Meteorology Final
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Heterosphere
above 80 km, gases separate based on weight = stratified layers
Hemisphere
lower atmosphere up to 80km, circulates and maintains uniform ration of gases
thermosphere
upper most atmospheric level, above 80km
mesopause
break between mesosphere and thermosphere
mesosphere
second upper atmospheric level between 49-80km
stratopause
break between stratosphere and mesosphere
stratosphere
level 2 of atmosphere from 13-49 km
tropopause
break between troposphere and stratosphere
troposphere
surface level to 12 km, our familiar atmosphere
stratosphere
the region of greatest ozone concentration and the atmospheric layer in which it resides
3 principle gases of Earth’s atmosphere (chief constituents)
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon
Greenhouse effect
Heating of Earths surface and lower atmosphere caused by absorption and emission of infrared radiation
Ozone is destroyed by
Chorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and photo association (UV energy)
Height of Polar Tropopause
6-8km
Height of Equatorial Tropopause
18-20km
7 parameters of weather data collection
dew point/humidity, temperature, visibility, sky coverage, barometric pressure, wind speed, wind direction
Air Masses take on the characteristics of their
source regions
Anticyclone
high pressure rotating clockwise
Cyclone
Low pressure rotating counterclockwise
Incoming solar radiation is depleted by
absorption, reflection, backscattering
ALBEDO
combination of reflected and backscattered solar radiation
Heat is transported from equatorial latitudes to polar latitudes by
ocean currents and atmospheric circulation (winds)
a belt of ____ pressure surrounds the vicinity of the equator
low
Stratus
a cloud in contact with the ground
incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere is _____ incoming radiation at the earth’s surface
greater than
direction the Coriolis force acts to in northern hemisphere
right
instruments used to gather atmospheric information
satellite, radiosonde, radar, dropsonde, rocketsonde
T/F infrared satellites sense reflected sunlight
false
T/F the stratosphere is a layer of the atmosphere where the temperature decreases with increasing altitude
false
TF a front is a separation between air masses
true
TF the dry adiabatic lapse rate (temp decrease with height in dry air) in the troposphere for earth at standard sea level temperature and pressure is 9.8ºC per kilometer
true
TF water reflects most of the spar radiator which strikes it when the sun is high in the sky
false
TF the creation of ozone in the upper atmostphere is carried out to a large extent by the absorption of infrared radiation
false
TF absorbed solar radiation is greatest at the equator where earths planetary or terrestrial radiation is minimized
true
TF radiant energy or heat increases proportionately toward shorter wavelengths
true
TF the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum lies between 0.4-0.74 micrometers, where violet-blue is found at short wavelength and orange/red is found at long wavelength
false
TF terrestrial or planetary radiation is short wave radiation
false
TF the earth is closest to the sun during the norther hemisphere winter solstice
true
TF at the pole 90N and 90S terrestrial radiation emitted to space is greater than the solar radiation absorbed
true
TF a city is an island of warmth surrounded by cooler air, a so called urban heat
true
TF isotherms are constant lines of pressure
false
TF isobars are lines of constant temperature
false
TF the doppler effect refers to a frequency shift between sound waves or electromagnetic waves emanating from a moving source— change in pitch
true
RADAR
radio detection and ranging
TF a visible satellite image sense heat energy emitted from cloud tops
false
TF water vapor is an invisible gas
true
TF in general atmospheric motion flows from low to high pressure
false
TF aerosols are largely responsible for haze layers near industrial centers, photochemical smog and heat islands associated with large population centers (cities)
true
TF electromagnetic energy contains both electrical and magnetic energy fields and interacts with all things within the Earth-Atmospheric System
true
air mass
huge volumes of air covering thousands of sq. km horizontally relatively uniform with temperature and humidity
temperature
measure of hotness and coldness in scale of celsius or Fahrenheit
dew point
temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, can no longer hold in gas form
air has to be cool to retain saturation
barometric pressure
weight per unit area of overlying air in a column of air from Earths surface to top of atmosphere
Cumulus development
vertical
Cirrostratus development
high
altocumulus development
middle
cumulonimbus development
vertical
stratocumulus development
low
cirrus development
high
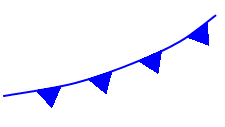
what kind of front is this
cold front
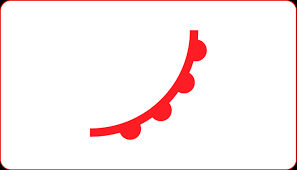
what type of front
warm front
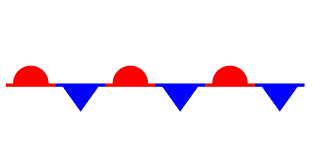
what kind of front is this
stationary front

what kind of front is this
occluded front
Cumulus stage (1) of air mass thunderstorm
all updraft
no precipitation
occurs for 10-12 minutes
mature stage (2) of air mass thunderstorm
both up and down drafts
heavy precipitation
occurs for 15-25 minutes
stratus stage (3) of air mass thunderstorm
all downdraft
little to no precipitation
occurs for 10-15 minutes
Baroclinic Pressure
density varies with pressure and temperature
TF air pressure drops more rapidly with altitude within a cold/denser column of air than in a warm/less dense column of air
true
the greater concentration of water vapor means the air is
less dense
Ideal Gas Law
states the pressure exerted by a gas is directly proportional to the product of its density and temperature
Collision-Coalescence
the primary precipitation mechanism in warm type clouds
TF freezing rain and drizzle is precipitation that freezes before hitting the ground
false
Bergeron-Findeisen ice crystal process
the primary precipitation mechanism in cold type clouds
TF readout obtained by doppler radar (weather echoes) are a power spectrum
true
Ground Clutter
a form of anomalous propagation (AP)
average standard sea level atmospheric pressure
980-1050 millibars
cold air advection
the horizontal movement of cooler air by the wind, resulting in a decrease in temperature at a specific location
warm air advection
the horizontal transport of warm air into an area where cooler air was previously present, causing a temperature increase at that location.
compressional warming
air pressure moves together to create temp change
expansional cooling
air pressure moves separate to create temp change
humidity
amount of moisture air is holding compared to max amount
cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)
water in clouds working with particles to precipitate
orographic lifting
a meteorological process where wind is forced to rise up a mountain or other topographic barrier
virga
rain or snow that evaporates before reaching the ground due to dry air below a cloud
supercooled water droplets
liquid water droplets that exist below their normal freezing point (0°C or 32°F) without freezing
barotropic atmosphere
temperature, pressure, density are in phase
geostrophic winds
wind flowing directly from west to east
planetary boundary layer
the lowest part of the troposphere that is directly influenced by the Earth's surface
vapor pressure
partial pressure contributed by water vapor molecules on the atmosphere
mixing ratio
the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the mass of dry air (g water vapor/kg of dry air)
dew point temperature
the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to attain saturation
conditional instability
the atmospheric lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate but greater than the moist adiabatic lapse rate
relative humidity
the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere relative to what the atmosphere can hold at a given temperature (vapor pressure/saturated vapor pressure x 100%)
absolute stability
the temperature of the air drops more slowly than the moist adiabatic lapse rate or the temp does not change with altitude (isothermal) or the temp increases with with altitude (inversion)
point of occlusion
where the occluded, cold, and warm fronts meet
cold fronts typically move ___ than warm fronts
faster
the jet stream is stronger in ____ (summer/winter)
summer
what kind of jet is most often found in the proximity of the mid latitude cyclones
polar jet
there may be as few as __ troughs in the long wave (Rossby) trough pattern
2
there may be as many as __ troughs in the long wave (Rossby) trough pattern
5