BIOL 310 Physiology Final
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
skeletal muscle composition
striated multinucleate cells
cardiac muscle
striated uninucleate cells joined by intercalated discs, contractile
smooth muscle
uninucleate lack striations
muscle origin
muscle attachment closest to the stationary bone
muscle insertion
Movable attachment point of a muscle.
flexor
brings bone together
extensor
moves bone away
myocites
muscle cells
satelite cells
stem cells that build and repair muscle cells
fascicles
bundled muscle fibers surrounding connective tissue sheets
sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
sarcoplasm
muscle cell ICF
sarcoplasmic reticulum
stores calcium
myofibril
muscle fibers responsible for contraction
t tubules
infoldings of sarcolemma
cisternae
endings of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
actin
thin filament
myosin
thick filament
regulate muscle contraction
tryponin and trypomyosin
muscle contraction
generation of force by muscle
muscle relaxation
Ca removed from ICF ending the active force generating process
load
force or weight opposing contraction
crossbridge cycling
how the molecular components of muscle interact to cause contraction
excitation coupling
how stimulation from a motor neuron causes contraction
motor division
single excitatory CNS neuron connects to the skeletal muscle
neuromuscular junction
axon terminals with motor neurons synapse at the motor end plate
motor end plate
region of sarcolemma with a lot of AcH receptors
acetylcholine binds to
nicotinic receptors
systole
contraction
dystole
Relaxation
Late diastole
ventricles fill passively and the chambers are relaxed
Atrial systole
contraction forces a small amount of blood into ventricles
heart sound S1
AV close, pressure greater in ventricle than atrium
end diastolic volume EDV
max vol of blood in ventricle
isovolumic ventricular contraction
AV valves close
stroke volume
vol blood ejected from heart in a contraction
Ventricular ejection
ventricular pressure rises above that of the arteries and blood is ejected
Isovolumic ventricular contraction
ventricle pressure decreases and semilunar valves close
cardiac cycle
late diastole, atrial systole, isovolumic ventricular contraction, ventricular ejection, isovolumic ventricular contraction
cardiac output
vol blood ejected by one ventricle at a point in time
contraction force depends on
contractility and lenght
contractility
sensitivity to ca
tunica intima
blood vessel endothelium inner layer
tunica media
vascular smooth muscle responsible for vasoconstriction/dilation
`tunica externa
outer layer of connective tissue
arteries
thick layers of vascular smooth muscle and connective tissue, a pressure reservoir
arterioles
more muscular and provide resistance against vasoconstriction/dilation
metarterioles
Short vessels that link arterioles and capillaries
capillaries
exchange between blood and muscles
venules
small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
veins
bring blood to the heart less elastic than arteries
continuous capillaries
have leaky junctions for exchange to occur, ie muscle
fenestrated capillaries
poors, ie kidneys
paracellular transport
fluid/ solutes move around cells and through poors
endothelial transport
fluid/ solutes move through cells via diffusion
transcytosis
vesicles carry large molecules across cells
lymphatic system
returns fluid and protein to the blood and protects from pathogens
edema
accumulation of fluid in interstitial space due to inadequate draining
septum
heart left and right halves
atrium
recieves blood, thin walls
ventricles
pump blood out, thick walls
systemic circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs
pulmonary circulation
Circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs
coronary circulation
supplies blood to the heart
pericardium
fluid filled sac that encompasses the lungs
atrioventricular valves
separate the atria from the ventricles
semilunar valves
separate ventricles from arteries
long refractory periods
prevent summation and tetanus
pacemaker potential
spontaneous depolarization of autorhythmic cells to trigger action potential
P wave
atrial depolarization
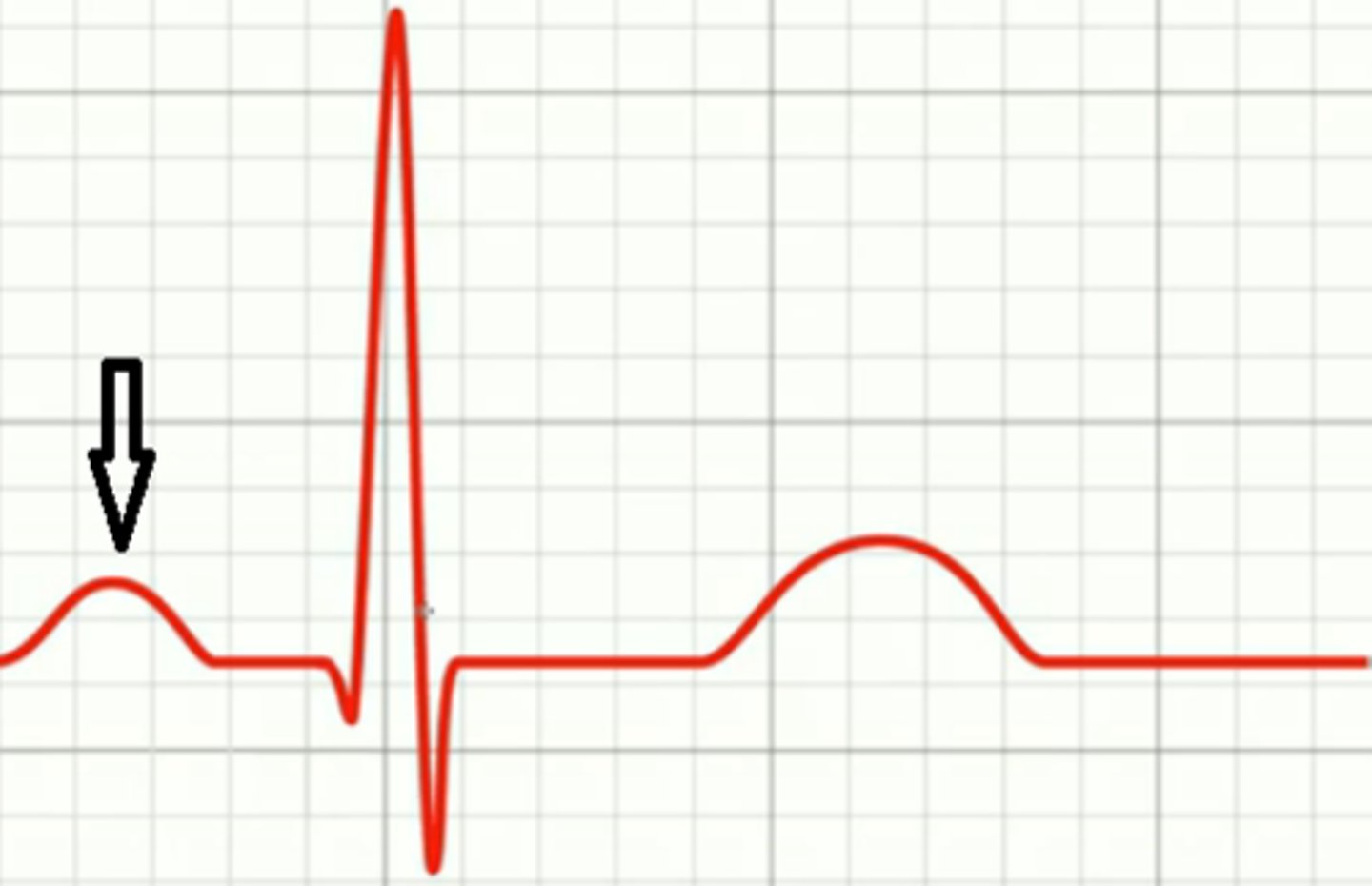
P R segment
conduction through AV node and AV bundle
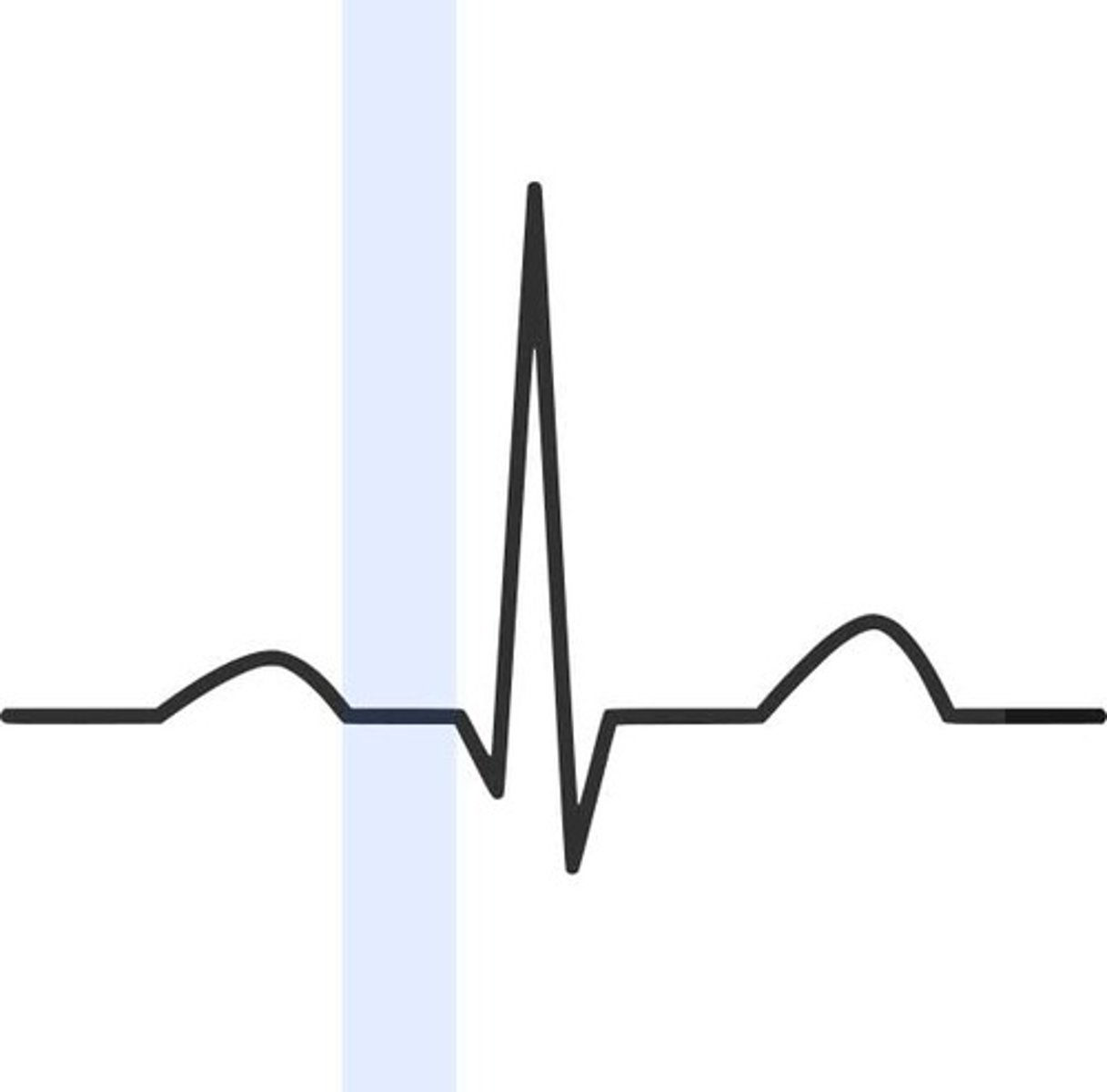
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
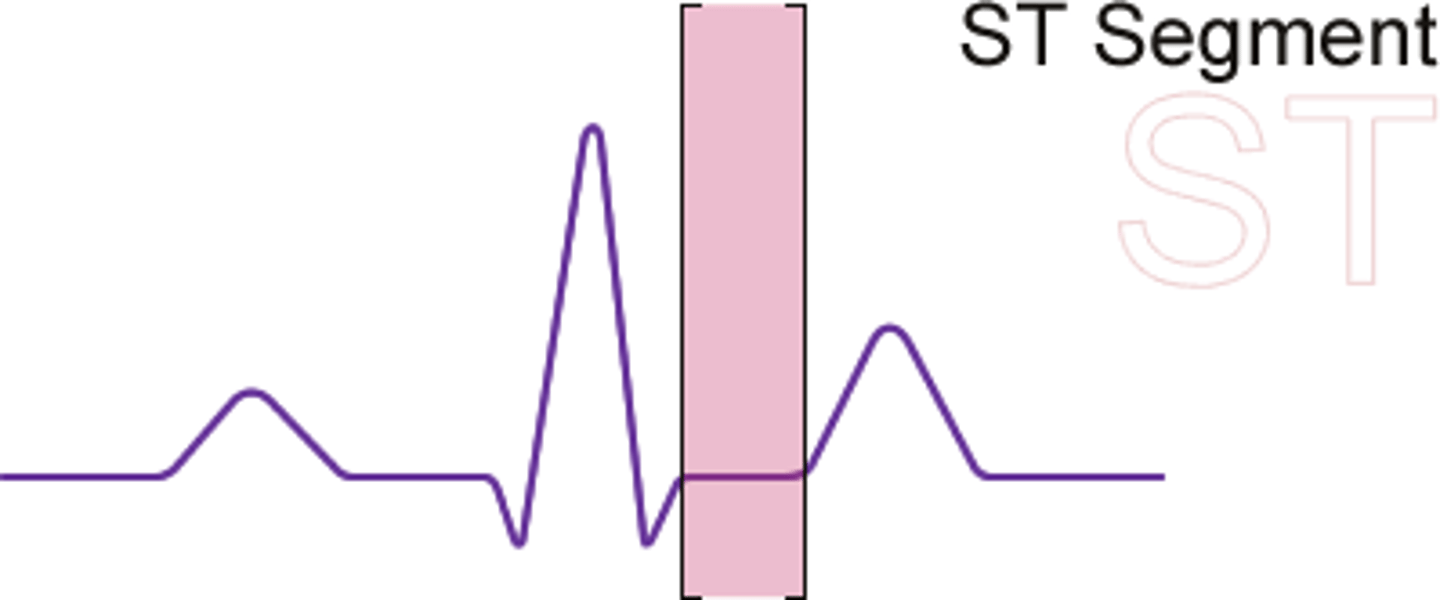
S T segment
time between ventricular depolarization and repolarization
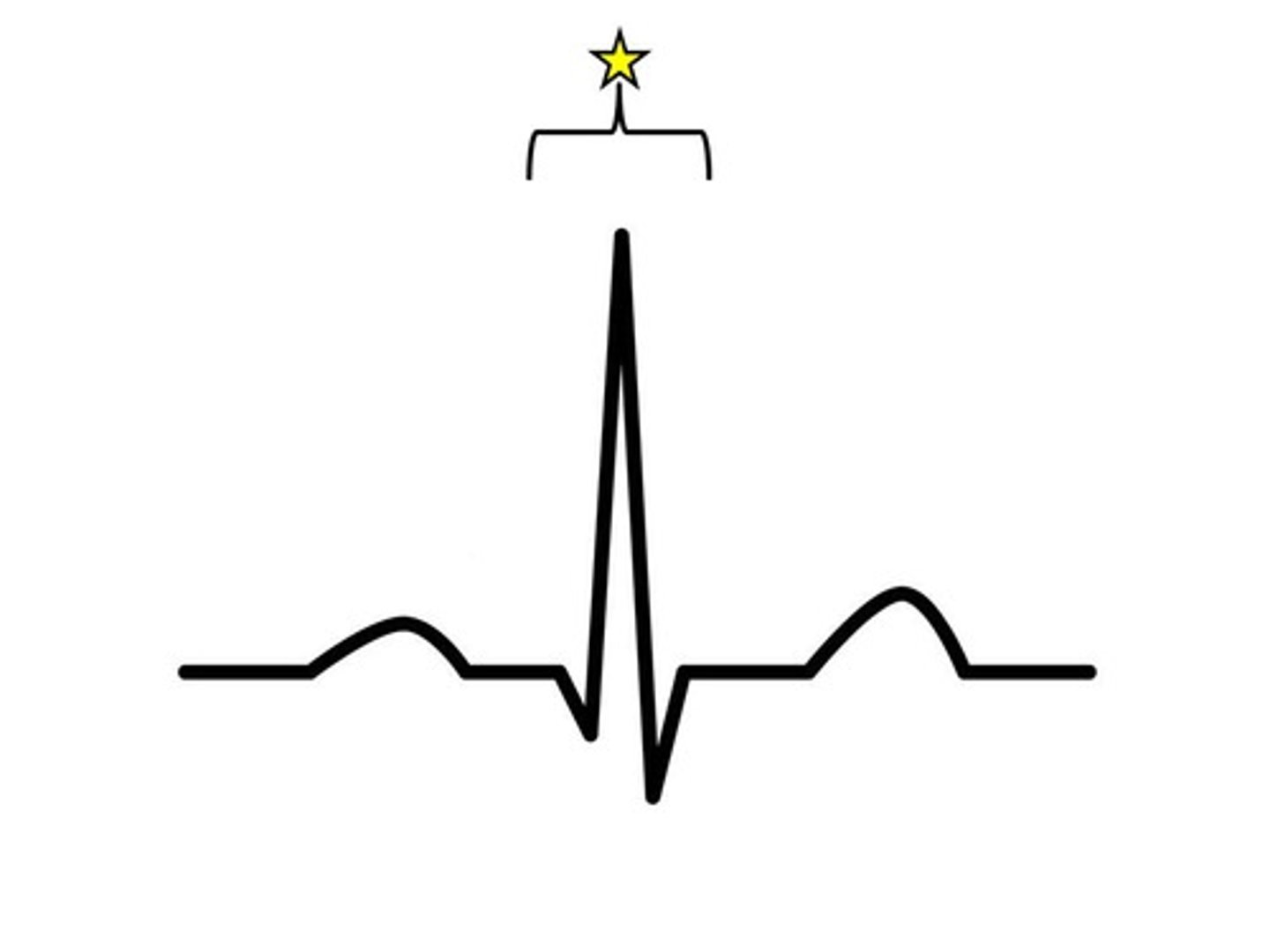
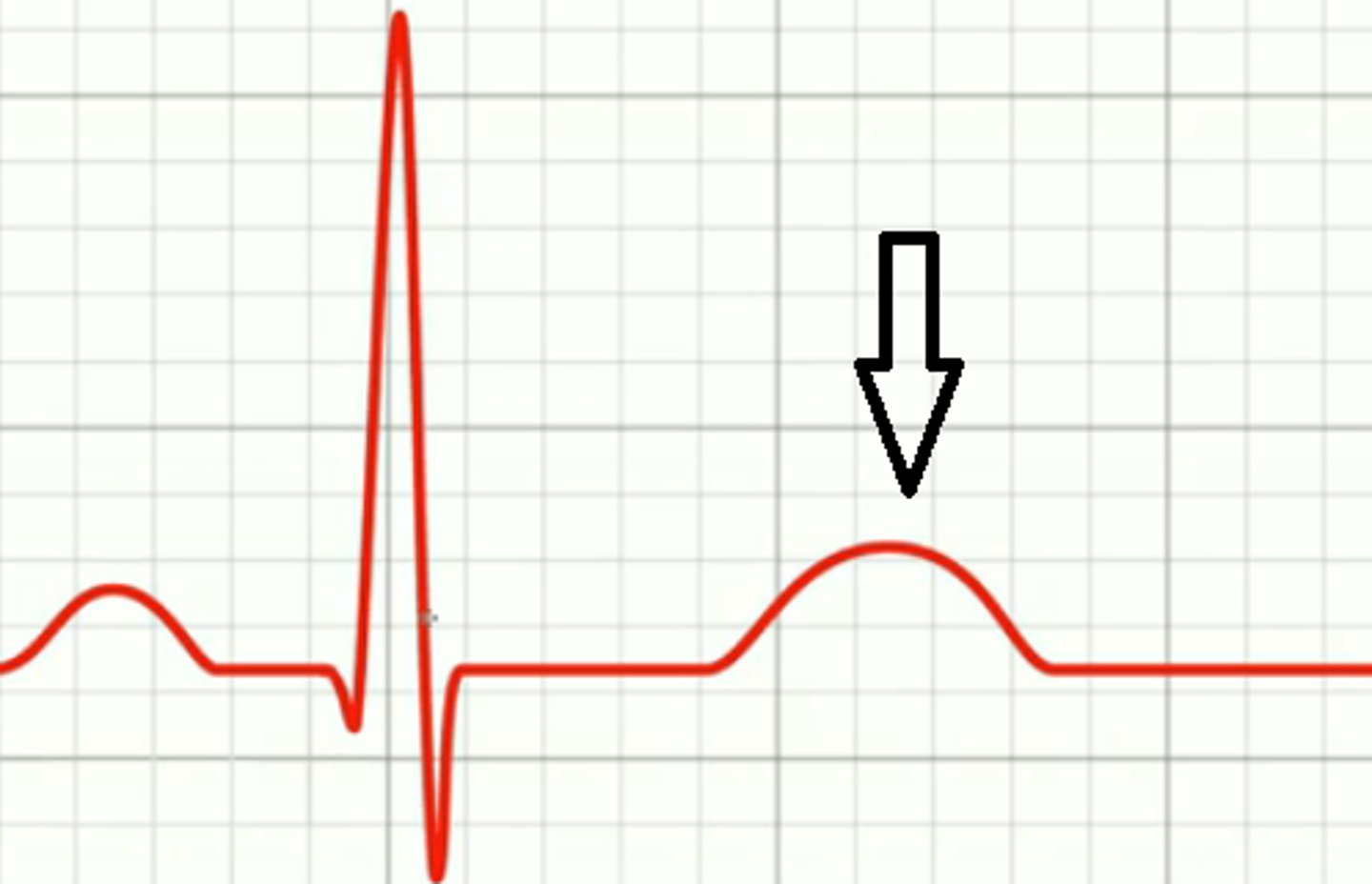
T wave
ventricular repolarization
hydrostatic pressure
pressure of a liquid against its container walls
velocity of flow
The distance a fixed volume of blood travels in a given period of time
systolic pressure
peak pressure in arteries from ventricular contraction
diastolic pressure
min pressure in arteries from ventricular relaxation
pulse pressure
systole-diastole
peripheral resistance
opposition to blood flow caused by friction of the blood vessel walls
baroreceptors
sensory receptors in aorta and carotid artery that sense blood pressure
orthostatic hypotension
low blood pressure in the head when you move from lying down
kidneys
filter blood and modify plasma into urine
ureters
pass urine from kidney to bladder
urinary bladder
stores pee until micturition
urethra
passes urine from bladder to toilet
nephron
microscopic tubules responsible for creating urine
cortical nephrons
85% of nephrons, short loops in cortex
juxtaglomerular nephrons
Glomerulinear the Long loops of Henle
juxtaglomerular apparatus
Specialized cells next to the glomerulus that help to regulate blood pressure and filtration
70% of filtrate is reabsorbed at the
proximal tube
20% of filtrate is reabsorbed at the
loop of henle
9% of filtrate is reabsorbed at the
distal tube
we produce _L urine per day
1.5
filtration barriers of the renal corpuscle
glomerular capillary walls, basement membrane, podocytes
macula densa cells
detect salt in filtrate
granular cells
secrete the enzyme renin
transport maximum
transport rate at saturation
saturation
maximum rate of transport when all carriers are occupied with substrate
renal threshold
the plasma concentration at which a solute first appears in the urine due to saturation