BIO 101-Chapter 9: Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
conjugation
one bacterial cell uses an outgrowth called a sex pilus to transfer genetic material to another bacterium.
diploid cells (2n)
Cells that contain two full sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.

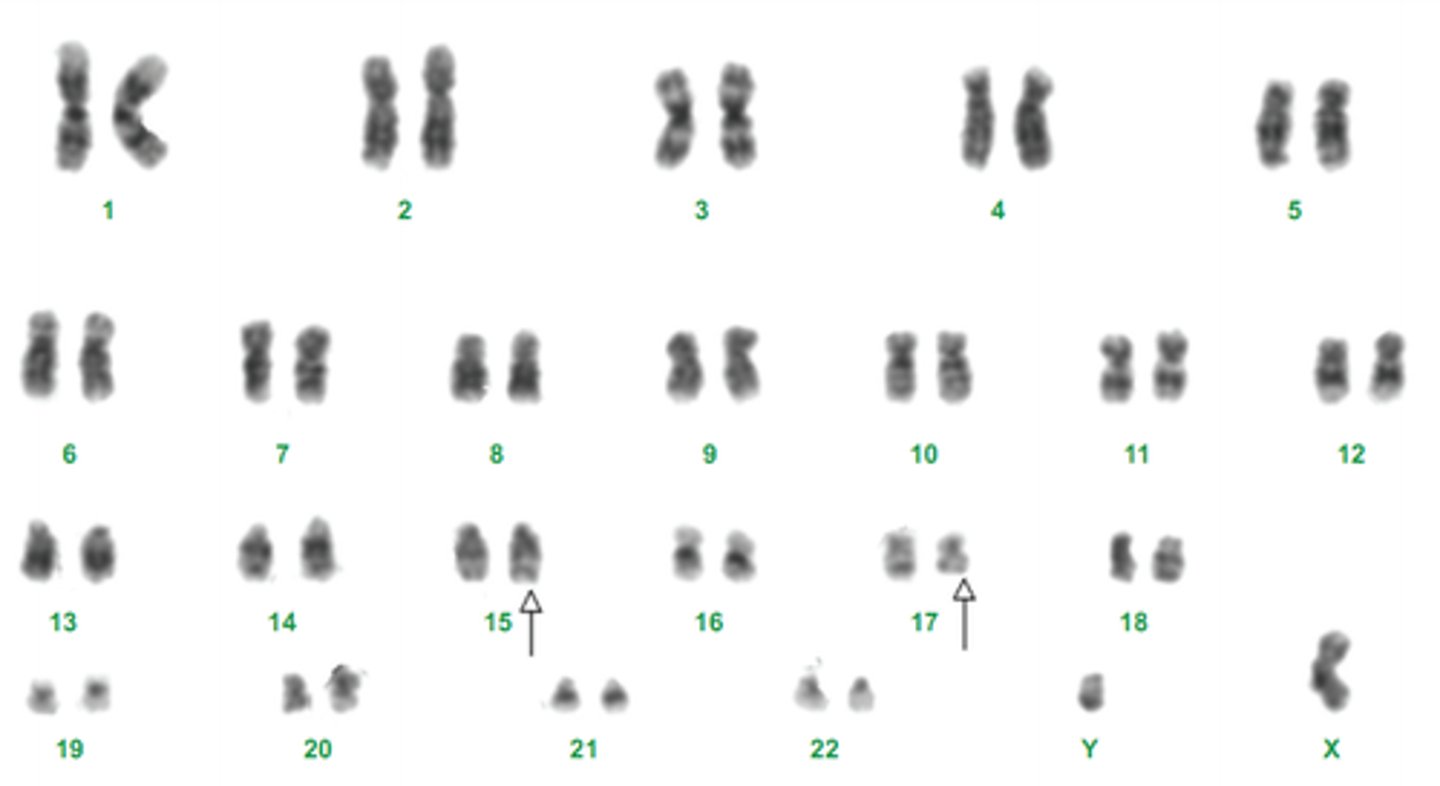
karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
autosomes
Chromosomes that are the same for both sexes.

sex chromosomes
One of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human, contains genes that will determine the sex of the individual.
homologous pair
a pair of chromosomes, one from each parent, that have relatively similar structures and gene values

haploid cells (n)
cells that contain only one full set of genetic information rather than two. Also called gametes.

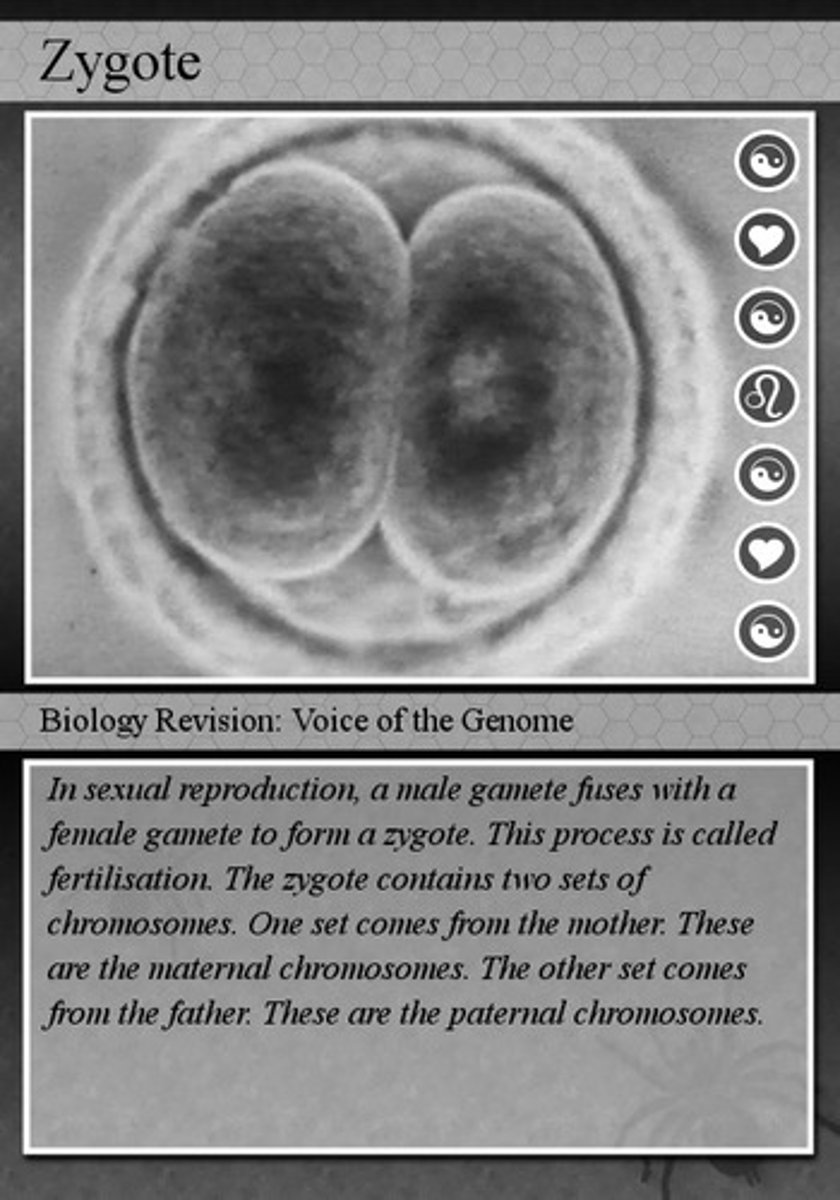
zygote
The first cell of a new organism formed by the union of a sperm and an egg.
meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms

germ cells
Special diploid cells used for reproduction. Produces gametes through meiosis that occur only in ovaries and testes.

somatic cells
All diploid cells that are not germ cells. These cells do not participate direction in reproduction.
interphase
Phase just before meiosis I. DNA replicates. cell produces proteins needed for cell division.

meiosis I prophase I (early)
Chromosomes condense and become visible
meiosis I prophase I (late)
Crossing over occurs. Spindle forms. Nuclear envelope breaks up.
meiosis I metaphase I
paired homologous chromosomes align along equator of cell.
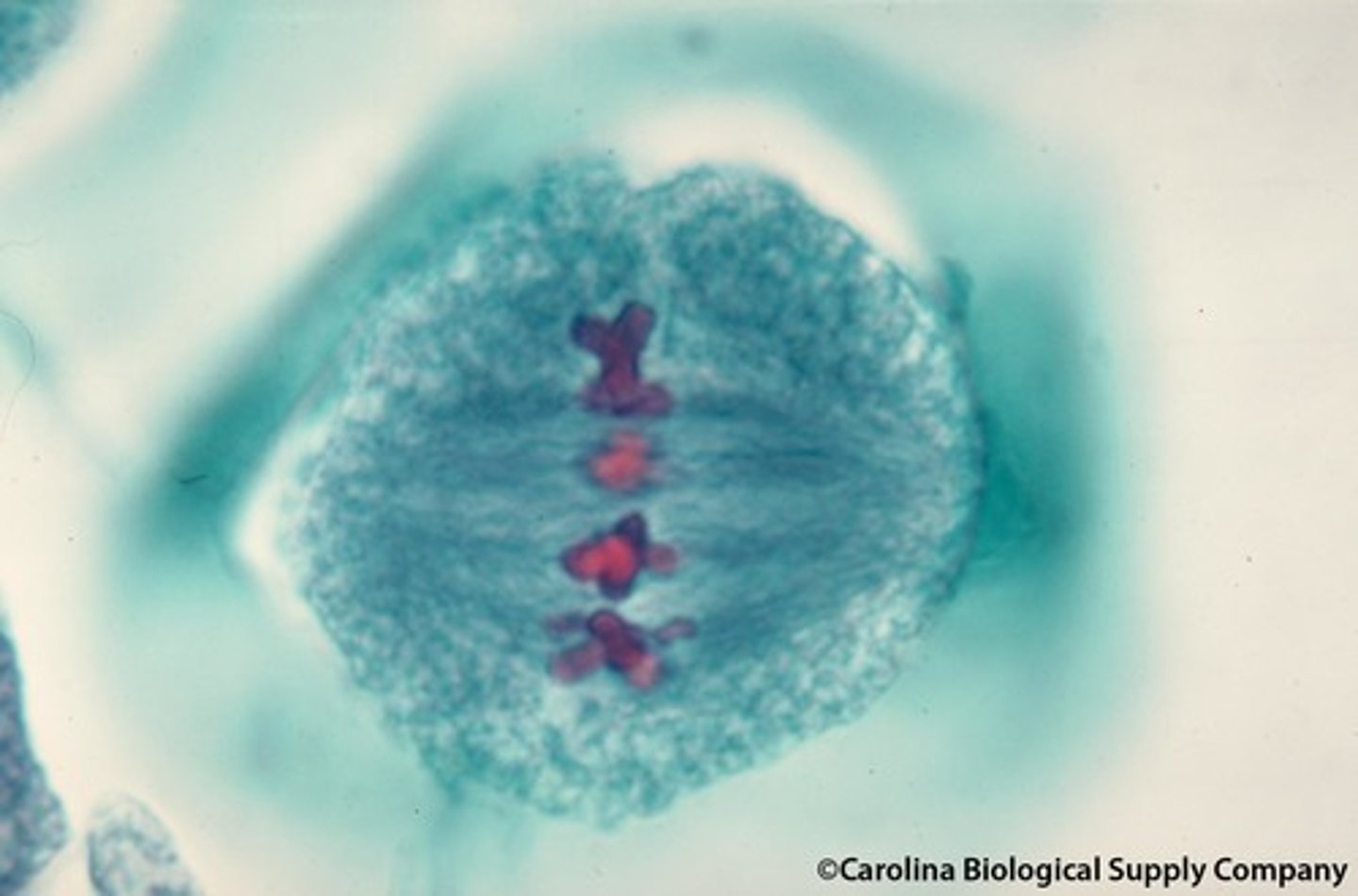
meiosis I anaphase I
homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles of cell sister chromatids remain joined
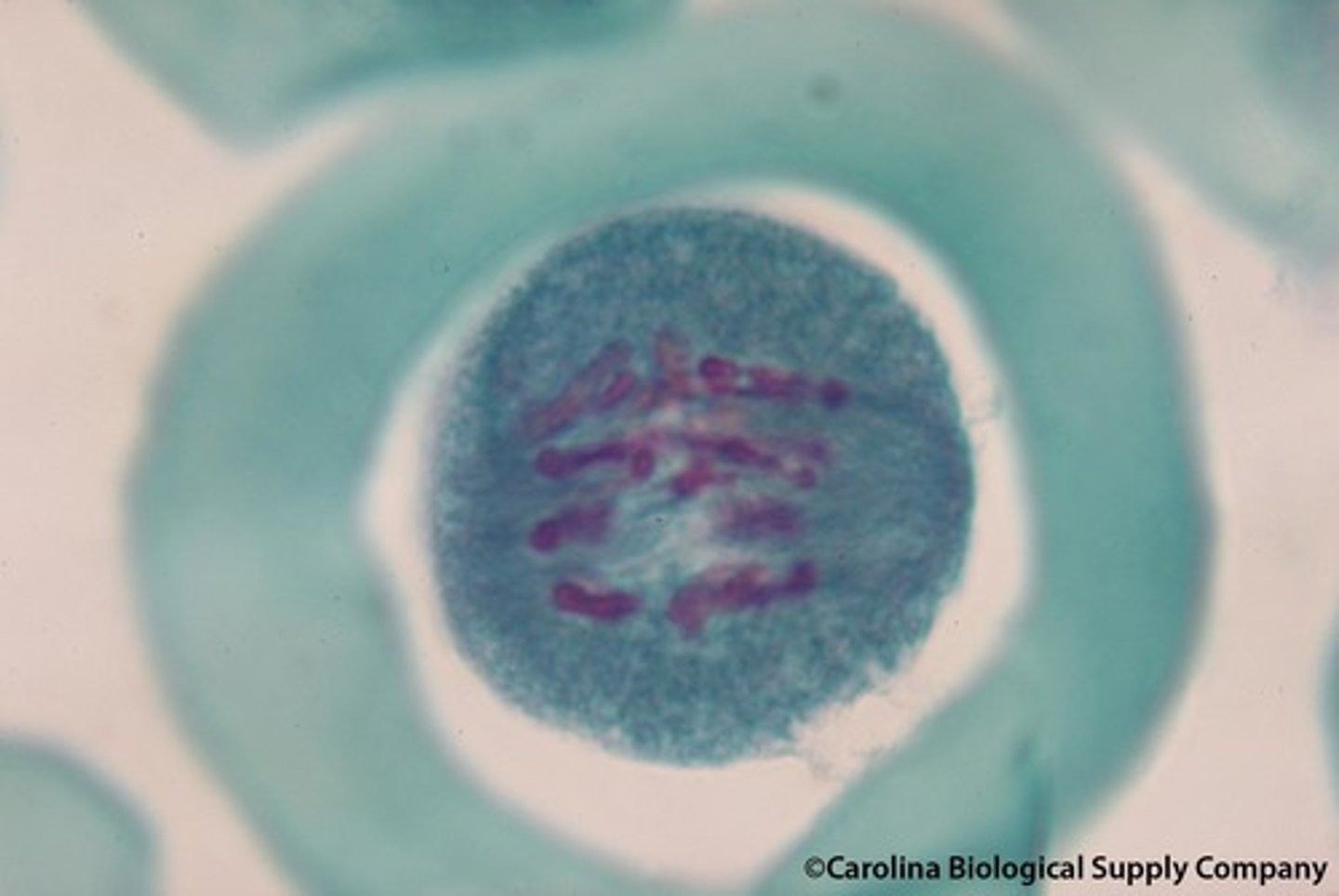
meiosis I telophase I and cytokinesis
nuclear envelopes form around chromosomes which may temporarily decondense. Spindle disappears. Cytokinesis may divide cell into two.
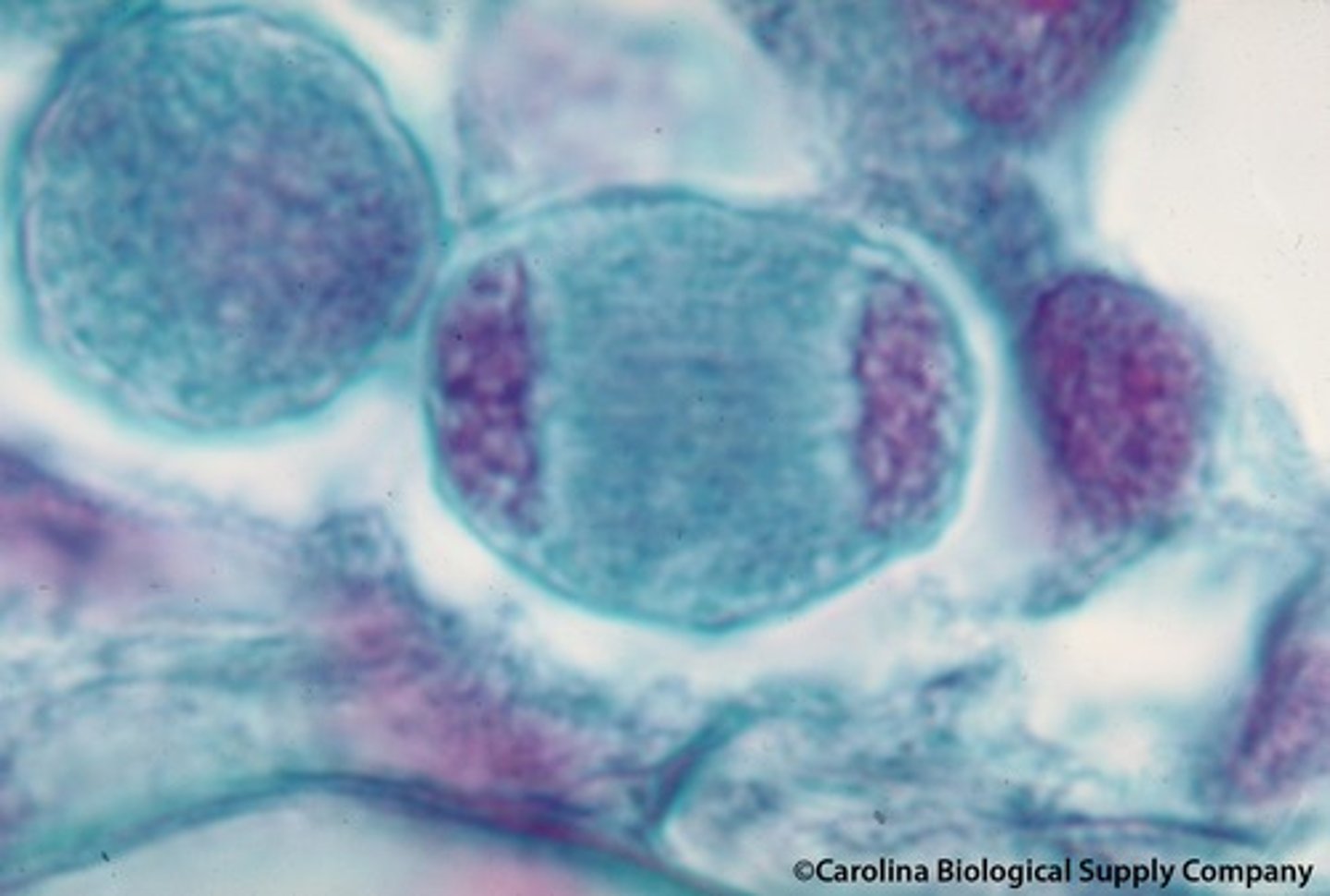
meiosis II prophase II
Spindles form. Nuclear envelopes break up.
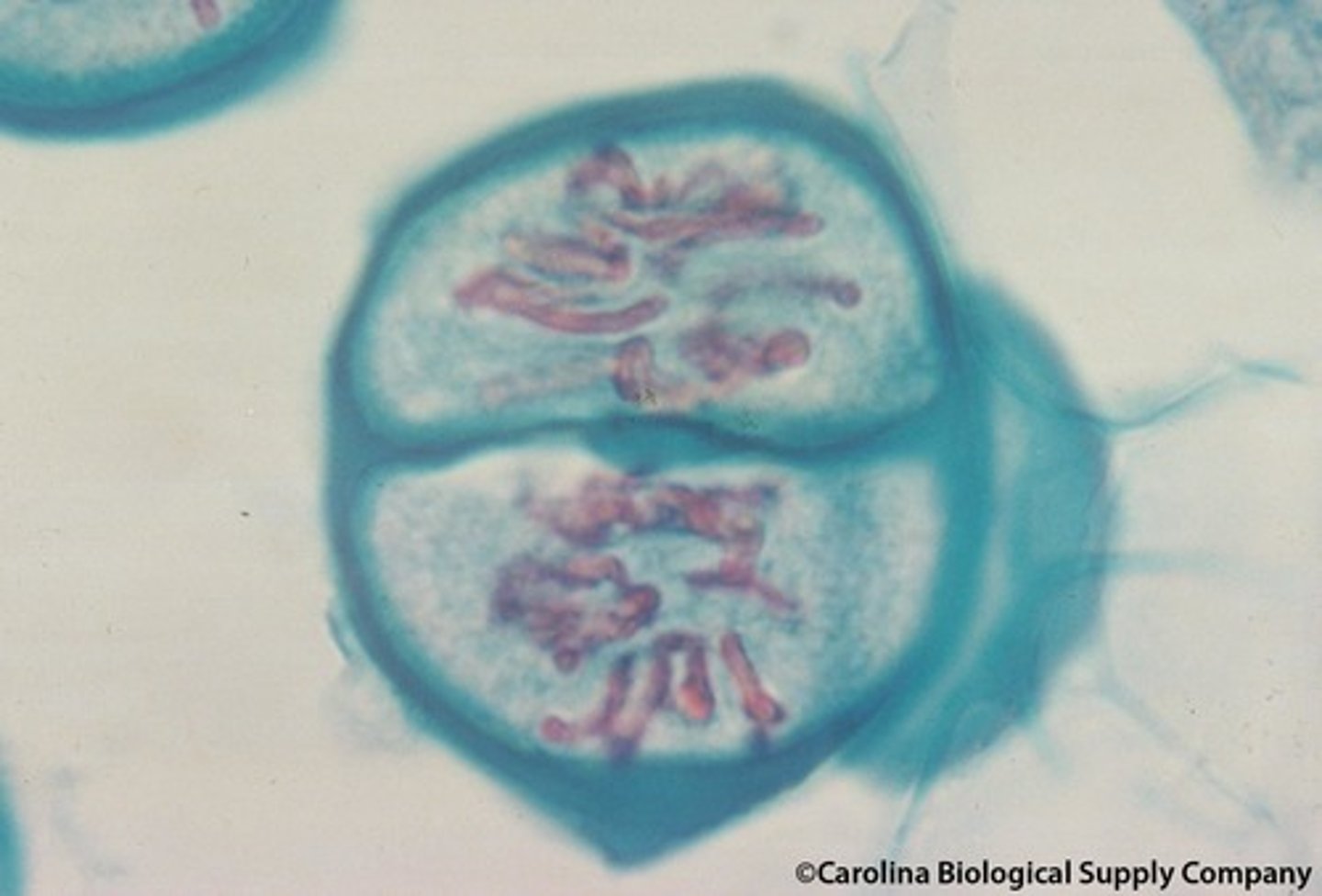
meiosis II metaphase II
chromosomes align along equator of cell
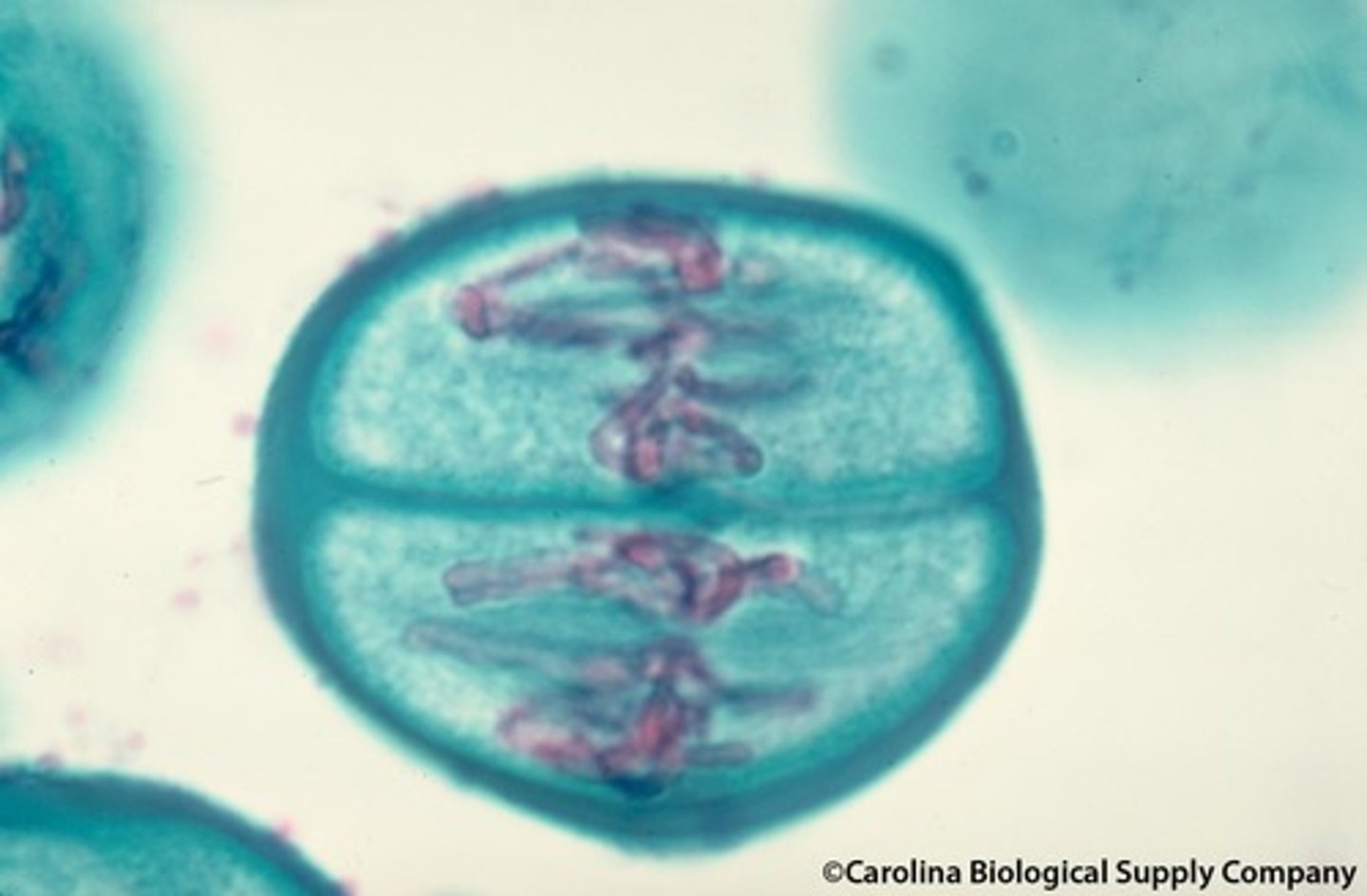
meiosis II anaphase II
centromeres split as sister chromatids separate to opposite poles of cell.
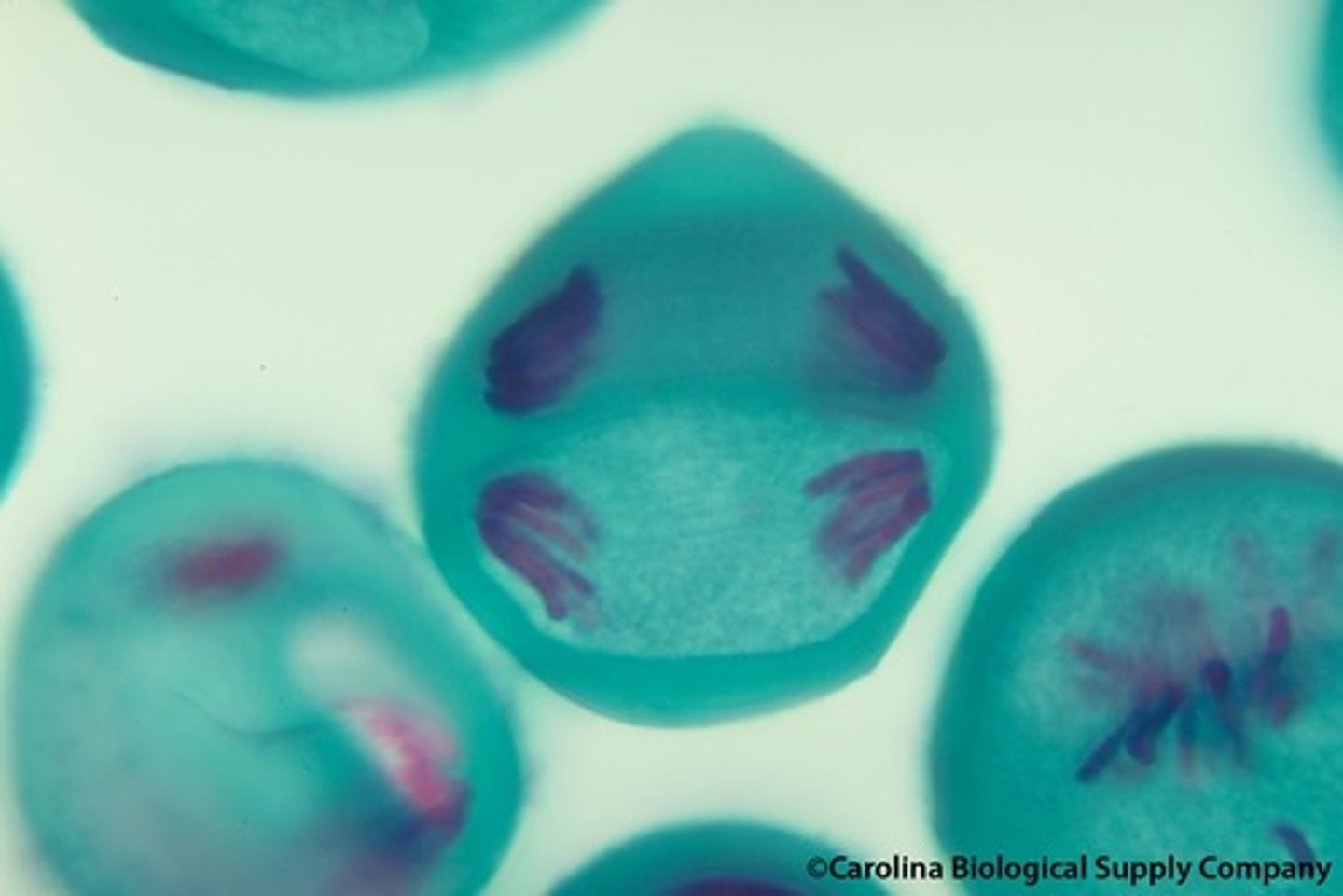
meiosis II telophase II and cytokinesis
Nuclear envelopes assemble around daughter nuclei. Chromosomes recondense. Spindles disappear. Cytokinesis divides cells into four nonidentical haploid daughter cells.
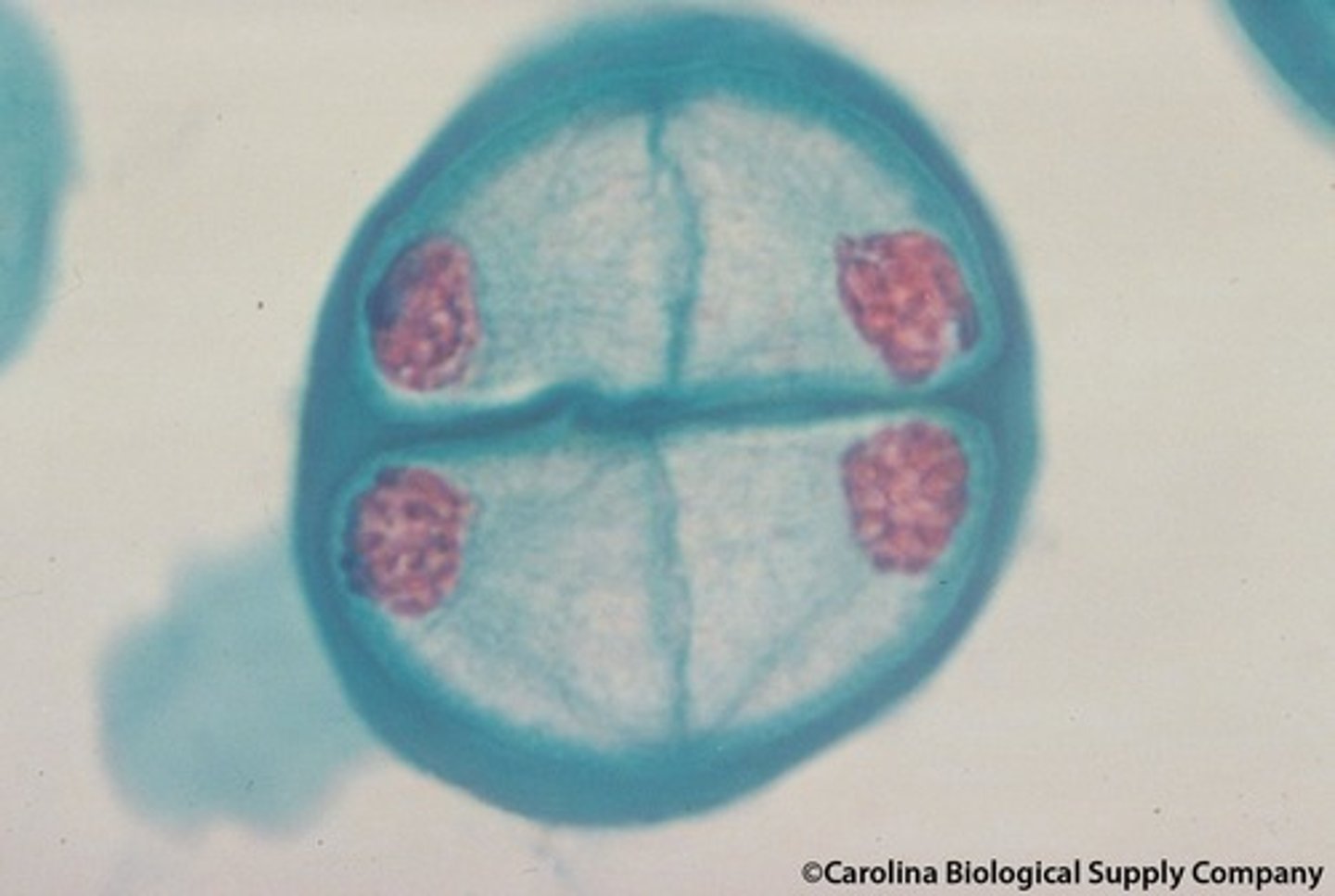
crossing over
A process in which two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material.
polypoid cell
cell with extra chromosome sets

nondisjunction
An error in meiosis that occurs when chromosomes fail to separate at either the first or second meiotic division. The result is a sperm or egg cell with two copies of a particular chromosome or none at all rather that the normal one copy. The resulting zygote has either 45 or 47 chromosomes.
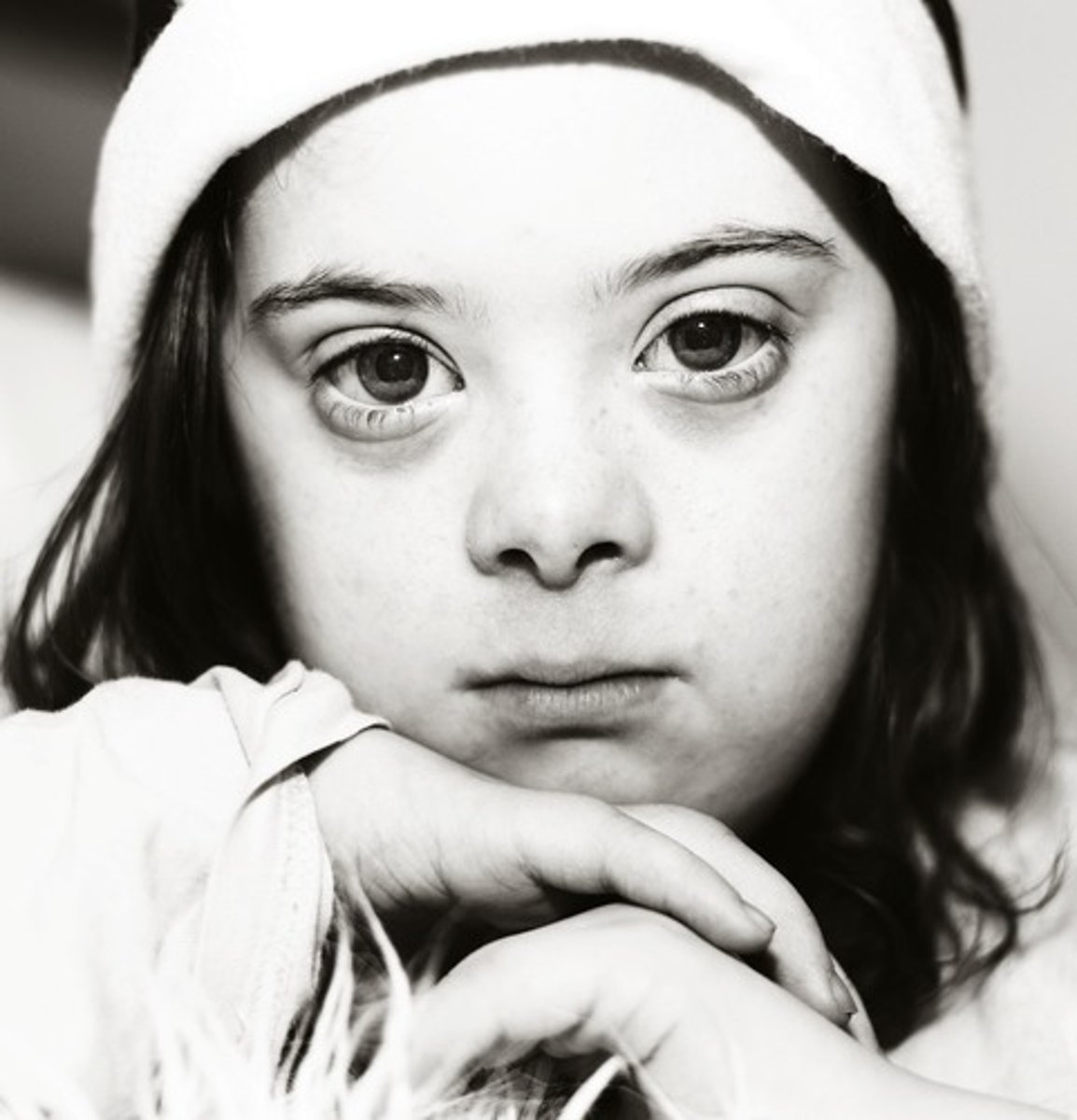

chromosomal deletion
results in the loss of one or more genes. i.e. cri du chat syndrome.

chromosomal duplicaton
produces multiple copies of a part of a chromosome. i.e. fragile x syndrome.
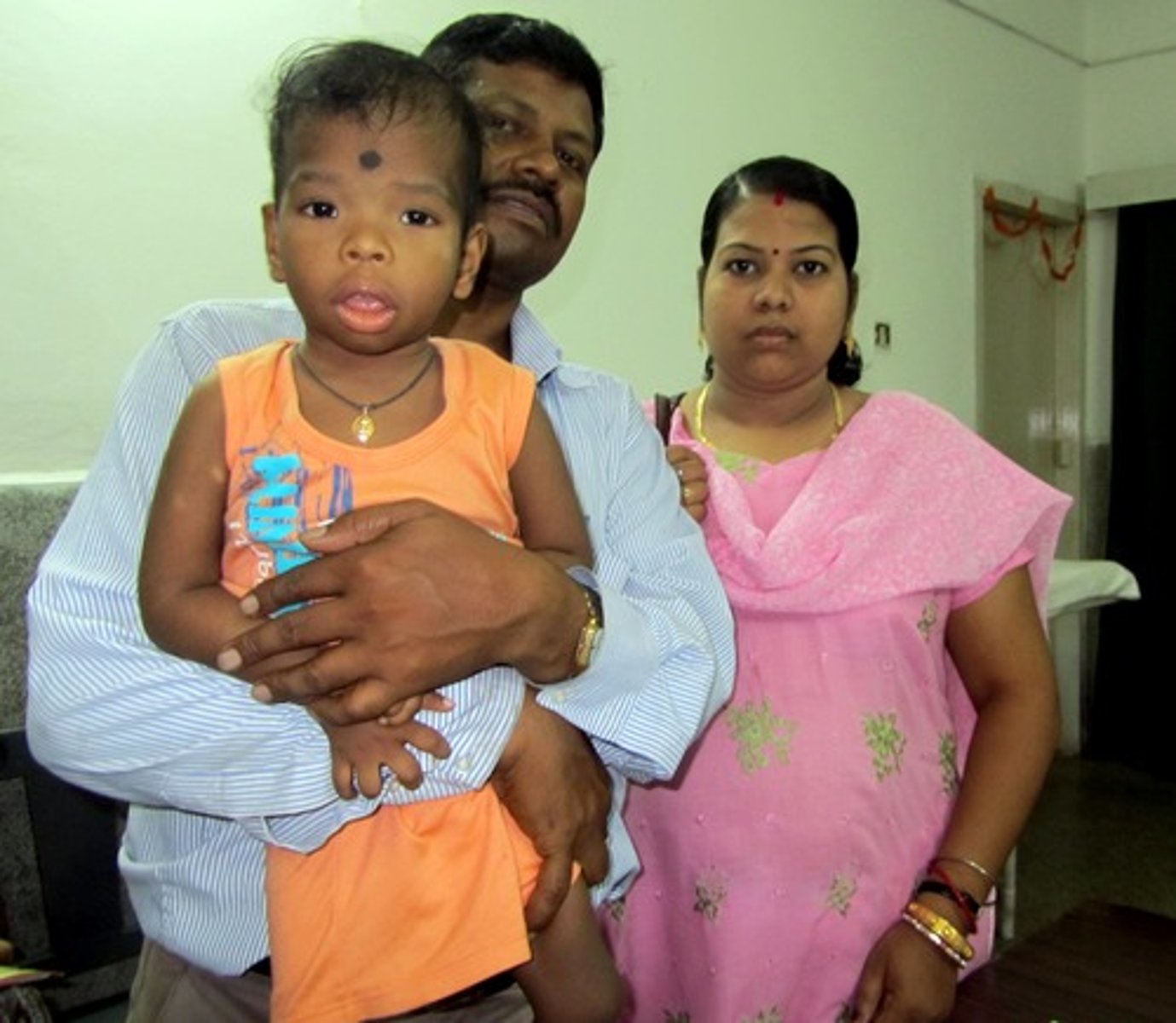

chromosomal inversion
when part of a chromosome flips and reinserts, changing the gene sequence.

chromosomal translocation
when non homologous chromosomes exchange parts.