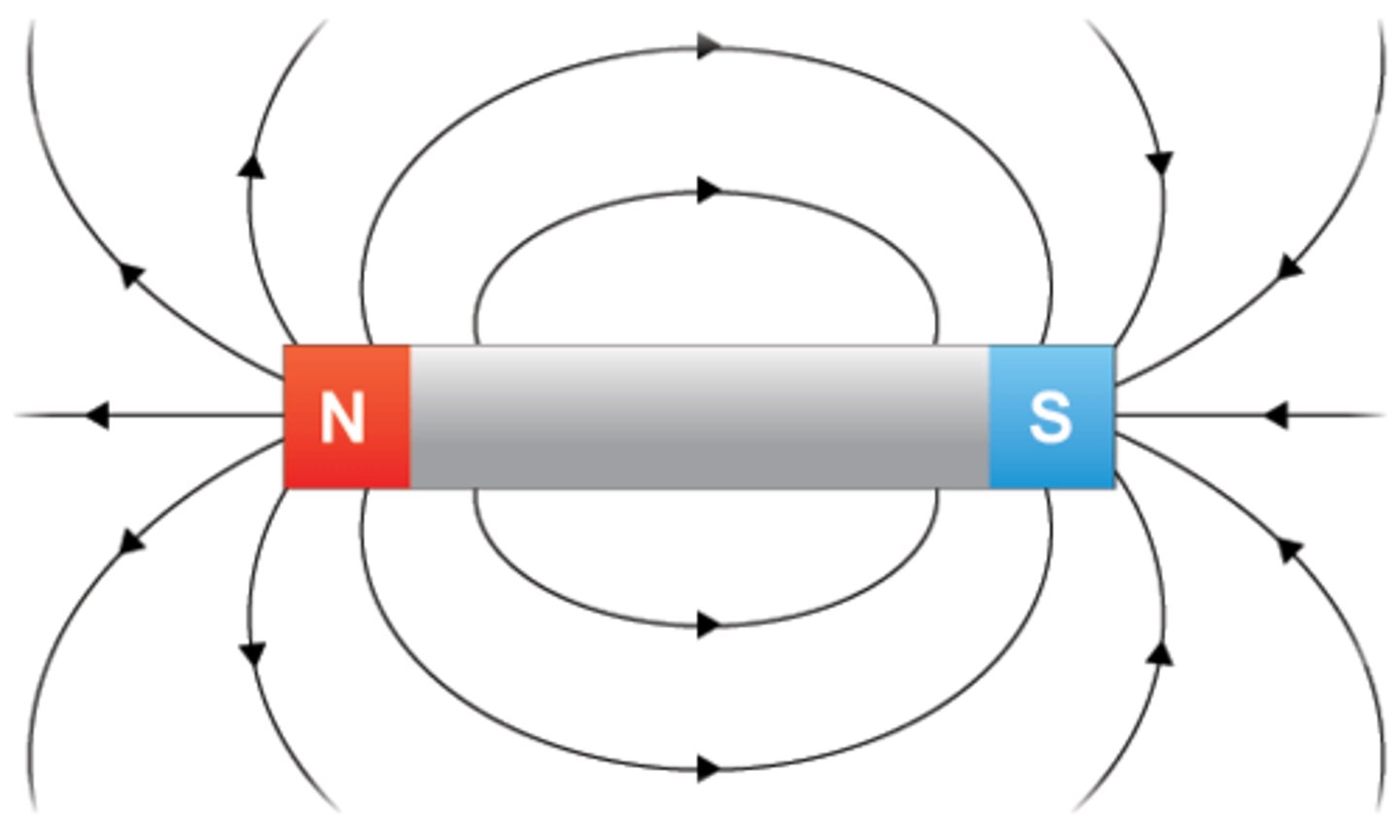
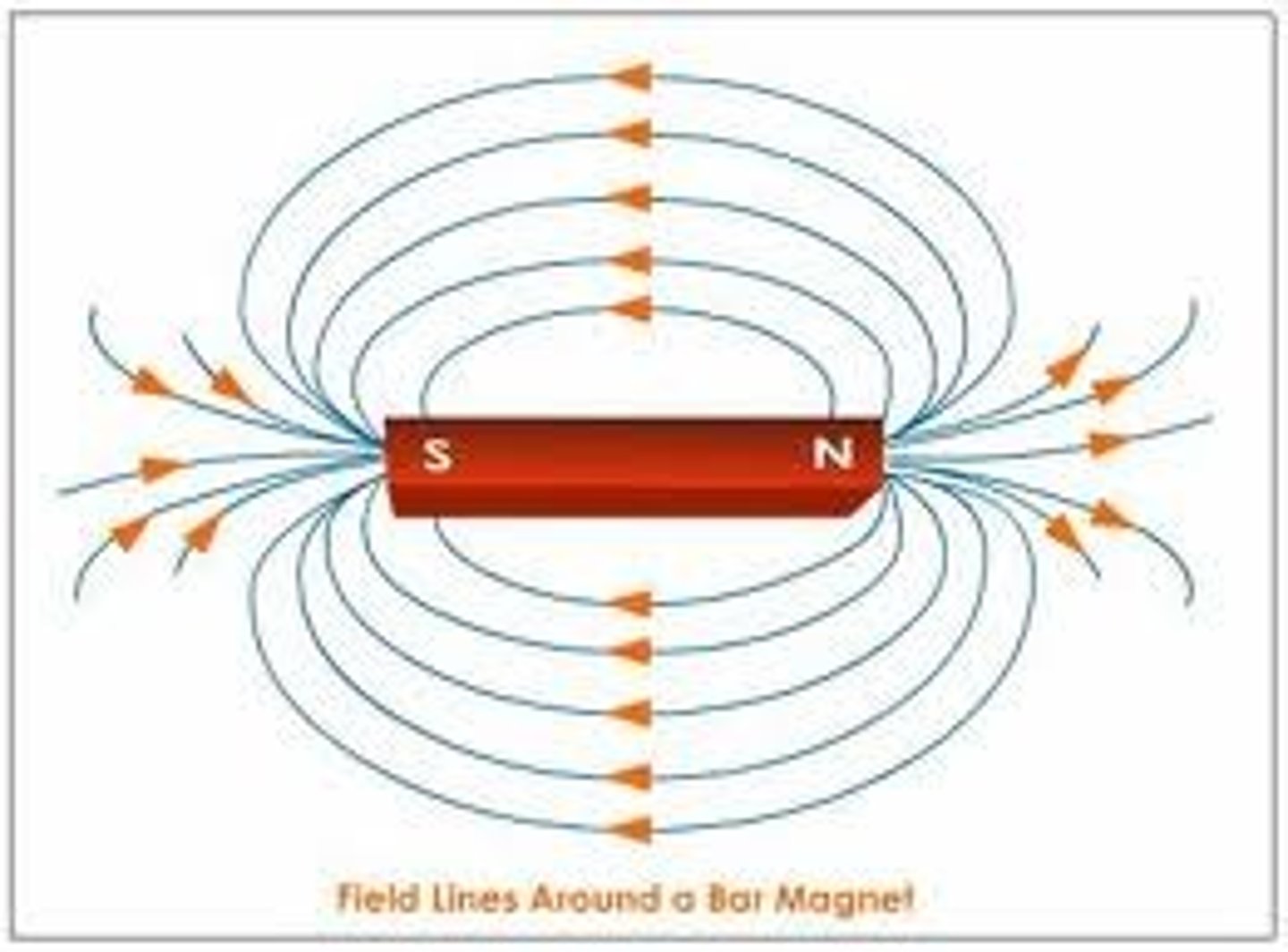
In which direction do magnetic field lines go?
Out from the North pole and into the South pole.
What are magnetic domains?
Tiny regions inside a material where atoms' magnetic fields are aligned, acting like mini magnets.
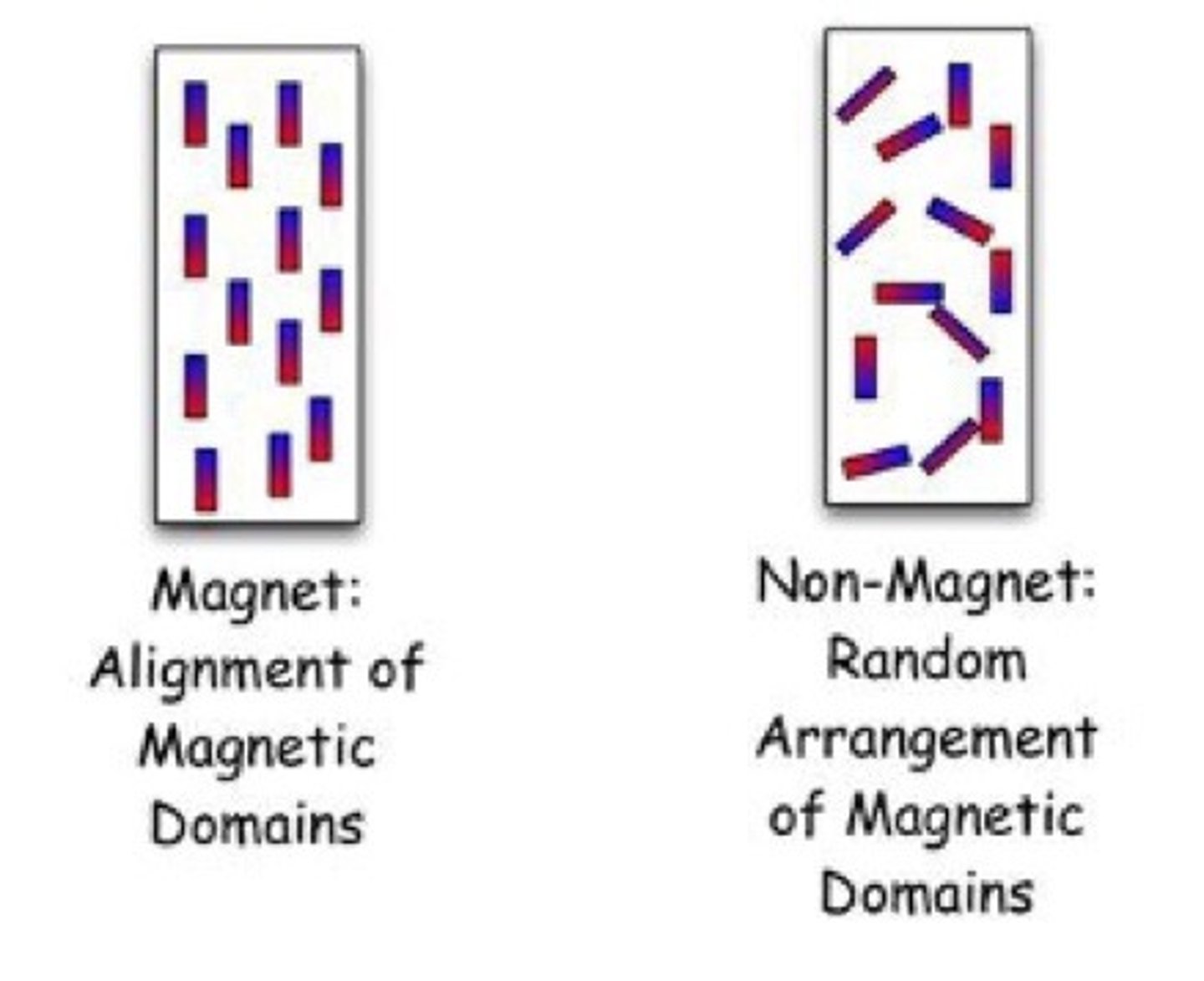
How are domains arranged in an unmagnetised object?
Randomly, cancelling each other out.
How are domains arranged in a magnetised object?
Mostly aligned in the same direction, creating a strong magnetic field.
Which metals are magnetic?
Iron, nickel, cobalt, and steel.
Why can these metals become magnets?
Their atomic structure allows magnetic domains to align easily.
What is a temporary magnet?
A magnet made from soft magnetic material that loses magnetism easily.
What is a permanent magnet?
A magnet made from hard magnetic material that keeps its magnetism for a long time.
How can you magnetise a material?
By aligning its domains using stroking with a magnet or using electricity.
What are the main differences between soft and hard magnetic materials?
Soft iron: easy to magnetise, loses magnetism quickly. Hard steel: harder to magnetise, keeps magnetism longer.
What is an electromagnet?
A type of magnet that only works when electric current flows through a coil wrapped around a core.
How does an electromagnet work?
Current through a wire coil creates a magnetic field, and a soft iron core amplifies it.
How can you increase the strength of an electromagnet?
Increase the current, increase the number of coils, or use a soft iron core.
Give examples of electromagnets.
Cranes lifting metal, electric bells, MRI machines.
Why are electromagnets preferred?
Because you can control the strength using current and switch it on or off
What is a solenoid?
A coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when electric current flows through it.
How does a solenoid work?
Current through the coil creates a magnetic field; if there is a soft iron core, it becomes a temporary magnet.
What is the purpose of a solenoid?
To create a controlled magnetic field, often to convert electrical energy into mechanical movement.
How do solenoids and electromagnets relate?
A solenoid with a soft iron core acts as an electromagnet by aligning magnetic domains.
What happens to the magnetic domains in a soft iron core inside a solenoid?
The domains align with the solenoid's magnetic field, magnetising the core.
What happens when the current stops in an electromagnet or solenoid?
The magnetic domains randomize, and the core loses most of its magnetism.