Altered Mental Status // Neurological Emergencies
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Aneurysm
Ballooning of a weakened portion of an arterial wall
-Note: An aneurysm is NOT mean a leaking vessel.
-Prone to bursting
CVA Meaning
Cerebrovascular accident; stroke
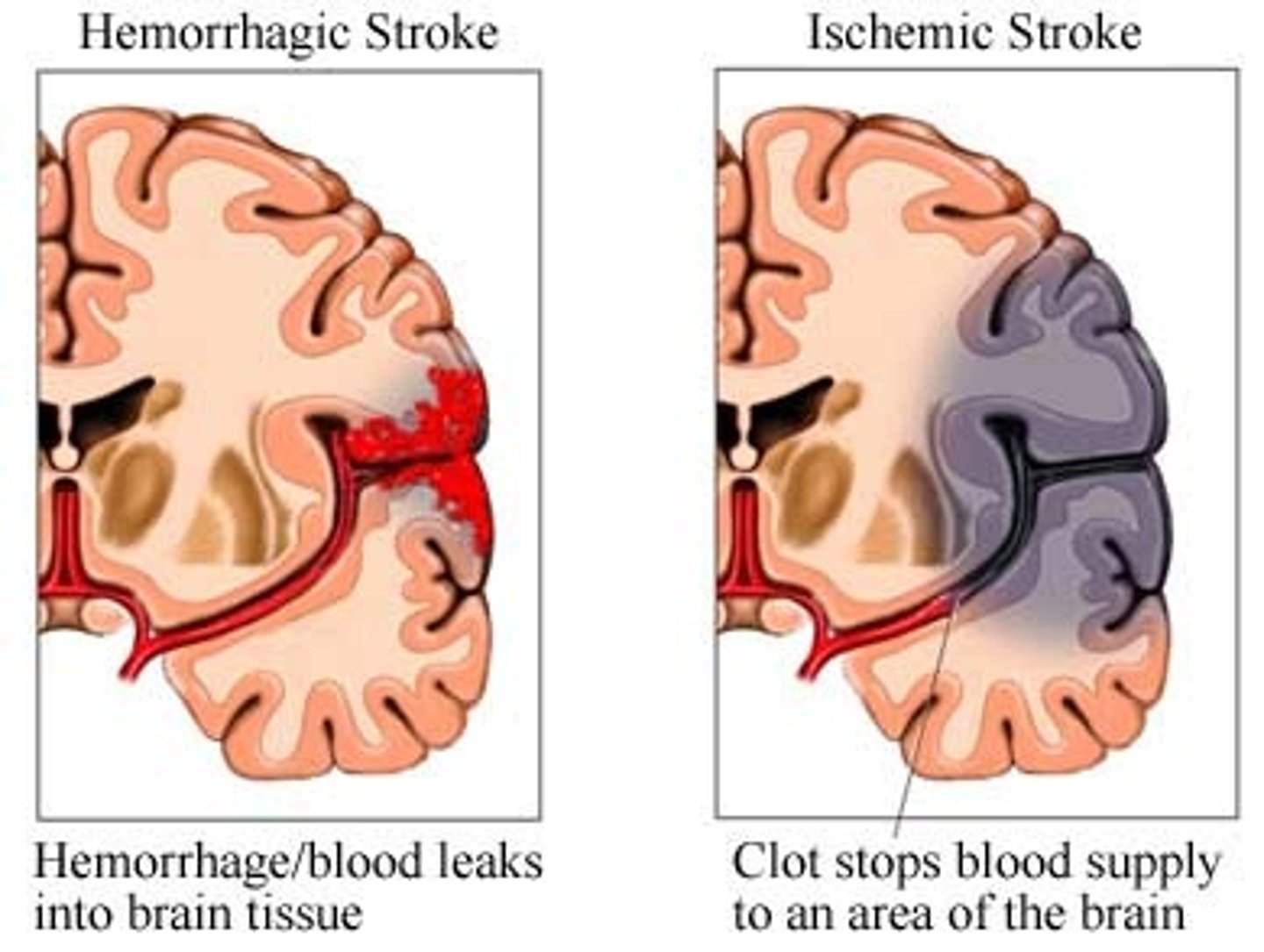
Ischemic Stroke
A type of stroke that occurs when the flow of blood to a certain part(s) of the brain.
~75-85% of strokes are these
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Occurs when a blood vessel in the brain leaks, can be caused by an aneurism. Massive blood loss.
-May see Cushings Triad as pressure builds (ICP)
Ischemic Stroke Risk Factors
Embolism/thrombosis, high cholesterol.
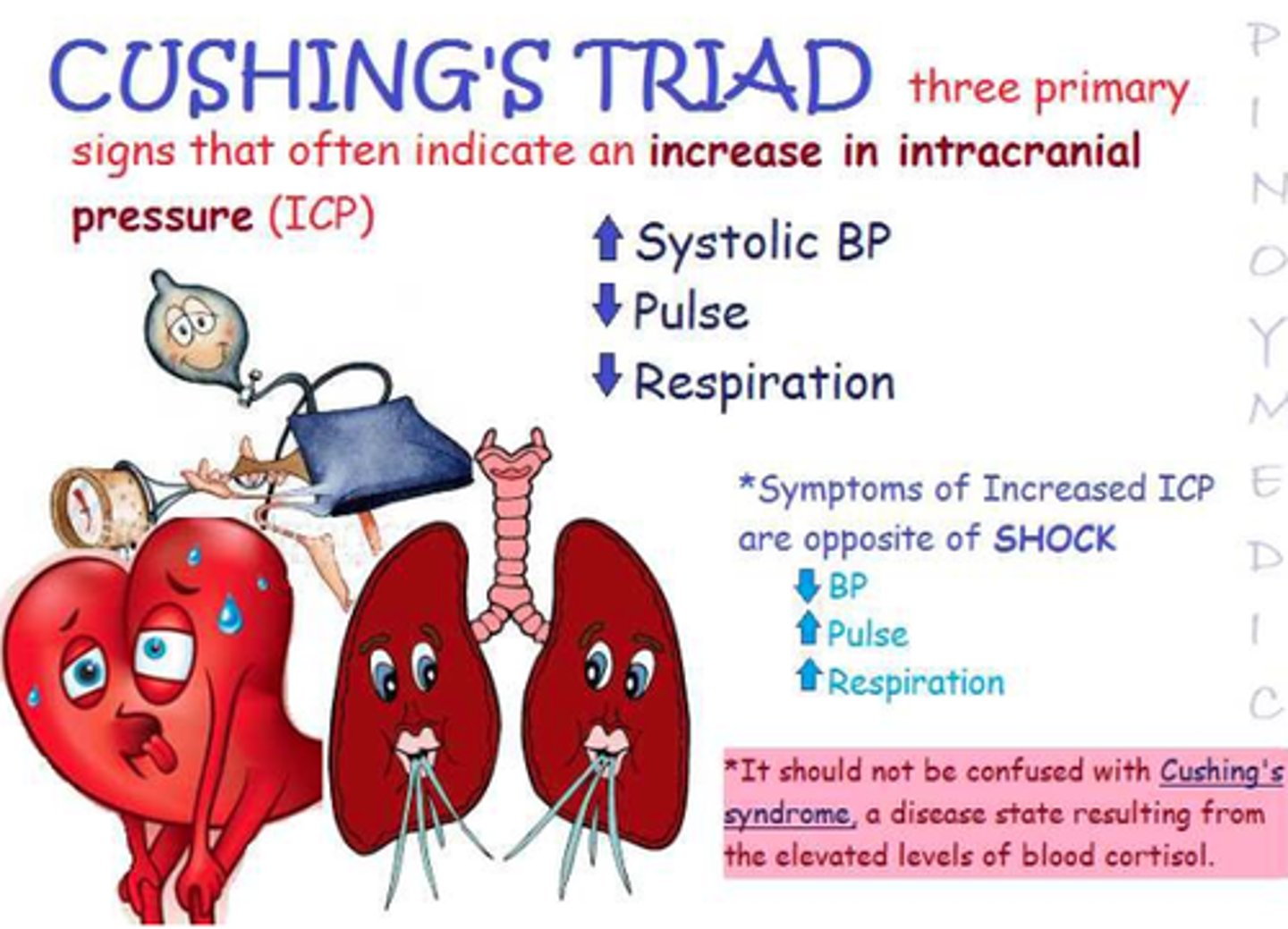
Cushing's Triad
Sign of ICP
-High blood pressure
-widening pulse pressure
-projectile vomiting
-Erratic respirations (cheyne-stokes)
-Bradycardia/lowering pulse rate
Hemorrhagic Stroke Risk Factors
Hypertension, diabetes, smoking
How can you tell the difference between an ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
Hard to in field, needs heat CT for definitive diagnosis.
Is TPA given for hemorrhagic strokes? If so, within how many hours?
It is not given
Is TPA given for ischemic strokes? If so, within how many hours?
It is given for ischemic, within 3 hours of symptom onset.
S/S of stroke
Asymmetry, facial droop, BP different on arms, unequal pupils, may appear drunk, headache
Note: A patient may have one of these symptoms, or maybe none.
Stoke Care
Mainly supportive
-Elevate head 8 to 10 inches if BP is good. Place on side to protect airway. Some stroke patients may have dysphagia, and may have lost some or all ability to swallow.
Cincinnati Stroke Scale
Facial droop, arm drift, slurred speech

TIA stands for:
Transient ischemic attack
What is a TIA?
A mini stroke
-Similar S/S of a stroke but person returns "normal" within about 24 hours (no long lasting effects)
-Can be a partial blockage that resulted in ischemia, or the blockage broke away
-TIA's are often precursors to CVA's
What is a seizure?
Temporary abnormal electrical activity of the brain
-Seizure is generally not considered a non-life threatening event as long as airway remains patent.
Seizure causes
low/high sugar, low/high temperature, trauma to the brain, cancer in brain, vision into the brain, smells, swelling of brain, drugs, lack of O2, acids in brain, high BP, infections of brain, or congenital abnormalities.
-Anything that can get into the brain can cause a seizure
Grand Mal Seizure (tonic-clonic)
Full body contractions, may urinate and defecate on self, lasts about 45 seconds to 2 minutes
-Major problem is patient is not breathing during that time
Focal Seizure (partial seizure)
Isolated area only, not the entire body
Petit Mal Seizure
Also called absence attack. A seizure that is characterized a loss of awareness and inability to recall events surrounding the seizure. The seizure does not include convulsing
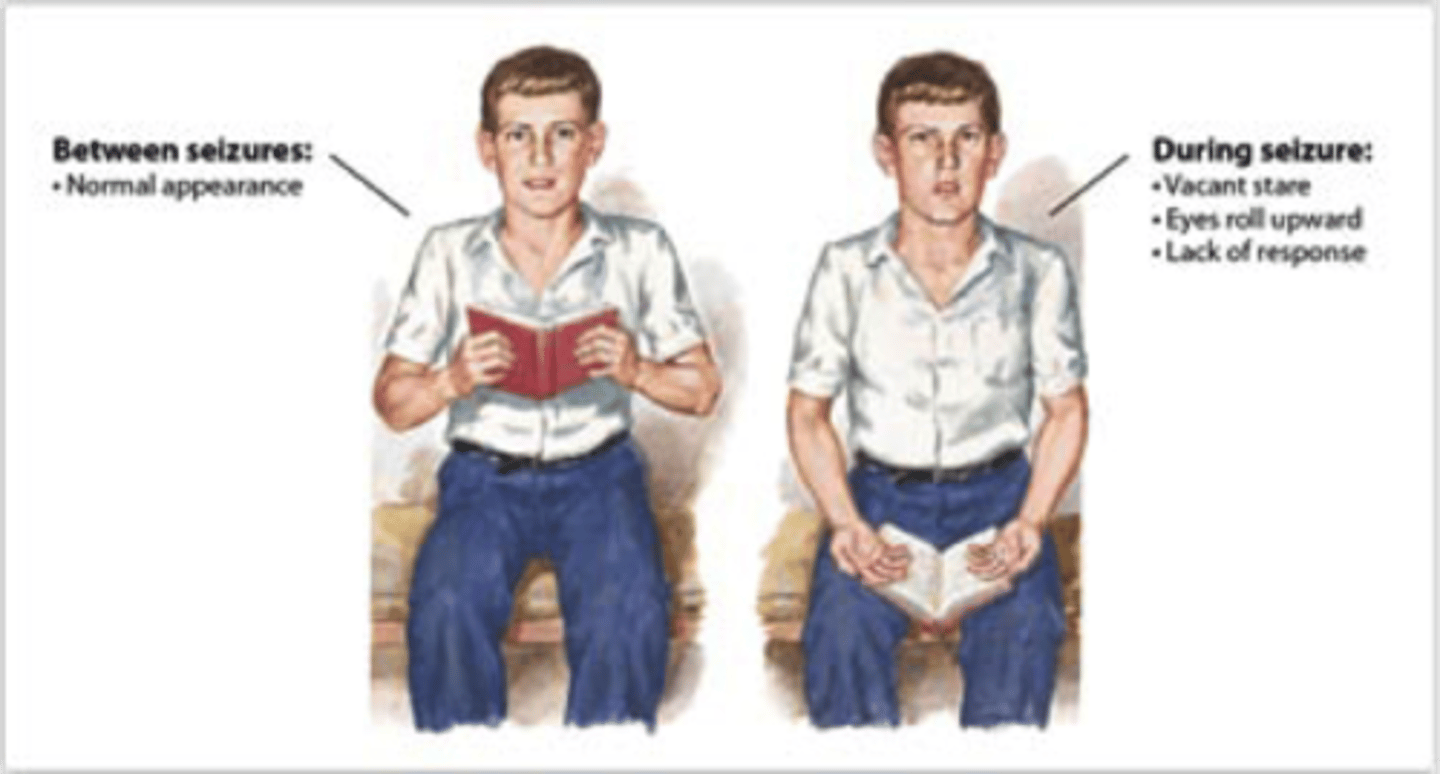
Postictal State
A period following a seizure that lasts between 5 and 30 minutes; a state of decreased/altered mental status following a seizure
Seizure Care
Protect the patient from injury, maintain an open airway (recovery position as needed), do NOT put anything in the mouth
Most common reason adults have seizures
Not taking medications
Most common reason children have seizures
Febrile seizure
When are seizures concerning?
Typically not medical emergency especially if patient has a history of seizures. Things you should ask after someone has a seizure:
-Have you had seizures before?
-If you have a history of seizures, was there anything different about this seizure? (typically would have to ask a family member who knows their seizures)
-Has your prescription changed? Have you been taking your medicine?
Causes of AMS
Anything that can cause a seizure, can also cause AMS
-Typical first cause is hypoxia so give O2, other common causes could be hypoglycemia
AMS Care
Always protect airway, place in recovery to prevent aspiration