unit 6 humerus and shoulder girdle x-rays
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
procedural considerations for humerus and shoulder girdle
40 inches (100 cm) minimum SID
Gonadal shielding
Four-sided collimation when possible
Long axis of part to long axis of IR
Side markers visible
CR directed perpendicular to IR unless otherwise indicated
how many inches minimum SID?
40 (100 cm)
_____ axis of part to _____ axis of IR
long, long
CR is directed ________ to IR unless otherwise indicated
perpendicular
what are the routine and special positions/projections for the humerus?
routine:
> AP
> Rotational Lateral
special:
> horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus)
> transthoracic lateral (proximal to full humerus)
what are the routine positions/projections of the humerus?
AP, rotational lateral
what are the special positions for the humerus?
horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus)
transthoracic lateral (proximal to full humerus)
the horizontal beam lateral projection of the humerus is a projection of the ….
distal humerus
the transthoracic lateral projection/position is proximal to….
full humerus
for all projections/positions of the humerus, the patient will be either _____ or ________
erect, recumbent

name the position/projection
AP humerus

name the projection/position
AP humerus
AP humerus guidelines
extend arm fully with hand supinated
rotate body toward affected side as needed to bring shoulder and arm close to IR
abduct arm slightly
epicondyles parallel to IR
CR to mid humerus
in an AP humerus projection, your arm should be fully _____ with your hand _____
extended, supinated
in an AP humerus projection, the epicondyles should be _____ to IR
parallel
in an AP humerus projection, the CR should be to the
mid humerus
evaluation criteria for AP humerus
entire humerus to include elbow/shoulder joints
greater tubercle in profile
medial/lateral epicondyles in profile
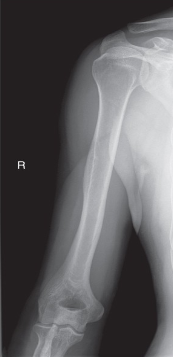
name the position/projection
AP humerus

name the projection/position
rotational lateral humerus (lateromedial)

name the projection/position
rotational lateral humerus (mediolateral)
guidelines for a rotational lateral humerus (lateromedial)
patient facing tube with arm extended, elbow partially flexed
rotate body toward affected side as needed to bring shoulder/arm close to IR
internally rotate arm until epicondyles are perpendicular to IR (back of hand against thigh)
when the back of the hand is against the thigh in a Rotational lateral humerus (lateromedial) projection/position, the epicondyles are ______ to the IR
perpendicular
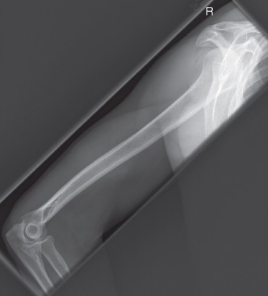
name the position/projection
rotational lateral humerus (mediolateral projection)
evaluation criteria for rotational lateral humerus
entire humerus to include elbow/shoulder joints
lesser tubercle in profile
epicondyles superimposed
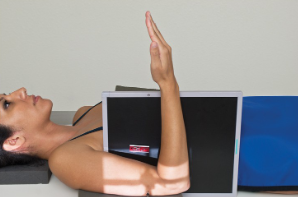
name the position/projection
horizontal beam lateral distal humerus
the horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus) position is done usually on what kind of patient?
trauma
guidelines to horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus)
patient supine with arm supported by sponge
elbow flexed 90 degrees w/ hand and wrist in lateral position
epicondyles perpendicular to IR
IR placed between arm and thorax
CR directed horizontally to midpoint of distal 2/3 of humerus
in a horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus) position, the epicondyles are ______ to the IR
perpendicular
in a horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus) position, the CR is directed ______ to ______ of _____ ___ of _____
horizontally, midpoint, distal, 2/3, humerus
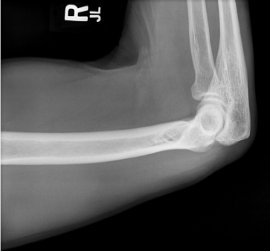
name the position
horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus)
evaluation criteria for horizontal beam lateral (distal humerus) position
distal 2/3 of humerus and elbow demonstrated
epicondyles superimposed
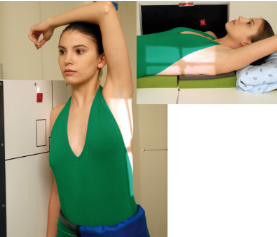
name the position
transthoracic lateral humerus
guidelines for transthoracic lateral humerus
affected arm in neutral rotation, drop shoulder if possible
unaffected limb raised over head
CR to mid aspect of humerus (horizontal beam if patient supine)
breathing technique:
2-3 second exposure while patient takes shallow breaths
blurs our superimposing ribs/lung structures
in a transthoracic lateral humerus position, the CR is to the ___ ___ of the ______
mid aspect, humerus
if the patient is supine in a transthoracic lateral humerus position, the beam should be ______
horizontal
if the patient cannot drop affected shoulder in a transthoracic lateral humerus position, what should be done? what does it prevent?
the CR should be angled 10-15 cephalad, prevents superimposition of the shoulders
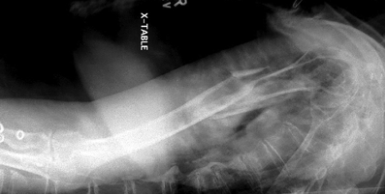
name position/projection; in what position is the beam in? what position is the patient in? is there a breathing technique present?
transthoracic lateral humerus, horizontal beam lateral, supine, yes
evaluation criteria for transthoracic lateral humerus
proximal 2/3 of humerus OR entire humerus w/ elbow joint
overlying ribs and lung marking blurred
non-trauma shoulder positions
routine:
AP external rotation
AP internal rotation
special:
AP posterior oblique (grashley method)
inferosuperior axial (lawrence method)
PA transaxillary (Hobbs method)
name the routine positions for a non-trauma shoulder
AP external rotation
AP internal rotation
name the special positions for a non-trauma shoulder and the methods
AP posterior oblique (grashley method)
inferosuprior axial (lawrence method)
PA transaxillary (hobbs method)
for a non-trauma shoulder, the patient can be ______ , _______ , or ______ for all projections/positions
erect, seated, recumbent

name the projection/position
AP shoulder external rotation
guidelines for AP shoulder external rotation
extend arm fully with hand supinated
abduct arm slightly and externally rotate until epicondyles parallel to IR
CR directed 1” inferior to coracoid process
in an AP shoulder external rotation, the epicondyles are _____ to IR
parallel
in an AP shoulder external rotation, the CR is directed ___ ____ to _____ _______
1 inch, coracoid process
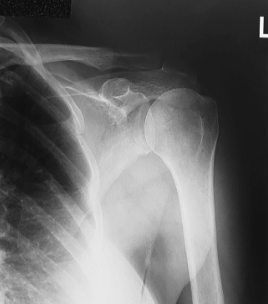
name the position/projection
AP shoulder external rotation
evaluation criteria for AP shoulder external rotation
greater tubercle seen in profile laterally
scapulohumeral joint centered
proximal humerus, upper scapula, clavicle visualized
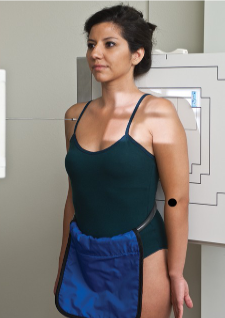
name the position/projection
AP shoulder internal rotation
guidelines for AP shoulder internal rotation
extend arm fully with hand pronated
abduct arm slightly and internally rotate until epicondyles perpendicular to IR
CR directed 1” inferior to coracoid process
in an AP shoulder internal rotation position, the epicondyles are ______ to IR
perpendicular
when the epicondyles are perpendicular to the IR, the ____ of your hand is _____ the ____
back, against, thigh
in an AP shoulder internal rotation position, the CR is _____ ___ _____ _____ to _______ ______
directed 1 inch inferior, coracoid process
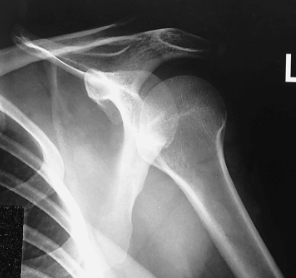
name the position/projection
AP shoulder internal rotation
evaluation criteria for AP shoulder internal rotation
lesser tubercle seen in profile medially
scapulohumeral joint centered
proximal humerus, upper scapula, clavicle visualized
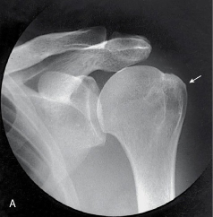
name the projection and rotational; label the part of the humerus the arrow is pointing to
AP external, greater tubercle
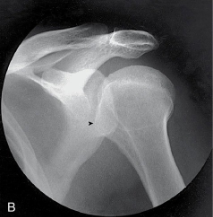
name the projection and rotational; label the part of the humerus the arrow is pointing to
AP internal, lesser tubercle

name the projection/position and method
AP posterior oblique shoulder (grashley method)

guidelines for AP posterior oblique shoulder (grashley method)
patient AP, extend arm fully
body rotated 35-45 toward affected side
abduct arm slightly and place hand in neutral position (palm facing thigh)
CR directed to scapulohumeral joint — 2” inferior and medial from superolateral border of humerus
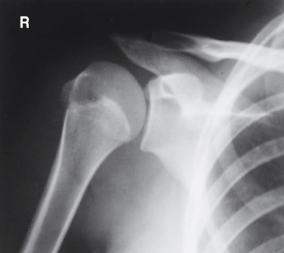
name the position/projection and method if applicable
AP posterior oblique shoulder (grashley method)
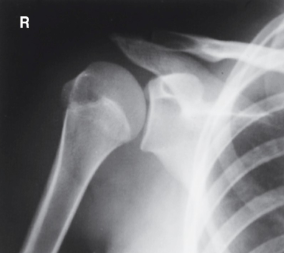
evaluation criteria for AP posterior oblique shoulder (grashley method)
glenoid cavity seen in profile
scapulohumeral joint centered
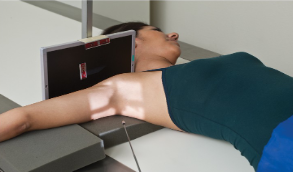
name the position/projection and method
Inferosuperior Axial Shoulder (Lawrence Method)
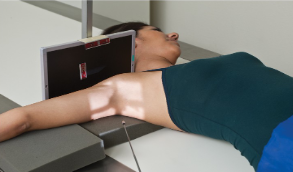
guidelines for inferosuperior axial shoulder (lawrence method)
patient supine
arm abducted 90 degrees if possible; keep in external rotation
head rotated toward opposite direction
IR placed against neck on superior aspect of arm
CR directed medially 25-30 degrees to axilla
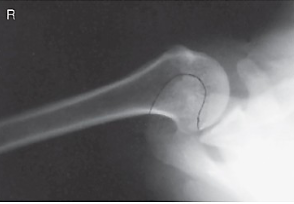
name the position/projection and method if applicable
inferosuperior axial shoulder (lawrence method)
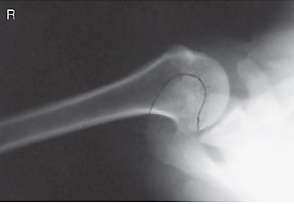
evaluation criteria for inferosuperior axial shoulder (lawrence method)
lateral view of scapulohumeral joint
lesser tubercle profiled anteriorly
humeral head and glenoid fossa profiled
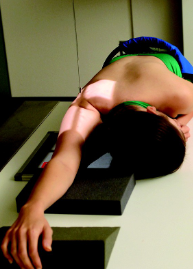
name the position/projection and method
PA transaxillary shoulder (hobbs method)
guidelines for PA transaxillary shoulder (hobbs method)
Patient erect, seated, or leaning
over x-ray table
Arm extended over head
Head turned away from affected
side
IR place under axilla & arm
CR directed to the posterior
aspect of the shoulder at the
level of the axilla & humeral
head
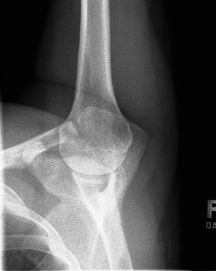
name the position/projection and method if applicable
PA transaxillary shoulder (hobbs method)
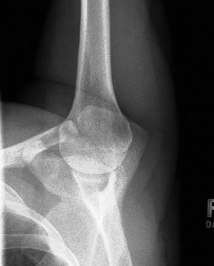
evaluation criteria for PA transaxillary shoulder (hobbs method)
Lateral view of scapulohumeral joint
Coracoid process seen on end
name the positions for a shoulder (trauma)
routine:
AP neutral rotation
scapular Y lateral
transthoracic lateral (lawrence method)
for a traumatic shoulder injury, the patient can be ______, _______, or _______ for all projections/positions
erect, seated, recumbent
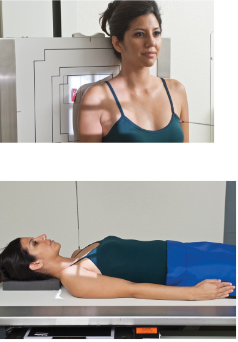
name the position'/projection
AP shoulder neutral rotation
guidelines for AP shoulder neutral rotation
Arm at patient’s side in neutral position (palm against thigh; epicondyles 45º to IR) or left “as is”
CR directed to mid scapulohumeral joint - approximately ¾” inferior & slightly lateral to the clavicle
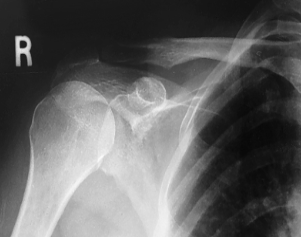
name the position/projection
AP shoulder neutral rotation
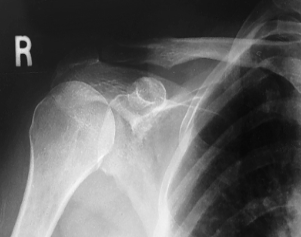
evaluation criteria for AP shoulder neutral rotation
Greater & lesser tubercles superimposed
Scapulohumeral joint centered
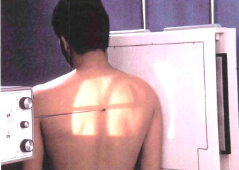
name the position/projection
Scapular Y Lateral Shoulder – Anterior Oblique Position (PA Projection)
guidelines for scapular Y lateral shoulder
Patient erect
Rotate patient into 45º-60º
oblique:
RAO for R shoulder
LAO for L shoulder
Abduct arm slightly or leave “as is”
CR directed to scapulohumeral joint; enters back 2” to 2½” below top of shoulder
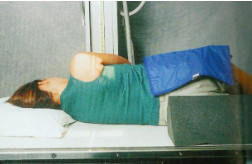
name the position/projection
Scapular Y Lateral Shoulder – Posterior Oblique Position (AP Projection)
Guidelines for Scapular Y Lateral Shoulder – Posterior Oblique Position (AP Projection)
Patient erect or recumbent
Rotate patient into 45º-60º oblique:
RPO for L shoulder
LPO for R shoulder
Abduct arm slightly or leave “as is”
CR directed to scapulohumeral joint; enters front 2” to 2½” below top of shoulder
the Scapular Y Lateral Shoulder – Posterior Oblique Position (AP Projection) is often done _____ in place of anterior oblique positions, but results in greater magnification due to increased OID
erect
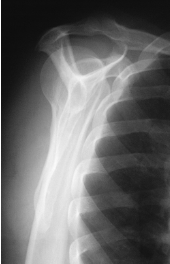
name the position'/projection
Scapular Y Lateral Shoulder – Posterior Oblique Position (AP Projection)
evaluation criteria for Scapular Y Lateral Shoulder – Posterior Oblique Position (AP Projection)
Lateral view of scapulohumeral joint
Body of scapula superimposed over shaft of humerus
Acromion and coracoid processes in profile
Humeral head and glenoid cavity superimposed
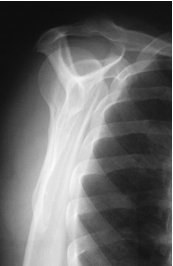
is this a normal or dislocated shoulder? how do you know?
normal, head of humerus superimposed over base of Y
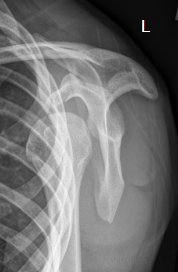
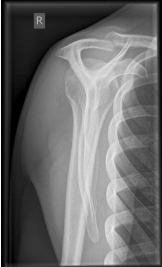
is this a normal or dislocated shoulder? in which direction is it dislocated?
dislocated, anterior
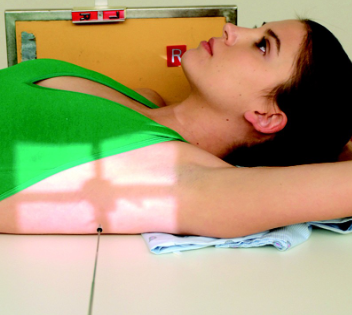
name the x-ray position/projection and method
Transthoracic Lateral Shoulder (Lawrence Method)
guidelines for a transthoracic lateral shoulder lawrence method
Patient erect or recumbent
Affected arm in neutral rotation;
drop shoulder if possible*
Unaffected limb raised over head
CR to surgical neck; enter inferior
to axilla (horizontal beam if patient
supine)
where should the CR be for a transthoracic lateral shoulder lawrence method?
surgical neck, inferior to axilla
what is the breathing technique for a transthoracic lateral shoulder lawrence method?
2-3 second exposure while patient takes shallow breaths
by using a breathing technique for a transthoracic lateral shoulder lawrence method, what does it do to the lungs and ribs?
blurs them out
if patient cannot drop affected shoulder for a transthoracic lateral shoulder lawrence method, what should you do?
anglr CR 10-15 degrees cephalad to prevent superimposition of shoulders
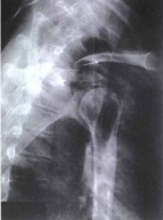
name the x-ray/position/method
transthoracic lateral shoulder (lawrence method)
evaluation criteria for transthoracic lateral shoulder (lawrence method)
Proximal ½ of humerus &
scapulohumeral joint
demonstrated without
superimposition of the
opposite shoulder
Overlying ribs & lung marking
blurred
what are the two routine views for a clavicle?
AP, AP axial

name the position/projection
AP Clavicle
guidelines for AP clavicle
arm at patient’s side in neutral position
chin raised
CR directed to mid clavicle
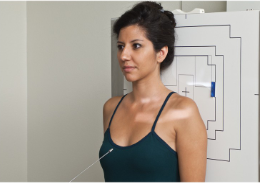
name the position/projection
AP axial clavicle
guidelines for AP axial clavicle
Arm at patient’s side in
neutral position
Chin raised
CR directed 15º-30º to mid
clavicle*
for asthenic patients, the CR will be angled more towards __ degrees in an AP axial clavicle
30
evaluation criteria for an AP clavicle/axial
Entire clavicle demonstrated along with acromioclavicular (AC) & sternoclavicular (SC) joints
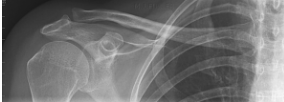
what position/projection is this? how can you tell?
AP clavicle — medial half of clavicle superimposed over scapula and ribs