Lesson 5: Introduction to Statistics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Biostatistics
science that studies biological phenomenon from a quantitative point of view
What is a sample?
-sample is a subset of the population to which we have access
-on which we make observations (measurements).
-should be “representative”
-consists of selected members of the population
Groups of health statistics
Demographic, vital, morbidity, resource, services
Descriptive statistics
describe and/or characterize a group of data.
Inferential statistics
draw conclusions about general situations beyond the set of data obtained.
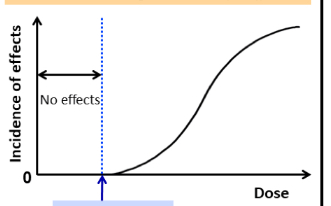
Deterministic
-no variation in result
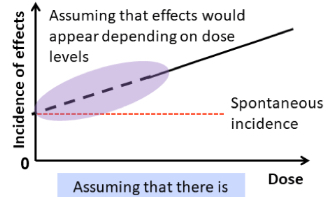
Stochastic
-different outcomes
Clinical epidemiology
Study of variations in disease outcomes and the reasons that lead to them.
What is the first health professional to apply the epidemiological method systematically?
John Snow, applied the method to cholera epidemics (London 1853–1854).
What are the two phases of the epidemiological method?
Descriptive Epidemiology: who, where, when
Analytical Epidemiology: how and why (tests hypotheses, quantifies associations)
Population
it is the set about which we are interested in drawing conclusions
What are the types of populations?
Finite (small), infinite (huge), real, hypothetical (do not but could exist).
Random sampling types
Simple random, systematic, stratified, cluster sampling.
What is non-random sampling?
Sampling chosen for convenience; high likelihood of bias (systematic error).
What is a variable?
An observable characteristic that varies among individuals; any measurable characteristic
What are qualitative variables?
Variables whose values cannot be associated with numbers.
Examples: sex, race, religion, civil status, level of academic studies.
Nominal
-Not not orderable
For ex: Sex, blood type, religion
Ordinal
-Orderable
-Pain intensity, level of disease
What is a dichotomous variable?
A qualitative variable that can only present two values (e.g., man/woman).
What is a polytomous/multichotomous variable?
A qualitative variable with multiple possible values
What graphs are used for qualitative variables?
• Bar diagrams — height of bar proportional to absolute or relative frequency; also used for discrete variables.
• Sector diagrams (pie, polar) — do NOT use with ordinal variables; area proportional to frequency.
• Pictograms — easy to understand; area of each symbol must be proportional to frequency.
What are quantitative variables?
Can be measured with numbers
Examples: number of children, age, weight, number of blood cells.
What are continuous variables?
Not entire numbers
(e.g., age, weight, height, blood pressure, cholesterol).
What are discrete (discontinuous) variables?
Variables that assume only whole values within a numerical scale (e.g., number of teeth, number of children, gestations, births).
What graphs are used for discrete variables?
Bar diagrams, leaving a gap between bars to indicate impossible values.
What graphs are used for continuous variables?
Histograms; the area under the histogram between two points indicates the number or percentage of individuals in that interval.
What are independent variables?
Variables that determine or cause the effect (dependent variable). They are risk factors.
What are dependent variables?
Variables that depend on independent variables; they represent diseases.
What is a confounder variable?
A variable that influences the effect (disease) but is not one of its causes.
What are controlled variables?
Variables kept constant to avoid affecting the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
FREQUENCY MEASUREMENTS
What is a frequency table?
A frequency table is a table where data are grouped by categories or values and the number of times each appears is recorded.
Absolute frequency
number of individuals in each modality
Ex: women with 2 children: 375
Relative frequencies (percentages)
divided by the total
Ex: women with 2 children: 24,7 % of tota
Cumulative frequencies
What percentage of individuals have fewer than 3 children
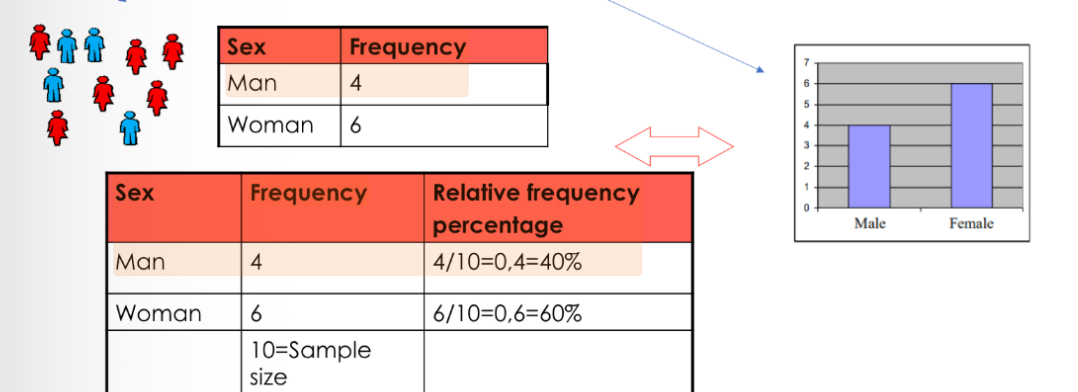
Frequency table
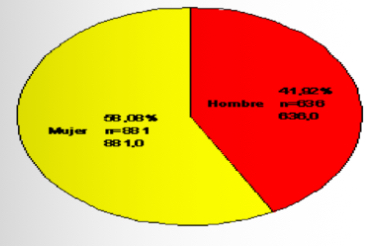
Pie chart

Pictogram
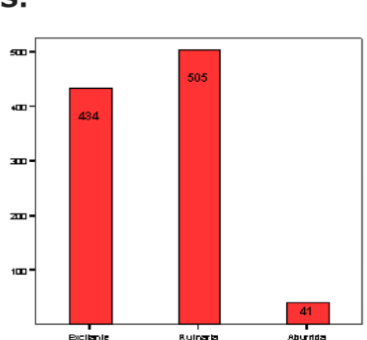
Bar chart
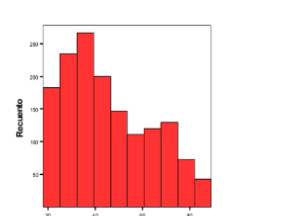
Histogram
Point cloud