Advanced Review of Pathology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Goals

How to approach a pathologic findings

Benign vs Malignant

Radiographic patterns to know
Periapical abscess, granuloma, cyst
inflammatory RL lesions
all periapical RL linked with non vital teeth=necrosis
can’t definitively differentiate radiographically
radiographic tendencies (not diagnostic)
abscess-PDL widening, diffuse borders
granuloma-small, well defined RL
cyst-larger, may show corticated border
diagnosis requires clinical tests (vitality testing) and/or biopsy
Dentigerous cyst
Developmental/odontogenic RL lesions
RL attached at CEH of an unerupted tooth
well defined, often corticated
displaces teeth
most common with mandibular 3rds and maxillary canines
Lateral periodontal cyst
Developmental/odontogenic RL lesions
RL between roots of vital tooth
well circumscribed
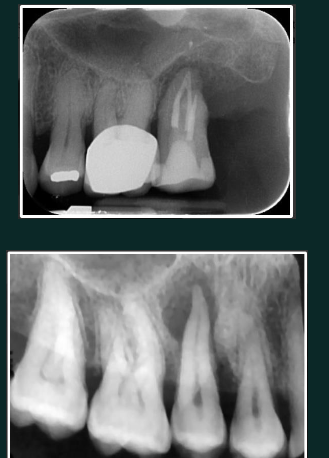
Odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
Developmental/odontogenic RL lesions
well defined RL
smooth borders, scalloping may occur between roots
can be uni or multiocular
strong preference for posterior mandible
high recurrence rate
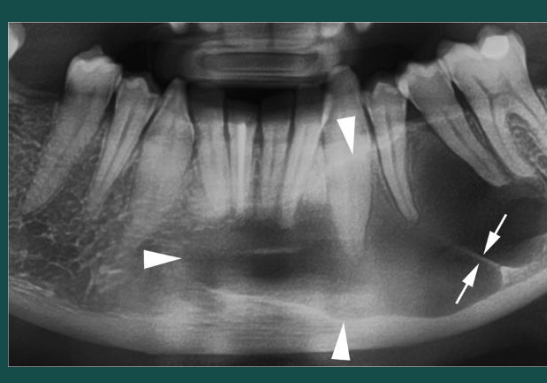
Simple bone cyst (traumatic bone cyst)
Developmental/odontogenic RL lesions
scallops between roots
vital teeth
uniocular RL
rarely any resorption or displacement of adjacent teeth
unlike OKC, SBC is NOT corticated or expansile
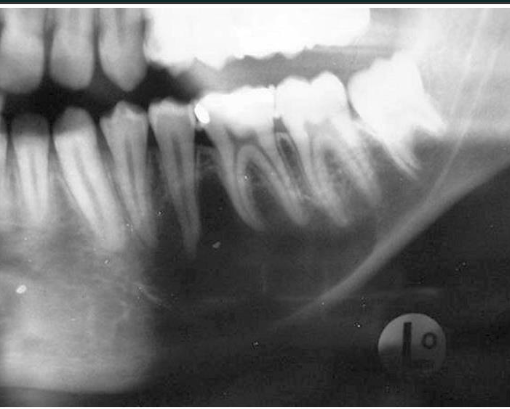
Ameloblastoma
neoplastic RL
multiocular “soap bubble” or “honeycomb”
may look uni when small
cortical expansion + thinning
aggressive but benign
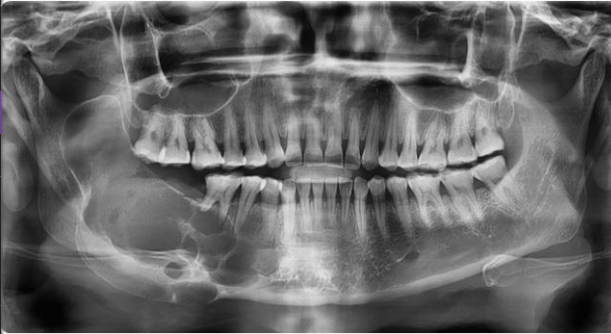
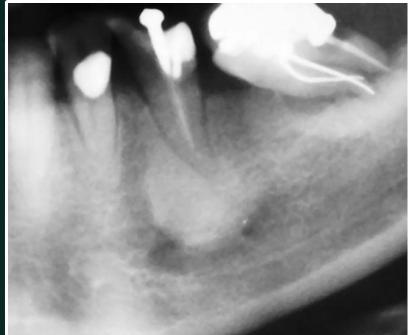
Condensing osteitis
RO lesion
RO at apex
linked with non vital tooth
no RL halo
Odontoma
RO
Compound
tooth like structure; denticles
anterior maxilla
Complex
RO mass with no tooth structures
posterior mandible

Cementoblastoma
RO mass fused to root
surrounded by RL halo
may cause expansion
may cause displacement, resorption can occur
tooth remains vital
pain may be present, but not always

Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia (PCOD)
Mixed lesions
occurs in vital teeth
anterior mandible common
3 stage progression
RL
Mixed
RO with thin RL border
often bilateral and symmetrical

Fibrous dysplasia)
Mixed
ground glass look
borders blend into surrounding bone
loss of lamina dura
often unilateral expansion
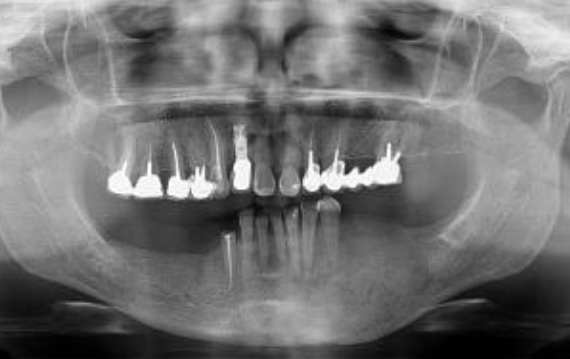
Paget’s disease
Mixed
cotton wool pattern
patchy irregular RO regions
may cause increased alveolar ridge size
possible increased spacing between teeth
linked with this disease (late stage)

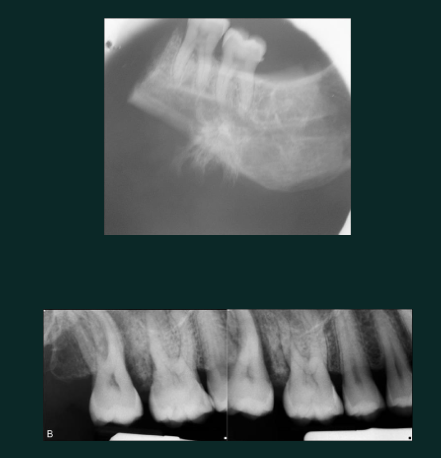
Osteosarcoma
Mixed
sunburst RO
widening PDL space without trauma
irregular destructive bone changes
pain and swelling clinically
malignant
Border characteristics

Location

Key takeaways

Osteomyelitis
malignancy
moth eaten destructive RL