Module 4 - SHS310
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is the velopharyngeal mechanism?
A muscular valve that extends from the posterior surface of the hard palate to the posterior pharyngeal wall. It includes the velum, the lateral pharyngeal walls, and the posterior pharyngeal wall
How can oral and nasal consonants be differentiated in mid-sagittal MRIs?
Oral consonants (b, p, t, d, k, g), the velum is raised and retracted, creating a tight seal that closes off the nasal cavity
Nasal consonants (m, n), the velum is lowered, which opens the velopharyngeal port and allows air and sound to flow through the nasal cavity.
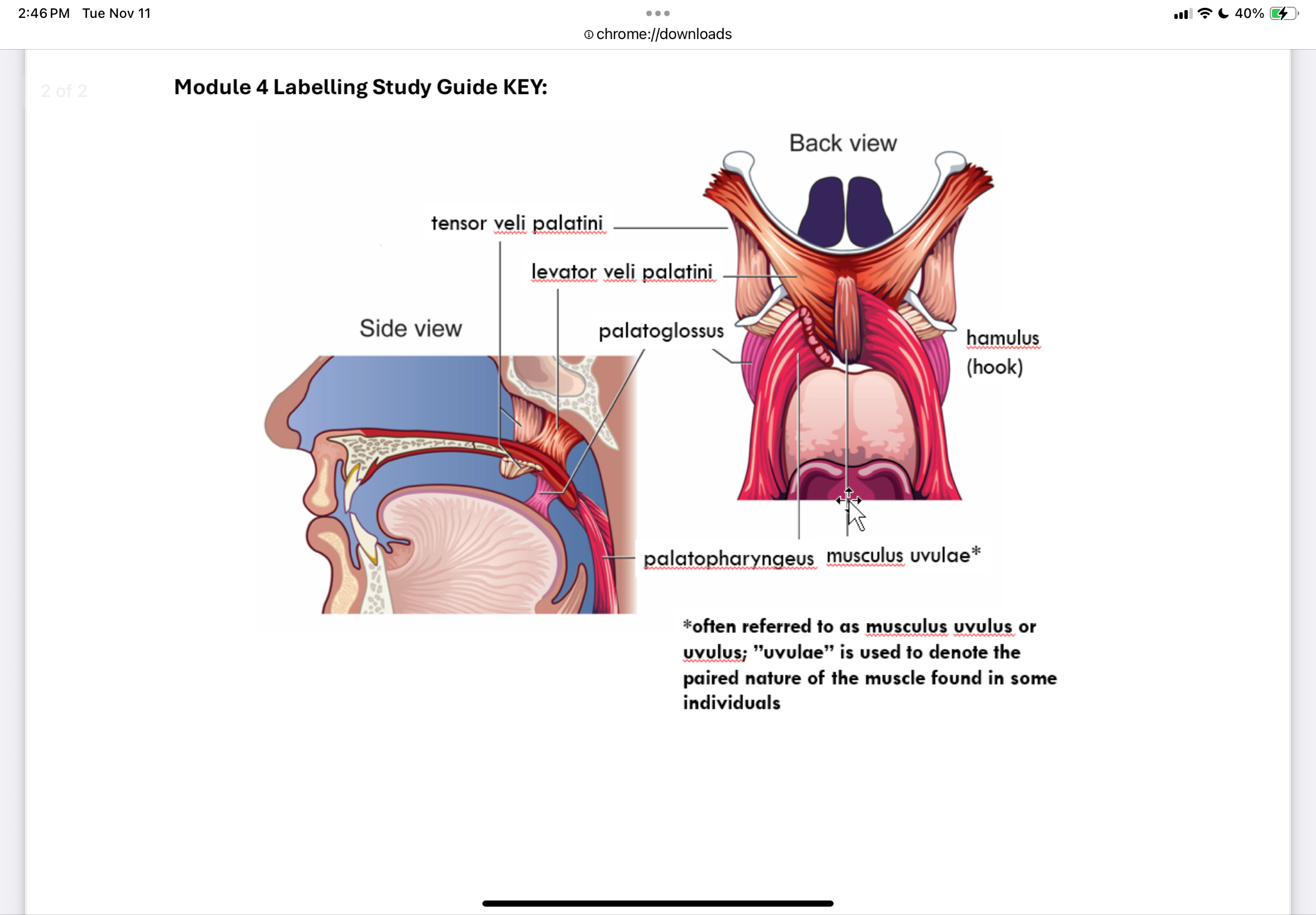
What are the muscles of the velum?
Levator veli palatini
Tensor veli palatini
Musculus uvulae (uvular muscle)
Palatoglossus
Palatopharyngeal
What muscles contract to open the velopharyngeal port?
The palatoglossus and palatopharyngeus muscles contract to lower the velum, which opens the velopharyngeal portand allows air to pass into the nasal cavity during nasal sound production (e.g., /m/, /n/, /ŋ/).
What muscles contract to close the velopharyngeal port?
The levator veli palatini and the musculus uvulae contract to elevate and retract the velum, helping to close the velopharyngeal port and separate the oral and nasal cavities during speech. The superior pharyngeal constrictor also assists in achieving full closure by moving the pharyngeal walls inward
What muscle opens the Eustachian tube?
The tensor veli palatini opens during swallowing and yawning
What muscle ensures a tight velopharyngeal seal?
The musculus uvulae ensures a tight velopharyngeal seal by shortening and increasing the bulk of the velum, filling any small gaps between the velum and the posterior pharyngeal wall during closure
List all movement patterns of which the velum is capable?
Upward and backward movement
Downward and forward movement
Shortening and increasing bulk
List all movement patterns of which the pharyngeal walls are capable of?
Forward and backward movement of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Inward and outward movement of the lateral pharyngeal walls
How are adenoids and tonsils may impact velopharyngeal closure
In children, the adenoids often help achieve closure because the velum can make contact with the adenoid pad to create a seal
If the adenoids atrophy (shrink) with age or are surgically removed, which leads to velopharyngeal insufficiency and symptoms like hypernasal speech
Conversely, enlarged tonsils can impede velopharyngeal closure by occupying too much space in the pharynx
What is resonance?
Is the process by which sound is amplified, modified, or enriched as it travels through the vocal tract
What is resonator?
Any structure that can vibrate in response to an input vibration and amplify certain frequencies while reducing others
What is impedance?
The resistance to airflow or sound energy within the vocal tract
What is attenuate?
To reduce or weaken the amplitude of certain sound frequencies as they pass through a medium or resonator
What is dampen?
To decrease the vibratory energy of a sound wave, often reducing resonance or loudness.
What is the difference between oral and nasal resonance?
Oral resonance occurs when the velopharyngeal port is closed directing all sound energy through the oral cavity (b, t, k)
Nasal resonance occurs when the velopharyngeal port is open, allowing sound and airflow to pass through the nasal cavity (m, n, ng)
How does Source0filter theory incorporates nasal resonance?
Explains how speech sounds are produced by the vibration of the vocal folds (source) and then shaped by the resonating cavities of the vocal tract (filter). However, when the velopharyngeal port is open, the nasal tract becomes coupled with the oral tract.
What are the three conditions of vocal tract/nasal tract coupling
Velopharyngeal port closed
Velopharyngeal port open with vocal tract occluded
Velopharyngeal port open with vocal tract unoccluded
What are the conditions for velopharyngeal port is closed?
There is no coupling. The velum is raised and sealed against the posterior pharyngeal wall. The oral and nasal tracts are separated, so sound and airflow travel only through the oral cavity.
What are the conditions of the velopharyngeal port that is opened with vocal tract occluded?
It is coupled, but output through nose only. The velum is lowered, and the oral cavity is blocked by the tongue or lips. Air and sound travel through the nasal cavity, existing only through the nares (nostrils)
What are the conditions of the velopharyngeal port that is opened with vocal tract unoccluded?
It is coupled with dual output. The velum is lowered, and the oral cavity is open, allowing air and sound to pass through both the mouth and the nose.
What is the role of the sinuses in nasal sound production?
The sinuses act as side branches or resonating cavities connected to the main nasal passage. During nasal sound production, when the velopharyngeal port is open, air and sound energy can resonate within these sinus cavities. The sinuses help modify and filter the sound energy of nasal phonemes, giving them their characteristic “nasal” timbre
What is the definition of velopharyngeal inadequacy or dysfunction?
A condition in which the velopharyngeal valve does not function normally, preventing consistent and complete closure between the oral and nasal cavities during speech.
What is the velopharyngeal insufficiency?
A structural or anatomical defect prevents adequate closure of the velopharyngeal port. Common causes include cleft palate, short velum, or deep pharynx
What is velopharyngeal incompetence?
A neurophysiological disorder results in poor or inconsistent movement of the velopharyngeal muscles. Common causes is TBI, stroke, motor speech disorders)
What is velopharyngeal misleading?
A learned or behavioral error in which the speaker uses incorrect articulation patterns, causing the velopharyngeal port to remain open when it should be closed
A person with a deep pharynx might suffer velopharyngeal insufficiency?
True because the problem is with the cleft palate, velopharyngeal dysplasia, and a deep pharynx
What is an example of velopharyngeal incompetence?
A person with cerebral palsy, stroke, neuromuscular disease, or brain stem tumor might experience this due to weak or uncoordinated muscle movement
What is an example of a velopharyngeal mislearning?
A child with a speech sound disorder who substitutes a pharyngeal fricative for /s/ or /z/, or a person with hearing loss
What is a commonly used instrumentation used to assess VPD?
Nasendoscopy
Perci-SARS aerodynamic system
Nasalance visualization system
Nasal air pressure cannula/transducer
What is hypernasality and an example?
When excessive sound resonates in the nasal cavity during speech due to incomplete velopharyngeal closure.
Example - a speaker produces the word “baby” sounding like “mamy”
What is hyponasality and provide an example?
Hyponasality occurs when nasal resonance is reduced or absent due to a blockage or obstruction in the nasal passages.
Example: A person with a cold produces /m/ as /b/, /n/ as /d/, or /ŋ/ as /g/ (e.g., “money” → “budd-ee”).
What is nasal air emission?
Nasal air emission occurs when air escapes through the nose during production of high-pressure consonants (stops, fricatives, affricates) due to poor velopharyngeal closure.
What is “cul-de-sac resonance and provide an example?
Cul-de-sac resonance occurs when sound resonates in a cavity (nasal, oral, or pharyngeal) but is trapped due to an obstruction at the cavity’s exit.
Examples -
Oral cul-de-sac: Large tongue obstructing oral cavity.
Nasal cul-de-sac: Blockage at the nostrils (e.g., deviated septum).
Pharyngeal cul-de-sac: Enlarged tonsils trapping sound in the pharynx.
What is hyponasality and denasality and provide examples?
Hyponasality: Partial blockage of the nasal cavity → reduced nasal resonance during nasal sounds.
Example: During a cold, /m/ sounds like /b/.
Denasality: Complete blockage → no nasal resonance.
Example: A person with severely swollen adenoids may produce no nasal airflow at all; /n/ and /m/ become completely oral (e.g., “man” → “bad”).
What is mixed resonance and provide an example?
Mixed resonance is a combination of hypernasality and hyponasality.
Example - A person with cleft palate and enlarged adenoids may show hypernasality in vowels but reduced resonance for nasal consonants.
What is nasality?
A perceptual quality of speech — how much nasal sound a listener hears. It is subjective and judged by ear.
What is nasalance?
An objective measurement of nasal sound energy, obtained using a nasalance system (which compares nasal and oral sound pressure levels).
How is nasal port area estimated using airflow measurement?
The Perci-SARS aerodynamic system measures oral pressure and nasal airflow during speech.
By comparing these values, the system estimates the size (area) of the velopharyngeal port.
Small or zero area = adequate closure (normal speech).
Larger area = incomplete closure (hypernasality or nasal air emission).
What is the difference between nasal airflow and nasal air pressure?
Nasal airflow: Measures the flow of air through the nose during speech.
Best for detecting nasal emissions in older children or adults who can tolerate a mask.
Nasal air pressure: Measures pressure changes at the nares (using a nasal cannula).
Often used with infants or individuals who can’t tolerate airflow masks because it’s less intrusive.
What clients are nasal airflow and nasal air pressure for measures?
Both measures help determine whether the velopharyngeal port is open or closed, but nasal airflow provides quantitative flow data, while nasal air pressure provides a binary open/closed indication.
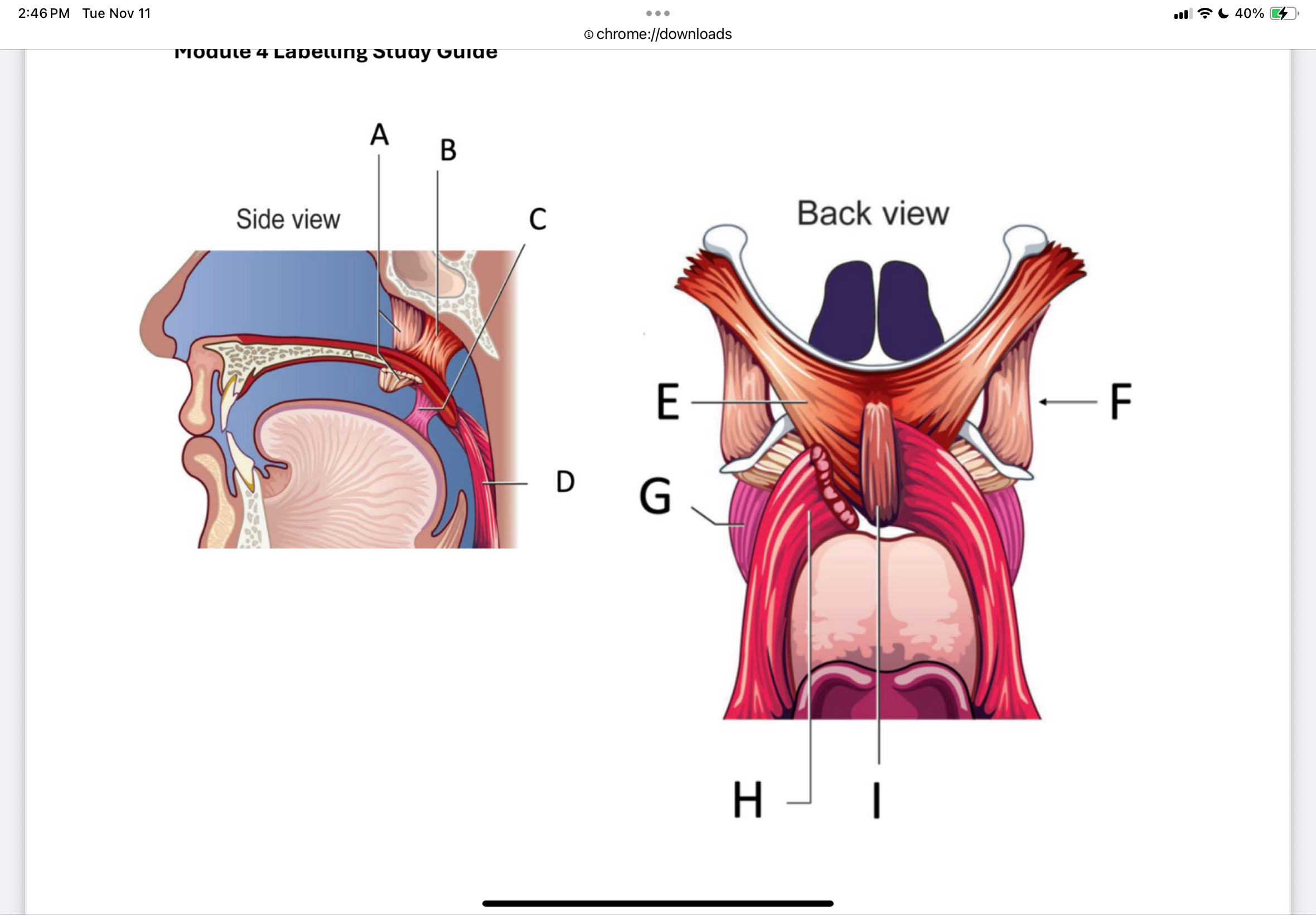
Label A through I
A - Tensor veli palatini
B - Levator veli palatini
C - Palatoglossus
D - Palatopharyngeus
E - Levator veli palatini
F - hamulus (hook)
G - Palatoglossus
H - Palatopharyngeus
I - Musculus uvulae