Basal Ganglia
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
motor modulation
cortex → basal ganglia → thalamus → cortex
where do the basal ganglia and cerebellum receive signal from?
the cerebral cortex
they do not directly deal w spinal cord
Striatum
putamen + caudate
putamen looks like an egg, caudate is a C shape
main components of the basal ganglia
caudate nucleus
putamen
globus pallidus: external and internal
subthalamus
substantia nigra
substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr): neuron contain GABA send to thalamus
substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc): neuron contain dopamine and send to striatum
direct pathway
pro movement
SNc releases dopamine → activates the D1 receptors @ striatum → inhibit the indirect pathway thru D2 receptor → excite the thalamus
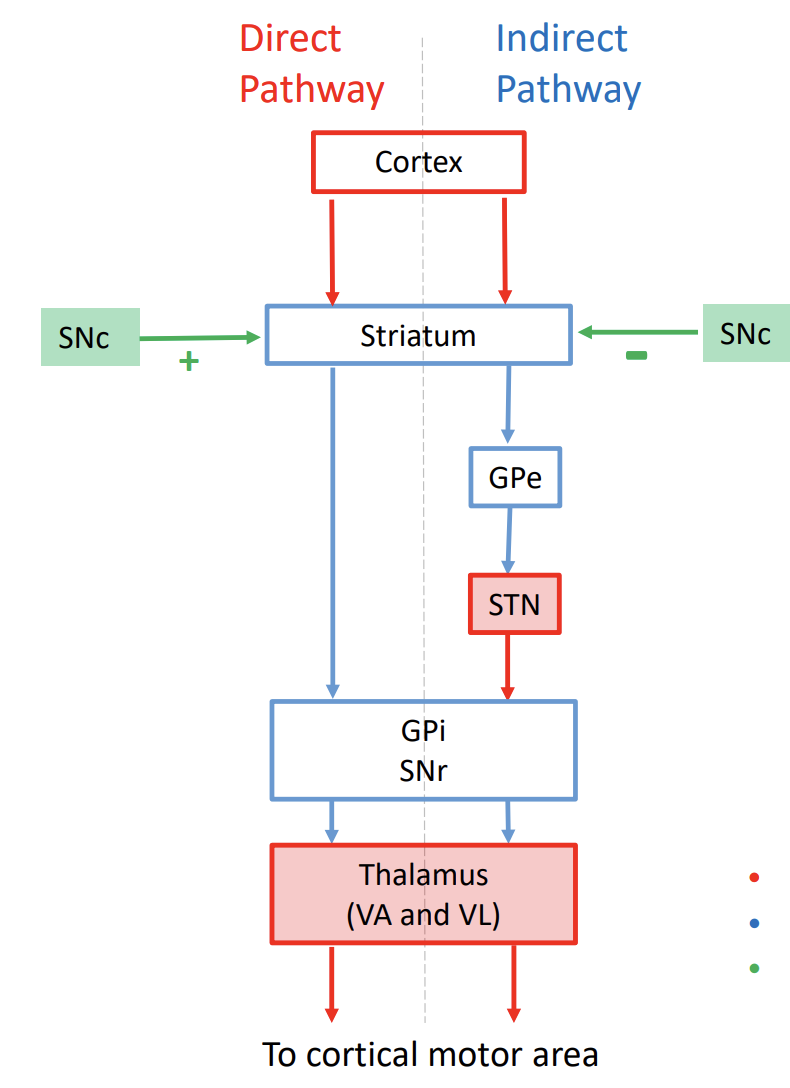
indirect pathway
anti movement
NO dopamine from SNc → inhibit the thalamus
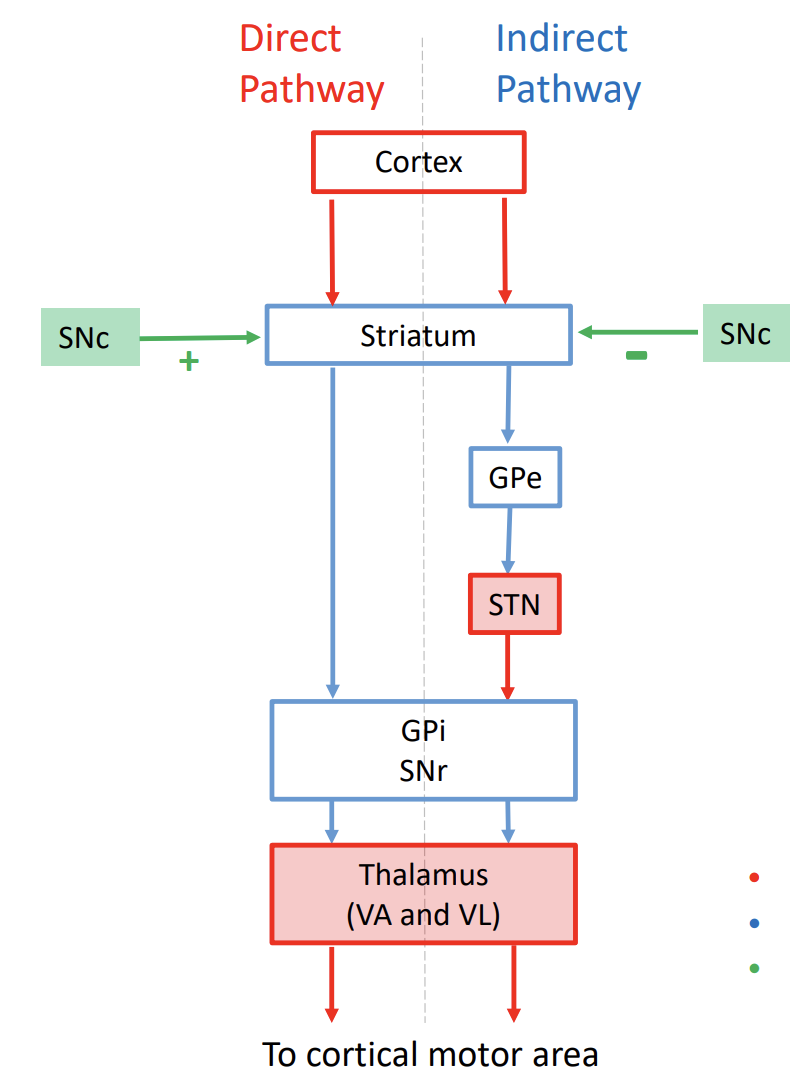
Parkinson’s disease
indirect pathway
degeneration of the SNc → inhibit thalamus → difficulty w initiate movement
Hemibolism
indirect pathway problem
result from a stroke → subthalamic nucleus is affected → inhibition process is damaged → involuntary movement
Huntington’s disease
caudate and putamen degeneration - genetic disorder
early stage: affect indirect pathway → uncontrolled movement
later stage: affect direct pathway → movements slow down (Parkinson’s like symptom)