physics - toppic 5 forces and motion Hookes law + Forces and motion using F=ma
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
scalar
what does it tell us
how are they represented
examples
scalars tell us a magnitude (an amount) of something
tgey are represented by numbers è.g 20 m/s
È.G mass, distance, time, speed
vector
what does it tell us
how are they represented
examples
vectors tell us BOTH the magnitude and direction of something
vectors are represented by numbers and arrows
e.g velocity, acceleration
distance define
ghe distance is something travels us how far it actually goes
displacement define
the displacement ment is how far away something ends up from it’s starting position
equation linking distance, speed and time
Speed(m/s) = distance(m) / time(s)
acceleration define
when things are getting faster or a change in direction
deceleration
is when things get closer
equation linking acceleration, change jn speed and time
acceleration(m) = change in speed(m/s²) / time(s)
other acceleration equation tgat cannot be put in an equation triangle
(final velocity)² - (initial velocity)² = 2 X acceleration X distance
V² - U² = 2 AD
how do you work out … from the acceleration equation
final velocity
distance
initial velocity
V² - U² = 2 AD
V = square root 2AD + U²
D = V² - U² / 2A
U = square root V² - 2AD
displacement time graphs
constant speed
acceleration
stationary
displacement
displacement = whrn goes down it goes to starting point

displacement time graphs
gradient
is the speed
speed = gradient = change in y (distance) / change in x (time)
displacement time graphs
instantaneous speed
if the graph shows a curved line (accelerating) draw tangent at point on curve
gradient of tangent = instantaneous speed
Velocity - time graphs
constant speed
velocity increasing / accelerating
gradient (acceleration)
gradient (acceleration) = change jn y (speed) / change in x (time taken)
force define
a push or a pull that acts on an object (because of an interaction with another object)
define contact force
a force where objects are physically touching e.g air resistance, normal, friction
non contact force define
a force where objects arent physically touching e.g gravity, weight, magnets
define friction
where the contact between two objects resists movement
example of a contact force
define air resistance
where the air particles hitting the object slow down a falling object
a type of contact force
define weight
fall due to the force of gravity
type of non contact force
define magnets
magnets attract objects with magnetic force
type of non contact force
define mass
the amount of matter something contains, measured in kf
mass of an object doesn’t depend on anything else. It is constant
define weight
the force of an object due to gravity, measured in Newtons - because it is a force
weight ig an object isn’t constant - depends on the force of gravity experienced by the object
equation linking weight mass gravitational field strength
weight(N) = mass(kg) x gravitational field strength(N/kg)
weight and mass are…
directionally proportional
centre of mass
where is our centre of mass
where does weight act
when are you less likely to fall
for people our centre of mass is in our torso
weight acts straight downwards from our centre of mass
your less likely to fall if your centre of mass is closer to the ground
how can you change the shape of an object (3)
compressing - two forces activing towards each other → ←
stretching - two forces acting away from each other ← →
bending - two forces balance to hold the object steady. Another force acts to bend the object
what’s the difference between elasticity vs inelastic
elasticity- returns to original shape once force removed
inelastic - remains deformed after force is removed
hooked law
equation linking force, spring constant and extension
force = spring constant X extension
finding the extension of a spring - RP
method
set up equipment by attaching 2 bosses and 2 clamps to a clamp stand, place a heavy weight on the clamp stand (to stop it from falling over), attach a metre ruler and spring to the clamps (the top of the spring must be at the zero point on the metre ruler or otherwise a zero error) and attaching a wooden splint to the bottom of the spring to act as a pointer (pointer must be horizontal or readings will be inaccurate) gs
read the position of the pointer on the meter ruler - this is the un strength length of the spring with no force attached
Then attach a one N wait on the spring and read the new position of the pointer on the meter ruler
Continue adding one Newton weight to the spring I’m reading the position of the pointer
write readings on your table and create a graph
finding the extension of a spring - RP
what does the graph look like (3)
directly proportional
linear (straight line)
spring is elastic because if you remove the weight the extention returns ro 0
finding the extension of a spring - RP
IDC variables
I - weight (N)
D - extention (m)
C - same spring
finding the extension of a spring - RP
equipment
clamp stand
boss
clamp
heavy weight - stops stand from falling over
metre ruler - is vertical (as reading will be inaccurate otherwise)
spring
wooden splint (used as a pointer) - is vertical as otherwise it will be innacurate
newton weights
what is the spring constant on hooks law
what is the relationship between extension and weight
the gradient → change in y. (extinction) / change in x (weight)
directionally proportional
limit of proportionality
amount of force that will inelastically deform a spring
newtons 2nd law equation
Force(N) = mass(Kg) X acceleration(m/s²)
Newtons 2nd law-RP
method
the trolley is attached to a string on the runway
as you add more and more mass to the weight hanger the trolley moves faster
as the trolley passes the light gate it measures the acceleration and shows on the data logger so wr don’t have to measure
repeat 3x and find a mean
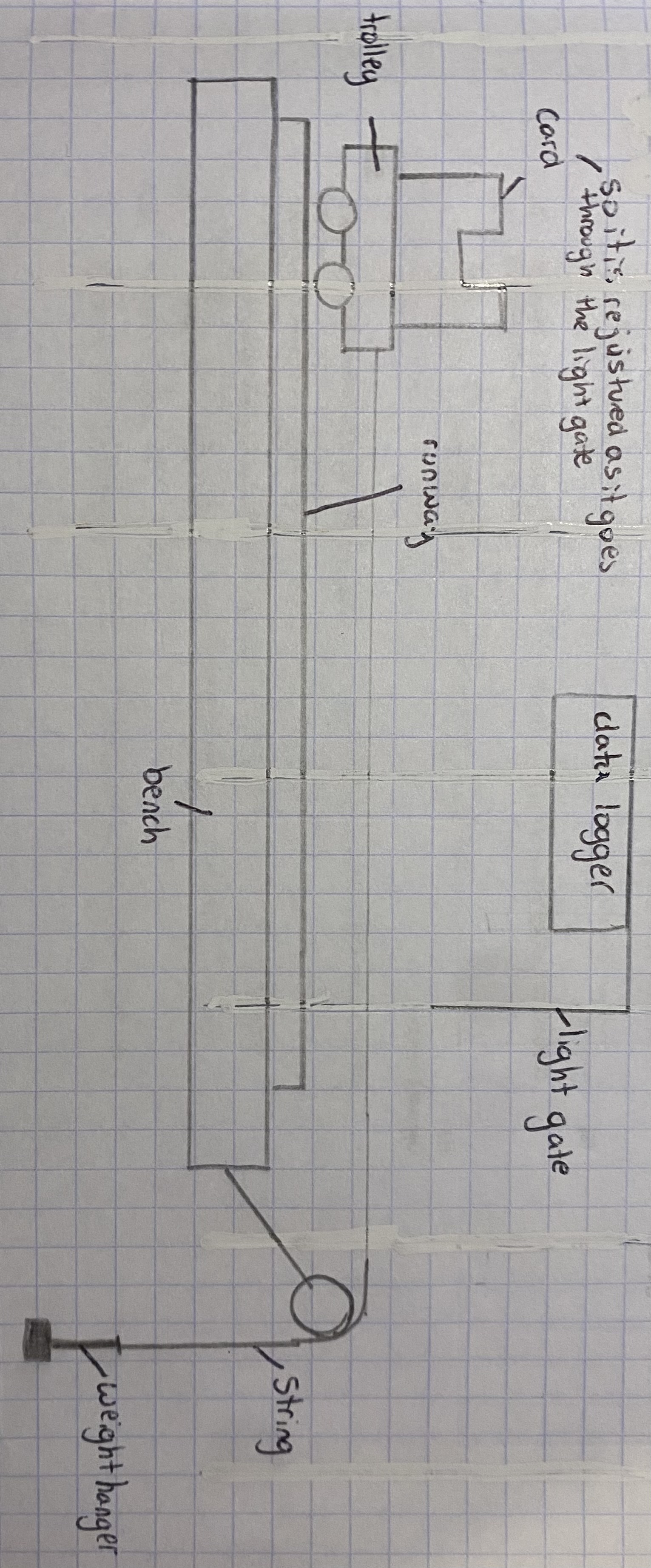
Newtons 2nd law-RP
equipment
trolley
runway
bench
weight hanger
string
card - so it is rejusted as it goes through the light gate
data logger
light gate

Newtons 2nd law-RP
IDC variables
I - mass
D - acceleration
C - the same trolley, other equipment
what’s the relationship between force and acceleration
directionally proportional
define work
a force causes energy to be transferred into an object
can be measured in Joules (is energy transfer) but can sometimes be measured in Newton Metres
Energy transfer
when a change in height happens there has been a change to the gravitational energy store
when a change in speed happens, there has been a change to the kinetic energy store
equation linking work done, force applied, distance moved
work done W (J or Nm) = force applied F (N) X distance moved s (m)
stopping distance define
the distance a car travels between seeing something that makes it need to stop and actually stopping
stopping distance (how far we travel before we stop)= thinking distance (how far you travel BEFORE hitting the brakes)+ braking distance(distance travelled AFTER vrakes have been pressed)
factors affecting breaking distance (6)
road/weather condition
weather condition - an incy wet road wold have a larger breaking distance than a dry road as it is more slippery
tyre condition/age - older tyres =less grooves →less friction inc braking distance
condition/age of cars brakes - car with older brakes/worse condition wont break as effectively
speed - car going faster will have more momentum + will be harder to stop
mass of vehical - heavy lorry will be harder to stop than a light weight smart car
Factors affecting thinking distance (5)
distraction - loud music, conversation, PHONE
drugs/alcohol - impairs judgement + lengthens reaction time/caffeen would improve
speed of driving
tiredness
age
whats the force that is brought down by gravity
weight
terminal velocity
the top speed a falling object can reach
what jappens between when a skydiver falls drom a plane to being on the ground
sky diver leaves plain - sskdiver is speeding up quickly - more weight than air resistance
bit later - skydiver is still speeding up but less than before - air resistance increases as he gets faster
later still - sky diver is going at constant speed - ai resistance and weight are balanced
skydiver opens parachute - sky diver starts slowing down - air resistace is greater than weight
some time later - sky dver is going at a constant speed (terminal velocity) forces are balanced
skydiver has landed - sky diver is stood still/stationary - normal force and weight are balanced