9.3 Transpiration
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Transpiration
Loss of water vapour from leaves & stems of plants
Inevitable consequence of gaseous exchange
Transpiration Stream
Movement of water from roots to leaves
What happens when stomata are open?
CO2 & O2 exchanged
Water moves out
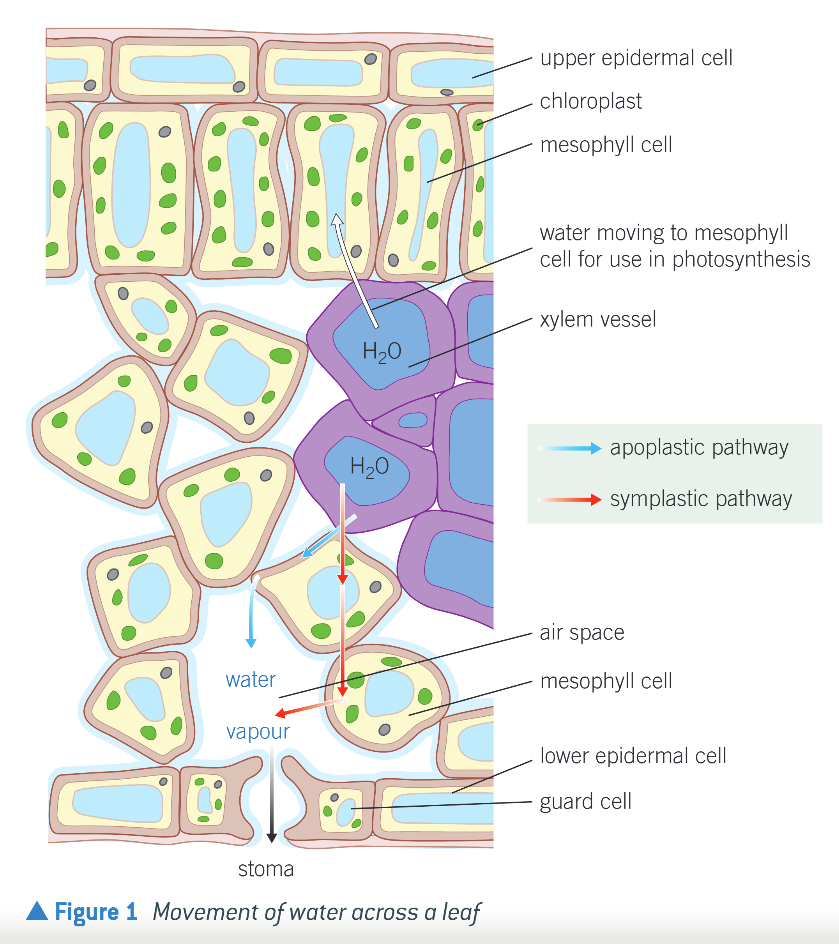
Transpiration Stream - How it Works
Water evaporates from surface of mesophyll cells into air spaces in leaf & move out of stomata into surrounding air by diffusion down conc. gradient
Loss of water by evaporation lowers water potential of cells, so water moves into cell from an adjacent cell by osmosis, along BOTH apoplast & symplast pathways
Is repeated across leaf to xylem
Water moves out of xylem by osmosis into cells of leaf
Adhesion and trasnpiration
Water molecules form hydrogen bonds w. carbohydrates in walls of narrow xylem vessels
Cohesion and transpiration
Water molecules form hydrogen bonds w. each other & so tend to stick together
What do the combined effects of adhesion & cohesion result in?
Water exhibiting capillary action
Capillary action of water
Process by which water can rise up a narrow tube against the force of gravity
Transpiration pull
Water is drawn up xylem in continuous stream to replace water lost by evaporation
Results in a tension in xylem, which helps to move water across roots from soil
Transpiration Stream
Water moves by osmosis across membranes and by diffusion in apoplast pathway from xylem thru cells of leaf
Evaporates from freely permeable cellulose cell walls of mesophyll cells in leaves into air spaces
Water vapor then moves into air thru stomata along diffusion gradient
Rate of water uptake
Distance moved by air bubble / time taken for air bubble to move
Factors affecting transpiration (5)
Light (increasing gives high no. of open stomata, increases rate)
Relative humidity (high = lowers rate due to reduced water vapor gradient)
Temperature (increases rate)
Air movement (Increases rate)
Soil-water availability (If soil dry, transpiration rate reduced)
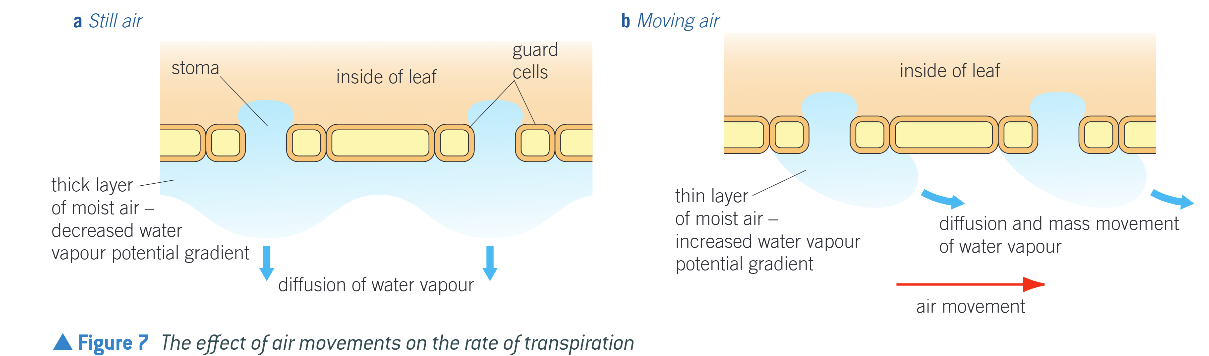
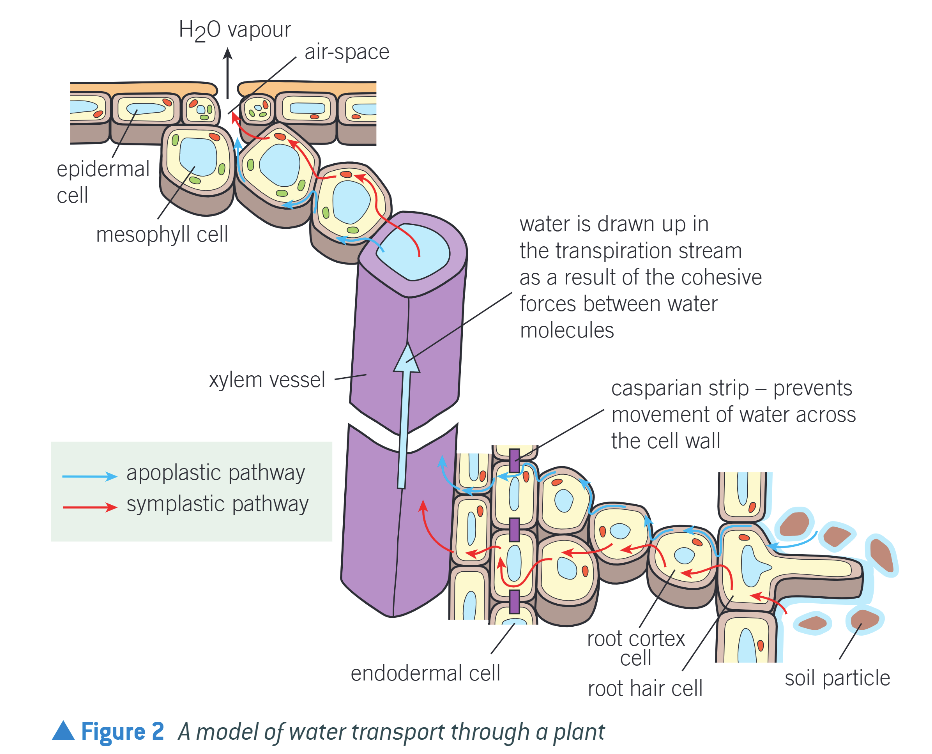
Cohesion & Tension (Transpiration)
Allow mass flow of water over long distances up the stem
Water evaporates from leaves (transpiration)
Creates tension, pulling more water into leaf
Water molecules are cohesive, so when are pulled into leaf, others follow
Whole column of water in xylem moves upwards
(Adhesion helps water rise up as water molecules attracted to walls of xylem vessels)
Evidence for cohesion-tension theory
Changes in diameter of trees
During day, transpiration & tension in xylem vessels lowest, diameter shrinks
Night, transpiration & tension in xylem vessels lowest, diameter increases
When xylem vessel broken, air drawn in, plant can’t move water up stem, cohesive forces broken
How to measure water uptake of plant
Using potometer
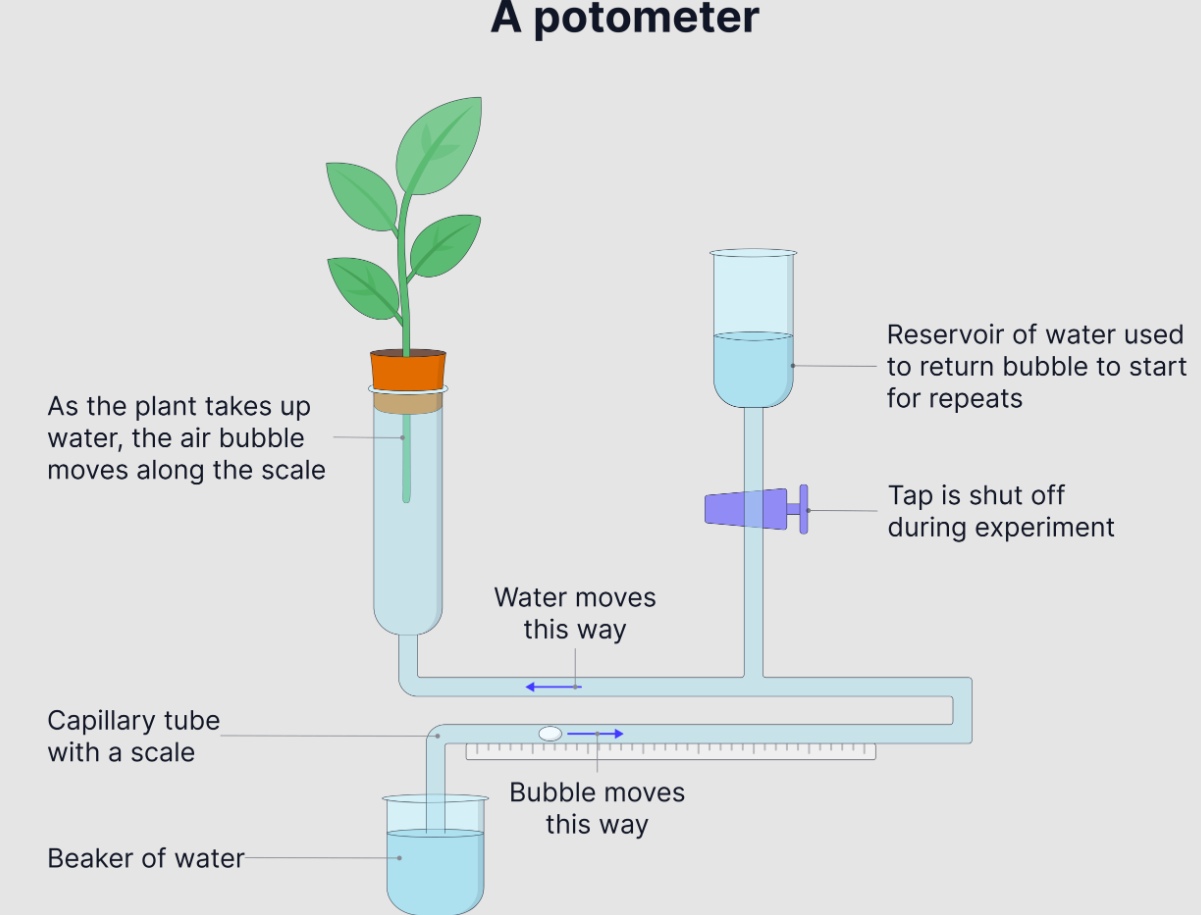
Why do you cut the shoot underwater and slanted?
To prevent air bubbles in xylem
Slant to increase SA available for water uptake
Why do you assemble the potometer underwater?
So no air enters stem
Using the potometer

Equation for rate of water uptake
Distance moved by air bubble / time for air bubble to move
Units = cm s-1