SHS 300 Quiz 5
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
What makes up the cranial bones?
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
sphenoid
ethmoid
Frontal Bone
encases frontal lobe of brain
Parietal Bone
encases parietal lobe
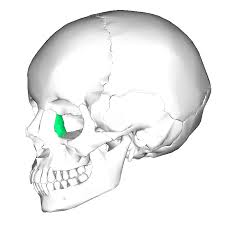
Temporal Bone
encases temporal lobe
What are the divisions of the temporal bone?
squamous portion
Petrous Portion
What makes up squamous portion of temporal bone division?
zygomatic process
What makes up petrous portion of temporal bone division?
mastoid process
styloid process
cochlea and semicircular canals of inner ear
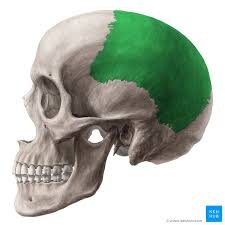
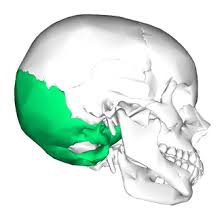
Occipital Bone
Encases occipital lobe of brain
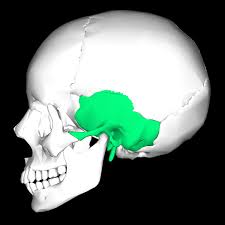
Sphenoid bone
Forms base of skull - bat wings
What are the sphenoid bone divisions?
body
greater wings
lesser wings
pterygoid process
Ethmoid Bone
separates nasal cavity from brain
What parts make up ethmoid bone?
middle and superior nasal conchae
perpendicular plate
What are the facial bones
mandibular
maxillary
palatine
nasal
inferior nasal conchae
vomer
zygomatic
lacrimal
Mandible
large bone that forms lower jaw
Landmarks of Mandible
corpus
ramus
anglem
mental symphysis
condylar process
coronoid process
Maxillae
upper jaw that forms roof of moth and floor of nasal cavity
What does maxillae form?
Hard palate
What makes up the hard palate?
anterior 2/3 - palatine process
alevolar ridge
Palatine bone
posterior portion of hard palate
horizontal plate
Nasal bone
small bones that form superior nasal surface
Inferior Nasal Conchae
form lateral surface of nasal cavity
Vomer
Midline bone that forms nasal septum
divided into two nasal cavities
Zygomatic Bone
forms cheek bones
What are the divisions of Zygomatic Bone?
temporal process
frontal process
maxillary process
What makes up temporal process of zygomatic bone?
1/3 zygomatic arch
other ½ formed by zygomatic process of temporal bone
Lacrimal Bone
very small bones
form part of lateral nasal wall and medial orbit
Pharynx
an oval tube larger side to side then front to back
What is pharynx composed of at the top?
connective tissue - pharyngeal aponeurosis
What is pharynx composed of at the bottom?
muscle predominates at the bottom
What are the three cavities of the pharynx?
nasopharynx
oropharynx
hypopharynx
What does the nasophayrnx contain?
auditory tubes (Eustachian tubes)
pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids)
What does oropharynx contain?
palatine tonsils
lingual tonsils
Opening of Oropharynx
through the faucial isthmus
What makes up faucial isthmus?
anterior faucial pillar
posterior faucial pillar
Velum
consists of the soft palate and uvula
What is the velum covered in?
connective tissue - palatal aponeurosis
What are the components of nasal cavities?
cartilage at front
bone at back
floor is hard palate
What is the nasal cavities rich in?
blood supply
What does the nasal cavities contain?
nasal vestibule
nasal concahe
meatuses
choana
sinuses
What are the muscles of the pharynx?
pharyngeal constrictors
long muscles
What are the muscles of the pharynx do?
change shape and size of pharynx?
What do the muscles of velum do?
position and reconfigure the velum
What do the pharyngeal constrictors form?
vertical muscular tube of pharynx
What do the pharyngeal constrictors do?
act as a group of constrict of pharynx for swallowing
What is the innervation of pharyngeal constrictors?
CN IX, X
What are the 3 sets of pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
superior
middle
inferior
Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor Action
Upper most fibers assist with velopharyngeal closure
move posterior wall of pharynx forward and narrows diameter of pharynx
Middle Pharyngeal constrictor action
move posterior wall of pharynx forward and narrows diameter of pharynx
Inferior Pharyngeal Constrictor Action
moves posterior wall of pharynx forward and narrows diameter of pharynx
cricopharyngeus
Cricopharyngeus
allows passage of food/liquid into esophagus
Salpingopharyngeus action
Move the lateral walls of the pharynx upward and inward
shortens/elevates the pharynx
helps equalize pressure in middle ear
Palatopharyngeus action
move the lateral walls of the pharynx upward and inward
shorten and elevate the pharynx
Stylopharyngeus innervation
CN IX
Stylopharyngeus action
elevate pharynx and larynx and dilate pharynx - widens
What speech sounds do muscles of velum help with?
all speech sounds EXCEPT /m/, /n/, /ng/
What does soft palate consist of?
muscles, aponeurosis, nerves, blood supply
Palatal Aponeurosis
mid front portion of soft palate
Pharyngeal Plexus
CN IX , X
Levator Veli Palatini Action
elevate and retract the velum to close the velopharyngeal port
Tensor Veli Palatini Innervation
CN V
Tensor Veli Palatini Action
Dilate auditory tube, allowing aeration of middle ear
tense soft palate - may assist VP closure
Muscle Uvulae Action
Shorten and elevate the velum
Palatoglossus Action
Lower soft palate and elevate back of tongue
Palatopharyngeus action
lower the velum and narrow the upper pharynx
Muscles of the outer nose action
dilate or compress nares (nostrils)
What are the three functions of the velopharyngeal nasal?
ventilation
speech production
swallowing
Movements of the pharynx
mobile tube
lengthening/shortening
inward/outward of lateral laryngeal walls
forward/backward movements of posterior pharyngeal wall
Movements of the Velum
upward and backward to close velopharyngeal port
downward and forward to open velopharyngeal port and close the posterior oral cavity
Movements of velopharyngeal port
elevate and retract velum
move the lateral pharyngeal walls
move the posterior pharyngeal wall forward
rapid opening and closing during speech
Open Velopharyngeal Port
for nasal sounds
/m/, /n/, /ng/
Tightly Close Velopharyngeal Port
for high pressure sounds
Closed Velopharyngeal Port
for non nasal speech sounds
all vowels
/l/, /r/, /w/, /j/
What are the three velopharyngeal nasal control variables?
airway resistance
sphincter compression
acoustic impedance
NP Nasal control variables - airway resistance
opposition to air flow through velopharyngeal nasal airway
NP Nasal control variables - airway low resistance
during breathing
NP Nasal control variables - airway high resistance
VP closure - no airflowing in the nasal cavity
NP Nasal control variables - sphincter compression
velopharyngeal sphincter can be closed with low compression force (gentle) or high compressive force (forcefully)
What determines sphincter compression?
muscles
NP Nasal control variables - Acoustic Impedance
opposition to flow of sound offered by the velopharyngeal nasal apparatus
NP Nasal control variables - Acoustic Impedance - closed VP
sound energy directed to oral cavity
NP Nasal control variables - Acoustic Impedance - Opened VP
distributed sound energy in nasal and oral cavities
frontal bone

Parietal Bone
Temporal Bone
Occipital Bone
Sphenoid Bone
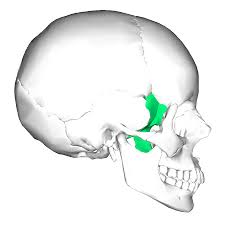
ethmoid bone
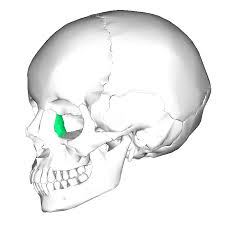
Mandible
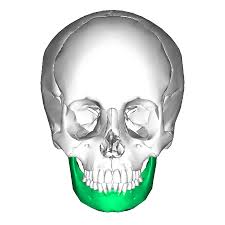
Mandible - Ramus
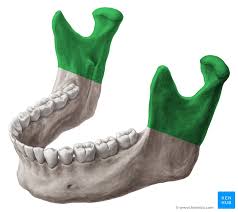
Manidble - Angle
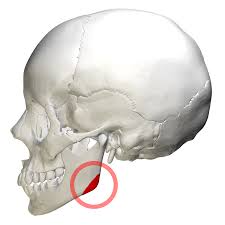
Mandible - Mental Symphysis
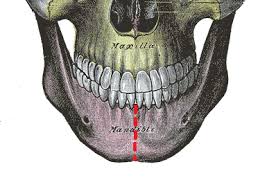
Mandible - Condylar Process
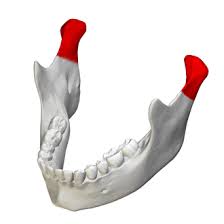
Mandible - Coronoid Process
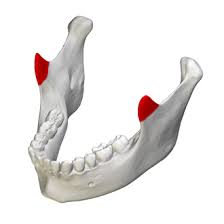
Maxillae
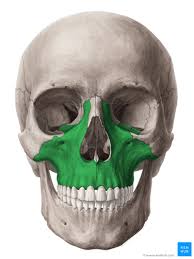
Palatine Bone
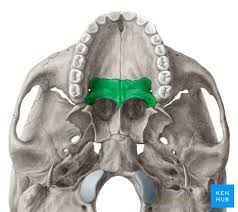
Nasal Bone
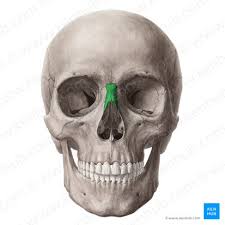
Inferior Nasal Conchae
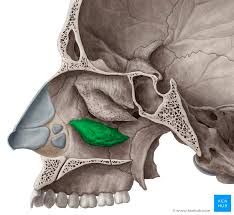
Vomer
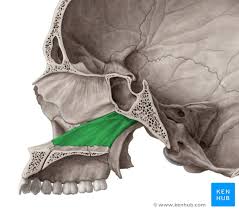
Zygomatic Bone
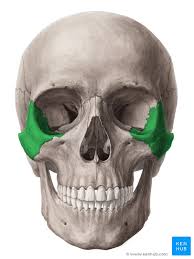
Lacrimal Bone