A&P I Exam 3 - Skeletal & Smooth Muscle
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
3 different types of muscle
1). Skeletal
2). Smooth
3). Cardiac
Location of skeletal muscle?
Attached to bones, skin (some facial muscles) or other muscles (tendons)
Location of smooth muscle?
In the walls of hollow visceral (involuntary) organs (except the heart), eye muscles, airways, large arteries, etc.
Ex). stomach, skin, blood vessels, esophagus, intestines, etc.
Location of cardiac muscle?
Walls of the heart (makes up most the mass of the heart)
Appearance of skeletal muscle?
1). Single, LONG, cylinder fibers
2). Striations
3). Multinucleated
Appearance of smooth muscle?
1). Single, spindle-shaped fibers. Arranged in sheets (since smooth muscle contracts as a single unit).
2). No striations
3). Uninucleated (one nucleus)
Appearance of cardiac muscle?
1) Branched, shorter fibers connected by intercalated discs
2). Striations
3). Uninucleated (one nucleus)
Function of skeletal muscle?
1). Contractions move the skeleton
2). Mostly voluntary, however, reflexes are involuntary.
Function of smooth muscle?
1). Propelling content in organs (digestion) & blood vessels, regulating blood flow, etc.
2). Involuntary
Function of cardiac muscle?
1). Covers the heart and pumps blood throughout the body
2). Involuntary
Other features of skeletal muscle?
1). A part of somatic nervous system (voluntary)
2). Contains neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
Other features of smooth muscle?
1). A part of autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
→ Includes sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
2). Inherent tonicity: has an inherent muscle tone (steady state), thus does not require nerve stimulation (no NMJ).
3). Influenced by hormones, sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of ANS, ECF conditions, etc.
4). May respond to stretch (e.g., uterus stretches when drinking lots of fluids, childbirth, etc.).
Other features of cardiac muscle
1). A part of autonomic nervous system (involuntary)
→ Includes sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
2). Inherent contractility: does not require nerve stimulation (no NMJ). It beats on its own as it has its own intrinsic conduction system (e.g., why heart transplants work).
3). Influenced by hormones, sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of ANS, etc.
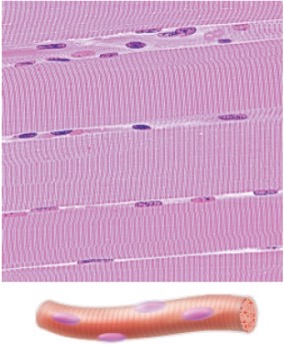
Identify this type of muscle
Skeletal muscle

Identify this type of muscle
Smooth muscle
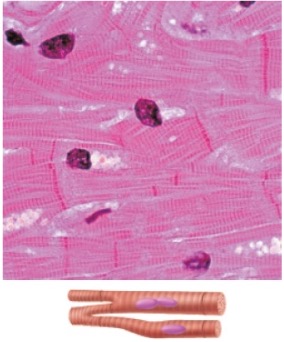
Identify this type of muscle
Cardiac muscle
4 characteristics of all muscle tissue
1). Excitability
→ Conductivity
2). Contractility
3). Extensibility
4) Elasticity
Excitability
(responsiveness) ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Contractility
ability to shorten forcibly when stimulated
Conductivity
ability to set off a wave of excitation that travels along muscle fiber
Extensibility
ability to be stretched
Elasticity
ability to return to original shape after being stretched (recoil)
4 Main functions of skeletal muscle
1). Movement: SKM contractions move skeleton
2). Posture:
3). Joint stability
4). Heat production (thermogenesis): SKM produces 20-30% of body heat at rest and up to 85% during exercise.
Anatomical Organization of SKM
1a). Epimysium (CT layer)
1b). Individual whole muscle
2a). Perimysium (CT layer)
2b). Fascicles
3a). Endomysium (CT layer)
3b). Muscle fibers (cell)
4). Myofibrils
5). Sarcomeres
6). Myofilaments
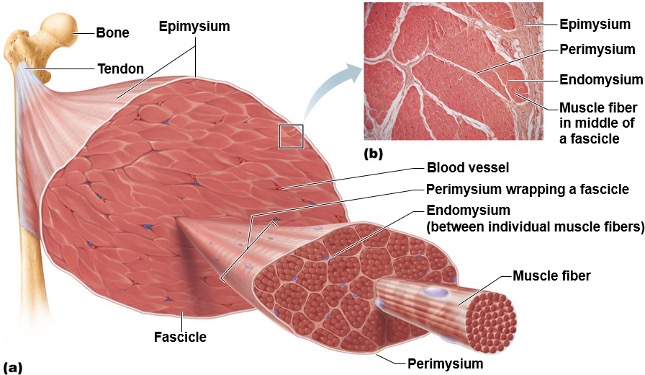
Epimysium
Outer most connective tissue layer that surrounds an entire individual muscle.
Ex). surrounds the deltoid, rectus abdominis, etc.

Muscle (organ)
Individual muscles, including the deltoid, rectus abdominis, etc.
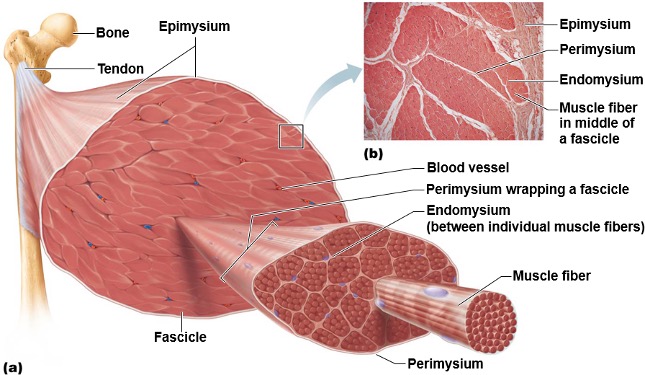
Perimysium
Middle connective tissue layer that surrounds individual fascicles.
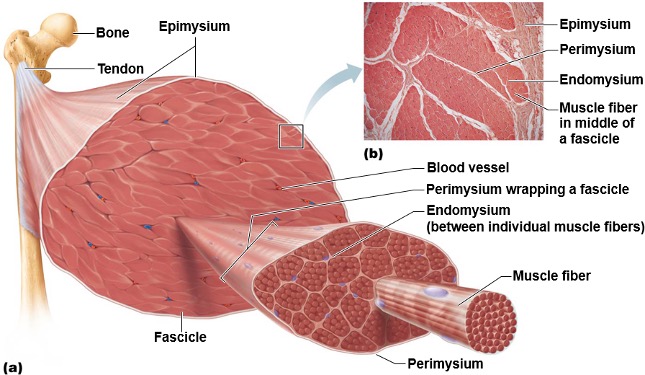
Fascicles
Bundles of 20-30 muscle fibers
Epimysium
Inner most connective tissue layer that surrounds individual muscle fibers
→ the boundary for the extracellular environment (since it surrounds the muscle cell).
Muscle fiber (cell)
The fundamental contractile unit of skeletal muscle
Myofibril
Threadlike structure within muscle fiber that are arranged in sarcomeres.

Sarcomere
Region of myofibril between 2 Z discs (functional unit).
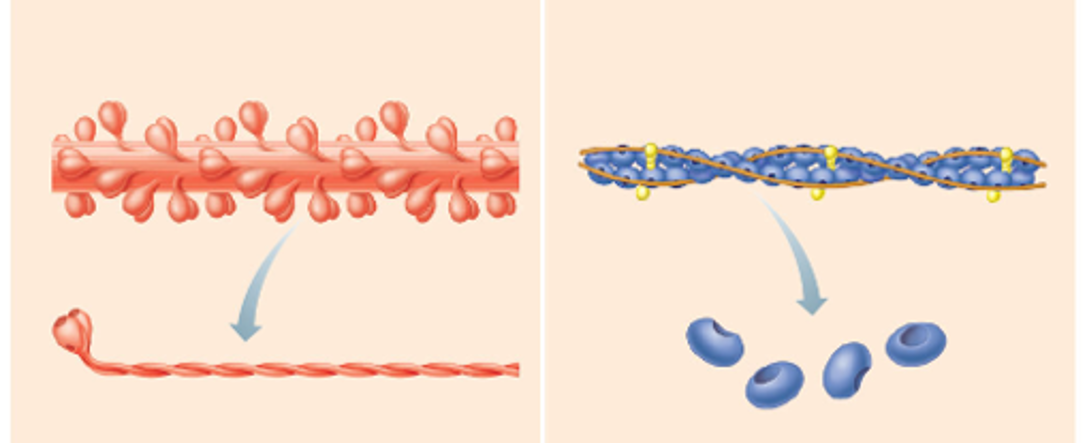
Myofilaments
Thick and thin filaments composed of various proteins (e.g., myosin, actin, tropomyosin, and troponin) that work together to produce muscle contractions.
→ smallest unit of muscle tissue
Sarco- and Myo-
Prefixes that mean muscle
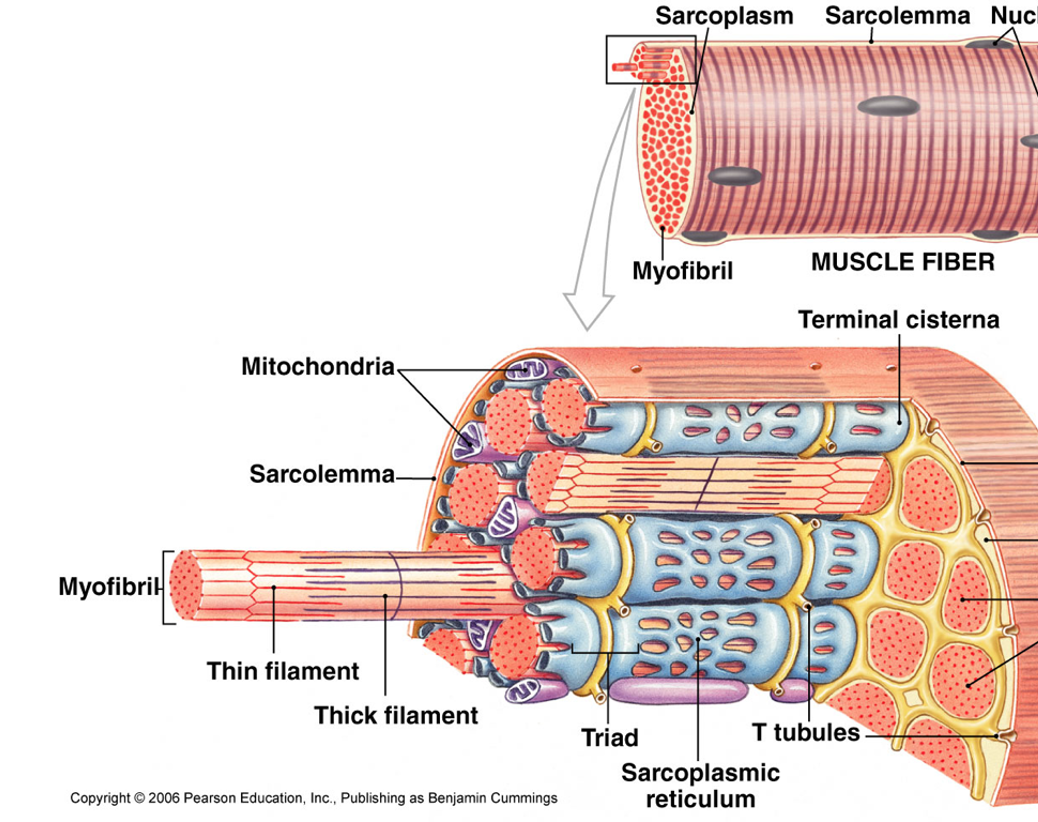
6 specialized structures of muscle cell (fiber)
1). Sarcolemma
2). Sarcoplasm
3). Transverse (T)-Tubules
4). Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
→ Terminal cistern
5). Triad
6). Myofibrils
Additional Structures
1). Mitochondria
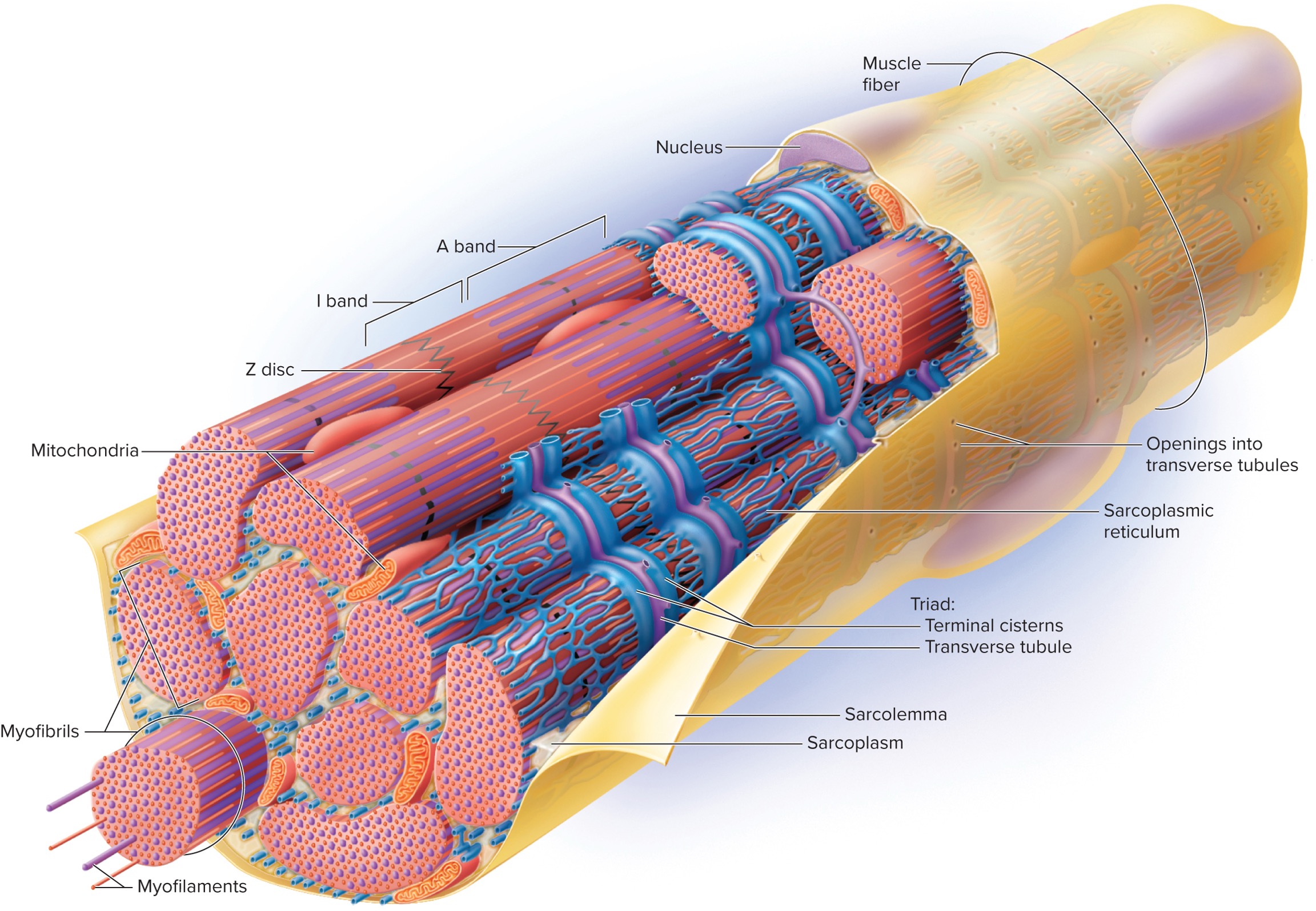
Sacrolemma
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber (cell) that is involved in the propagation of action potentials.
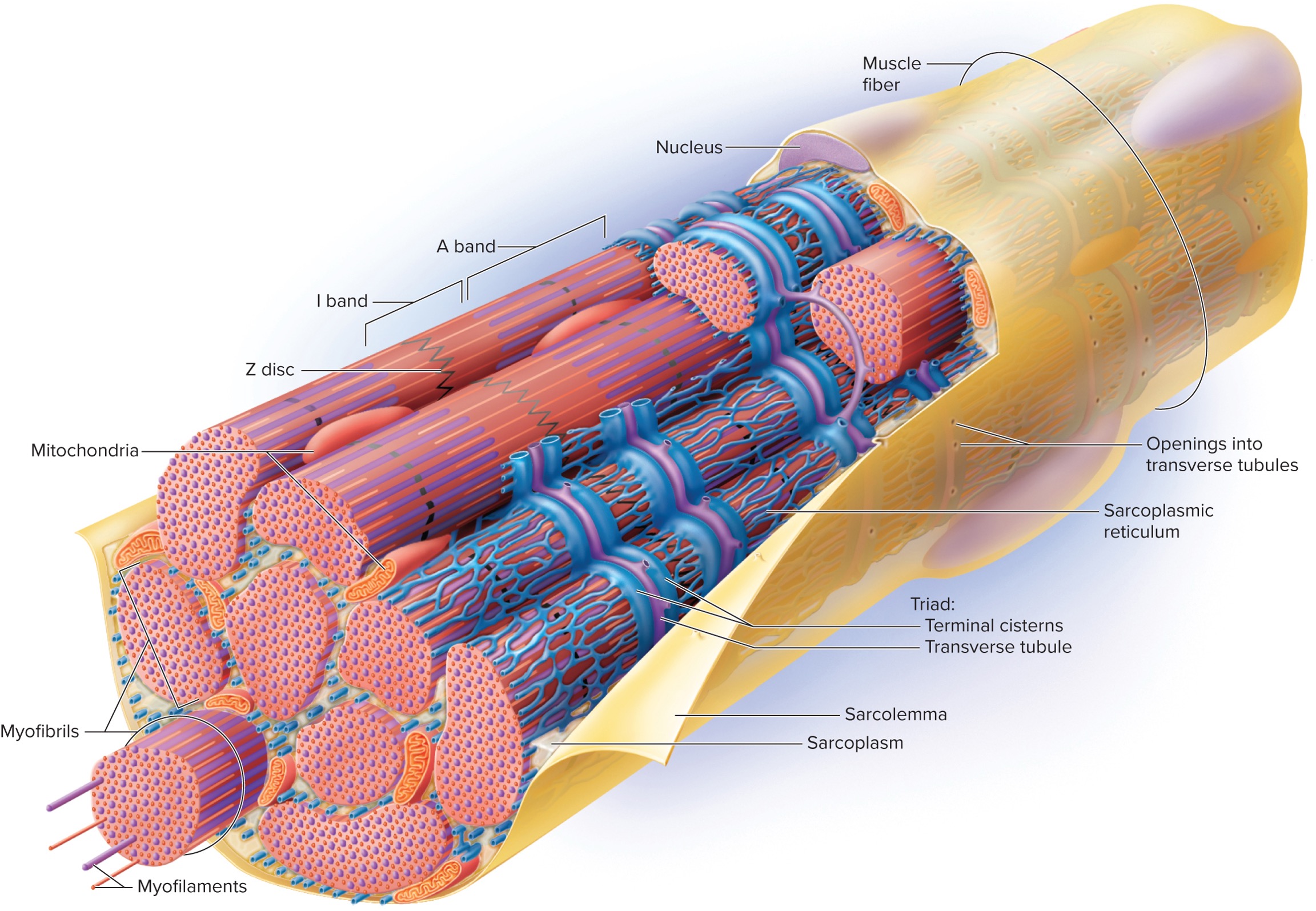
Sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber (cell) that contains organelles and myofibrils.
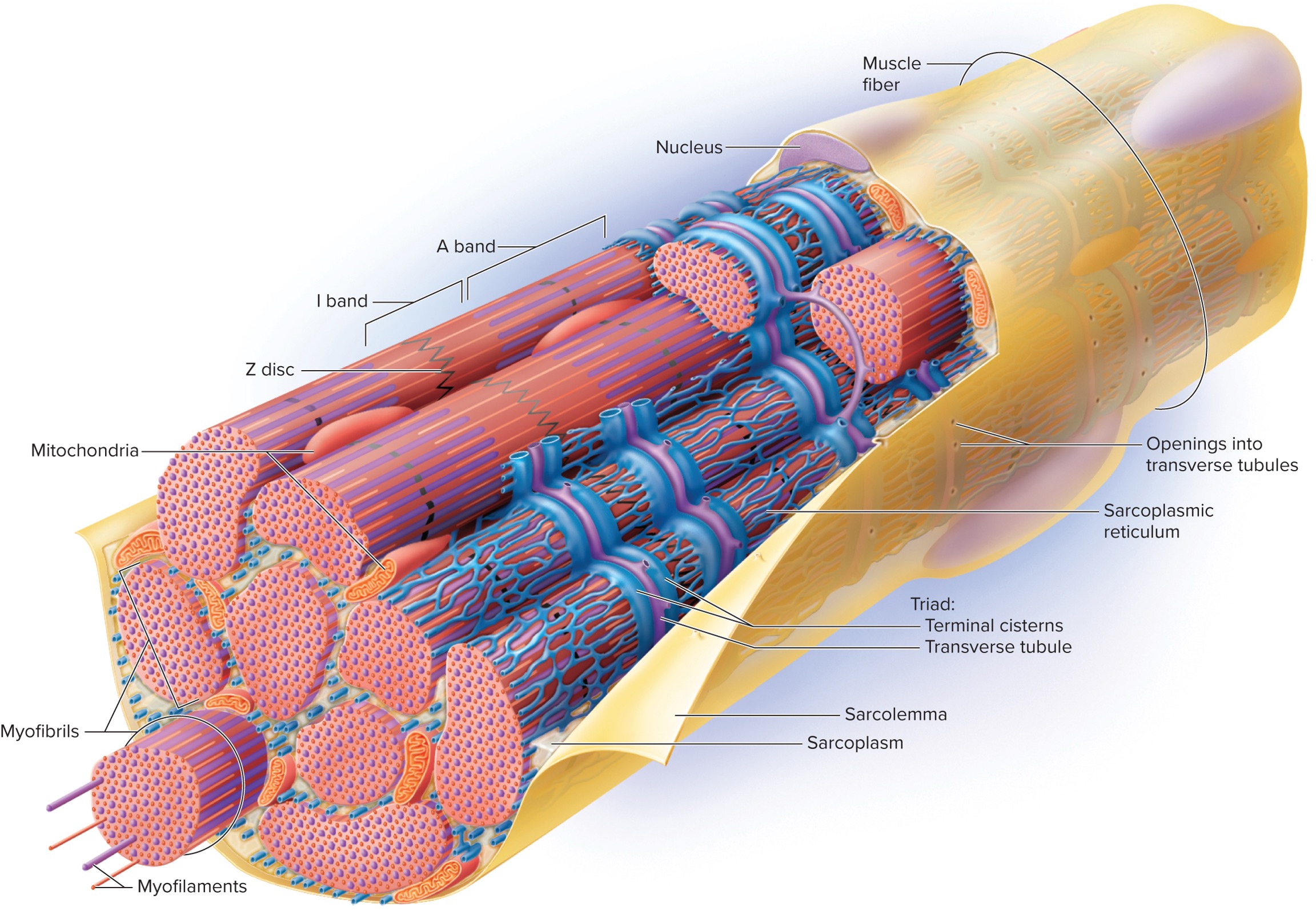
Transverse (T)-Tubules
Extensions of the sarcolemma that extend into sarcoplasm and cut across the transverse plane (horizontal) in a muscle fiber (cell).
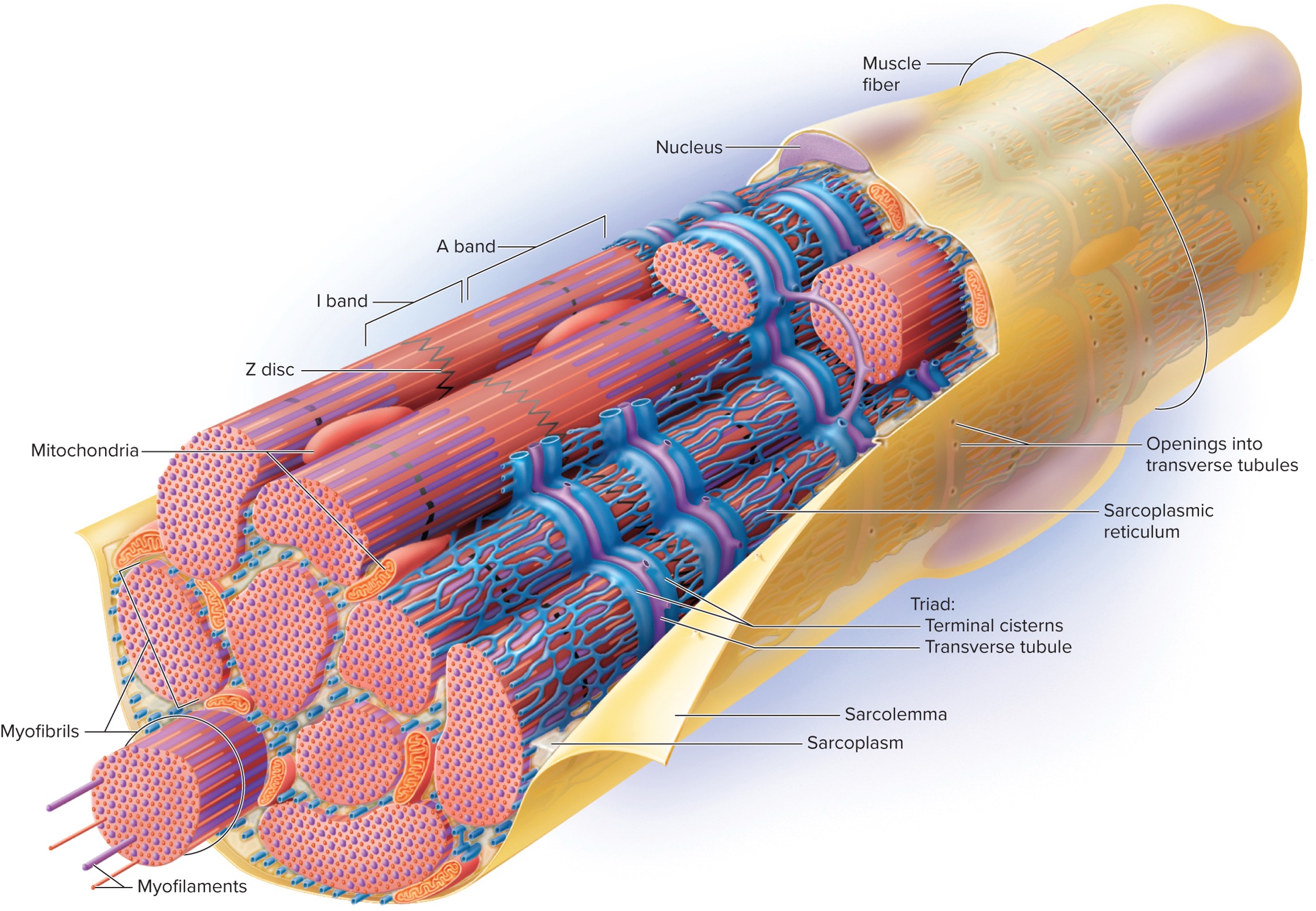
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
A specialized endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in muscle fibers (cells) that are specialized in carrying calcium ions.
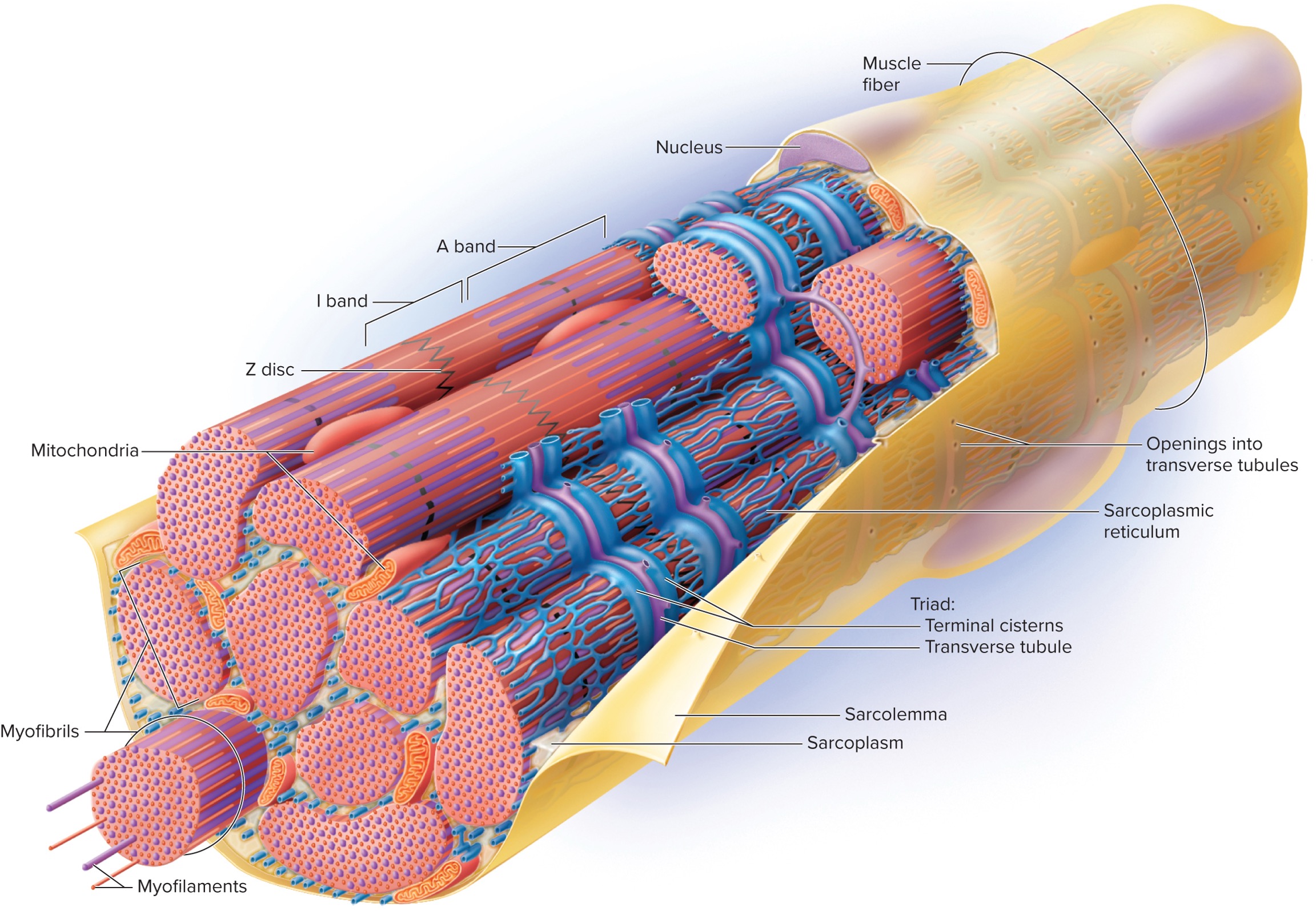
Terminal Cisternae
Enlarged areas of the sarcoplasmic reticulum that store calcium ions. They reside on both sides of the T-tubules; thus, they also cut across the transverse plane (horizontal).

Triad
A structure formed by two terminal cisterns and one T-tubule. Cuts across the transverse plane (horizontal) in the muscle fiber (cell).
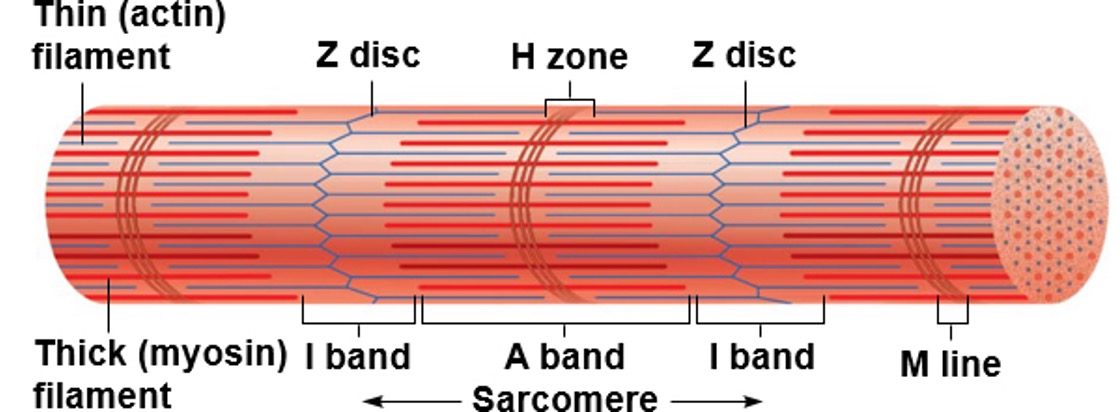
Repeating subunits that compose myofibrils
Sarcomeres
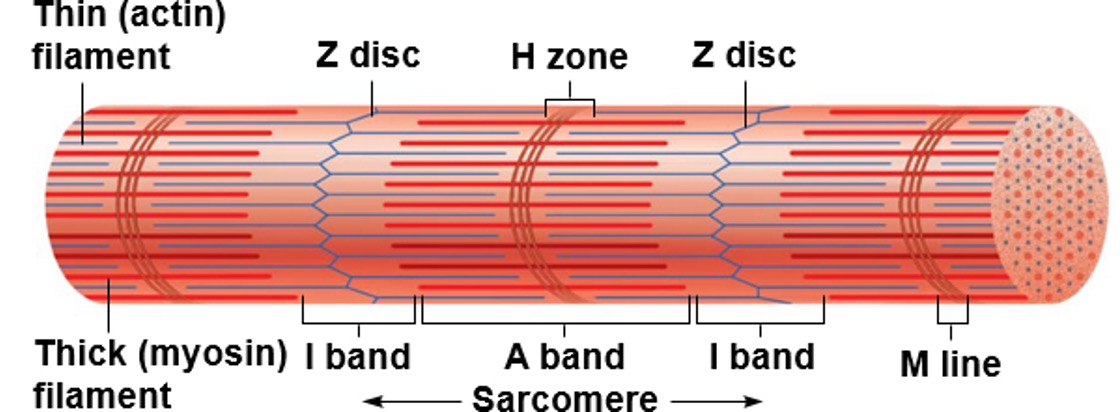
Components of Sacromeres
1) Thick filaments
2). Thin filaments
3). Banding patterns
→ I band
→ A band
→ H zone
→ Z disc
→ M line
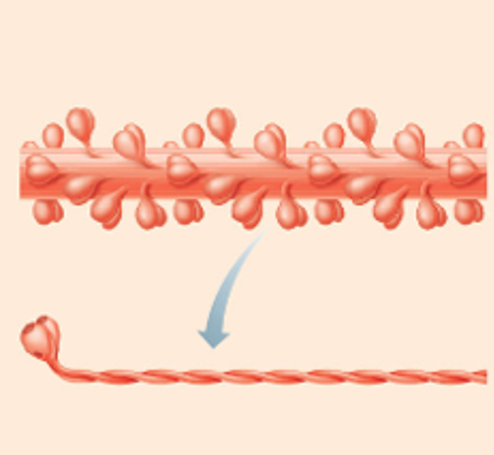
Components of thick filament
1). Myosin (protein)
2). Titin core (protein)
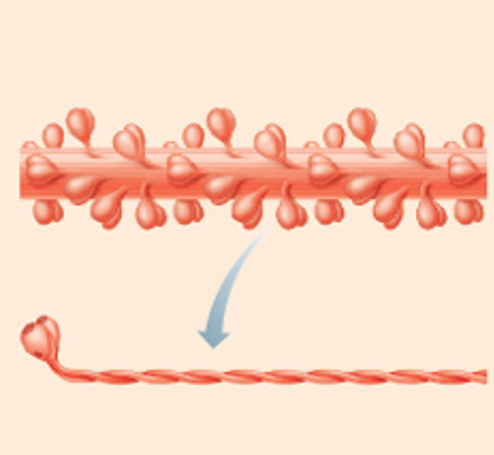
Myosin molecule components
1). 2 myosin heads
→ 2 binding sites to actin
→ 2 binding sites for hydrolyzing ATP
2). 2 twisted myosin tails
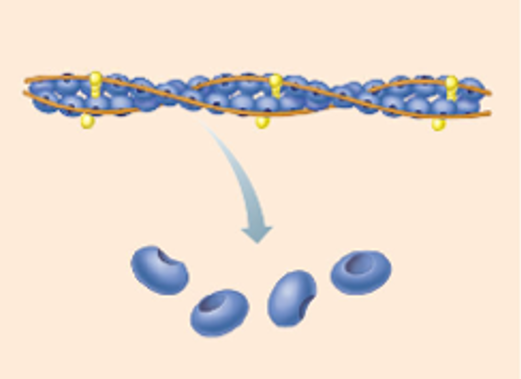
Components of thin filament
1). Actin (protein)
2). Tropomyosin (protein)
3). Troponin (protein)
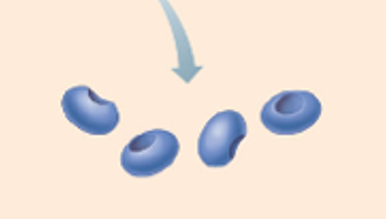
G-action
Individual actin subunits (globular form). Location of the binding site for myosin heads.
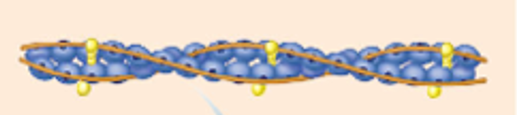
F-Action
Chains of g-action subunits (filamentous form). 2 chains of f-action twisted together form the thin filament backbone.
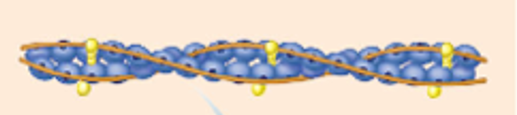
Tropomyosin
Structure: double-stranded protein wrapped around F-action.
Function: “bike chain.” At rest, it covers myosin binding sites, thus preventing myosin from binding to actin at rest.

Troponin
Structure: 3 subunits, attached to tropomyosin, which forms the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Also attached to g-actin.
Function: “bike lock".” Holds tropomyosin in place and contains binding sites for calcium ions.
Calcium Ions = KEY!
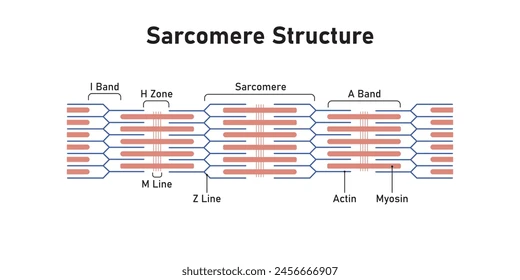
I Band
Section of all thin filaments (light)
→ I =”THIN” letter, thus contains only THIN filaments
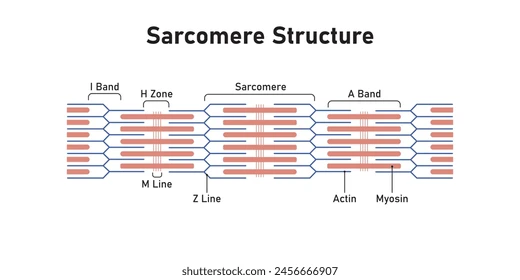
A Band
Section of mostly thick filaments, with small thin filament overlap.
→ A = “AND” since contains thin AND thick
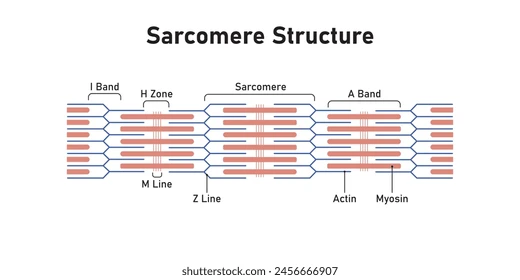
H Zone
Section of all thick filaments within the A band.
→ H = “THICK” letter, thus contains only THICK filaments
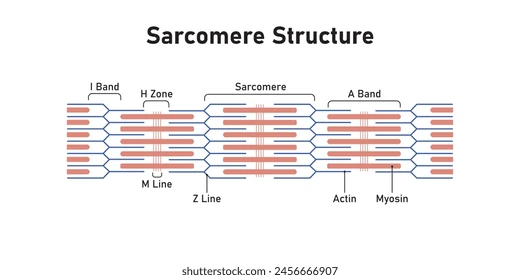
Z Disc
Structure: Vertical lines between sarcomeres or cut down the middle of I band.
Function: anchor points for thin and thick filaments
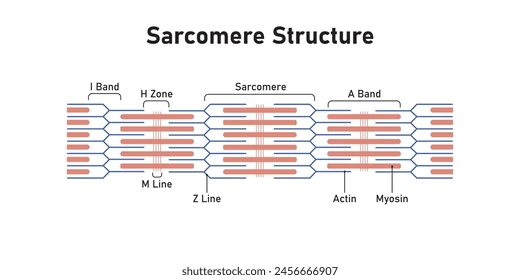
M Line
Runs down the middle of sarcomeres, A band and H zone.