Storage and inventory
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FNS200
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Storage
holding of products under proper conditions to ensure quality unit time of use
links receiving and production
Proper storage maintenance, temperature control and cleaning and sanitation are major considerations in ensuring quality of stored foods
ventilation etc
Storing
check stock dates
check temperature
fridge should be 4 degrees
freezer should be -3 → -17
keep storage areas clean
store items 6 inches off the floor
Requirements for storage areas
ventilated
adequate lighting
appropriate temperature range
slip resistant and easy to clean floors
windows opaque to protect from direct sunlight
humidity range
shelving - sturdy, non absorptive surfaces
Storage areas- dry storage
no freeze or fridge
provide protection from elements, insects, rodents and theft
separate from cleaning and pesticide storage
Goods should be 6 inches off the floor
shelves should be 5cm or 2 inches from the wlal
Humidity range for dry storage
50-60%
Temperature range for dry storage
50 -70 degrees F
10-21 degrees C
room temperature or a little colder
Low temp storage
walk in or reach in fridge or freezer
for preservation of quality and nutritive value
storage space must meet production needs and menu needs
Fridge
tempering box → thaws foods
Temperature should be monitored min 2 times a day
Humidity of low temp storage
75-95% humidity
higher than other because fresh foods require this
Refrigerator temperature
below 4 degrees c (41 f)
Foods in fridge top to bottom
Cookes and RTE foods
raw fish
raw unground beef
raw pork, ham, sausage, bacon
raw ground beef and pork
raw poultry
Storage freezer temp
-10 → 0 F
-23 → -18 C
Why is proper storage important
important in spoilage prevention
can be a criticla control point
prevent food adulteration
prevent theft and pilferage
inventory control
Inventory
record of all material assets owned by an organization
supported by the presence of products in storage areas
valuable resources to the operation
accurate records are important for
information of food and supplies stock
determine purchase needs
data for food cost control
prevention of theft and pilferage
Physical inventory
periodic actual counting and recording of products in stock in all storage areas
Perpetual inventory
purchases and issues continuously are recorded for each product in storage
balance in stock is avaialbel at all times
supported by computerized inventory systems
Food cost determination
Cost of food available - ending inventory = cost of food used
Begining inventory = total of all products in storage + purchases
Inventory control
must have accurate pricing and accurate counts
count by item or count by case
Inventory control tools
all subsystems owrk together
major function of control system
coordinate activities
influence decisionss and actions
assure that objectives are being met
make sure that you have enough of the correct resources to make the products that you want
decision making
Inventory turnover
estimation of how quickly products being brought in are used
done on a monthy basis
food cost would be food cost for that month
ability to control the amount of product held in inventory
turnover of 2 to 4x per month is what you want to have
monitors the effectiveness of inventory control
Inventory turnover calculation
Inventory turnover = cost of food used / average food inventory
Average food inventory = (Begining + ending inventory) / 2
ABC method of inventory
classify products with ABC according to value
a is the highest and C is the lowest
Effort, time and money for inventory control should be allocated among products according to their value
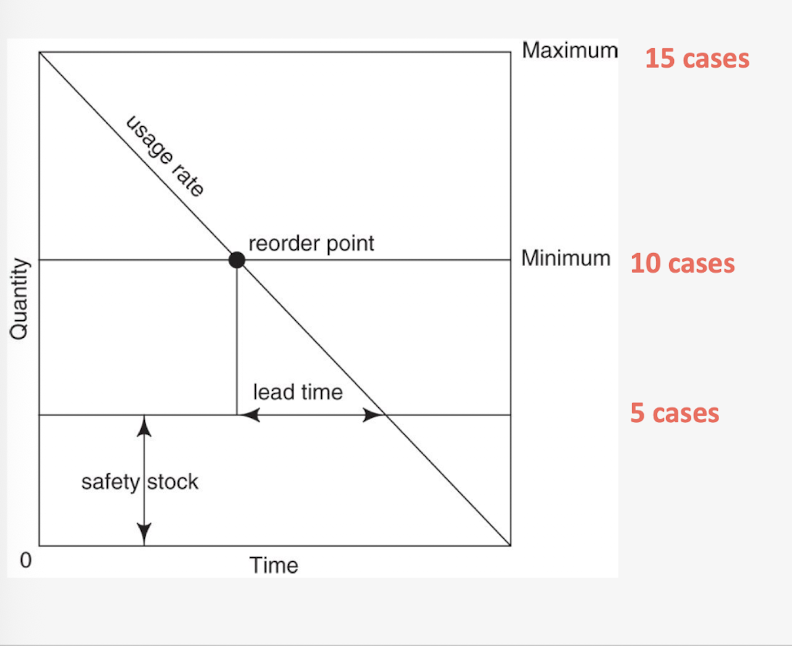
Minimum - maximum method
tool for controlling inventory by establishing lower and upper levels for each product in storage
min is the safety stock that has to be maintained at a constant level
max is the highest quantity desired to be in inventory
When lookign to reorder look at
lead time - how long it takes from ordering to receiving the item (may be longer depending on how far away the supplier is
Usage rate - how fast you use the product
determined by experience and forecasting
Reorder point - established by the lead time and usage rate
Inventort valuation mehtods
ensuring that valuing is consistend within an accounting period
actual purchase price
weighted average
FIFO
LIFO
Latest purchase price
Ethical considerations
buyers face ethics whcih change how they buy things
this can affect their performance
3 categories of ethical considerations
efforts to gain inside information about competitors that will benefit competition
Activities that allow buters to gain personal benefits from suppliers
try to persuade you with bribery
activities that manipulate suppliers to benefit the purchasing
suppliers may be local and scared not to give you waht you want
takign advantage of suppliers
Rules in code of ethics
set of rules for standards of professional practice or behaviour established by a group
no accepting gifts
influneced by codes of individuals
standard- the measure of what is expected to happen
many things have standards in the food industry
eg. no child labour etc
Ethics management
implmentation by managers of planning, organizing, staffing, leading and controlling you can ensure that ethics are established formally and explicitly in daily organizational life
to control ethical conduct, performance standards must be established and continually monitored and appropriate appreciative or corrective action should be taken
There must be transparancy and should be able to see if things are not being handled ethically