OCR GATEWAY GCSE BIOLOGY B1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
B1
Name Eukaryotic cells
Plant, animal
Name Prokaryotic cells?
Bacteria
\\\\e.g E.Coli
State the main differences in the structures found in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
EUKARYOTIC: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochrondria
PROKARYOTIC:cell wall, genetic material, cell membrane, cytoplasm, flagellum, plasmid
Equation that links magnification, image size and real size
image size = magnification x real size
What is resolution?
Resolution is how well you can separately distinguish 2 points close together.
Identify the main components of a light microscope
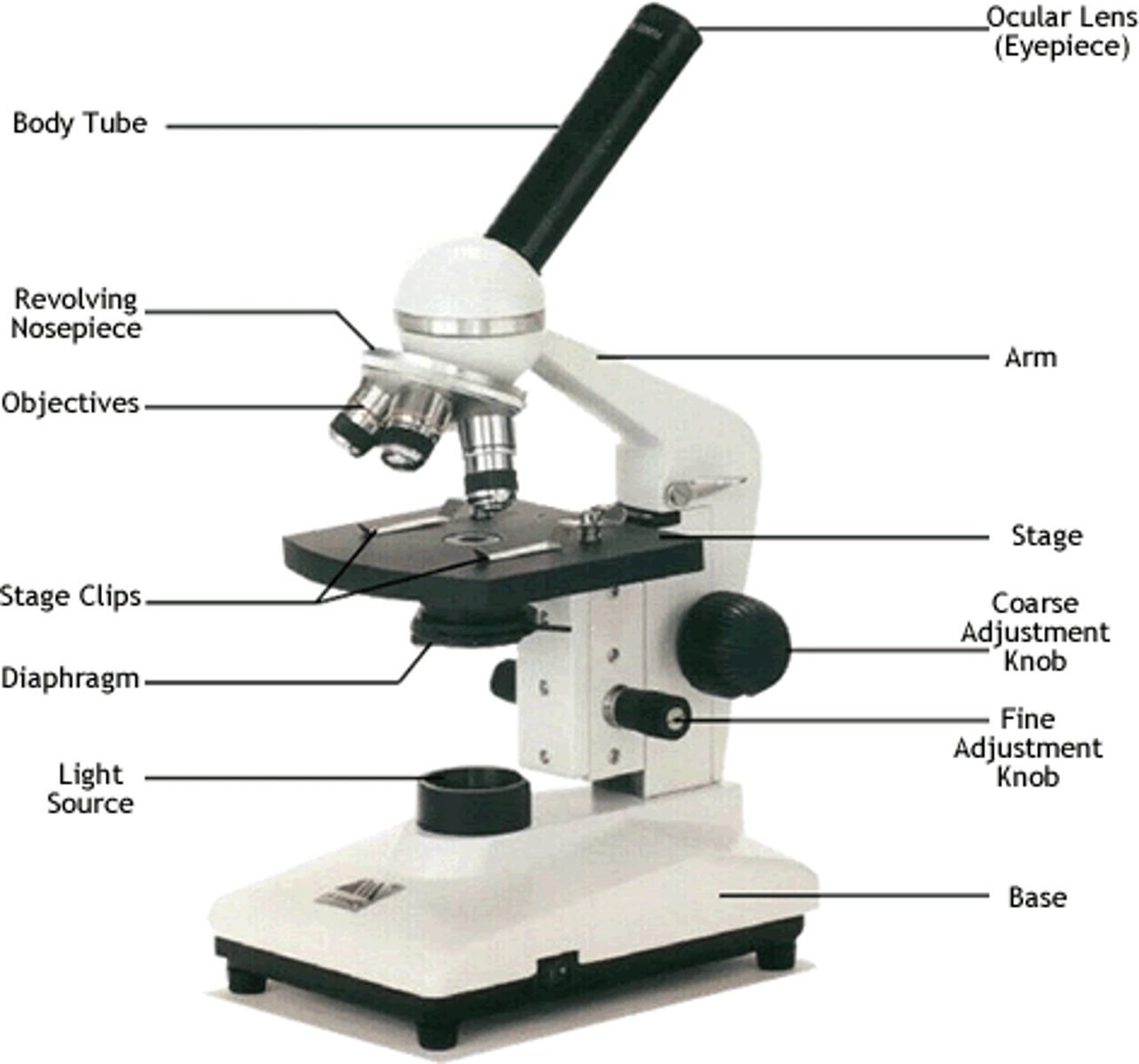
Steps to observing cells through a microscope
1. Move stage to its lowest position
2. Select objective lens with lowest magnification
3. Place slide on stage
4. Turn coarse focus knob until you see object
5. Turn fine focus knob slowly until object is in focus
6. THEN repeat steps but with higher magnification objective lens
Explain how staining is used to highlight cell features
-particular stains colour specific structures or give colour to colourless cells
-METHYLENE BLUE -nucleus of an animal cell
IODINE - plant cell nuclei
CRYSTAL VIOLET - stains bacterial cell walls
What is a electron microscope?
-high energy electrons as the light source
-greater resolution
-allowed scientists to see detail within subcellular structures like chloroplasts
State differences between light and electrons
PriceSizeResState(PSRS)
LIGHT - cheap, small/portable, simple to prepare sample, specimens can be living or dead, resolution up to 0.2μm, shows images in natural colour
ELECTRON - expensice, large/difficult to move, sample prepartion is complex, shows image in b&w, specimens need to be dead, resolution up to 0.1μm
TAKE A BREAK: its DNA next ew

State the role of DNA in the body
-chemical instructions to individual characteristics
Describe the structure of DNA
-two strands joined by bases (A+T, G+C)
-made of nucleotides(slice of pizza) joined all together
-each nucleotide(slice) is made of a sugar, phosphate group and base
Differences between mRNA and DNA
-DNA itself is too big to leave nucleus
-copy of the DNA is made called mRNA-
-mRNA is like a single strand of DNA
What is transcription?
Transcription is process where mRNA is produced
Describe process of transcription
1. DNA around a gene unzips so both strands are separated
2. One of DNA strands acts a template
3. Complementary bases attach to the strand being copied
4. This forms a strand of complimentary mRNA
What is translation?
Translation is the process where proteins are made. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome.
Describe process of translation?
1. Ribosome 'reads' the nucleotides on the mRNA in groups of three called codons. Each triplet codes for a specific amino acid
2. Ribosome keeps reading and adds more amino acids
3. Amino acids join in a chain forming a protein
Describe the function of an enzyme using named examples
-build larger molecules from small ones e.g protein synthesis
-break down large molecules into smaller ones e.g digestion
Describe the structure of an enzyme
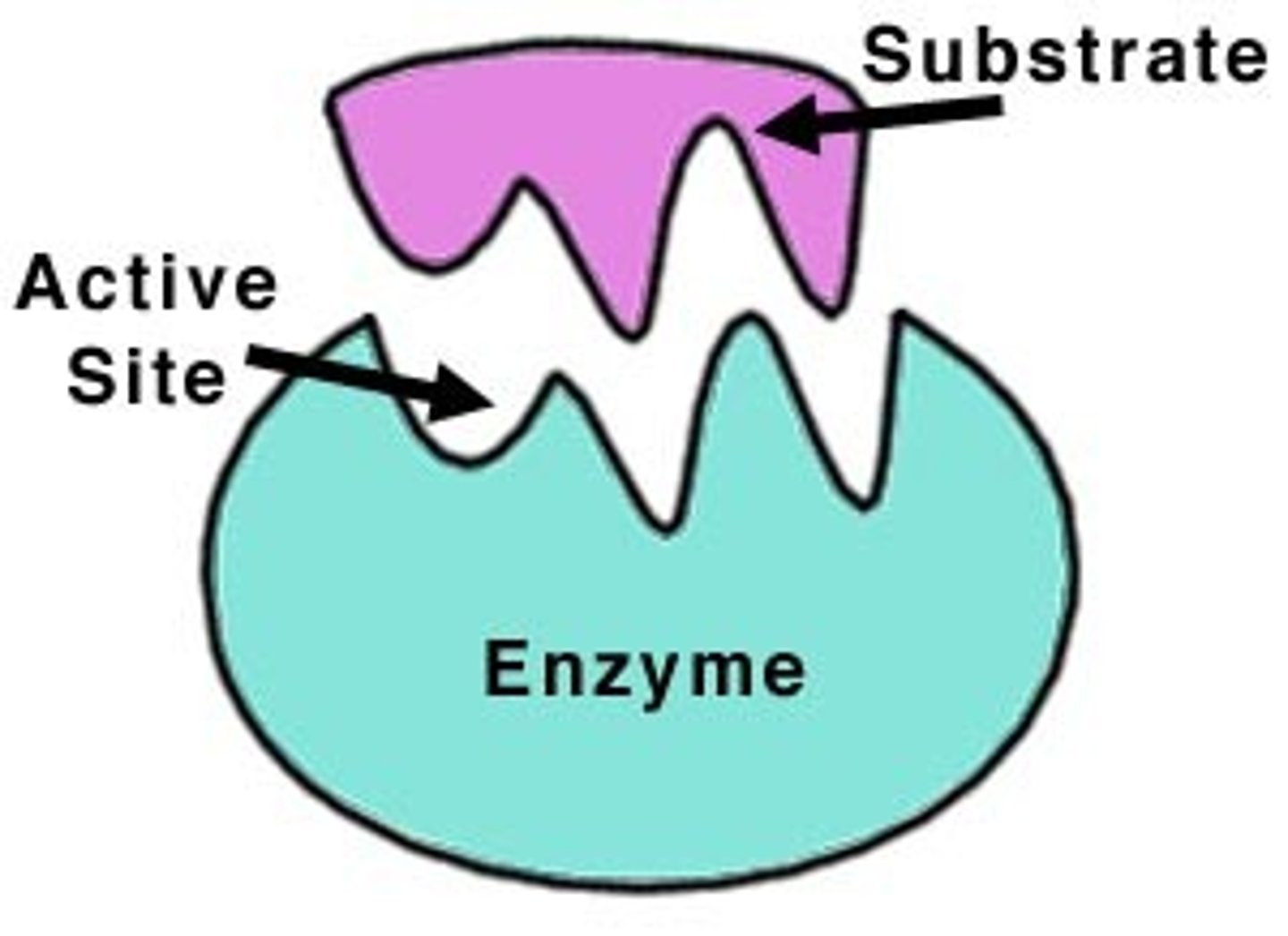
Describe what happens when an enzyme is denatured
-the substrate no longer binds so rate of reaction decreases
-when all are denatured, reaction stops completely
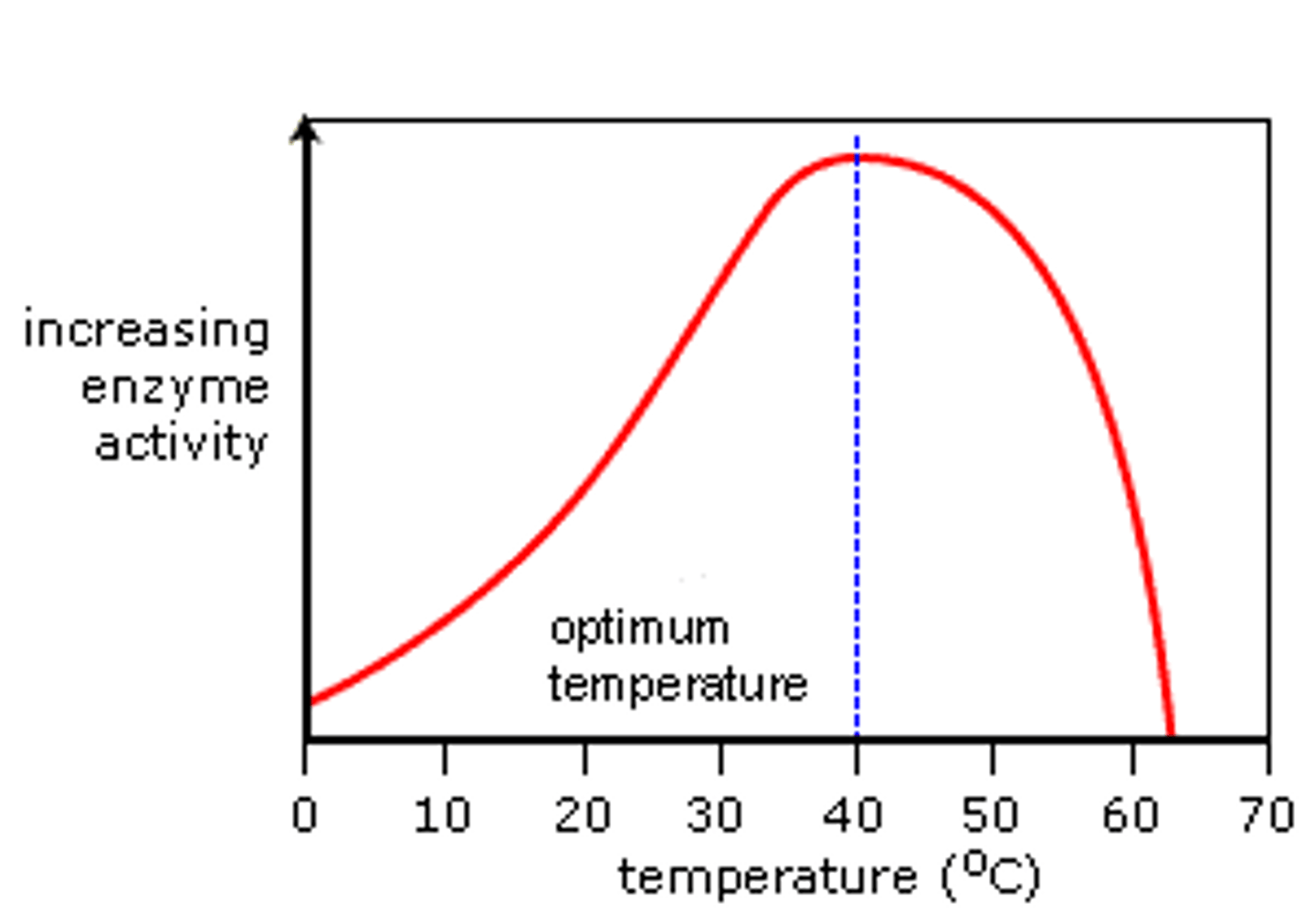
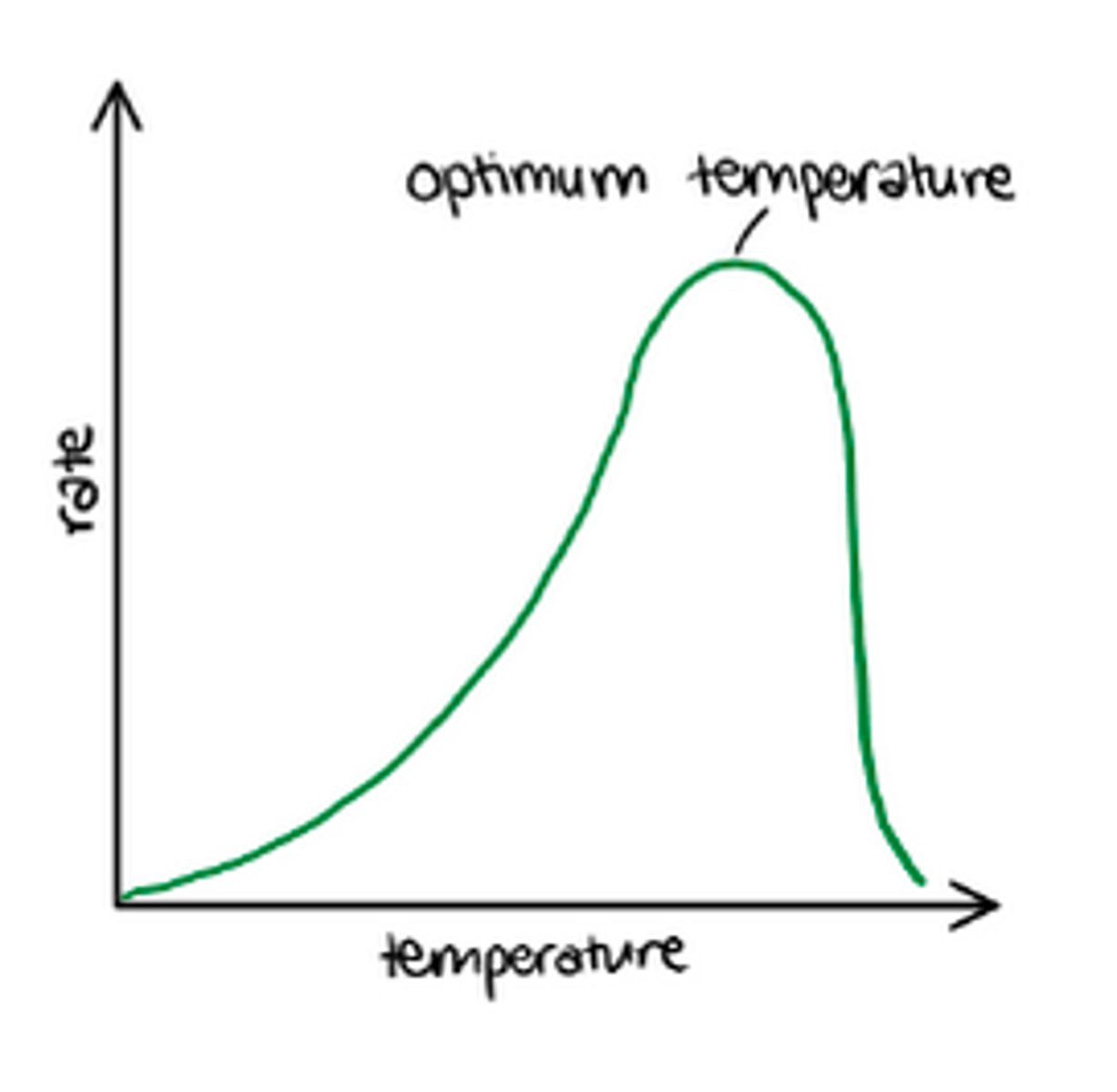
How does temperature affect enzymes?
-the higher the temp, the faster the reaction
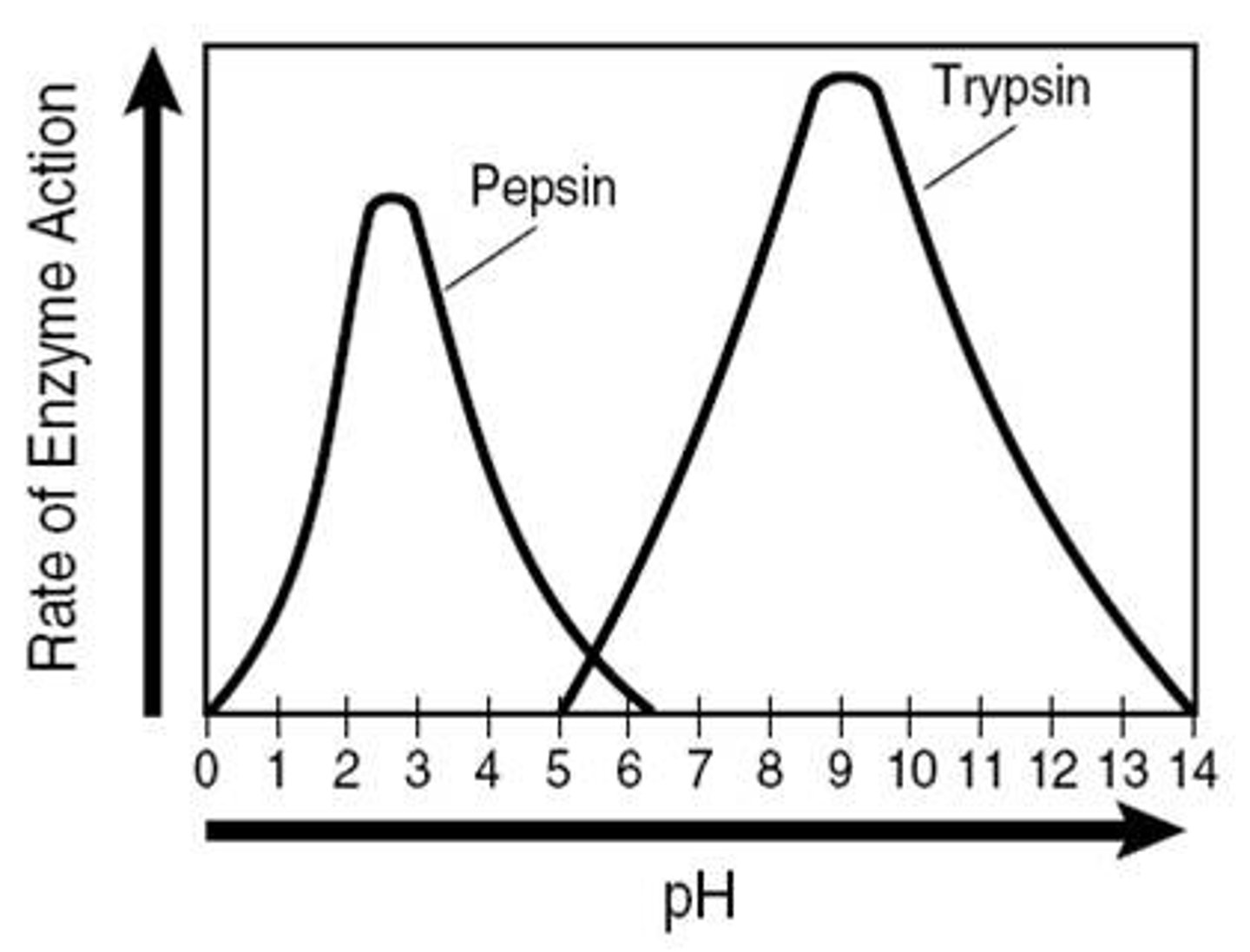
-each enzyme has its optimum pH
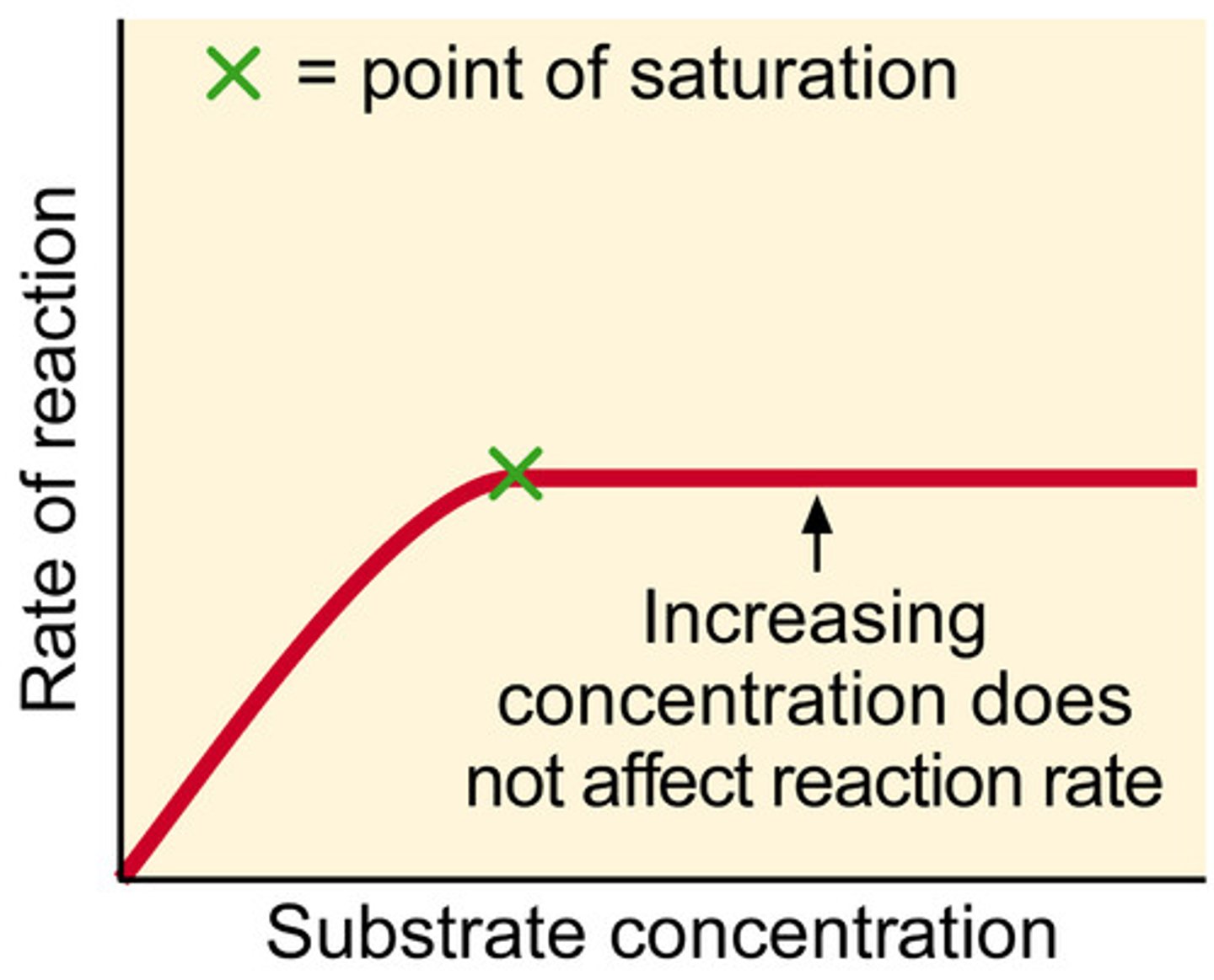
-the higher the substrate concentration, the faster the rate of reaction but then becomes constant
What does the graph look like? (temperature)
What does the graph look like? (pH)
What does the graph look like? (substrate)
TAKE A BREAK: photosynthesis and respiration is next its ok

State what is meant by metabolic rate
-the speed at which the chemical reactions in your cells transfer energy from its chemical stores in food
-the higher the metabolic rate, the more food you need to eat
Explain how carbohydrates are synthesised and broken down
-synthesised from glucose monomers
-starch is a carbohydrate
- starch is broken down with enzyme amylase
Explain how proteins are synthesised and broken down
-synthesised from amino acids
-broken down by protease enzymes
Explain how lipids(fats) are synthesised and broken down
-synthesised from 3 fatty acids and glycerol molecule
-broken down by lipase in small intestine
- contain bile to increase SA
What is equation of aerobic respiration?
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
What is equation of anaerobic respiration?
in animals = glucose => lactic acid (cramp)
FERMENTATION
in plants = glucose=> ethanol (C2H5OH) + carbon dioxide
Main differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
-anaerobic = 2 atp
- aerobic = 38 atp
TAKE A BREAK: next up photosynthesis!!

What is equation of photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water=> glucose+ oxygen
What are the 2 main stages of photosynthesis?
STAGE 1- light dependent
energy transferred from light splits water molecules into O2 and H+ ions
STAGE 2- light independent
CO2 combines w the H+ions to make glucose. The glucose produced is immediately used in respiration
How to test for starch
1. take leaf and place in boiling water to kill it
2. place leaf into boiling tube of boiling ethanol to remove all chlorophyll to stop the plant from photosynthesising
3. wash leaf with water to remove the ethanol and soften the lead and spread it out on a white tile
4. add drops of iodine solution if starch is present iodine will turn from yellow-brown to blue-black.
How to make the test for starch more accurate
test that the plant has photosynthesised by destarching the plant. meaning making sure that no starch is present in the leaves. to do this, keep the plant in dark for min 24 hrs.
How to prove that light is needed for photosynthesis
take a destarched plant and cover part of 1 of its leaves with black card or tin foil. light cannot reach the covered area of the leaf. place plant in sunlight for several hours and remove the card from leaf. finally test leaf for presence of starch
How to prove that CO2 is needed for photosynthesis
take a destarched plant and place insdie a polythene bad before sealing the bag add a pot of soda lime that will absorb CO2 and water vapour.
leave plant in sunlight. then test for starch
How to prove that O2 is given off during photosynthesis
place upturned test tube above an aquatic plant eg cabomba.
put apparatus in light for max photosynthesis.
once you have a full tube of gas, place glowing splint inside tube. it should relight if oxygen is actually present
What factors affect photosynthesis
light intensity, CO2, temperature
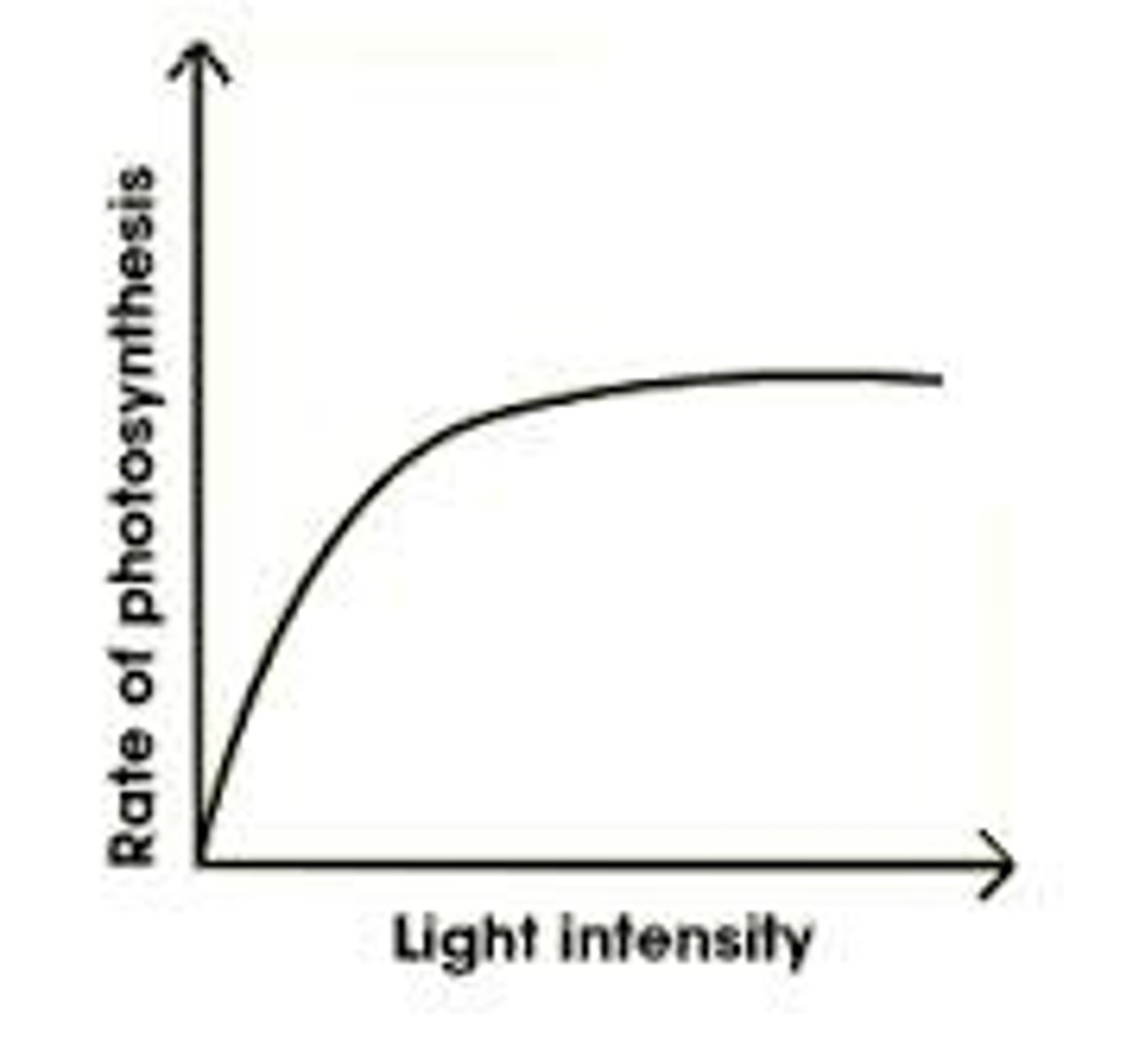
How does light affect photosynthesis
when testing this couting bubbles w ur eyes is bad bc u could miss one n bubbles could be different sizes
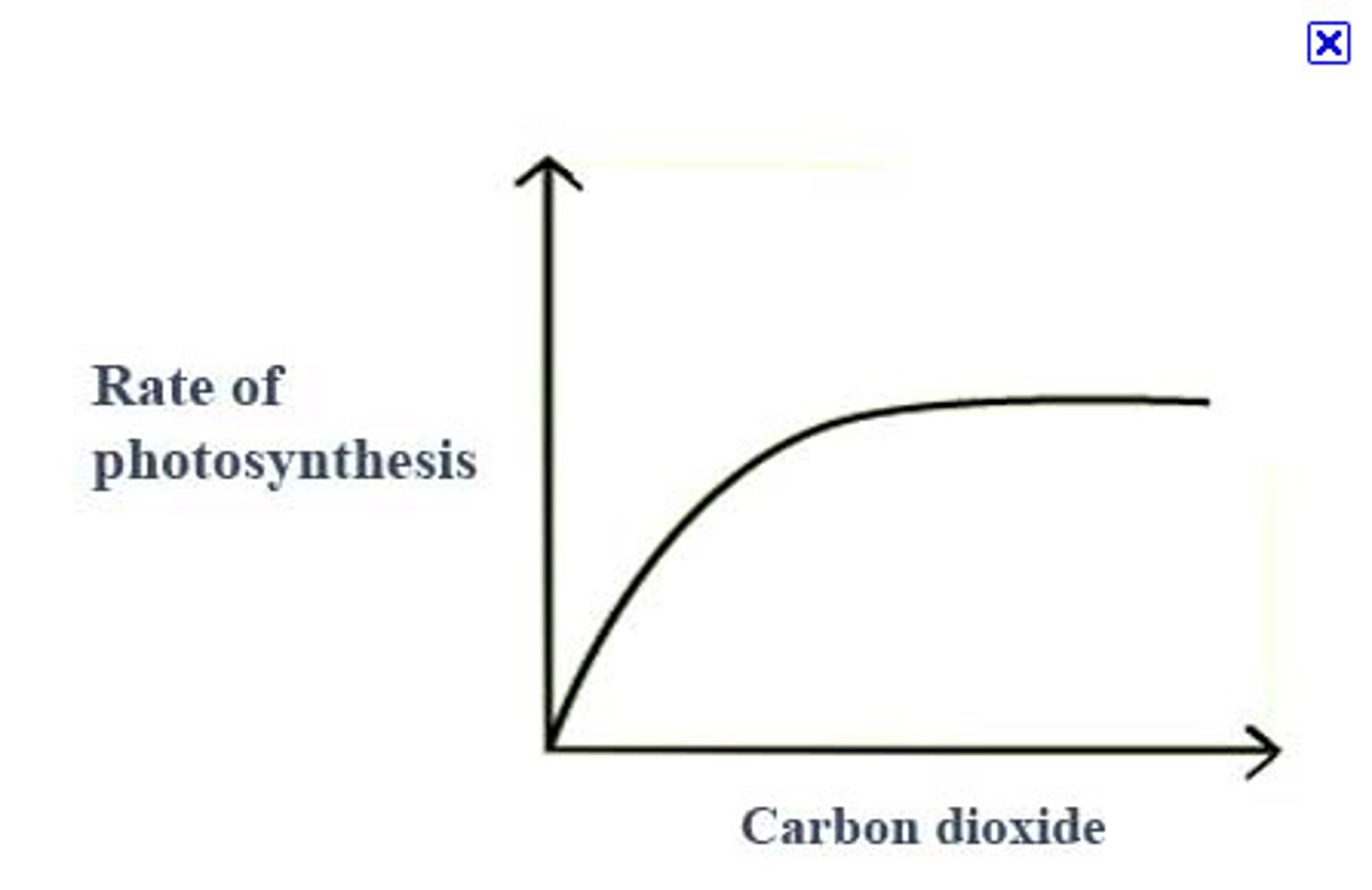
How does CO2 affect photosynthesis
How does temperature affect photosynthesis
Calculate relative light intensity using the inverse square law
RLI= 1/distance from light source "2
Explain how factors interact to limit the rate of photosynthesis
at some point increasing the factor no longer make sa difference to rate bc one of the other factors is short supplied