Education
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
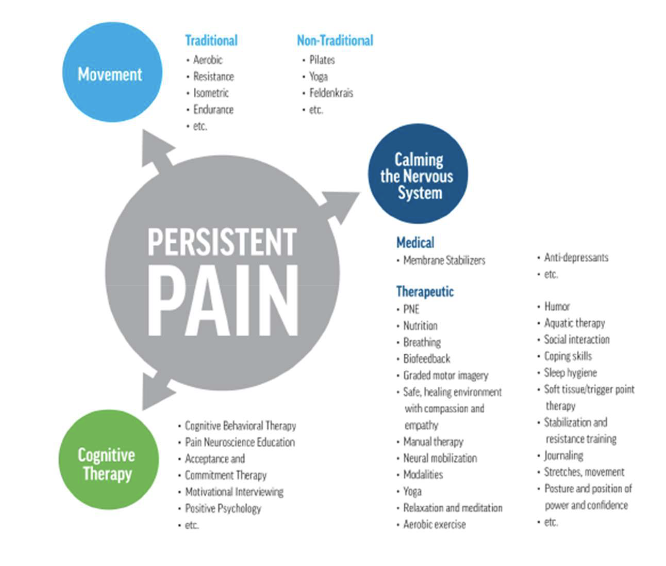
Review - Treatment of Persistent Pain
What Patients Want..
Provide Education on
Louis Gifford 4 questions
additional question
what is provide education
– Diagnosis
– Prognosis
– POC
– Self help
what is louis gifford 4 questions ?
1. What is wrong with me?
2. How long will it take?
3. What can I do for it?
4. What can you do for it?
what is the additional question?
How much will it cost?
what is Cognitive Therapy?
• Typically associated with psychologists, psychiatrists, and counselors
• Large scale of pain means cognitive therapy must expand to other health care providers
– Including physical therapists
Cognitive interventions include:
– Pain Neuroscience Education (PNE)
– Motivational Interviewing (MI)
– Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBE)
– Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT
what is Motivational Interviewing?
– collaborative communication style for activating a persons own motivation and commitment to change
what is 3 essential elements of Motivational Interviewing?
1. Conversation about change
2. Collaborative (person-centered)
3. Evocative (person’s own motivation)
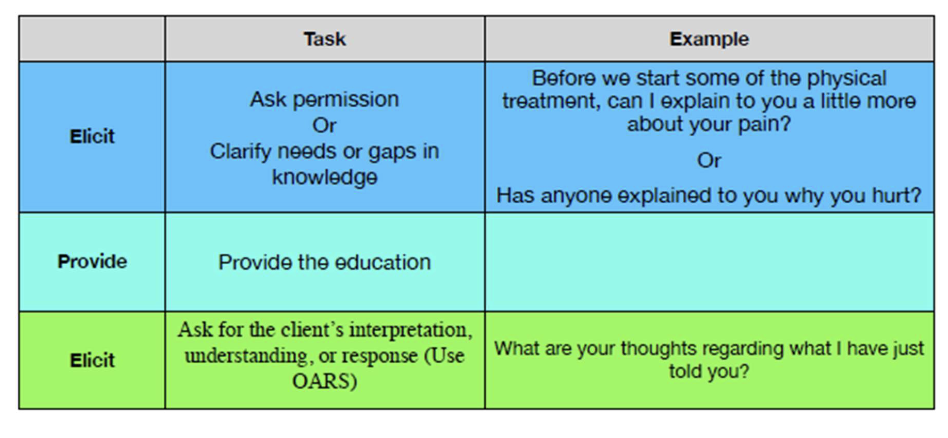
MI and PNE
what is Pain Neuroscience Education (PNE)?
Increase the patient’s understanding of pain to improve their pain experience
what is there to educate on for Pain Neuroscience Education (PNE)?
Educates patients about the non-tissue related factors that contribute to the pain experience
what is positive influences for Pain Neuroscience Education (PNE)?
– Pain ratings
– Knowledge
– Disability
– Pain catastrophizing
– Fear avoidance
– Physical movement
– Healthcare utilization/cost
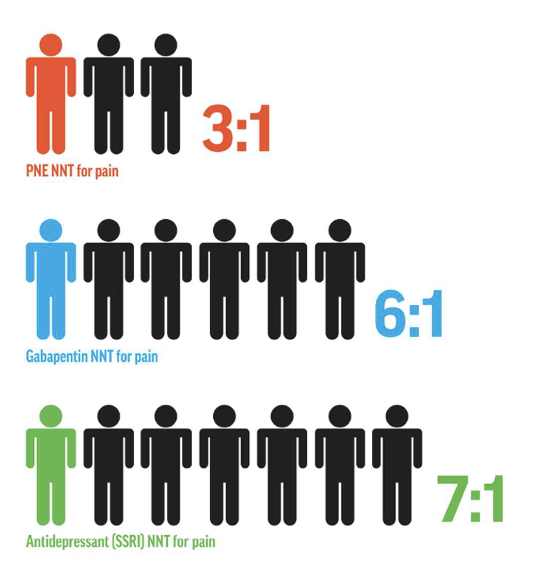
NNT (Number Needed to Treat)
– Lower values = higher treatment effectiveness
No known harm or fatalities from PNE
Medications carry risk of serious side effects; PNE does not
PNE shows strong efficacy with minimal risk
PNE – Efficacy
Focuses on pain neuroscience (e.g., sensitization, plasticity) using metaphors and visuals, not medical jargon to explain pain
script consistency
audience reach
delivery methods
PNE is not limited to chronic pain patients—it's broadly applicable
PNE Content and Delivery
what is under script consistency?
delivering a unified message
what is under audience reach?
effective across diverse group

Who Needs PNE?
• Patients presenting with central sensitization
• Patients with high fear- avoidance
• Patients with high pain catastrophizing
• Patients with persistent (long- lasting) pain
• Patients ready to change
– contemplation and preparation phases
screen for safety
identify candidates for PNE
seek patient permission
set expectations
pace the education
keep sessions short and focused
use tailored metaphors
incorporate visuals
apply across pain types
Clinical Application of PNE
what is under screen for safety?
Conduct a thorough patient examination
what is under Identify candidates for PNE?
Determine if the patient is likely to benefit
what is under Seek patient permission?
ask if they’d like to learn more about their pain?
what is under set expectations?
Clarify that education is part of the treatment, not psychological counseling
what is under pace the education?
Deliver information gradually
what is under Keep sessions short and focused?
– Limit each PNE session to ~10 minutes, targeting one pain-related concept
what is under use tailored metaphors?
Match metaphors to the patient’s specific complaint
what is under incorporate visuals?
Use images or drawings to enhance understanding
what is under apply across pain types?
Use PNE for acute, perioperative, and persistent pain conditions.
Has anyone explained to you why you hurt?
Would you like to know why your pain is not getting better?
Before we start some of the “physical” treatment, I’d like to explain to you a little more about your pain
Starting the “Pain Talk”
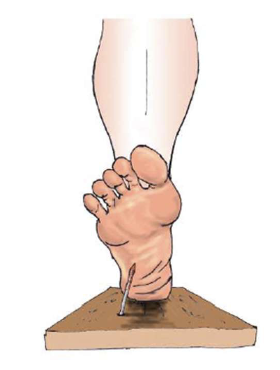
if you step on a rusted nail, would you want to know about it? why?
get help
get a tetanus shot
take the nail out
be careful of walking barefoot where there might be nails
how do you know there is a nail in your foot?
the message travels from the foot to the SPC, then on to the brain
the brain produces pain to grab your attention and get you to take care of the problem
it contains 400 individual nerves, totaling 45 miles (or 72 km for the metric people)
all the nerves are connected like an information superhighway
this is the bodys nervous system
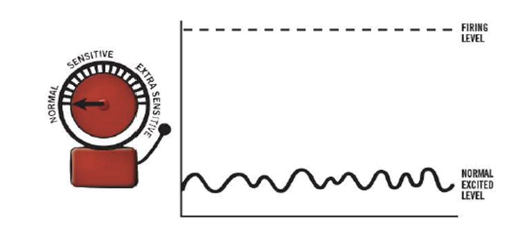
all 400 nerves have a little bit of electricity flowing through them
this is normal and shows you are alive
nerves are like our alarm systems, designed to send us danger messages when there is a threat, such as stepping on a rusted nail
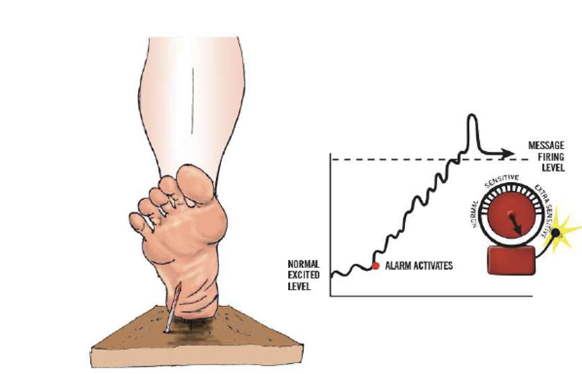
so when you step on a rusted nail, the alarm in your foot goes off
the alarm sends a danger message to your brain
the brain porduces pain to grab your attention and get you to take care of the problem
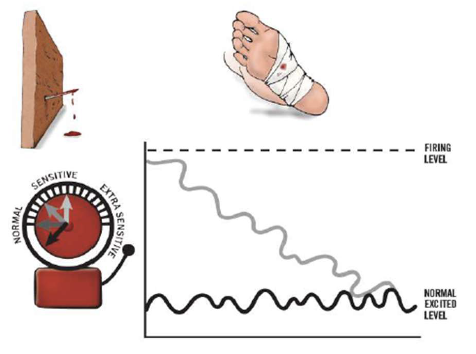
once you take the nail out, the alarm should go back down
thje alarm goes down slowly
you will likely feel discomfort or pain in the foot for a day or two
this is normal
once the alarm is back to its normal level, it is ready for the next danger
this is key: in approximately 1 in 4 people, the alarm does not go back down
the alarm (nervous system) stays extra sensitive
if pain lasts beyond the normal healing time, it is likely due to an extra sensitive alarm
your extra sensitive nervous system might be a big part of your pain, limited movement and sensitivity
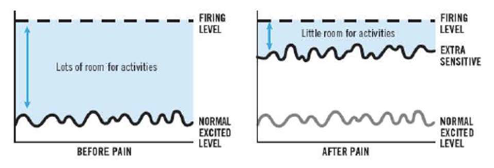
an extra sensitive alarm system can impact your life considerably
in the days before pain, you had lots of room for movement and activities without causing pain
since you developed pain, it takes far less activity or movement before you experience pain
the limited activity and movement is not necessarily due to injury or tissue damage but an extra sensitive alarm system
Adapt or Personalize PNE to your patient
– Consider patient’s age, culture, education level, hobbies, and fears.
– Replace generic examples with personalized stories that resonate with their life.
– Avoid jargon; use clear, relatable language.
Adapting PNE to your Patient
what are tips for success for Adapting PNE to your Patient?
• Ask: “What activities matter most to you?”
• Adapt metaphors to daily routines or interests (sports, music, parenting).
• Use visuals or props if helpful.
• Divide into 6 Groups
• Review the concept: The alarm system becomes overly sensitive, signaling danger even when tissue damage is not present.
Personalizing PNE - Instructions
what is task for Personalizing PNE - Instructions?
Create a new metaphor or story that explains the same concept in a way that fits your patient’s lifestyle or context
what is, Include these elements in your adapted story:
– Trigger: What sets off the alarm?
– Response: Why does the alarm go off too easily now?
– Reassurance: Explain that the alarm is not broken but overly sensitive, and therapy helps recalibrate it.
• Prepare a 2-minute patient-friendly explanation.
• Patients will typically as these 3 questions
1. How do you know this?
2. Why did the alarm not calm down?
3. How do we turn the alarm down?
Patient Questions
You Told Us
– Subjective examination
– Widespread pain
– Sensitivity to light touch
– Decrease ability to move and function
Your Doctor Told Us
– Medications
• Membrane stablizers
• Antidepressants
• Muscle relaxers
– Calm down the nervous system
Your Exam Told Us
• Findings form the exam align
• Limited ROM
• Decrease performance on neurodynamics
• Sensitivity to palpation
• When we experience injury, surgery, or emotional stress, the body's alarm system may stay elevated.
• Several factors can contribute
– Failed treatments
– Relationship stress
– Emotional strain
Why did the alarm not calm down?
• So what can I do to feel better?
– positive sign —means they’ve accepted the PNE message
– seeking help and ready to engage in solutions
OR
• You think it’s in my head?
• You do not understand, I have...
– Try another approach
– Pre-contemplation
How do we turn the alarm down?
• Introduce tools and techniques that support nervous system regulation
• Education and reconceptualization of pain
• Graded activity and movement
• Mindfulness and relaxation strategies
• Sleep hygiene and pacing
Answer - PNE+
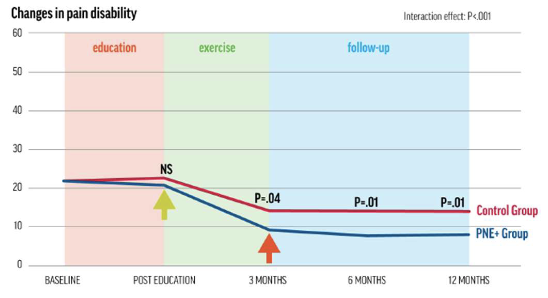
• PNE by itself does not produce strong clinical outcomes
– Not a standalone treatment
– Acts as a primer
• PNE + movement-based therapy was significantly more effective than PNE alone
– PNE enables movement, but movement itself reduces pain and disability
PNE+