AP Microeconomics unit 3 Test
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
total revenue
is the amount a firm receives from the sale of g/s (items sold x price)
total cost
is the amount a firm spends to produce and/or sell g/s (sum of individual costs of the resources) (explicit+implicit costs)
profit
results when total revenue is higher than total cost
loss
results when total revenue is less than total cost
explicit costs
tangible out-of-pocket expenses (seen on balance sheet (wages))
implicit costs
the costs of resources already owned, for which no out-of-pocket payment is made (oppurtunity costs, each alternative use of the money is an implicit cost, hard to calculate _)
accounting profit
is calculated by subtracting the explicit costs from total revenue(total revenue - explicit costs)
economic profit
calculated by subtracting both the explicit costs and the implicit costs from total revenue (gives a more complete assessment of how the firm is doing, always less than accounting profit, can be negative (firm not doing well))
output
the product a firm creates
factors of production
the inputs (land, labor, and capital) used in producing g/s
productino function
describes the relationship between the inputs a firm uses and the output it creates (keep costs down, specialization, production per worker increase as additional works increase their specialization)
marginal product
the change in output associated with one additional unit of an input (normally starts positive and goes negative)
diminishing marginal product
occurs when successive increases in inputs are associated with a slower rise in input (after all inputs are fully utilized, additional units cause the marginal product to decline, managers hire the number of workers that maximizes their total output)
variable costs
change with the rate of output (number of workers, electricity used, ingredients, (things the company doesn’t need without customers)
fixed costs
unavoidable; they do not vary with output in the short run, fixed costs are aka overhead (building insurance, property tax, rent, ect)
average variable cost (AVC)
determined by dividing variable cost by the output (quanity)
average fixed cost (AFC)
determined by dividing fixed costs by the output (as output incerase AFC decreases, it is often not pictured on the graph, so it is just the difference between ATC and AVC, decreasaing line on the graph)
in the short run do both fixed and variable costs exist?
yes
in the long run do both fixed and variable costs exist?
no, you can change everything in the long run
average total cost
sum of average variable cost and average fixed costs
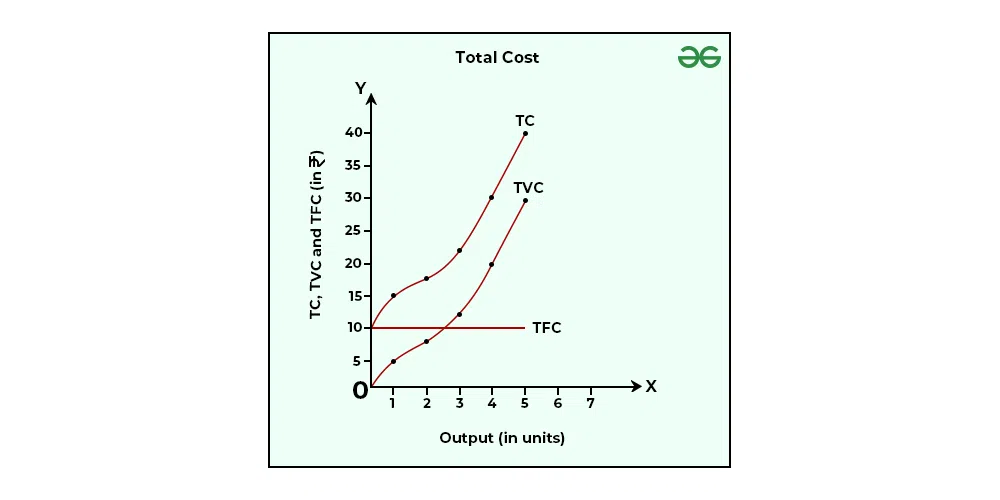
what does a total cost curve look like
what does an average cost curve look like
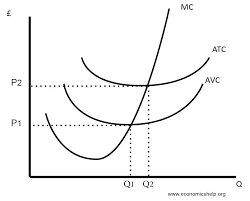
marginal cost
increase in cost that occurs from producing 1 additional unit (reaches its lowest point before the lowest point of the AVC and ATC curves(signal that the total cost will increase)
scale
refers to the size of the production process (increase or decrease operations, avoid a situation of negative marginal product)
efficient scale
output level that maximizes average total cost in the long run
economies of scale
long run AC fall as more output is produced (getting bigger is cheaper)
diseconomies of scale
AC increasing as more product is produced. Company becomes so big that they have to hire extra people and add stuff to their buildings and increase their AVC
constant returns to scale
Average costs will level off (when producing a product, there is no way to get below a certain cost)
what is the relatoinship between MC and MP
MC is the opposite graph of MP`
How does AVC work in the long run
follows MC and intersects at AVC lowest point, increases as output increases, ATC and AVC get closer but never touch because the difference between them is AFC
what are the axis on a average cost curve graph
y = price, x = quantity
How does ATC work in the long run
sum of AFC and AVC, follows the mc, lowest point will intersect the MC
where is constant returns to scale on a long run graph
the middle
where is economics of scale on a long run graph
left side
where is diseconomics of scale on a long run graph
right side
price takers
have no control over the price set by the marke. it takes (accepts) the price determined from the overall supply and demand conditions that regulate the market (each seller is a small compared to the overall market, an indicidual sellers choices have no impact on the market price)
what is the impact of barries to entry and exit
High barriers to entry reduce competition, leading to higher profitability for established firms, while low barriers lead to high competition and lower profit margins
profit-maximizing rule
states that profit maximization occurs when a firm chooses the quantity of output that equates marginal revenue and marginal cost (MR = MC)
How do you decide how much to produce in a competitive market
Locate point at which the firm will maximize its profits (MR = MC) then look for the profixt maximizing output (move down the vertixal dashed line to the x axis at point q (point of maximum profit quantity) (any quanityt greater than or less than Q would result in lower profit)
how do firms decide whether to shut down or not
Short-run calculation - if the firm would lose less by shutting down than staying open it should shut down (as long as the MR > minimum point on the AVC, the firm will choose to operate )
sunk costs
unrecoverable costs that have been incurred as a result of past decisions
the firms long-run supply curve
firms decisions are directly tied to profits, only exists when the firm expects to cover its total costs of production
signals
of profits and losses convey information about the profitability of various markets
what do profit/losses signal
profits - encourage new market entry / losses - encourage exiting the market
what are the characteristics of competitve markets
homogeneous goods, many buyers and seller, price takers, free entry and exit
why is MC u-shaped?
because marginal costs are the opposite of the marginal product curve. due to initial increasing returns followed by diminishing marginal returns
why does average follow the marginal?
because the lowest AVC and ATC intersect at the MC
what does the side by side graph look liked in a perfeclty competitve market in the long run
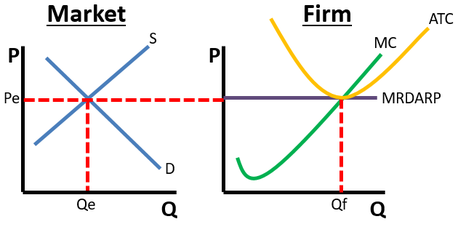
what is the profit in a perflectly competitive industry?
$0
why do you stay in this market even if the profit is $0?
economic profit at $0 is okay because all explicit costs are covered by revenue and becasue all of the implicit costs are covered by revenue
what does a profit look like in a perfectly competitve short run firm?
ATC below MR/D/AR/P (important point where MC intersects MR/D/AR/P (where long run ATC should be), important point where ATC intersects the profit maximizing quantity (dashed line from the previously mentioned important point)
what does a loss look like in a perfectly competitve short run firm?
ATC above the MR/D/AR/P line
how do you change from SR → LR?
supply and demand shift causes MR/D/AR/P to increase/decrease and intersect ATC at its lowest point
is there DWL?
NO
how do you find the profit/loss rectangle?
for profit it is the difference between the point MC intersects MR/D/AR/P and the point where ATC are at the profit maximizing qunaity.
For loss it is the differemce between the same two points but you have to bring the dashed line up wards
what does a change in fixed costs do to the margin
does not change it
when the MR is below the AVC and ATC line what will happen?
shut down because it is not covering any fc and not all VC
when the MR is above the lowest point of AVC what will they do?
stay open because it is covering all variable costs and some fixed costs
When the MR is at the lowest point of AVC what will they do?
shut down because they are only covering VC and ont fixed costs
Where does diminishing marginal returns begin?
point where MC is minimized because the next unit of output iwll be produced at a higher cost, which is a result of diminishing returns
What are the axis for the marginal product curve?
y - output
x - input
why does the TVC dip in the short run total cost curve?
because of specialization
law of diminishing marginal return
firms max profit when MC = MR
What is marginal analysis
a decision-making process that compares the additional benefits of one more unit of an action against the additional costs of that action
what does a change in variable costs do
changes avc, atc, and mc
what does a change in fixed costs do
changes afc and atc